South West Africa Territorial Force
| South West African Territorial Force | |
|---|---|
|
SWATF Insignia | |
| Active | 1977–1989 |
| Country |
|
| Branch |
|
| Size |
10,100 (1981) 22,000 (1987) |
| Part of | Department of Defence for South West Africa |
| Garrison/HQ | Windhoek, South West Africa |
The South West Africa Territorial Force (SWATF) was an auxiliary arm of the South African Defence Force (SADF) and comprised the armed forces of South West Africa (now Namibia) from 1977 to 1989.[1] It emerged as a product of South Africa's political control of the territory which was granted to the former as a League of Nations mandate following World War I.[2]
History and Background
From 1966 until 1989, South African security forces waged a long and bitter counterinsurgency conflict against indigenous nationalists in what was then South West Africa, represented by the Marxist South West African People's Organisation (SWAPO) and its military wing, the People's Liberation Army of Namibia (PLAN). As the guerrilla war intensified, however, it became clear that the local civilian police alone were not enough to cope with SWAPO/PLAN incursions and escalating unrest. Consequently, military units were deployed for the first time; 60,000 South African combat troops were engaged in South West Africa by the late 1970s.[3]
Establishment
As part of a general policy of military and social reform, Pretoria initiated the establishment of local defence and police agencies for its protectorate beginning in 1977.[1]
Structure and Activation
A start was also made with the regrouping of existing units into four formations:
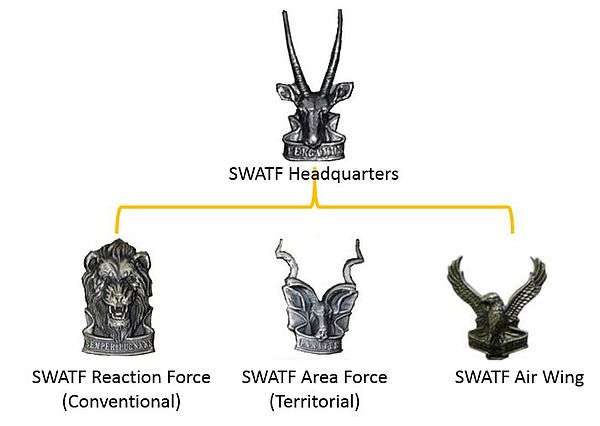
- a Formation Headquarters Staff,
- a Reaction Force (conventional),
- an Area Force (unconventional) and
- an Air Force.
As regarding the latter, the South African Air Force would remain responsible for aerial operations although provision was made for an air commando squadron consisting of private and commercially qualified air crews. Their main function was to assist the South African Air Force in reconnaissance and communication flights and to provide operational officers for the operational service.
The new South West African Territorial Force was officially created on 1 August 1980, from South West African citizens already serving with the South African Defence Force.[4]
Operationally, the SWATF was further divided into a Permanent Force infantry component, logistic/administrative divisions, a training wing, and a Citizen Force, which included at least three motorised infantry battalions.[4] The 'permanent force' comprised mostly volunteer auxiliaries and national servicemen, who formed eight battalions.[4] A militia system was also developed for local security, including over twenty 'area protection units'.[1]
By 1981, SWATF's total strength numbered some 10,100 men, organised into both tribal-based battalions (including separate units for Ovambo, Herero, and Coloured ethnic groups) and multiethnic units partially manned by at least 10,000[5] white South West African personnel.[1][6]
By 1987, SWATF had an estimated 22,000 troops, including additional units of engineers, signals personnel, mounted troops, a parachute battalion, and a commando squadron.[7]
Training
A school cadet program similar to that in South Africa was developed for South West Africa.

Primarily all SWATF members received their initial training at 2 SA Infantry Battalion at Walvis Bay, (considered South African territory at that stage)[8]
Advanced training, NCOs and Officer development however occurred at the SWA Military School at Okhandja.
SADF Supervision
For all practical purposes, SWATF remained firmly integrated into existing SADF command structures.[1] Its primary goal was protection of the territory of SWA from SWAPO incursions.[9] The SWATF was placed under the control of the Department of Defence for South West Africa and was always headed by a SADF general. There was also a joint SWATF/SADF committee established for "planning, liaison, and coordination" efforts.[4]
SWATF Uniform, Rank Structure, Corps Emblems,Proficiency and Ops Badges
The first major step in the establishment of an independent territorial defence force in SWA was the introduction of a new uniform on 6 September 1979 through which SWA units could be distinguished from SADF units.


The rank structure of the SWATF was identical to that of the SADF. The insignia however differed considerably.
| Rank insignia of the South West African Territorial Force | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Warrant officers and other ranks | Formation warrant officer | Warrant officer class 1 | Warrant officer class 2 | Staff sergeant | Sergeant | Corporal | Lance corporal | Private | |||
 |
|
|
|
||||||||
| Rank insignia of the South West African Territorial Force | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Officer ranks | Major general | Brigadier | Colonel | Commandant | Major | Captain | Lieutenant | Second lieutenant | |||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
||||


SWATF Commanders
- 1980 – 9 November 1983[10]: Major-General Charles Lloyd
- 9 November 1983[10] – 23 January 1987[10]: Major-General Georg Meiring SSA SD SM MMM
- 23 January 1987[10] – 1989: Major-General Willie Meyer
Tactical Breakdown
Headquarters Formation

The Reaction Force

Brigade
- Reaction Force Brigade, mainly a Citizen and cross corps force, 91 Brigade had a motorised sub-brigade composing two (later three) infantry battalions, an armoured car regiment, and an artillery regiment. The Brigade also included a training battalion and a mobilisation center.


- Logistics Brigade

Battalions
- Eight full-time battalions
- 31 Bushman Battalion (became 201 Battalion) HQ at Omega Base,

- 32 Battalion at Buffalo,

- 33 Eastern Caprivi Battalion, (became 701 Battalion)

- 34 Kavangoland Battalion, (became 202 Battalion)

- 35 Ovamboland Battalion, (became 101 Battalion) The Quick reaction force.

- 36 Bushman Battalion, (became 203 Battalion)

- 37 Kaokoland Battalion, (became 102 Battalion)

- 41 Multi-ethnic Regiment Windhoek (became 911 Battalion) (As 911 Battalion – it became known as "Swing Force" due to its ability to operate as a conventional unit or as a Counter-insurgency (COIN) unit.It recruited from South West Africa at large and deployed predominantly as a reserve force. An infantry element, a mechanised contingent, artillery, and a regiment of Eland armoured cars was included.[11] The unit was never mobilised en masse.

- 31 Bushman Battalion (became 201 Battalion) HQ at Omega Base,
- Five ‘Modular’ Infantry Battalions
- 51 Battalion at Ruacana,

- 52 Battalion at Oshakati,

- 53 Battalion at Ondangwa,

- 54 Battalion at Eenhana and

- 55 Battalion at Nepara.

- 51 Battalion at Ruacana,
Modular Battalions main function was internal operations. Sub units were attached according to the requirements of a specific situation, i.e. the "modular nature". They were made up from elements (or ‘modules’) from a variety of units and would be deployed in company patrol bases along the border. There was usually a company of SWATF attached to each Modular Battalion on rotation to provide ‘local knowledge’ and various elements of 1 SWA Specialist Unit were also attached to provide tracking and patrolling expertise. Koevoet or Romeo-Mike teams were also frequently stationed in these company bases for mutual protection, but would generally operate independently. The Modular Battalions’ heavy weapons often included a wide variety of captured Soviet and obsolete British World War II-era items, which were usually static, being primarily intended for base defence. Motor transport was limited, with a few Buffels being retained for patrolling and SAAF helicopters often being utilised for inter-base liaison. The companies of a Modular Battalion were generally weak during the quiet dry season (maybe 30- 50% strength), but would each be brought up to the full strength of five platoons in time for the Wet Season, which was when the bush would become jungle and SWAPO-PLAN infiltration teams would stream southwards. Their main responsibility was to secure their assigned area in which they conducted cordon and search operations, patrols, checkpoints, mine sweeping and the protection of roads and water systems.
SWATF Special Forces
Although SWATF relied heavily on South Africa's special forces, but over time it developed its own capability.

- 1 SWA Recon Regiment: started out as a sub unit under the command of the Commanding General SWATF in 1982, staffed mainly by ex South African operators.
- Front-line Recon Wings: most front-line battalions, such as 31, 36 and 101 also had their own Recon Wings.

- 1 SWA Specialist Unit: at Otavi – containing trackers, dogs, horses and dirt bikes. By 1984, 1 SWA SPES was based at Omaruku and at Omathoni together with 32 Battalions Recce Wing.

- 1 SWA Parachute Battalion: By 1987, 1 SWA Parachute Battalion and 32 Battalion's Recce Wing were amalgamated to become 2 SWA Specialist Unit or 2 SWA SPES and relocated to Luipersvallei, Windhoek.

The Area Force

South West African Military Operations Sectors
By 1979, South West Africa was subdivided into Operational Sectors. Three Frontline Sectors, 10, 20 and 70 fell under direct South African Army Command. Four additional Sectors, 30, 40, 50 and 60 covered the rest of South West Africa and was commanded directly by SWATF officers from 1980.

Frontline Sectors
Frontline Sectors were used for the massing of forces in preparation for external operations into Angola, acting as a buffer with the rest of the territory and reaction to immediate threats. Although theoretically under control of the Area Force, due to their proximity to Angola the vast majority of conventional forces was based in these areas.

Sector 10
(Kaokoland and Owambo) - HQ Oshakati
- 51 Battalion at Ruacana,

- 52 Battalion at Oshakati,

- 53 Battalion at Ondangwa,

- 54 Battalion at Eenhana,

- 101 Battalion at Ondangwa and
- 102 Battalion at Opuwa,
Combined SADF and SWATF forces in Sector 10


- SADF's Air Force Base Ondangwa,
- SADF's 5 Maintenance Unit at Ondangwa,
- SADF's Sector 10 Training Unit at Oshivelo,

- SADF's Sector 10 Signals Unit at Oshikati,
- SADF's Sector 10 Maintenance Unit at Oshikati,
- SADF's Sector 10 Provost Unit at Oshikati,
- SADF's 25 Engineering Squadron at Oshakati, and
- SADF's 61 Mechanised Battalion Group at Omuthiya (although not SWATF, 61 Mech had its origins in South West Africa)
Sector 20
(Kavango and Western Caprivi) - HQ Rundu
- 55 Battalion at Nepara.

- 32 Battalion at Buffalo.

- 201 Battalion at Omega base,
- 202 Battalion at Rundu and
- 203 Battalion at Mangeti.
Special Service Companies for Quick Reaction
These frontline Sectors also had immediate reaction forces (Special Service Companies) to deal with any attack and were primarily infantry company strength and fully motorised.

- 905 SSC was based at Nepara in Sector 20 and deployed on Buffels.
- 906 SSC was based at Omahoni in Sector 20 and deployed on Buffels. Local Kwanyama troops made up the bulk of the personnel.
SADF units in Sector 20
- SADF's Air Force Base Rundu and
- SADF's 6 Maintenance Unit at Rundu.
Sector 70
(Eastern Caprivi) - HQ Mpacha Encompassed the Eastern Caprivi covering the Zambian border from Cuado to the Zambezi River.
- SWATF 701 Battalion, at Mpacha with attached SWATF armoured car and artillery battery.

SADF units in Sector 70
- SADF's Air Force Base at Mpacha,
- SADF's Navy Marine Company utilized for river patrols and
- SADF's 9 Maintenance Unit at Mpacha.
Countrywide Sectors
Apart from the Frontline Sectors, four additional Sectors existed. 26 Area Force Units, similar to the South African commando system, was established for these less vulnerable parts of the territory.
Sector 30
HQ Otjiwarongo (Citadel).
- 301 Bn at Otjiwarongo.

SWATF Otjiwarongo AME (Area Force Unit - Area Mag Eenheid), Outjo AME, Grootfontein AME, Tsumeb AME, Herreroland AME, Ethosa AME, Otavi AME, Damaraland AME and UIS PL. Its area of responsibility was likewise the Grootfontein, Tsumeb, Otavi, Outjo, Otjiwarongo, Hereroland and Damaraland regions.

SADF Units in Sector 30
- SADF's Air Force Base Grootfontein
- SADF's Northern Logistics Command at Grootfontein comprising:
- NLC 101 Workshop
- NLC Provost Unit
- NLC 6 Signals Unit
- NLC 16 Maintenance Unit
Sector 40
HQ Windhoek.
SWATF Alte Feste AME, Khomas AME, Hochl AME, Okahandja AME, Omaruru AME, Swakopmund AME, Rehoboth AME, Katatura AME and Khomasdal AME.

Other Units in this Sector:

- Regiment Windhoek

- 1 SWA Provost Unit
Sector 50
HQ Gobabis.
SWATF Aranos AME, Auob AME, Bo-Nossob AME, Aminius PL, Gobabis AME, Rietfont AME, Mariental AME and Maltahohe AME.

Sector 60
HQ Keetmanshoop.
SWATF Karasburg AME, Keetmanshop AME, Hoop AME, Bethanien AME, Oranjemund AME, Luderitz AME and Namaland AME.

SWATF Air Wing

SWATF Aircrews
While the SWATF relied heavily on the South African Air Force for combat and heavy logistics transportation, it did have its own Air Wing, which consisted mainly of civilian aircraft.

1 SWA Commando Squadron was established as 112 Air Commando on 24 September 1963 in Windhoek. The unit was staffed by volunteer civilian aircraft. From 1968, control of 112 Commando squadron passed from the SA Army to the SAAF and it was transferred to Light Aircraft Command. In 1970, it was disbanded, but in 1980 it was re-established as part of the SWATF.

SWATF Medical Command

SWATF Equipment
Small arms
| Name | Type | Country of Origin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beretta 92 | Semi-automatic pistol | |
|
| Star | Semi-Automatic Pistol | |
Model 1920, 1921, 1922. |
| Uzi | Submachine gun | |
Some of local manufacture. |
| AK-47 | Assault Rifle | |
Captured. |
| AKM | Assault Rifle | |
Captured. |
| R1 | Battle Rifle | |
Belgian design |
| Heckler & Koch G3 | Battle Rifle | |
G3A3, received from Portugal. |
| R4 | Assault Rifle | |
Derived from the Galil |
| Bren | Light machine gun | |
Mk 3. |
| Browning M2 | Heavy machine gun | |
|
| Browning M1919 | Medium machine gun | |
Helicopter-mounted weapon. |
| FN MAG | General purpose machine gun | |
MAG-58. |
| SS-77 machine gun | General purpose machine gun | |
|
| PKM | General purpose machine gun | |
Captured. |
| RPD | Light machine gun | |
Captured. |
| RPK | Light machine gun | |
Captured. |
| FN Browning Auto-5 | Shotgun | |
|
| Armsel Striker | Shotgun | |
|
| Dragunov | Sniper rifle | |
Captured. |
| Armscor M963 | Fragmentation grenade | |
Made in South Africa, derived from INDEP's licence-made M26 grenade |
| Armscor 42 Zulu | Anti-personnel rifle grenade | |
Derived from the Belgian PRB 424 |
| Armscor AP-65[12] | Anti-personnel rifle grenade | |
Successor to the 42 Zulu, utilising a M26 and resembling a Dilagrama m/65 |
| Mecar Energa | Anti-tank rifle grenade | |
Made in South Africa |
| M18 Claymore | Anti-personnel mine | |
|
| Mine G.S. Mk V | Anti-tank mine | |
|
| M79 grenade launcher | Grenade Launcher | |
Known as "snotneus" |
| Milkor MGL | Grenade Launcher | |
|
| M20 Super Bazooka | Anti-tank weapon | |
3.5 inch rocket launcher. |
| STRIM 89mm rocket launcher | Anti-tank weapon | |
M20 replacement. |
| RPG-2 | Anti-tank weapon | |
Captured. |
| RPG-7 | Anti-tank weapon | |
Captured. |
Vehicles
Armoured
- Buffel APC
- Casspir APC
- Eland Mk7 Armoured Car
- Wolf APC manufactured by Windhoeker Maschinenfabrik
Soft-skinned
- Samil 20
- Samil 50
- Samil 100
- Kwevoel 100
|
Counter Insurgency
A lot of effort was used to interdict insurgent groups that had crossed over the Angolan border. These Insurgents were on foot, but knew the land and moved fast. There have been stories of the insurgents moving incredible distances with little supplies, whilst being chased and if cornered putting up a good resistance to their followers. Adrenaline injections were found at some of the incident scenes after a fire fight.
These insurgents were normally stalked by using trained trackers, who directed the reaction force. In some instances a stopper group was choppered in to cut off the insurgents before they reached the border.
SWATF Demobilisation
Under UN resolution 435, the United Nations Transition Assistance Group was mobilised, while SWATF was demobilised, its strength in the last years of operation was at about 22,000.
Special arrangements were made for two San units of SWATF, as they originated from local tribal communities. They were thus allocated land near their previous bases.
All citizen force units were demobilised.
The SWATF was completely demobilised on 1 June 1989.
Withdrawal of some units to South Africa
UN Resolution 435 additionally called on South Africa to reduce its forces in Namibia to 12000 before the start of any peace process and finally to 1500 by 1989.
Several thousand especially from the San people, fearing reprisal or intimidation, left for South Africa with the SADF.


32 Battalion, whose members to a large extent could not claim Namibian citizenship, also withdrew to South Africa completely.

References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Duignan, Peter. Politics and Government in African States 1960–1985. pp. 345–377.
- ↑ "SWAPO – SWATF/Koevoet". Swapoparty.org. Retrieved 30 April 2013.
- ↑ Fryxell, Cole. To Be Born a Nation. pp. 1–357.
- 1 2 3 4 Modern African Wars (3): South West Africa (Men-At-Arms Series, 242) by Helmoed-Romer Heitman (Author), Paul Hannon (Illustrator) Osprey Publishing (28 November 1991) ISBN 1-85532-122-X and ISBN 978-1-85532-122-9
- ↑ Tonchi, Victor; Lindeke, William; Grotpeter, John. Historical Dictionary of Namibia. p. 405.
- ↑ FishEagle (21 February 2010). "I Luv SA: The Namibian Border War: an appraisal of the South African strategy (Part 6)". Iluvsa.blogspot.com. Retrieved 30 April 2013.
- ↑ "SADF.info". SADF.info. Retrieved 30 April 2013.
- ↑ http://www.historicalpapers.wits.ac.za/inventories/inv_pdfo/AG1977/AG1977-A5-63-16-004-jpeg.pdf
- ↑ "Military Chronicle of South West Africa". Rhodesia.nl. Retrieved 30 April 2013.
- 1 2 3 4 "SWATF Operations". SADF.info. Retrieved 23 December 2014.
- ↑ Helmoed-Römer Heitman. Modern African Wars: South West Africa (1991 ed.). Osprey Publishing. p. 17. ISBN 978-1855321229.
- ↑ "Armed soldier of the 911 Batallion" (image/jpeg). Bush of Ghosts. Photographed by John Liebenberg. Cape Town: www.uct.ac.za/. 1989. Retrieved 5 May 2016.
911 Battalion patrol, the front soldier armed with an R4 rifle with an AP-65 (anti-personnel) rifle grenade.
Further reading
- Overview of the rank insignia used by SWATF
- Military operations carried out by SWATF from 1975 up to its disbandment
- The SADF, A Survey. Supplement to the Financial Mail July 10, 1987 Introducing the SWATF.
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to South West Africa Territorial Force. |


.jpg)

