South London line
| South London Line | |
|---|---|
|
A London Overground train at Clapham High Street | |
| Overview | |
| Type | Commuter rail, Freight rail |
| System | National Rail |
| Status | Operational |
| Locale | Greater London |
| Termini |
London Victoria London Bridge |
| Stations | 10 |
| Operation | |
| Owner | Network Rail |
| Operator(s) |
London Overground Southern Southeastern |
| Rolling stock |
Class 378 "Capitalstar" Class 465 "Networker" Class 466 "Networker" |
| Technical | |
| Track gauge | Standard gauge |
| Electrification | 750 V DC third rail |
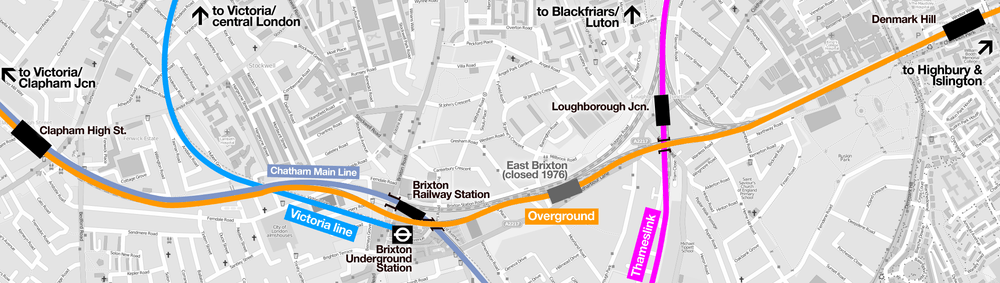
The South London Line is an Inner London part of the London Overground rail network. The line is run together with the East London Line to provide direct services between Clapham Junction and Highbury & Islington. It consists of eight stations, one of which marks the crossover into the East London Line network and runs 8.5 miles (13.7 km). Most of the line is on high viaduct over other transport infrastructure. Interchanges with the London Underground are at Clapham High Street and the closest on its London Overground extension is Canada Water. The line is in Travelcard Zone 2.
From the early 20th century until 2012 a shorter precursor route ran from the major terminus Victoria in Westminster to the interchange station London Bridge adjoining the City of London.[n 1] Sections of the line are used by other passenger railways and a section of the line was used by Eurostar when the London terminus was Waterloo International.[n 2]
It is proposed to use the spare capacity of the line as part of a Victoria-Bellingham service, to the south-east of the capital.
| South London Line (London Overground) Stations served are shown bold | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
History
The London, Chatham and Dover Railway (LCDR) was authorised to build the former route of the line by the South London Railway Act 1862. Designed and engineered under Frederick Banister,[1] it re-used the Wandsworth Road to Brixton section built as part of the LCDR main line.[1] The line was quadrupled and extended to London Bridge. The northern pair of tracks (becoming the Chatham Lines), without stations, was used by the LCDR to Kent; the southern (becoming the Atlantic lines) were used by the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway (LBSCR) into east Surrey parts of which became Greater London. Several stations were shared by the two companies.[1]
The LBSCR scheme, authorised in 1903, pioneered main-line rail electrification in the UK, and the first electric train ran on 1 December 1909. For the following three years, steam trains alternated with electrics, the latter operating every 15 minutes from 7.30am to midnight. Passenger numbers had fallen on introducing electric tramways in South London by 1.25 million in six months. In the first year of the rival line's electric operation passengers increased from 4 million to 7.5 million. The electrification used the overhead system at 6700 V AC, supplied by a power station at Deptford.[1] After creation of the Big Four railway companies, the Southern Railway installed standard third-rail 660 V DC supply on 17 June 1928.[1]
- Pre-extension route
| South London Line | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Southern service between London Victoria and London Bridge was axed in favour of joining to Clapham Junction and the London Overground's East London Line leading to a reduction to peak-hour and Saturday services, adopting the west end of the old route (between London Victoria and Peckham Rye).
East London Line extension into South London Line

In 2012 a 2.5-kilometre (1.6 mi) diversion was made to the eastern end to join to the East London Line, a former London Underground line which was reconverted to main line operation as part of Phase 2 of its extension project reinstating an alignment between Rotherhithe and Peckham that had been disused since 1911, via Old Kent Road station. This created the route from Surrey Quays to Clapham Junction via Queens Road Peckham, Peckham Rye, Denmark Hill, Clapham High Street and Wandsworth Road. Completion was scheduled for May 2012 in time for the London 2012 Summer Olympic and Paralympic Games,[2][3] which was not achieved as the line opened on 9 December 2012.[4]
The East London line connects to the North London line at Highbury & Islington, completing an orbital rail route around Central London, fulfilling the Orbirail concept.
Services
Passenger rail services were provided post-privatisation in the 1991 until 2012 by Southern, as with continuing services on the eastern section from Peckham Rye to London Bridge.[5]
Services along part of the line are operated by Southeastern on the Victoria-Dartford and the Chatham Main Lines, calling only at Denmark Hill and Peckham Rye.
From January 2015
The Thameslink Programme caused Southeastern to make these timetable modifications:[6][5]
Off-peak & Saturday
- 4tph between Clapham Junction & Highbury Islington (London Overground)
- 2tph between London Victoria & Dartford via Bexleyheath (Southeastern)
- 1tph between London Victoria & Dover Priory via Chatham (Stopping at Denmark Hill Only - Southeastern)
Evenings:
- 4tph between Clapham Junction & Highbury Islington (London Overground)
- 2tph between London Victoria & Dartford (Southeastern)
- 1tph between London Victoria & Dover Priory via Chatham (Stopping at Denmark Hill Only - Southeastern)
Sundays:
- 4tph between Clapham Junction & Highbury Islington (London Overground)
- 2tph between London Victoria & Dartford (Southeastern)
- 1tph between London Victoria & Dover Priory via Chatham (stop on route: Denmark Hill - Southeastern)
Addition of New Bermondsey station
The East London Line extension plans of 2001 proposed a new station at Surrey Canal Road near the Bermondsey/New Cross border.[7] A campaign group was formed in 2009 by Bermondsey residents to press for funding to be made available.[8][9] In September 2010, the £7 million funding was refused by the Department for Transport,[10] which Property developer Renewal in 2012 agreed to fund as part of a development scheme and Lewisham Council accordingly granted planning permission.[11] During a presentation at the site as part of the Open House 2014 weekend, Renewal announced a process of choosing a more recognizable name was underway with TfL. The decision reached for this part of the former south London dockyards is New Bermondsey.[12] Construction work began in 2016.[13]
Proposed developments
Victoria to Bellingham service
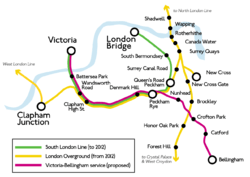
Speed of access of major destinations has changed as a result of the 2012 re-routing. The line since 2012 takes in Canada Water tube station, closely linked to Canary Wharf; similarly from Clapham Junction the West London Line (including Kensington Olympia) is made directly available.
London Victoria and London Bridge since 2012 became indirectly linked — via Clapham Junction or Peckham respectively. A demonstration took place to restore the route during the month when the route changed.[14][15] A survey by London Travelwatch found that 88% of passengers on the line felt they would be inconvenienced by the changes (although the survey also noted that respondents were generally unaware of the East London Line/Overground proposals or of any possible benefits they might bring).[16]
To compensate for the loss of services, it was proposed to introduce a Victoria-Bellingham service. This would restore the old route to Peckham Rye and take in part of the Catford Loop Line, to Bellingham in south-east London. The proposal was abandoned due to funding issues.[17]
Pressure groups and local MPs urged the Mayor to reconsider who secured funding in principle from the Secretary of State for Transport for greater line use or branches to be added. TfL compiled a shortlist of proposals to address the upset in commuting times.[17][18]
Lobbying for additional stations
Between Denmark Hill and Clapham High Street, the line passes through Brixton, crossing over Loughborough Junction and Brixton stations but without its own stations.[19] In 2004, concerns were raised by local politicians and residents that the Brixton area was not being served by the line and campaigners criticised the East London Line Extension project for missing opportunities to create interchange stations with Thameslink and the London Underground Victoria line.[20][21][22]
Plans were not produced for such stations as the line is on high viaduct, increasing the costs prohibitively.[23] The Mayor of London, Ken Livingstone, expressed doubts that any proposals to construct these stations would pass a cost-benefit analysis and that they would be unlikely to be approved.[20] Lambeth Council and the East London Line Group have expressed support for an interchange station at Brixton and have requested that this proposal be considered for future funding.[24][25] Suggestions have been made that the East Brixton could be re-opened as an alternative.[26]
See also
Notes and references
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Federick Dale Banister". GracesGuide.co.uk. Retrieved 10 February 2013.
- ↑ "London rail link gets green light". BBC News. 12 February 2009. Retrieved 16 February 2009.
- ↑ Cahalan, Paul (12 February 2009). "Approval for £75m rail plan linking Clapham Junction to Docklands in 20 minutes". Wandsworth Guardian. Retrieved 14 December 2012.
- ↑ "London Overground Clapham Junction to Surrey Quays". Transport for London. n.d. Retrieved 4 July 2012.
- 1 2 "Clapham Junction to Surrey Quays". Transport for London. Retrieved 6 November 2012.
- ↑ "January 2015 Draft Timetable" (Press release). Southeastern Railways. 2 July 2014. Retrieved 28 July 2014.
- ↑ "Tube line extensions 'approved'". BBC News. 9 October 2001. Retrieved 17 December 2012.
- ↑ "Surrey Canal Road Station campaign". Archived from the original on 14 June 2010. Retrieved 17 December 2012.
- ↑ "NEW CROSS: Agreement on Surrey Canal Road station draws closer". This Is Local London. 27 November 2009. Retrieved 17 December 2012.
- ↑ "Surrey Canal Road station campaign must continue says Caroline Pidgeon". Rail News. 2 September 2010. Retrieved 17 December 2012.
- ↑ "Surrey Canal Road station". Lewisham Council website. Retrieved 17 December 2012.
- ↑ London Housing Zones https://www.london.gov.uk/sites/default/files/Housing%20Zones%20-%20The%20First%20Nine%20Zones.pdf
- ↑ New Bermondsey http://www.newbermondsey.com/transport
- ↑ "Demonstrators 'mourn' loss of South London Line service". BBC News. Retrieved 14 December 2012.
- ↑ "Stop the rail cuts campaign". Southwark Rail Users' Group. Retrieved 18 October 2009.
- ↑ The Railway Consultancy Ltd. "South London Line Research Study". London TravelWatch. Archived from the original on 28 July 2011. Retrieved 31 October 2009.
- 1 2 "Boris slammed on South London Line". South London Press. 12 October 2009. Retrieved 18 October 2009.
- ↑ "The Price of ELL Phase 2: Victoria-Bellingham Cancelled". London Reconnections (blog). 23 April 2009. Retrieved 31 October 2009.
- ↑ Transport for London (2006). "The Tube in 2010". Retrieved 3 November 2007. (map illustrating future development phases as proposed by TfL in 2006, subject to change)
- 1 2 Shawcross, Val (17 November 2004). "Mayor answers to London - Loughborough Junction and Brixton Stations". London Assembly. Retrieved 22 December 2012.
- ↑ "Junction joy South". South London Press. Streatham. 24 April 2004. Archived from the original on 9 May 2004. Retrieved 3 November 2007.
- ↑ Linton, Martin, MP (19 July 2006). "Parliamentary Debate: London Orbital Rail Network". Hansard (House of Commons). UK Parliament. Retrieved 3 November 2007.
- ↑ "East London Line Extensions - Loughborough Junction". AlwaysTouchOut. 9 November 2006. Retrieved 3 November 2007.
- ↑ "ELLG response to the South London Route Utilisation Strategy" (PDF). Network Rail. 26 October 2007. Retrieved 19 December 2012.
- ↑ "East London Line extension". Public transport consultation. Lambeth Borough Council.
- ↑ "Then and Now: East Brixton station". Urban75. Retrieved 18 October 2009.
- Notes
- ↑ Since 1988 Thameslink makes London Bridge at the centre of a north-south railway axis covering South-East England.
- ↑ between Wandsworth Road and Clapham High Street
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to South London Line. |
- South London Press article: 'Boris slammed on South London Line'
- South London Press article: 'Bid to save the South London Line'
- "'The South London Line And Its Traffic'" (PDF). (1.03 MiB) - a reproduction of a September 1953 article from The Railway Magazine, courtesy of the Southern E-mail Group.