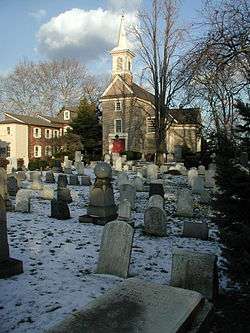South Philadelphia
| South Philadelphia | |
|---|---|
| Neighborhood of Philadelphia | |
|
Gloria Dei (Old Swedes') Church, Queen Village, South Philadelphia | |
|
South Philadelphia district, highlighted on a map of Philadelphia County | |
| Coordinates: 39°55′23″N 75°10′31″W / 39.9231°N 75.1753°WCoordinates: 39°55′23″N 75°10′31″W / 39.9231°N 75.1753°W | |
| Country |
|
| State |
|
| County |
|
| City |
|
| Area | |
| • Total | 9.7 sq mi (25 km2) |
| Population (2010) | |
| • Total | 168,782 |
| • Density | 17,000/sq mi (6,700/km2) |
| ZIP code | 19145, 19146, 19147, 19148 |
| Area code(s) | 267, 215 |
South Philadelphia, nicknamed South Philly, is the section of Philadelphia bounded by South Street to the north, the Delaware River to the east and south, and the Schuylkill River to the west.[1] A diverse community, South Philadelphia is known for its large Italian American population. South Philadelphia also contains large Irish American and African American populations as well.
History

South Philadelphia began as a satellite town of Philadelphia, with small townships such as Moyamensing and Southwark.[2] Towards the end of the Industrial Revolution, the area saw rapid growth in population and urban development. This expansion was in part due to an influx of working class laborers and immigrants looking for factory jobs and dock work, as well as the first wave of mass immigration of refugees and impoverished immigrants from Ireland in the wake of the Great Irish Hunger. South Philadelphia's urbanized border eventually expanded to reach that of Philadelphia proper, or what is today known as Center City Philadelphia. Along with all other jurisdictions in Philadelphia County, South Philadelphia became part of the City of Philadelphia proper with passage by the Pennsylvania legislature of the city/county Act of Consolidation, 1854.
The area continued to grow, becoming a vital part of Philadelphia's large industrial base and attracting immigrants from Italy, Ireland, Poland, and many Southern European and Eastern European countries during the late 19th and early 20th centuries, as well as Black American migrants from the southern United States during the Great Migration of the early 20th century. The immigrants and migrants became the basis of South Philadelphia's unique and vibrant culture that developed over the next several decades. Struggling to maintain their Catholic identity in a mostly Protestant city, the Irish built a system of Irish Catholic churches and parochial schools for their children, including Catholic high schools. The later immigrant populations of Italians and Poles were also Catholic. Initially, these populations attended existing Catholic churches but built their own ethno-national churches when possible. However, the more established Irish-American ethnic community controlled the Catholic clergy and hierarchy for decades in Philadelphia and throughout the region, often excluding the more recent Italian (and, to a lesser extent, Polish) populations from participating in the church hierarchy. In addition to the influx of Catholic immigrants, many Polish Jews and other Jews from Eastern Europe settled in South Philadelphia during the first half of the 20th century, especially in the diverse area now known as Queen Village where Jewish immigrants lived among Catholic Polish immigrants, Irish-Americans, and Italian immigrants. A smaller but significant Greek immigrant community also flourished around this time, leading to the establishment of Greek Orthodox parishes in South Philadelphia. Despite this dramatic growth in population, the low funding of education by the city resulted in the first public high school not being formed in South Philadelphia until 1934.[3]
Attracted to the industrial jobs, the new residents of South Philadelphia created communities that continued many of their Old World traditions. While many of the new arrivals were Catholic, neighborhood parishes reflected their ethnic and national traditions. Monsignor James F. Connelly, the pastor of the Stella Maris Catholic Church and an editor of the 1976 work The History of the Archdiocese of Philadelphia, said in a 2005 Philadelphia Inquirer article that each parish church "offer[s] the immigrants the faith they were familiar with."[4] With the dramatic loss of industrial jobs during mid-20th century restructuring, there were population losses in South Philadelphia as well as other working-class parts of the city, and some neighborhood Catholic schools had to close.
Today, many of South Philadelphia's communities are largely Italian American. Many of these communities contain both older and more recent Italian immigrants and Italian speakers, and Italian saint festivals and cultural celebrations, including the South 9th Street Italian Market festival, are popular in the South Philadelphia Italian-American communities. In addition, South Philadelphia continues to be home to many ethnic Irish American communities and African American communities. Both Irish American and African American communities can be found in the neighborhoods of Grays Ferry and Southwest Center City, while the nearby neighborhood of Point Breeze is largely African American and is often considered the center of the South Philadelphia's African American communities. The neighborhood of Pennsport remains primarily a working class Irish-American neighborhood and the cultural center of Irish-American South Philadelphia. An increase in late 20th-century and early 21st-century immigration has given South Philadelphia significant populations from Asia, particularly Southeast Asia, including populations from Vietnam, Cambodia, Indonesia, and Thailand. In addition, there has been an increase in recent years of immigrants from Russia, Mexico, and Central American nations such as Honduras, Guatemala, and El Salvador. Today, many vendors that work alongside the Italian-Americans at the Italian Market are of Asian descent and Mexican or Central American descent, and Vietnamese, Thai, Mexican, and Central American restaurants are interspersed with historic Italian restaurants in the Market area. The recent revitalization of Center City Philadelphia and the subsequent gentrification of adjacent neighborhoods has also led to dramatic rises in prices of housing in the neighborhoods of historic Queen Village, Bella Vista, and some other northern parts of South Philadelphia, leading to an influx of young urban professionals in those more northern neighborhoods.
Many of the community clubs that create the annual Mummers Parade every New Year's Day have traditionally been from South Philadelphia, especially those located on the largely Irish American S. 2nd Street ("Two Street") in the Pennsport neighborhood.[5][6][7]
Government and infrastructure
Portions of South Philadelphia are within Philadelphia City Council Districts 1 and 2. As of 2014 Councilman Mark Squilla and Councilman Kenyatta Johnson represent the two districts.[1]
The Philadelphia Fire Department operates nine fire stations serving South Philadelphia.[8] Most of South Philadelphia resides in Fire Battalion 1, headquartered at 711 South Broad Street. Portions of South Philadelphia reside in Battalion 4, headquartered at North 4th Street and Arch Street, and Battalion 11, headquartered at 43rd Street and Market Street.[1]
The Philadelphia Police Department patrols three districts located within South Philadelphia. The three patrol districts serving South Philadelphia are the 1st, 3rd, and 17th districts.[9]
Geography
According to the United States Census Bureau, South Philadelphia has an area of 9.7 sq. miles, of which none is water.
Demographics
In 2010, the area's population was 168,782. Though largely known for its Italian American population, South Philadelphia contains a diverse population of Italian Americans, Irish Americans, African Americans, and Mexican Americans, as well as growing populations of Vietnamese Americans, Chinese Americans, Cambodian Americans, Indonesian Americans, Thai Americans, and Central Americans. In addition, the area contains smaller but historically significant Greek American and Jewish American communities. Many residents have lived in the neighborhood for decades. Many family-owned businesses are found in South Philadelphia.
On January 22, 2010 the Associated Press said "South Philadelphia has been growing more diverse for decades, but the last 20 years have seen the greatest influx of Asian and Hispanic families."[10] David Elesh, a Temple University urban sociologist, said that of the almost 60,000 Philadelphia residents who reported being born in China, many lived in South Philadelphia.[10]
As of the 2010 Census, there are 168,782 people in 78,440 housing units. The population density is 16,771 people per square mile. 46.6% of the population is male, and 53.4% is female. The South Philadelphia area comprises the zip codes of 19145, 19146, 19147, and 19148. Data for the zip codes that make up South Philadelphia as of the Census 2000 Summary File:
Racial demographics[15][16]
- Non-Hispanic White: 87,268 (51.8%)
- African-American: 43,404 (25.7%)
- Asian: 20,926 (12.4%)
- Hispanic or Latino: 12,866 (7.6%)
- Mixed or Other: 10,531 (6.1%)
- American Indian: 656 (0.3%)
Italian Americans
The largest and oldest Italian settlements in Philadelphia are in South Philadelphia.[17] Though rare and small in size, some early Italian settlements appeared in South Philadelphia prior to the 1860s; however, these small settlements generally consisted of skilled workers, merchants, and artists from Genoa and other wealthier areas of Northern Italy.[18] In contrast, the vast majority of Italian immigrants that settled in Philadelphia came from impoverished regions of Southern Italy beginning after the Italian unification in 1861, with most Italian immigration to Philadelphia occurring in the 20th century. Though Italians in Philadelphia emigrated from various Southern Italian regions, most Italians in Philadelphia emigrated from or have origins in three main areas: the previously combined regions of Abruzzo and Molise; the city of Messina in Sicily and the surrounding province; and Salerno and Avellino in Campania. To this day, dialects from those regions mixed with English are spoken in many South Philadelphia households and neighborhoods.
Italians in South Philadelphia experienced widespread discrimination from the larger majority populations of Philadelphia. For example, Italian neighborhoods in South Philadelphia were heavily redlined for decades specifically due to their Italian-American demographics. However, Italian-Americans in South Philadelphia have contributed greatly to the culture of Philadelphia, establishing the Italian Market, creating both the cheesesteak and the hoagie, and introducing roast pork sandwiches, water ice, tomato pie, and pizza to the cuisine of Philadelphia. Recently, some Italian-American South Philadelphians have moved to Southern New Jersey.[17] However, the Italian-American population in Philadelphia remains the second largest in the country.
The Italian Market is located in South Philadelphia. In 1852 St. Mary Magdalen de Pazzi in South Philadelphia,[17] the first Italian Catholic parish in the United States, was founded by pre-mass immigration Italians.[18] Donna J. Di Giacomo, author of Italians of Philadelphia, wrote that this church "was a hallmark of the neighborhood and touched many a South Philadelphia Italian's and Italian American's life in one way or another for generations."[17]
Irish Americans
Much of South Philadelphia's Irish population is located is the eastern part of the section. Pennsport, which is also locally referred to as "Two Street", is arguably the most well known Irish neighborhood in South Philadelphia. Pennsport is also home to many of the cities Mummers clubs, where some are known for their Irish American themes. Other Irish neighborhoods include Grays Ferry, Devil's Pocket, and areas of Girard Estate, Southwest Center City, and Whitman.
Philadelphia's large Irish community, however, is more prominent in other sections of the city, most notably Northeast Philadelphia.
Mexican Americans
As of 2000 the largest Mexican community in Philadelphia was in the area bounded by Front Street, 18th Street, Oregon Avenue, and Washington Avenue in South Philadelphia.[19] As of 2011 most Mexicans in South Philadelphia originate from the state of Puebla.[20]
Black Americans
Black Americans have lived in South Philadelphia since the early 19th century at the very least, though the city of Philadelphia proper was home to a significant population of free blacks and fugitive slaves since at least the 18th century. The majority of the current black population in South Philadelphia, however, is descended from Southern black migrants that moved into the city in high numbers during the first Great Migration in the early 20th century. South Street was originally considered the cultural and commercial center of this community, though the community became increasingly concentrated to western areas below South Street, including Point Breeze, Southwest Center City, Schuylkill, and Grays Ferry.[21] Point Breeze and South Street particularly served as Philadelphia's "Harlem" during the first half of the 20th century. The first Black staffed police station and fire station were located on South Street. Famous Black South Philadelphians include opera contralto Marian Anderson and musicians Kenny Gamble and Chubby Checker. The Udunde Festival, arguably the largest street festival in Philadelphia, is an African-American celebration that is held annually in the South Street area. As of 2013, those that identified as "Black alone" or in combination with another race totaled 45,482 persons living in the zip codes 19145, 19146, 19147, and 19148.[22] The Black population in South Philadelphia has historically constituted between 25% and 30% of South Philadelphia's population - 27% Black alone and in combination with another race as of a 2013 population estimate.
Transportation
I-95 runs north and south through South Philadelphia and, in this area, provides commuters with access to Philadelphia International Airport, I-76, the South Philadelphia Sports Complex, and the Walt Whitman Bridge. The Girard Point Bridge section of I-95 crosses over the mouth of the Schuylkill River, where it merges with the Delaware River.
I-76 becomes the Schuylkill Expressway at Passyunk Avenue in South Philadelphia and allows access between this section of the city and University City, Center City, 30th Street Station, and the western suburbs.
In addition, PA Route 291 serves as a major artery between the area and Delaware County, crossing the Schuylkill River via the Platt Bridge (named for Medal of Honor recipient George C. Platt). Broad Street is part of PA Route 611.
SEPTA's Broad Street Line subway services South Philadelphia and provides quick access to Center City and North Philadelphia. A number of SEPTA bus routes also serve South Philadelphia, ferrying commuters to and from Center City and its immediate suburbs, mostly those in Delaware County.
South Philadelphia is served by bike lanes on many streets going in all directions.[23] Snyder Avenue has bike lanes going East and West. Columbus Boulevard has North and South bike lanes. 22nd Street provides Northward lanes for cyclists. Some streets such as 11th Street have both Bike lanes and Sharrows or Shared lane marking.
As of 2016 two Taiwanese airlines, China Airlines and EVA Air, provides private bus services to and from John F. Kennedy International Airport in New York City for customers based in the Philadelphia area. These bus service stop in South Philadelphia.[24][25]
Crime
In a 2007 Philadelphia Weekly article, the journalist Steve Volk stated that anti-drug activists said that South Philadelphia has secretive recreational drug dealing. More neighborhoods in the region are mixed-income than neighborhoods in some other regions; therefore, many drug dealers hide their activities. As in other parts of the city, drugs have contributed to crime.[26]
The Italian-American Mafia family known as the Philadelphia Crime Family is active in the area, maintaining much of its operations in South Philadelphia. The African-American Black Mafia and its offshoot, the Junior Black Mafia, have also had a presence in the Point Breeze section of South Philadelphia since the late 1960s.
Historical gangs include the Italian Philadelphia poison ring as well as the Lanzetta brothers, a gang of six Italian-American brothers who were drug traffickers and bootleggers. All six brothers were born in the Third Ward of South Philadelphia. South Philadelphia (along with Atlantic City and Little Italy) was a part of their territory, in which they fought with rival bootleggers William Michael "Mickey Duffy" Cusick and Joe Bruno during Prohibition.
Education
Primary and secondary schools
Public schools
Residents are with the School District of Philadelphia's South District.[1] Zoned public high schools in South Philadelphia include South Philadelphia High School, Audenried High School, and Furness High School.[27][28][29][30]
Girard Academic Music Program and The Philadelphia High School for the Creative and Performing Arts (CAPA), both magnet schools, are in South Philadelphia-at Broad and Carpenter Streets and 21st and Ritner Streets, respectively.[31]
The Mastery Charter Schools system operates the Thomas School (grades 7-12) in South Philadelphia. It was formerly the district school Thomas Middle School,[32] and shares a campus with a district elementary school, D. Newlin Fell School, at 9th Street and Oregon Avenue.
Private schools
Saints John Neumann and Maria Goretti Catholic High School is in South Philadelphia. It is a merger of the former Saint John Neumann High School and the Saint Maria Goretti High School.[33][34][35] In addition, there are several Catholic elementary schools in South Philadelphia, usually tied to a local parish church. Notable examples include St. Anthony of Padua School (9th and Pierce Streets)[36] and St. Monica School (17th and Ritner Streets).[37] Philadelphia Free School, patterened on the Sudbury school model, is located at the intersection of 21st and Christian Streets.[38]
Public libraries
Free Library of Philadelphia operates six branches in South Philadelphia: Charles Santore, Fumo Family, Queen Memorial, South Philadelphia, Thomas F. Donatucci, Sr. and Whitman.[39] Prior to its 1999 reopening in a new building, the Fumo Branch was known as the Ritner Children's Branch.[40]
Places of note

South Street has long been considered the border between South Philadelphia proper and Center City. It originally ran east and west (although traffic is now routed east one-way). Many bars, nightspots, shops, and restaurants are located along this neon-lit hotspot, with occasional live music venues (including the TLA) along the way.
The intersection of 9th Street and Passyunk Avenue is home to the regionally famous Geno's Steaks and Pat's King of Steaks cheesesteak shops, fierce competitors in the local deli market for decades. Also, nearby is the city's open-air Italian Market, specializing in fresh produce, meats, and other foods. It is lined by specialty shops, such as butchers, bakeries and cheese/grocery stores, as well as one for kitchen goods, and new cafes and coffee houses. The area was featured in the film Rocky and its sequels. This is the heart of an annual street festival celebrating the neighborhood's food.
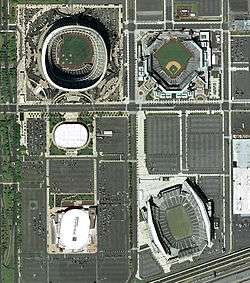
Among the largest landmarks in South Philadelphia is the South Philadelphia Sports Complex at the corner of Broad Street and Pattison Avenue. Here, the Philadelphia Phillies (professional baseball), Philadelphia Eagles (professional football), Philadelphia 76ers (professional basketball), Philadelphia Flyers (professional ice hockey), Philadelphia Soul (professional arena football), Temple Owls (college football) and the annual Wing Bowl (an event sponsored by the sports talk radio station, WIP-FM 94.1) make their home in the massive state-of-the-art sports arenas surrounding the well-known intersection: Citizens Bank Park, Lincoln Financial Field, and the Wells Fargo Center.
The sports complex was once home to Veterans Stadium (The Vet) which stood from 1971 to 2004; John F. Kennedy Stadium, which stood from 1925 to 1992; and the Spectrum, which was in use from 1967 to 2009 and was demolished in 2011. The NovaCare Complex, located on Pattison Avenue just west of the stadium area, serves as the practice facility of the Philadelphia Eagles. They now play at Lincoln Financial Field.
The American Swedish Historical Museum is located in Franklin Delano Roosevelt Park. One of Philadelphia's last pre-World War I rowhouse synagogues, Congregation Shivtei Yeshuron-Ezras Israel, remains active in Pennsport.
The Philadelphia Naval Shipyard is located in this section of town along the Delaware River. For decades during the World Wars and after, the shipyard was a major employer, whose craftsmen built new ships and repaired and maintained existing ones. With the decline in the military uses, the area is being redeveloped by the Navy and city for a variety of business and industrial uses.
The Sunoco oil corporation bases its headquarters along South Philadelphia's Passyunk Avenue.
A refurbished area of South Philadelphia alongside Columbus Boulevard/Delaware Avenue (near the Walt Whitman Bridge), Columbus Commons, provides big box shopping and chain restaurants.
Washington Avenue, between 16th St. on the west and Front St. on the east, is home to many Asian businesses, including Vietnamese, Chinese and Korean. Among these are restaurants of all types, two large Asian supermarkets, jewelers and a wide variety of specialty shops.
Passyunk Avenue, running on a diagonal from Broad Street to South Street, is a formerly thriving consumer district currently undergoing revitalization efforts. Within the past few years, several coffeeshops, restaurants and bars have opened which appeal to the younger population beginning to live in the area. In addition, a farmers' market is held on Wednesday nights at one of the squares.
2300 Arena (better known as the ECW Arena) at the corner of Swanson Street and Ritner Street is a venue known for hosting boxing and professional wrestling events.
Notable people
- Al Alberts, singer and composer; co-founder and lead singer of The Four Aces[41]
- Marian Anderson, opera singers and Congressional Gold Medal recipient[41][42]
- Frankie Avalon, actor, singer, teen idol[41]
- Joey Bishop, actor, comedian, member of the "Rat Pack"[41][43]
- Black Thought, MC and co-founder of The Roots[44]
- Danny Cedrone, bandleader, guitarist for "Rock Around the Clock"[45][46]
- Chubby Checker, singer of The Twist[41][47]
- Stanley Cowell, jazz pianist, founder of Strata-East Records, member of the Heath Brothers[48]
- Jim Croce Singer-Songwriter[49]
- Joey DeFrancesco, jazz organist, trumpeter, vocalist[48]
- Buddy DeFranco, jazz clarinet player[48]
- James DePreist, conductor of the Tokyo Metropolitan Symphony Orchestra, director at the Juilliard School, laureate music director of the Oregon Symphony[48]
- Fred Diodati, lead singer of The Four Aces[48][50]
- Charles Earland, jazz composer, organist, saxophonist[48]
- Fabian 1950s teen idol[41][48]
- Wilhelmenia Fernandez, soprano, star of the film Diva[48]
- Larry Fine, member of the comedy act The Three Stooges[48][51]
- Linda Fiorentino, actress (Dogma, Men in Black, The Last Seduction)[48]
- Al Fisher, guard for the Kent State Golden Flashes[48]
- Eddie Fisher, singer, entertainer ("Oh My Papa", "Lady of Spain")[41]
- Edwin Forrest, 19th century stage actor[48]
- Kenny Gamble, Rock and Roll Hall of Fame songwriting and record production team Gamble and Huff[48]
- Dusolina Giannini, soprano (Metropolitan Opera)[48]
- Vittorio Giannini, composer of operas, symphonies, and band music[48]
- Charlie Gracie, rock pioneer and singer[48]
- Isadore Granoff, founder of the Granoff School of Music[52]
- Buddy Greco, singer ("The Lady is a Tramp") and pianist[41][48]
- William Guarnere, nicknamed "Wild Bill", member of 506th Parachute Infantry Regiment E, "Easy Company"[53]
- Frank Guarrera, baritone (Metropolitan Opera)[48]
- Albert "Tootie" Heath jazz drummer, member of the Heath Brothers[48]
- Jimmy Heath jazz tenor saxophonist, member of the Heath Brothers[48]
- Percy Heath double bass player for the Modern Jazz Quartet, member of the Heath Brothers[48]
- Edward "Babe" Heffron, member of 506th Parachute Infantry Regiment E, "Easy Company"[54]
- Sherman Hemsley, actor (All in the Family, The Jeffersons, Amen)[55]
- Dom Irrera, comedian[48]
- Albert Innaurato, playwright, theatre director, and writer[48]
- Jerry Jaye, country/rockabilly singer ("My Girl Josephine")[48]
- Kitty Kallen, singer ("Little Things Mean a Lot")[48]
- Irvin Kershner, director (The Empire Strikes Back, RoboCop 2)[48]
- Jack Klugman, actor (The Odd Couple, Quincy, M.E., 12 Angry Men)[41][48]
- Kenny Koplove, baseball player[56][57]
- Joseph Kramm, playwright (Pulitzer Prize for The Shrike), actor, and director[48]
- Eddie Lang, jazz guitarist[48]
- Mario Lanza, tenor and actor (The Great Caruso)[41][48]
- Joseph Anthony "Uncle Joe" Ligambi, current boss of the Philadelphia crime family.
- Hy Lit, Philadelphia-area DJ from the 1950s until 2005[48]
- George Litto, film producer (Thieves Like Us, Dressed to Kill and Blow Out)[48]
- Bernie Lowe, songwriter, producer, arranger, founder of Cameo Records, launched careers of Chubby Checker, Charlie Gracie, Dee Dee Sharp, Bobby Rydell, The Orlons[48]
- Man Ray, modernist/Dada/Surrealist artist[48]
- Gloria Mann, pop singer ("Earth Angel")[48]
- Guy Marks, actor, singer, comedian and impressionist[48]
- Al Martino, singer ("Here in My Heart", "Volare") and actor (The Godfather, The Godfather Part III)[41][48]
- Pat Martino, jazz guitarist and composer[48]
- Meek Mill, rapper (He was born in South Philadelphia but was raised in North Philadelphia) [58]
- N. Richard Nash, writer and dramatist (The Rainmaker)[48]
- Fayard Nicholas, dancer (Nicholas Brothers)[48]
- Harold Nicholas, dancer (Nicholas Brothers)[48]
- Harry Olivieri, co-inventor of the cheesesteak[59]
- Pat Olivieri, co-inventor of the cheesesteak[59]
- Frank Palumbo, restaurateur, humanitarian and power broker; owner of Palumbo's"[60][61]
- Vince Papale, former professional football player for the Philadelphia Eagles in the late 1970s. His story of making the team and his playing career is the subbject of the 2006 film Invincible.
- Lisa Peluso, actress (Saturday Night Fever, Search for Tomorrow, Loving, Another World, One Life to Live)[48]
- Vincent Persichetti, composer, pianist, teacher at the Juilliard School (students included Philip Glass, Hall Overton, Kenneth Fuchs and Thelonious Monk)[48]
- Questlove, drummer and co-founder of The Roots[44]
- Florence Quivar, mezzo-soprano (Metropolitan Opera, Grammy Award for Porgy and Bess)[48]
- Peter Mark Richman, actor (Santa Barbara, Dynasty, Three's Company, Friday the 13th Part VIII: Jason Takes Manhattan)[48]
- Frank Rizzo, mayor of Philadelphia (1972–1980)[62]
- LaVaughn Robinson, tap dancer, choreographer (a National Endowment of the Arts "Living National Treasure" and NEA National Heritage Fellowship award)[48]
- Bobby Rydell, singer ("Wild One", "Volaire"), actor (Bye Bye Birdie), teen idol[48]
- Jodie Sands, singer ("With All My Heart", "Someday (You'll Want Me to Want You)")[48]
- Dee Dee Sharp, singer ("Slow Twistin'" (with Chubby Checker), "Mashed Potato Time")[48]
- Beanie Siegel, rapper[63]
- Sylvester Stallone, actor (Rocky, Rambo, The Expendables (film series) franchises)[48]
- Joseph Stefano, Edgar Award winning screenwriter (Psycho)[48]
- George Tunnell, vocalist (Jan Savitt and the Top Hatters)[48]
- Charlie Ventura, tenor saxophonist and bandleader[48]
- Joe Venuti, jazz violin pioneer[48]
- Stanley Weintraub, professor, historian, and biographer[48]
- Ed Wynn, Emmy Award winning (The Ed Wynn Show) and Academy Award nominated (The Diary of Anne Frank) actor (Ziegfeld Follies, The Great Man, Mary Poppins)
See also
- Aquarama Aquarium Theater of the Sea
- Benjamin Franklin Bridge
- Franklin Delano Roosevelt Park
- Italian Market, Philadelphia
- Little Saigon, Philadelphia
- Moyamensing Prison
- Naval Hospital Philadelphia
- Philadelphia Naval Shipyard
- Sesquicentennial Exposition
- Settlement Music School
- South Philadelphia High School
- South Philadelphia Sports Complex
- Walt Whitman Bridge
- Whitman Plaza
Further reading
- Di Giacomo, Donna J. Italians of Philadelphia. Arcadia Publishing, 2007. ISBN 0738550205, 9780738550206.
- Juliani, Richard N. Building Little Italy: Philadelphia's Italians Before Mass Migration. Penn State Press, 2005. ISBN 0271028645, 9780271028644.
References
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for South Philly. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to South Philadelphia. |
- 1 2 3 4 "The Political and Community Service Boundaries of Philadelphia." City of Philadelphia. Retrieved November 8, 2008.
- ↑ Where Pennsylvania History Began(by Henry D. Paxon, The Swedish Colonial Society, 1926)
- ↑ Allen, Davis; Haller, Mark, eds. (1973). The Peoples of Philadelphia: A History of Ethnic Groups and Lower-Class Life, 1790—1940. Temple University Press. p. 256. ISBN 0-87722-053-0.
- ↑ Woodall, Martha. "Unsteady times for neighborhood Catholic schools; Population changes have meant fewer elementaries and an unexpected merger." Philadelphia Inquirer. March 16, 2005.
- ↑ Max L. Raab (2001). Strut! The Movie (DVD). Philadelphia: Max L. Raab Productions.
- ↑ Welch, Jr., Charles E. (October–December 1966). ""Oh, Dem Golden Slippers": The Philadelphia Mummers Parade". The Journal of American Folklore. The Journal of American Folklore, Vol. 79, No. 314. 79 (314): 523–536. JSTOR 538218. doi:10.2307/538218.
- ↑ Dubin, Murray (June 1996). South Philadelphia; Mummers, memories, and the Melrose Diner. Temple University Press. ISBN 1-56639-429-5.
- ↑ "Fire Houses." Philadelphia Fire Department. Retrieved November 7, 2008.
- ↑ PPD Online Patrol Districts, Philadelphia Police Department.
- 1 2 "Bullying against Asian students roils Philadelphia high school." Associated Press at the USA Today. January 22, 2010. Retrieved on January 20, 2013. "South Philadelphia has been growing more diverse for decades, but the last 20 years have seen the greatest influx of Asian and Hispanic families. Many of the city's nearly 60,000 residents who report being born in China live in the neighborhoods, said David Elesh, an urban sociologist at Temple University."
- ↑ http://factfinder.census.gov/servlet/QTTable?_bm=y&-qr_name=DEC_2000_SF1_U_DP1&-geo_id=86000US19145&-ds_name=D&-_lang=en&-redoLog=false
- ↑ http://factfinder.census.gov/servlet/QTTable?_bm=y&-qr_name=DEC_2000_SF1_U_DP1&-geo_id=86000US19146&-ds_name=D&-_lang=en&-redoLog=false
- ↑ http://factfinder.census.gov/servlet/QTTable?_bm=y&-qr_name=DEC_2000_SF1_U_DP1&-geo_id=86000US19147&-ds_name=D&-_lang=en&-redoLog=false
- ↑ http://factfinder.census.gov/servlet/QTTable?_bm=y&-qr_name=DEC_2000_SF1_U_DP1&-geo_id=86000US19148&-ds_name=D&-_lang=en&-redoLog=false
- ↑ Factfinder at census.gov
- ↑ "2010 Census". Medgar Evers College. Archived from the original on 2010-06-11. Retrieved 2010-04-13.
- 1 2 3 4 Di Giacomo, p. 11.
- 1 2 Di Giacomo, p. 8.
- ↑ "Latino Philadelphia at a Glance." (Archive) Historical Society of Pennsylvania. p. 1. Retrieved on January 15, 2014.
- ↑ "From Puebla to South Philly." Philadelphia Inquirer. October 28, 2011. Retrieved on January 15, 2014.
- ↑ Hunter, Marcus Anthony (2013). Black Citymakers: How The Philadelphia Negro Changed Urban America. OUP USA.
- ↑ U S Census Bureau , American Factfinder. census.gov 2009-2013 Population Estimate
- ↑ "Bike Maps". Bicycle Coalition. Retrieved August 13, 2012.
- ↑ "Service to Connect PA & NJ." EVA Air. Retrieved on February 29, 2016.
- ↑ "Free Shuttle Service To/From JFK Airport Archived 2016-03-06 at the Wayback Machine.." China Airlines. September 15, 2015. Retrieved on February 29, 2016.
- ↑ Volk, Steve. "Top 10 Drug Corners" Archived 2012-09-07 at Archive.is, Philadelphia Weekly, 2 May 2007. Retrieved on January 20, 2009
- ↑ "A Directory of High Schools for 2009 Admissions." School District of Philadelphia. Retrieved November 6, 2008.
- ↑ "From the Ashes." South Philly Review. November 1, 2007.
- ↑ "Academic standards differ in Philadelphia." The Loquitur. May 4, 2006.
- ↑ "SCHOOL'S FINALLY OUT FOR SUMMER STUDENTS." Philadelphia Inquirer. August 8, 1986. B01.
- ↑ Snyder, Susan. "It's good to be king - of your high school Guys get their own pageant." Philadelphia Inquirer. March 13, 2005. Retrieved on September 21, 2012.
- ↑ "Thomas Campus Information." Mastery Charter Schools. Retrieved on September 10, 2012. "927 Johnston Street Philadelphia, PA 19148"
- ↑ Woodall, Martha. "Neumann graduates its last all-male class." Philadelphia Inquirer. Saturday June 5, 2004. B02.
- ↑ SJNMGCHS. "School History". Saints John Neumann and Maria Goretti Catholic High School website. Retrieved 2007-05-11.
- ↑ "Ss. John Neumann and Maria Goretti Catholic High School". Newsweek website. Archived from the original on 2008-09-21. Retrieved 2007-05-11.
- ↑ "Saint Anthony of Padua Regional Catholic School". teacherweb.com. Retrieved 2017-07-15.
- ↑ "Saint Monica School". saintmonicaphilly. Retrieved 2017-07-15.
- ↑ "Philly Free School". www.phillyfreeschool.org. Retrieved 2017-07-15.
- ↑ "Branch Map (older version)." Free Library of Philadelphia. Retrieved on November 7, 2008.
- ↑ "Fumo Family Branch." Free Library of Philadelphia. Retrieved on November 7, 2008.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Broadcast Pioneers. Al Alberts, Broadcast Pioneer". Retrieved 6 November 2008.
- ↑ "Marian Anderson Biography". University of Pennsylvania Library Special Collections-MA Register 4 (Scope and Content Note). 31 January 2003. External link in
|work=(help) - ↑ McLellan, Dennis (2007-10-18). "Joey Bishop, 89; comedian was last surviving member of Rat Pack". Los Angeles Times. Archived from the original on 2007-11-06. Retrieved 2007-10-20.
- 1 2 DeLuca, Dan. The Philadelphia Inquirer August 2006, "They proclaim to all the land: Philly is cool".
- ↑ Dawson, Jim Rock Around the Clock: The Record That Started the Rock Revolution, Backbeat Books, 2005.
- ↑ Rockabilly Hall of Fame. "Danny Cedrone". Retrieved 6 November 2008.
- ↑ Chubbychecker.com Biography. Retrieved 6 November 2008.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 Dubin, Murray. South Philadelphia: Mummers, Memories, and the Melrose Diner. Temple University Press, 1996. ISBN 1-56639-429-5, ISBN 978-1-56639-429-1
- ↑ "Croce, James Joseph (Jim)". Retrieved 2010-05-16.
- ↑ South Philadelphia High School Alumni Association. "SPHS Hall of Fame". Retrieved 6 November 2008.
- ↑ Jon's Bar and Grille. "About Larry". Retrieved 6 November 2008.
- ↑ Porter, Lewis. John Coltrane: His Life and Music, University of Michigan Press, 1999. ISBN 0-472-08643-X, 9780472086436.
- ↑ Chang, David (March 11, 2014). ""Band of Brothers" WWII Vet Bill Guarnere Dies at 90". NBC 10.com. Retrieved March 11, 2014.
- ↑ Muse, Queen (December 3, 2013). "'Band of Brothers' WWII Vet "Babe" Heffron Dies at 90". NBC 10.com. Retrieved March 21, 2014.
- ↑ The Museum of Broadcast Communications. "HEMSLEY, SHERMAN". Retrieved 6 November 2008.
- ↑
- ↑
- ↑ http://www.indiehiphop.net/how-they-came-up-the-meek-mill-story/
- 1 2 Sims, Gayle Ronan (July 22, 2006). "Obituary: Harry M. Olivieri / Philadelphia cheesesteak's co-creator". Philadelphia Inquirer.
- ↑ Kane, Larry. Larry Kane's Philadelphia, 2000. Temple University Press, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. ISBN 1-56639-806-1.
- ↑ "MEMOIR: Me and Frank" Philadelphia Weekly, September 2005
- ↑ Dilulio, John J. Jr. Washington Monthly, July–August, 1993. "Frank Rizzo, The Last Big Man in Big City America pt. 1"
- ↑ USA Today. 26 September 2005, "Philadelphia rapper Beanie Sigel cleared". Retrieved 6 November 2008.