Epididymis
| Epididymis | |
|---|---|
|
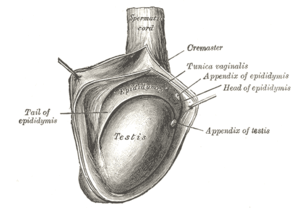
Adult human testicle with epididymis: A. Head of epididymis, B. Body of epididymis, C. Tail of epididymis, and D. Vas deferens | |
|
The right testis, exposed by laying open the tunica vaginalis. | |
| Details | |
| Precursor | Wolffian duct |
| Vein | Pampiniform plexus |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Epididymis |
| MeSH | A05.360.444.371 |
The epididymis (/ɛpɪˈdɪdɪmɪs/; plural: epididymides /ɛpɪdɪˈdɪmədiːz/ or /ɛpɪˈdɪdəmɪdiːz/) is a tube that connects a testicle to a vas deferens in the male reproductive system. It is present in all male reptiles, birds, and mammals. It is a single, narrow, tightly-coiled tube (in adult humans, six to seven meters in length[1]) connecting the efferent ducts from the rear of each testicle to its vas deferens.
Structure
The epididymis can be divided into three main regions:
- The head (Latin: Caput). The head of the epididymis receives spermatozoa via the efferent ducts of the mediastinium of the testis. It is characterized histologically by a thin myoepithelium. The concentration of the sperm here is dilute.
- The body (Latin: Corpus)
- The tail (Latin: Cauda). This has a thicker myoepithelium than the head region, as it is involved in absorbing fluid to make the sperm more concentrated.
In reptiles, there is an additional canal between the testis and the head of the epididymis and which receives the various efferent ducts. This is, however, absent in all birds and mammals.[2]
Histology
The epididymis is covered by a two layered pseudostratified epithelium. The epithelium is separated by a basement membrane from the connective tissue wall which has smooth muscle cells. The major cell types in the epithelium are:
- Main cells: columnar cells that, with the basal cells, form the majority of the epithelium. These cells extend from the lumen to the basal lamina,[3] They also have non-motile stereocilia, which are long and branching in the head region and shorter in the tail region.[3] They also secrete carnitine, sialic acid, glycoproteins, and glycerylphosphorylcholine into the lumen.
- Basal cells: shorter, pyramid-shaped cells which contact the basal lamina but taper off before their apical surfaces reach the lumen.[3] These are thought to be undifferentiated precursors of principal cells.[3]
- Apical cells: predominantly found in the head region[3]
- Clear cells: predominant in the tail region[3]
- Intraepithelial lymphocytes: distributed throughout the tissue.[3]
- Intraepithelial macrophages[4][5]
Stereocilia
The stereocilia of the epididymis are structures which aid in absorption. They are long cytoplasmic projections that have no motility.
Unlike the stereocilia of the inner ear, which play a role in hearing, stereocilia in the epididymis are more like the long, absorptive microvilli of other epithelia. These membrane extensions increase the surface area of the cell, allowing for greater absorption and secretion.[6]
The stereocilia in the epididymis are shaped by an internal actin network with no microtubule structure, and unlike true cilia are non-motile.[7] Because sperm are initially nonmotile as they leave the seminiferous tubules, large volumes of fluid are secreted to propel them to the epididymis. The core function of the stereocilia is to resorb 90% of this fluid as the spermatozoa start to become motile. This absorption creates a fluid current that moves the immobile sperm from the seminiferous tubules to the epididymis. Spermatozoa do not reach full motility until they reach the vagina, where the alkaline pH is neutralized by acidic vaginal fluids.
Development
In the embryo, the epididymis develops from tissue that once formed the mesonephros, a primitive kidney found in many aquatic vertebrates. Persistence of the cranial end of the mesonephric duct will leave behind a remnant called the appendix of the epididymis. In addition, some mesonephric tubules can persist as the paradidymis, a small body caudal to the efferent ductules.
A Gartner's duct is a homologous remnant in the female.
Function
Role in storage of sperm and ejaculant
Spermatozoa formed in the testis enter the caput epididymis, progress to the corpus, and finally reach the cauda region, where they are stored. Sperm entering the caput epididymis are incomplete—they lack the ability to swim forward (motility) and to fertilize an egg. It stores the sperm for 2–3 months. During their transit in the epididymis, sperm undergo maturation processes necessary for them to acquire these functions.[8] Final maturation is completed in the female reproductive tract (capacitation).
The epididymis secretes some proteins that blocks the receptors on the plasma membrane of sperm head which renders sperm infertile inside the male tract (decapacitation).
During ejaculation, sperm flow from the lower portion of the epididymis (which functions as a storage reservoir). They have not been activated by products from the prostate gland, and they are unable to swim, but are transported via the peristaltic action of muscle layers within the vas deferens, and are mixed with the diluting fluids of the seminal vesicles and other accessory glands prior to ejaculation (forming semen).
The epithelial cells of the epididymis possess numerous apical modifications that are often referred to as stereocilia, as under the light microscope they look like cilia. However, as electron microscopy has revealed them to be structurally and functionally more similar to microvilli, some now refer to them as stereovilli.[9]
Clinical significance
Inflammation
An inflammation of the epididymis is called epididymitis. It is much more common than testicular inflammation, termed orchitis.
Surgical removal
Epididymotomy is the placing of an incision into the epididymis and is sometimes considered as a treatment option for acute suppurating epididymitis. Epididymectomy is the surgical removal of the epididymis sometimes performed for post-vasectomy pain syndrome and for refractory cases of epididymitis.
Popular culture
Ghostbusters II
In the 1989 film, Egon Spengler (played by the late Harold Ramis) responds to a jibe made by Peter Venkman (Bill Murray) about his female colleagues being attracted to the size of his cranium with "I think they're more interested in my epididymis."[10]
Gallery
 Human Male reproductive system.
Human Male reproductive system. Testis
Testis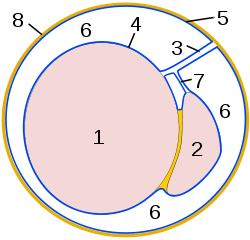 Schematic drawing of a cross-section through a testicle.
Schematic drawing of a cross-section through a testicle. Micrograph of an epididymis. H&E stain.
Micrograph of an epididymis. H&E stain.- Microscopic shot.
- Epididymis deep dissection.
See also
Notes
- ↑ Kim, Howard H.; Goldstein, Marc (2010). "Chapter 53: Anatomy of the epididymis, vas deferens, and seminal vesicle". In Graham, Sam D.; Keane, Thomas E.; Glenn, James F. Glenn's urological surgery (7th ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 356. ISBN 978-0-7817-9141-0.
- ↑ Romer, Alfred Sherwood; Parsons, Thomas S. (1977). The Vertebrate Body. Philadelphia, PA: Holt-Saunders International. pp. 394–395. ISBN 0-03-910284-X.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Kierszenbaum, Abraham L. (2002). Histology and cell biology : an introduction to pathology. St. Louis: Mosby. p. 556. ISBN 0-323-01639-1.
- ↑ Da Silva N, Cortez-Retamozo V, Reinecker HC, et al. (May 2011). "A dense network of dendritic cells populates the murine epididymis". Reproduction. 141 (5): 653–63. PMC 3657760
 . PMID 21310816. doi:10.1530/REP-10-0493.
. PMID 21310816. doi:10.1530/REP-10-0493. - ↑ Shum WW, Smith TB, Cortez-Retamozo V, et al. (May 2014). "Epithelial basal cells are distinct from dendritic cells and macrophages in the mouse epididymis". Biology of Reproduction. 90 (5): 90. PMC 4076373
 . PMID 24648397. doi:10.1095/biolreprod.113.116681.
. PMID 24648397. doi:10.1095/biolreprod.113.116681. - ↑ How sperm are re-absorbed into the body. vasectomy-information.com
- ↑ Efferent Ducts and Epididymis. umdnj.edu
- ↑ Jones RC (April 1999). "To store or mature spermatozoa? The primary role of the epididymis". International Journal of Andrology. 22 (2): 57–67. PMID 10194636. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2605.1999.00151.x.
- ↑ Ross, Michael H.; Pawlina, Wojciech (2011). Histology: A Text and Atlas. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 110–112. ISBN 978-0-7817-7200-6.
- ↑ http://www.imdb.com/title/tt0097428/quotes?item=qt0407325
External links
| Look up epididymis in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
- Histology image: 16903loa – Histology Learning System at Boston University
- inguinalregion at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (testes)