Spanish general election, 2011
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 350 seats in the Congress of Deputies and 208 (of 266) seats in the Senate 176 seats needed for a majority in the Congress of Deputies | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Opinion polls | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Registered |
35,779,491 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout |
24,666,441 (68.9%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Constituency results map for the Congress of Deputies | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The 2011 Spanish general election was held on Sunday, 20 November 2011, to elect the 10th Cortes Generales of the Kingdom of Spain. All 350 seats in the Congress of Deputies were up for election, as well as 208 of 266 seats in the Senate. An election had not been due until 8 April 2012 at latest,[n 1] but a call by Prime Minister José Luis Rodríguez Zapatero for a snap election five months ahead of schedule was announced on 29 July 2011. Zapatero would not be seeking a third term in office, and with political pressure mounting, a deteriorating economic situation and his political project exhausted, an early election was perceived as the only way out.[1][2]
The election campaign was dominated by the effects of an ongoing financial crisis, high unemployment, a large public deficit and a soaring risk premium. Opinion polls had shown consistent leads for the opposition People's Party (PP) over the ruling Spanish Socialist Workers' Party (PSOE), whose popularity had plummeted after Zapatero's U-turns in economic policy had forced him to adopt tough spending cuts and austerity measures. Massive anti-austerity protests had taken place in May 2011 under the form of the 15-M Movement, and in the local and regional elections held a few days later popular support for the PSOE fell dramatically. On 21 October, the armed organization ETA announced a permanent cessation of armed activity, turning the 2011 election into the first since the Spanish transition to democracy without ETA attacks.[3]
The election resulted in the PSOE being swept out from power in the worst defeat for a sitting government since 1982, losing 4.3 million votes and scoring its worst result in a general election ever since the first democratic election in 1977.[4] In contrast, PP's Mariano Rajoy won a record absolute majority in a landslide, being his party's best historic result as well as the second largest majority in democracy.[5] Also for the first time in a general election, the PSOE failed to come out on top in both Andalusia and Catalonia, with the nationalist Convergence and Union (CiU) emerging victorious, whereas the abertzale left Amaiur achieved a major breakthrough in both the Basque Country and Navarre.[6] United Left (IU) experienced a turnaround of its electoral fortunes and saw its first remarkable increase in 15 years,[7] whereas centrist Union, Progress and Democracy exceeded all expectations with over one million votes, 5 seats and just 0.3% short of the 5% threshold required for being recognized a party parliamentary group in Congress.[8][9]
Electoral system
The Spanish Cortes Generales were regarded as an imperfect bicameral system. The Congress of Deputies had greater legislative power than the Senate, having the ability to grant or revoke confidence from a Prime Minister and to override Senate vetoes by an absolute majority of votes. Nonetheless, the Senate possessed a few exclusive, yet limited in number functions—such as its role in constitutional amendment—which were not subject to the Congress' override.[10][11] Voting for the Cortes Generales was on the basis of universal suffrage, with all nationals over eighteen and in full enjoyment of all political rights entitled to vote. Amendments to the electoral law in 2011 required for Spaniards abroad to apply for voting before being permitted to vote, a system known as "begged" or expat vote (Spanish: Voto rogado).[12]
For the Congress of Deputies, 348 seats were elected using the D'Hondt method and a closed list proportional representation, with a threshold of 3 per 100 of valid votes—which included blank ballots—being applied in each constituency. Parties not reaching the threshold were not taken into consideration for seat distribution. Additionally, the use of the D'Hondt method might result in an effective threshold over three percent, dependant on the district magnitude.[13] Seats were allocated to constituencies, corresponding to the provinces of Spain. Each constituency was entitled to an initial minimum of two seats, with the remaining 248 allocated among the constituencies in proportion to their populations. Ceuta and Melilla were allocated the two remaining seats, which were elected using plurality voting.[10][14][15][16]
For the Senate, 208 seats were elected using an open list partial block voting, with electors voting for individual candidates instead of parties. In constituencies electing four seats, electors could vote for up to three candidates; in those with two or three seats, for up to two candidates; and for one candidate in single-member districts. Each of the 47 peninsular provinces was allocated four seats, whereas for insular provinces, such as the Balearic and Canary Islands, districts were the islands themselves, with the larger—Majorca, Gran Canaria and Tenerife—being allocated three seats each, and the smaller—Menorca, Ibiza-Formentera, Fuerteventura, La Gomera, El Hierro, Lanzarote and La Palma—one each. Ceuta and Melilla elected two seats each. Additionally, autonomous communities could appoint at least one senator each and were entitled to one additional senator per each million inhabitants.[10][14][15][16]
The electoral law provided that parties, federations, coalitions and groupings of electors were allowed to present lists of candidates. However, parties, federations or coalitions who had not obtained a mandate in either House of Parliament at the preceding election were required to secure at least the signature of 0.1 per 100 of the electors entered in electoral register of the constituency for which they were seeking election, whereas groupings of electors were required to secure the signature of 1 per 100 of electors. Electors were barred from signing for more than one list of candidates. Concurrently, parties and federations intending to enter in coalition to take part jointly at an election were required to inform the relevant Electoral Commission within ten days from the election call.[14][16]
Election date
Articles 68 and 69 of the Spanish Constitution of 1978 established that the term of each House of the Cortes Generales—the Congress and the Senate—expired four years from the date of their previous election, unless they were dissolved earlier. Article 42 of the General Electoral System Law of 1985 required for the election Decree to be issued no later than the twenty-fifth day prior to the date of expiry of the Cortes in the event that the Prime Minister did not make use of his prerogative of early dissolution. The Decree was to be published on the following day in the Official State Gazette, with election day taking place on the fifty-fourth day from publication. The previous election was held on 9 March 2008, which meant that the legislature's term would expire on 9 March 2012. The election Decree was required to be published no later than 14 February 2012, with the election taking place on the fifty-fourth day from publication, setting the latest possible election date for the Cortes Generales at Sunday, 8 April 2012.[14][16]
Article 115 of the Constitution granted the Prime Minister the prerogative to dissolve both Houses at any given time—either jointly or separately—and call a snap election, provided that no motion of no confidence was in process, no state of emergency under Article 116 was in force and that dissolution did not occur before one year had elapsed since the previous one. Additionally, under Article 99 both Houses were to be dissolved and a new election called if an investiture process failed to elect a Prime Minister within a two-month period from the first ballot.[10][15] While there was no constitutional requirement—aside from Article 99—for simultaneous elections for the Congress and the Senate, there were no precedents for separate elections, with governments having long preferred that elections for the two Houses take place simultaneously.
Parties and leaders
Background
The 2008 general election had resulted in a victory for the Spanish Socialist Workers' Party (PSOE) of José Luis Rodríguez Zapatero, which nonetheless fell 7 seats short of an absolute majority. The Socialists had been re-elected on a full employment platform,[17] despite the Spanish economy showing signs of fatigue and economic slowdown after a decade of growth.[18] As a result, Zapatero was sworn in as Prime Minister of Spain for a second term in office in April 2008. Zapatero's second term would be dominated by the 2008–11 economic and financial crisis.
Economic crisis
2008–09: First years
The effects of the economic crisis in Spain started to become apparent at the beginning of Zapatero's second term. The first measure adopted by the newly elected government to mitigate the economic slowdown was an injection of €10 billion into the Spanish economy, of which €6 billion were to fulfill a €400 tax reduction as part of the PSOE 2008 election pledges.[19] Over the next months the government was forced to lower its economic growth forecast for 2008 from 3.1% to 2.3%,[20] then to 1.6%.[21] The government also had to cope with a transport strike on 9–15 June, motivated by a rapid increase in oil prices.[22] Zapatero initially refused to publicly acknowledge the existence of the economic crisis, to which he referred as "intense temporary slowdown" or "economic weaknesses".[23][24] On 23 June 2008, Zapatero's cabinet adopted an "austerity plan" intended to save €250 million—consisting of a 70% reduction in the public job offer and a salary freeze for senior public servants—as well as financial stimulus measures—injection of €35 billion to SMEs and €2.5 billion annually until 2010 to improve the efficiency in the hotel sector—in order to soften the impact of job losses and rising oil prices,[25][26] with Zapatero finally acknowledging the crisis during an interview on 8 July.[27] Meanwhile, Martinsa-Fadesa bankruptcy filling in July 2008 as a result of the Spanish property bubble bursting turned into Spain's biggest ever corporate default.[28]
Job destruction in Spain became increasingly noticeable: by August 2008 2.5 million were already unemployed, the highest figure in 10 years.[29] By December 2008, Spain would become the country with the highest job destruction rate in the world, with unemployment nearing 3 million.[30] In October 2008, the government announced a €100 billion guarantee for bank debts[31] and the creation of a €30 billion worth fund—extendable to €50 billion—to purchase 'healthy' assets from banks and savings banks "to ensure the Spanish market liquidity".[32] From November 2008 to January 2009, the government proposed a €50 billion stimulus plan—with €8 billion destined to public investment in municipalities—expected to create 300,000 jobs throughout 2009,[33][34] which was later criticised for its spending unsustainability and for creating "unproductive" jobs.[35] In Q4 2008 the Spanish economy officially went into recession after a GDP fall of 1.1%—having already fallen by 0.3% on Q3 2008—putting an end to 15 years of uninterrupted economic growth.[36]
On 28 March 2009, the Spanish government launched a €9 billion bailout to rescue Caja Castilla La Mancha, the first Spanish savings bank to be intervened during the crisis,[37] to be followed by CajaSur in 2010, the nationalization of CAM, Unnim, CatalunyaCaixa and Novagalicia Banco in 2011 and the intervention and nationalization of Banco de Valencia in 2011–12.[38] As part of the bank restructuring, the FOBR was created in June 2009 to preside over the mergers and acquisitions of the failing savings banks.[39] In April 2009, Pedro Solbes was replaced as Spain's Economy and Finance Minister by the low-profile Elena Salgado as part of a major cabinet reshuffle, in a move seen as Zapatero seeking to take more direct control of economic policy himself.[40]
By Q2 2009, unemployment had grown to 17.9%—more than 4 million unemployed—and the GDP had fallen by 4.2%.[41][42] This prompted Zapatero to announce on 28 August 2009 that the 2010 budget would include a "limited and temporary" tax increase worth €16 billion—dubbed by many as the largest tax rise in history—to tackle the revenue fall and spending increase resulting from the crisis.[43][44] Further measures, such as the suppression of the €400 tax reduction and a VAT increase from 16% to 18%—in its standard rate—and from 7% to 8%—in its reduced rate—were announced in the following weeks.[45] The end of 2009 would see unemployment climbing to 18.8%,[46] with public deficit soaring—11.4% of GDP—and forcing the government to approve on 29 January 2010 a €50 billion worth-savings plan for the 2010–13 period, cutting all public spending except for social benefits, welfare state policies and those involving a production model renewal.[47]
2010: Zapatero's U-turn
However, despite the government's efforts, the economic situation kept worsening. On 5 February, Spain's risk premium reached the 100 basis point-mark in a black week for Madrid Stock Exchange—with the IBEX 35 falling by 9.3%.[48] By early May 2010, unemployment had reached the 20% mark for the first time since the 1993 economic crisis,[49] while the crisis in Greece, threatening to engulf the remained of the eurozone, caused the risk premium to rise dramatically by 60% to 170 basis points and the Madrid Stock Exchange to fall by 10%.[50] As a result, Zapatero announced a €15 billion austerity package on 12 May aimed at preventing the country's default. Among the adopted measures were a cut of 5% in public wages, a pension freezing for 2011, cuts into dependency spending and the removal of the €2,500 birth allowance, among others.[51][52][53] Zapatero's U-turn, breaching a previous pledge not to cut social spending, caused his and the PSOE's popularity ratings to plummet in opinion polls.[54]
On 9 September 2010, the PSOE government approved a labor reform, which included suspension of collective agreements during economic downturns, a lower redundancy pay in cases of wrongful dismissal—from 45 to 33 days per year worked—or cheaper dismissals for companies facing losses, among others.[55] The reform, coupled with the cut in public wages and the pension freeze, provoked the Socialist government to face its first general strike on 29 September.[56] In order to tackle dropping poll numbers, a major cabinet reshuffle took place on 20 October, resulting in a number of ministries being disbanded and long-time First Deputy Prime Minister María Teresa Fernández de la Vega being replaced by Interior Minister Alfredo Pérez Rubalcaba.[57][58] The risk premium kept growing and peaked at 270 basis points by the end of November.[59][60] Zapatero's government announced a new austerity package on 1 December—including the removal of a €426 allowance for long-term unemployed and the privatizations of AENA and the Lotteries—but also a tax cut for SMEs.[61] In the following weeks, Zapatero would also announce an increase of the retirement age from 65 to 67 to be applied "flexibly and progressively" until 2027.[62]
Opinion polls
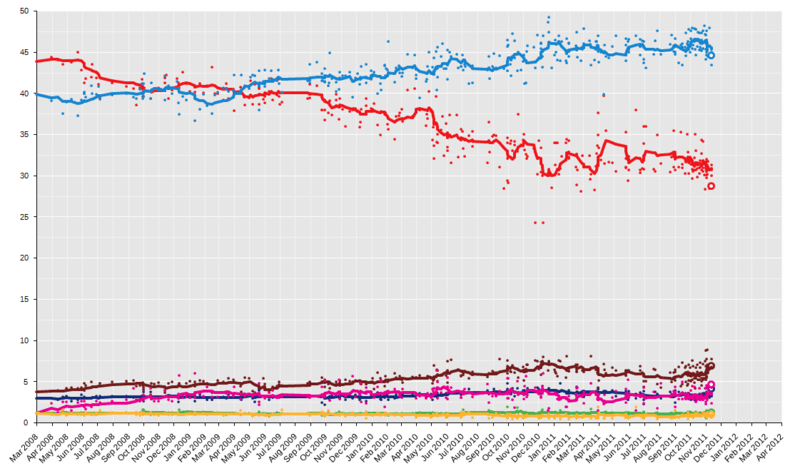
Date of the election
Timetable
The key dates are listed below (all times are CET. Note that the Canary Islands use WET (UTC+0) instead):[14][16][63]
| Date | Event |
|---|---|
| 26 September | The election Decree is issued with the countersign of the Prime Minister after deliberation in the Council of Ministers, ratified by HM The King[64][65] |
| 27 September | Formal dissolution of Parliament (in order for the election to take place on 20 November) and official start of ban period for the organization of events for the inauguration of public works, services or projects[14][65] |
| 7 October | Deadline for parties and federations intending to enter in coalition to inform the relevant Electoral Commission |
| 17 October | Deadline for parties, federations, coalitions and groupings of electors to present lists of candidates to the relevant Electoral Commission |
| 19 October | Submitted lists of candidates are provisionally published in the Official State Gazette |
| 22 October | Deadline for citizens entered in the Register of Absent Electors Residing Abroad and for citizens temporarily absent from Spain to apply for voting |
| 23 October | Deadline for parties, federations, coalitions and groupings of electors to rectify irregularities in their lists |
| 24 October | Official proclamation of valid submitted lists of candidates |
| 25 October | Proclaimed lists are published in the Official State Gazette |
| 4 November | Official start (0 am) of electoral campaigning |
| 10 November | Deadline to apply for postal voting |
| 15 November | Official start of legal ban on electoral opinion polling publication, dissemination or reproduction and deadline for citizens entered in the Register of Absent Electors Residing Abroad to vote by mail |
| 16 November | Deadline for postal and temporarily absent voters to issue their votes |
| 18 November | Official end (12 pm) of electoral campaigning and deadline for citizens entered in the Register of Absent Electors Residing Abroad to vote in a ballot box in the relevant Consular Office or Division |
| 19 November | Official 24-hour ban on political campaigning prior to the general election (reflection day) |
| 20 November | Polling day (polling stations opened at 9 am and closed at 8 pm or once voters present in a queue at/outside the polling station at 8 pm had casted their vote). Counting of votes starts immediately |
| 15 December | Deadline for both Houses of Parliament to be re-assembled (the election Decree determines this date, which for the 2011 election was set for 13 December)[64] |
Campaign
Party manifestos and slogans
| Party/alliance | Manifesto (external link) | Campaign slogan(s) |
|---|---|---|
| Spanish Socialist Workers' Party (PSOE) | An Electoral Manifesto to Win the Future | "Fight for what you want".[66] |
| People's Party (PP) | What Spain Needs | "Join the change"[67] |
| United Left (IU) | Electoral Proposals | "Rebel!"[68] |
| Union, Progress and Democracy (UPyD) | My Vote Counts | "Each vote counts"[69] |
| Convergence and Union (CiU) | CiU Electoral Manifesto | "More for Catalonia"[70] |
| Basque Nationalist Party (EAJ/PNV) | Working for the Basque Country in Madrid | "For the Basque Country" & "The Basque Country cans"[71] |
| Amaiur (Amaiur) | Amaiur Commitments | "Bridging"[72] |
| Republican Left of Catalonia (ERC) | The Republic of Yes | "We Want the Republic of Yes"[73] |
Leaders' debates
| Spanish general election debates, 2011 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date | Organisers | Moderator(s) | P Present S Surrogate NI Non-invitee | ||||
| PSOE | PP | IU | CiU | PNV | |||
| 7 November | TV Academy | Manuel Campo Vidal | P Rubalcaba |
P Rajoy |
NI | NI | NI |
| 9 November | RTVE | María Casado | S Jáuregui |
S Gallardón |
S Llamazares |
S Macias |
P Erkoreka |
| Candidate viewed as "performing best" or "most convincing" in each debate | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Debate | Poll source | PSOE | PP | Notes |
| 7 November | Metroscopia[74] | 41.0 | 46.0 | 6.0% said none won, 6.0% it was a tie and 1.0% were undecided. |
| Sigma Dos[75] | 44.2 | 51.4 | 4.4% were undecided on who won. | |
| TNS Demoscopia[76] | 33.1 | 43.9 | 23.0% said none won. | |
| Invymark[77][78] | 39.9 | 48.6 | 11.5% said it was a tie. | |
| CIS[79] | 23.4 | 39.6 | 24.4% said none won, 5.4% it was a tie and 7.2% were undecided. | |
Results
Congress of Deputies
 | ||||||
| Parties and coalitions | Popular vote | Seats | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Votes | % | ±pp | Won | +/− | ||
| People's Party (PP)1 | 10,866,566 | 44.63 | +4.52 | 186 | +32 | |
| Spanish Socialist Workers' Party (PSOE) | 7,003,511 | 28.76 | –15.11 | 110 | –59 | |
| United Left–The Greens: Plural Left (IU–LV)2 | 1,686,040 | 6.92 | +3.00 | 11 | +9 | |
| Union, Progress and Democracy (UPyD) | 1,143,225 | 4.70 | +3.51 | 5 | +4 | |
| Convergence and Union (CiU) | 1,015,691 | 4.17 | +1.14 | 16 | +6 | |
| Amaiur (Amaiur)3 | 334,498 | 1.37 | +1.05 | 7 | +7 | |
| Basque Nationalist Party (EAJ/PNV) | 324,317 | 1.33 | +0.14 | 5 | –1 | |
| Republican Left (esquerra) | 256,985 | 1.06 | –0.10 | 3 | ±0 | |
| Equo (eQuo) | 216,748 | 0.89 | New | 0 | ±0 | |
| Galician Nationalist Bloc (BNG) | 184,037 | 0.76 | –0.07 | 2 | ±0 | |
| Canarian Coalition–New Canaries–Canarian Nationalist Party (CC–NC–PNC)4 | 143,881 | 0.59 | –0.24 | 2 | ±0 | |
| Commitment Coalition–Equo (Compromís–Q)5 | 125,306 | 0.51 | +0.39 | 1 | +1 | |
| Animalist Party Against Mistreatment of Animals (PACMA) | 102,144 | 0.42 | +0.25 | 0 | ±0 | |
| Asturias Forum (FAC) | 99,473 | 0.41 | New | 1 | +1 | |
| Blank Seats (EB) | 97,673 | 0.40 | +0.38 | 0 | ±0 | |
| Andalusian Party (PA)6 | 76,999 | 0.32 | +0.05 | 0 | ±0 | |
| Platform for Catalonia (PxC) | 59,949 | 0.25 | +0.24 | 0 | ±0 | |
| Regionalist Party of Cantabria (PRC) | 44,010 | 0.18 | New | 0 | ±0 | |
| Yes to the Future (GBai)7 | 42,415 | 0.17 | –0.07 | 1 | ±0 | |
| For a Fairer World (PUM+J) | 27,210 | 0.11 | +0.02 | 0 | ±0 | |
| Communist Party of the Peoples of Spain (PCPE) | 26,254 | 0.11 | +0.03 | 0 | ±0 | |
| Parties with less than 0.1% of the vote | 138,493 | 0.57 | — | 0 | ±0 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-capitalists (Anticapitalistas) | 22,289 | 0.09 | New | 0 | ±0 | |
| Pirates of Catalonia (Pirata.cat) | 21,876 | 0.09 | New | 0 | ±0 | |
| Communist Unification of Spain (UCE) | 15,869 | 0.07 | New | 0 | ±0 | |
| Humanist Party (PH) | 10,132 | 0.04 | ±0.00 | 0 | ±0 | |
| Spain 2000 (E–2000) | 9,266 | 0.04 | +0.01 | 0 | ±0 | |
| Internationalist Solidarity and Self-Management (SAIn) | 6,863 | 0.03 | +0.01 | 0 | ±0 | |
| Republicans (RPS) | 5,430 | 0.02 | New | 0 | ±0 | |
| Hartos.org (Hartos.org) | 3,820 | 0.02 | New | 0 | ±0 | |
| Pirate Party (Pirata) | 3,426 | 0.01 | New | 0 | ±0 | |
| Canarian Nationalist Alternative (ANC) | 3,180 | 0.01 | +0.01 | 0 | ±0 | |
| Spanish Falange of the JONS (FE–JONS) | 2,898 | 0.01 | –0.04 | 0 | ±0 | |
| Liberal Democratic Centre (CDL) | 2,848 | 0.01 | ±0.00 | 0 | ±0 | |
| Castilian Party (PCAS)8 | 2,431 | 0.01 | –0.01 | 0 | ±0 | |
| United for Valencia (UxV)9 | 2,210 | 0.01 | ±0.00 | 0 | ±0 | |
| Individual Freedom Party (P–LIB) | 2,065 | 0.01 | New | 0 | ±0 | |
| Regionalist Party of the Leonese Country (PREPAL) | 2,058 | 0.01 | +0.01 | 0 | ±0 | |
| Internationalist Socialist Workers' Party (POSI) | 2,007 | 0.01 | –0.02 | 0 | ±0 | |
| National Democracy (DN) | 1,867 | 0.01 | –0.04 | 0 | ±0 | |
| Regionalist Party for Eastern Andalusia (PRAO) | 1,784 | 0.01 | New | 0 | ±0 | |
| Caballas Coalition (Caballas) | 1,712 | 0.01 | New | 0 | ±0 | |
| XXI Convergence (C.XXI) | 1,443 | 0.01 | New | 0 | ±0 | |
| Unity of the People (UP) | 1,138 | 0.00 | ±0.00 | 0 | ±0 | |
| Convergence for Extremadura (CEx) | 1,090 | 0.00 | New | 0 | ±0 | |
| Andecha Astur (AA) | 1,087 | 0.00 | –0.01 | 0 | ±0 | |
| Citizens of Democratic Centre (CCD) | 1,074 | 0.00 | New | 0 | ±0 | |
| Citizens' Action for Málaga (ACIMA) | 966 | 0.00 | New | 0 | ±0 | |
| Family and Life Party (PFyV) | 829 | 0.04 | –0.04 | 0 | ±0 | |
| Death to the System (+MAS+) | 791 | 0.00 | New | 0 | ±0 | |
| Toledo Independent Citizens' Union (UCIT) | 785 | 0.00 | New | 0 | ±0 | |
| Let us Give the Change (DeC) | 778 | 0.00 | New | 0 | ±0 | |
| Centre and Democracy Forum (CyD) | 720 | 0.00 | New | 0 | ±0 | |
| Regionalist Unity of Castile and León (URCL) | 709 | 0.00 | ±0.00 | 0 | ±0 | |
| Party for the Regeneration of Democracy in Spain (PRDE) | 678 | 0.00 | New | 0 | ±0 | |
| Internet Party (Internet) | 603 | 0.00 | New | 0 | ±0 | |
| Left Republican Party–Republicans (PRE–R) | 419 | 0.00 | New | 0 | ±0 | |
| Enough is Enough, Open Grouping of Political Parties (Basta Ya) | 380 | 0.00 | New | 0 | ±0 | |
| Constitutional and Democratic Party (PDyC) | 304 | 0.00 | New | 0 | ±0 | |
| The Greens–Green Group (LV–GV) | 293 | 0.00 | –0.12 | 0 | ±0 | |
| Democratic Hygiene (HD) | 206 | 0.00 | New | 0 | ±0 | |
| Socialists for Teruel (SxT) | 169 | 0.00 | New | 0 | ±0 | |
| Navarrese and Spanish Right (DNE) | 0 | 0.00 | New | 0 | ±0 | |
| Blank ballots | 333,461 | 1.37 | +0.26 | ||||||
| Total | 24,348,886 | 100.00 | 350 | ±0 | |||||
| Valid votes | 24,348,886 | 98.71 | –0.65 | ||||||
| Invalid votes | 317,555 | 1.29 | +0.65 | ||||||
| Votes cast / turnout | 24,666,441 | 68.94 | –4.91 | ||||||
| Abstentions | 11,113,050 | 31.06 | +4.91 | ||||||
| Registered voters | 35,779,491 | ||||||||
| Source(s): Ministry of the Interior, historiaelectoral.com | |||||||||
| |||||||||
Senate
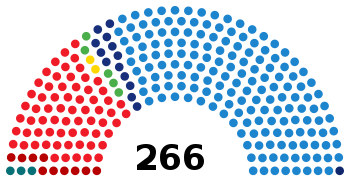 | |||||
| Parties and coalitions | Seats | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Won | +/− | Not up | Total seats | ||
| People's Party (PP)[lower-alpha 1] | 136 | +35 | 30 | 166 | |
| Spanish Socialist Workers' Party (PSOE) | 48 | –40 | 18 | 66 | |
| Convergence and Union (CiU) | 9 | +5 | 4 | 13 | |
| Agreement for Catalonia Progress (PSC–ICV–EUiA)[lower-alpha 2] | 7 | –2 | 3 | 10 | |
| Amaiur (Amaiur) | 3 | +3 | — | 3 | |
| Basque Nationalist Party (EAJ/PNV) | 4 | +2 | 1 | 5 | |
| Republican Left (esquerra) | 0 | –3 | — | 0 | |
| Canarian Coalition–New Canaries–Canarian Nationalist Party (CC–NC–PNC) | 1 | ±0 | 1 | 2 | |
| Asturias Forum (FAC) | 0 | ±0 | 1 | 1 | |
| Total | 208 | ±0 | 58 | 266 | |
| Source(s): Ministry of the Interior, historiaelectoral.com | |||||
Outcome
With an overall voter turnout of 68.9%—the lowest in a decade—the Spanish Socialist Workers' Party (PSOE) suffered its worst ever defeat in a general election, while also scoring one of the worst electoral performances for a ruling party in Spain since the UCD collapse in the 1982 election. The People's Party (PP) was able to win an historic absolute majority with 186 out of 350 seats—the largest obtained by a party since 1982—after almost eight years in opposition. The PSOE went on to finish below first place in all but two provinces—Barcelona and Seville—while also losing both Andalusia and Catalonia, which up to that point had been carried by the PSOE in every general election. The 2011 Spanish election marked the continuation of a string of severe government election losses across European countries since the start of the 2007–08 financial crisis, including Iceland, Greece, Hungary, the United Kingdom, Ireland or Portugal.
Minoritary national parties, such as United Left (IU) and Union, Progress and Democracy (UPyD), benefitted greatly from the PSOE collapse, winning 11 and 5 seats respectively—2 and 1 in the previous parliament. This was the first time since the 1989 election than more than one of the smaller nationwide-contesting parties obtained more than 1 million votes in a general election, as well as enough seats to form parliamentary groups on their own right. The PSOE collapse also resulted in nearly all parties winning parliamentary presence in the Congress of Deputies increasing their vote shares—only Republican Left of Catalonia (ERC) and Geroa Bai (GBai) lost votes compared to 2008. The Basque Nationalist Party (PNV) lost 1 seat despite scoring higher than in 2008, but this came as a result of Amaiur's irruption, with 6 out of its 7 seats being elected in the Basque Country.
Convergence and Union (CiU), the party federation formed by Democratic Convergence of Catalonia (CDC) and Democratic Union of Catalonia (UDC), was elected to an historic general election victory in the region of Catalonia. The Socialists' Party of Catalonia (PSC), PSOE's sister party in the region—which had, up until that point, been the first Catalan political force in every general election held since 1977—scored a poor showing by finishing in second place with 27% of the vote. The 2011 election would be the last time both parties would dominate the Catalan political landscape in a general election; the next election, held on 20 December 2015, would see the alliance between CDC and UDC broken and the PSC being crushed to third place regionally by both the En Comú Podem alliance and ERC.
In terms of vote share, PSOE's electoral result, with 28.76%, would remain the worst electoral performance for a sitting Spanish government in a nationwide-held election since 1982 until the European Parliament election, 2014 held two and a half years later, when the PP obtained 26.09% of the share, and in a general election until 2015—the PP obtaining 28.71%.
Aftermath
Investiture
| Investiture of Mariano Rajoy (PP) |
Yes | No | Abstentions | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 December 2011 (1st ballot) (176/350 required) |
• PP (185) • FAC (1) • UPN (1) |
• PSOE (110) • CiU (16) • IU–ICV–CHA (11) • UPyD (5) • ERC (3) • BNG (2) • Compromís (1) • GBai (1) |
• Amaiur (7) • PNV (5) • CC (1) • NC (1) | |||
| Source: historiaelectoral.com | ||||||
Notes
- ↑ Article 42.2 of the General Electoral System Organic Law provided for the election Decree to be issued no later than the twenty-fifth day prior to the date of expiry of Parliament and published on the following day in the Official State Gazette, with polling day taking place on the fifty-fourth day from publication. This meant that an election was not due until the thirtieth day from the legislature's expiry date. As the previous election was held on 9 March 2008, thirty days after the Cortes Generales' expiry four years later would be 8 April 2012.
References
- ↑ Garea, Fernando (29 July 2011). "Zapatero convoca el 20-N para que "otro Gobierno dé certidumbre"". El País (in Spanish). Madrid. Retrieved 10 July 2017.
- ↑ "Siete años de Gobierno de Zapatero". Cadena SER (in Spanish). 29 July 2011. Retrieved 13 July 2017.
- ↑ Europa Press (11 November 2011). "El Gobierno resalta que son las primeras elecciones sin atentados de ETA". eldiario.es (in Spanish). Madrid. Retrieved 10 July 2017.
- ↑ Fernández, Alberto (20 November 2011). "Rubalcaba bate la peor marca del PSOE en 30 años". RTVE (in Spanish). Retrieved 11 July 2017.
- ↑ Hernanz, Miriam (20 November 2011). "Rajoy rompe el techo de Génova y logra la segunda mayoría más amplia de la democracia". RTVE (in Spanish). Retrieved 11 July 2017.
- ↑ Martín Plaza, Ana (20 November 2011). "Rajoy logra para el PP una mayoría histórica con 186 diputados y el PSOE se hunde con 110". RTVE (in Spanish). Retrieved 11 July 2017.
- ↑ Vallejo, Mario (20 November 2011). "IU multiplica sus diputados y sale de una "larga travesía del desierto" por el descalabro del PSOE". RTVE (in Spanish). Retrieved 11 July 2017.
- ↑ Hernanz, Miriam (20 November 2011). "UPyD roza el grupo parlamentario al superar el millón de votos y obtener escaño por Valencia". RTVE (in Spanish). Retrieved 11 July 2017.
- ↑ Rojo, Iratxe (20 November 2011). "El PP se lleva por delante al PSOE". El Mundo (in Spanish). Madrid. Retrieved 12 July 2017.
- 1 2 3 4 Spanish Constitution of 1978, December 29, 1978 Official State Gazette (in Spanish). Retrieved on 27 December 2016.
- ↑ "Constitución española, Sinopsis artículo 66". congreso.es (in Spanish). Congress of Deputies. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- ↑ Reig Pellicer, Naiara (16 December 2015). "Spanish elections: Begging for the right to vote". cafebabel.co.uk. Retrieved 17 July 2017.
- ↑ "Effective threshold in electoral systems". Trinity College, Dublin. 30 July 2012. Retrieved 22 July 2017.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 General Electoral System Organic Law of 1985, Organic Law No. 5 of June 19, 1985 Official State Gazette (in Spanish). Retrieved on 28 December 2016.
- 1 2 3 "Constitution" (PDF). congreso.es. Congress of Deputies. Retrieved 19 June 2017.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Representation of the people Institutional Act". juntaelectoralcentral.es. Central Electoral Commission. Retrieved 16 June 2017.
- ↑ "The PSOE shows the "motives to believe in" his election proposal" (in Spanish). Público. 2008-02-04. Archived from the original on 20 September 2014.
- ↑ "The PSOE ignores the economic slowdown and says we are "much" better than four years ago" (in Spanish). Libertad Digital. 2008-01-07.
- ↑ "The government will approve on Friday an injection of €10 billion" (in Spanish). El Mundo. 2008-04-13.
- ↑ "The government says that "rising unemployment" and "the economic downturn" will solved by 2009" (in Spanish). Libertad Digital. 2008-05-06.
- ↑ "The government, at odds with the crisis" (in Spanish). El País. 2008-07-25.
- ↑ "The strike paves the way to the crisis" (in Spanish). El País. 2008-06-15.
- ↑ "Zapatero christens the crisis: "A now more intense temporary slowdown"" (in Spanish). Libertad Digital. 2008-05-09.
- ↑ "Neither crisis nor slowdown: Zapatero now talks about economic "weaknesses"" (in Spanish). El Confidencial. 2008-05-14.
- ↑ "The government's 21 measures to address the crisis" (in Spanish). La Voz de Galicia. 2008-06-23.
- ↑ "Zapatero promises profound reforms to address the crisis" (in Spanish). Cinco Días. 2008-06-24.
- ↑ "Zapatero first mentions the word "crisis" to refer to the economic situation" (in Spanish). El País. 2008-07-08.
- ↑ "Martinsa-Fadesa announces the largest default in Spain's history" (in Spanish). El País. 2008-07-14.
- ↑ "2.5 million unemployed in August, the highest figure in a decade" (in Spanish). hoy.es. 2008-09-03.
- ↑ "Spain nears 3 million unemployed and turns into worldwide employment destructor" (in Spanish). Expansión. 2008-12-03.
- ↑ "The government will support the bank debt with 100 billion" (in Spanish). El País. 2008-10-13.
- ↑ "The government will create a €30 billion worth fund to purchase 'healthy' assets banks and savings banks" (in Spanish). El Mundo. 2008-10-07.
- ↑ "Zapatero injects €11 billion to municipalities and the automotive industry" (in Spanish). El Mundo. 2008-11-27.
- ↑ "The government has injected €50 billion with the E Plan, about 2% of GDP" (in Spanish). Público. 2009-05-06.
- ↑ "Many jobs, but unproductive" (in Spanish). El País. 2009-08-30.
- ↑ "Recession comes to Spain after 15 years of uninterrupted growth" (in Spanish). finanzas.com. 2009-02-12.
- ↑ "Spain launches a £8.4bn bailout to rescue a stricken savings bank". The Guardian. 2009-03-29.
- ↑ "War report: Eight seized or nationalized banks in Spain" (in Spanish). El País. 2012-05-09.
- ↑ "Spain Gets 'FROB'bed-Off by the EU Commission". Seeking Alpha. 2010-01-21.
- ↑ "Spain’s prime minister brings in a new finance minister". The Economist. 2009-04-08.
- ↑ "Unemployment Q2 2009" (in Spanish). finanzzas.com. 2009-07-24.
- ↑ "GDP falls by 4.2%, new negative record in the Spanish economy" (in Spanish). El Mundo. 2009-08-27.
- ↑ "Zapatero: the tax rise will be "limited and temporary"" (in Spanish). El Mundo. 2009-08-28.
- ↑ "Zapatero launches the largest tax rise in history" (in Spanish). Expansión. 2009-09-10.
- ↑ "The government increases standard VAT to 18% and removes the €400 tax reduction" (in Spanish). El Mundo. 2009-09-26.
- ↑ "Unemployment rises to 18.8% in 2009, the highest in 12 years" (in Spanish). El Mundo. 2010-01-29.
- ↑ "Public deficit soars at 11.4%" (in Spanish). El País. 2010-01-29.
- ↑ "The country risk rises in the worst stock week in 11 months" (in Spanish). El País. 2010-02-06.
- ↑ "Long-term unemployment soars after two years of crisis" (in Spanish). El País. 2010-05-01.
- ↑ "Spain pays six more times than Germany for its two year-debt interests" (in Spanish). El País. 2010-05-07.
- ↑ "Zapatero cuts public servants' wages for the first time in history" (in Spanish). El Mundo. 2010-05-12.
- ↑ "Zapatero announces an historic cut in social spending" (in Spanish). Expansión. 2010-05-12.
- ↑ "Zapatero overturns his strategy with an unprecedented cut in public wages" (in Spanish). El País. 2010-05-13.
- ↑ "The PP advantage goes off after the cut" (in Spanish). El País. 2010-05-16.
- ↑ "Government approves law proposing urgent labour market reform". Eurofound. 2010-09-22.
- ↑ "The labor reform is launched on Sunday" (in Spanish). El País. 2010-09-19.
- ↑ "Zapatero extensively reshapes his government" (in Spanish). El País. 2010-10-20.
- ↑ "Zapatero puts his future in Rubalcaba's hands" (in Spanish). El Mundo. 2010-10-20.
- ↑ "Why I don't trust in Spain" (in Spanish). El País. 2010-11-28.
- ↑ "Spain follows Ireland and Portugal: the risk premium marks a new record" (in Spanish). Libertad Digital. 2010-11-29.
- ↑ "Zapatero announces a tax cut and privatizes AENA and Lotteries" (in Spanish). El País. 2010-12-02.
- ↑ "Zapatero announces retirement at 67 for 2027 and looks for a pact with Rajoy" (in Spanish). El País. 2010-12-31.
- ↑ "Elecciones Generales 20 de noviembre 2011. Calendario Electoral" (PDF) (in Spanish). congreso.es. Retrieved 10 July 2017.
- 1 2 "Real Decreto 1329/2011, de 26 de septiembre, de disolución del Congreso de los Diputados y del Senado y de convocatoria de elecciones" (PDF). Boletín Oficial del Estado (in Spanish) (232): 101835–101836. 27 September 2015. ISSN 0212-033X.
- 1 2 "Nuevo Gobierno a finales de diciembre". El País (in Spanish). Madrid. 26 September 2011. Retrieved 10 July 2017.
- ↑ ""Fight for what you want", PSOE campaign slogan" (in Spanish). Europa Press. 2011-10-20.
- ↑ "'Join the change', PP slogan for the 20-N election" (in Spanish). Cadena SER. 2011-10-25.
- ↑ "IU encourages to overcome the PP-PSOE "dichotomy" with its "Rebel!" slogan" (in Spanish). Público. 2011-10-15.
- ↑ "For UPyD, 'each vote counts' and will fight to obtain the citizens' trust" (in Spanish). Huelva 24. 2011-11-04.
- ↑ "20-N: Duran launches his web, Twitter and Facebook and pre-campaign slogan '+ x cat'" (in Spanish). Europa Press. 2011-10-06.
- ↑ "The PNV wants to be the first Basque force in the Cortes Generales" (in Spanish). EITB. 2011-10-20.
- ↑ "Amaiur or the 'bridge' that aims to bring the abertzale left again into Congress" (in Spanish). RTVE. 2011-11-18.
- ↑ "Alfred Bosch: "We Want the Republic of Yes"" (in Spanish). esquerra.cat. 2011-10-26.
- ↑ "Rajoy gana el debate por la mínima". El País (in Spanish). 7 November 2011.
- ↑ "Rubalcaba da por hecho que Rajoy ganará las elecciones". El Mundo (in Spanish). 8 November 2011.
- ↑ "Un 43,9% opina que Rajoy ganó el debate". Antena 3 (in Spanish). 8 November 2011.
- ↑ "Rubalcaba acorrala a Rajoy con su "programa oculto"". Público (in Spanish). 8 November 2011.
- ↑ "Todos los sondeos dan como ganador al líder del PP". El Plural (in Spanish). 8 November 2011.
- ↑ "Postelectoral Elecciones Generales 2011. Panel (2ª Fase)" (PDF). CIS (in Spanish). Retrieved 1 July 2017.
External links
 Media related to Spanish general election, 2011 at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Spanish general election, 2011 at Wikimedia Commons
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)


.jpg)
