Trowbridge's shrew
| Trowbridge's shrew | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Eulipotyphla |
| Family: | Soricidae |
| Genus: | Sorex |
| Species: | S. trowbridgii |
| Binomial name | |
| Sorex trowbridgii Baird, 1857 | |
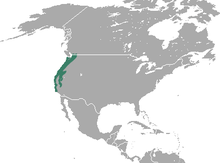 | |
| Trowbridge's shrew range | |
Trowbridge's shrew (Sorex trowbridgii) is a species of mammal in the family Soricidae.[2] It is found in southern British Columbia in Canada and in Washington, Oregon, and California in the United States.[1]
Taxonomy
Trowbridge's shrew was first described in the scientific literature in 1857 by Spencer Fullerton Baird, in a report of surveys and explorations conducted to find a suitable route for a railroad from the Mississippi to the Pacific Ocean.[3] The scientific name given was Sorex trowbridgii. The generic name Sorex is Latin, meaning "shrew-mouse."[4] The species name "trowbridgii" is a patronym to honor William Petit Trowbridge.[4] The type locality for the species is Astoria, Oregon. Baird's initial record describes four specimens made available to him.[5] The first two were provided by Trowbridge. They were skins that had been collected by "Jas. Wayne" in June 1855. The other two specimens were collected by George Suckley at Fort Steilacoom in 1856. Those two specimens were preserved in alcohol prior to submission to Baird.[6]
Description
Trowbridge's shrew is a medium-sized shrew with a long tail.[7] Non-breeding shrews weigh around 3.8 g (0.13 oz) while breeding shrews average around 5 g (0.18 oz).[8] The fur colorings change over the year, with a darker more brownish coat in the summer and a lighter gray in winter.[9][7] They have many long whiskers and their ears are mostly covered with fur. The young have a hairy tail, which becomes less hairy with age. The tail is bi-colored: darker on the top than the bottom, with a sharp line separating the colors. This feature can be used to distinguish Trowbridge's shrew from similar shrews.[7] They are pentadactyl, with whitish to lightly tan colored feet. The caps of the teeth have a dark reddish-brown pigmentation. There are five unicuspid teeth in the upper jaw and two in the lower. The upper jaw also has one bicuspid incisor and four molars. The lower jaw has an additional incisor and three molars. The skull is similar in size to that of other long-tailed shrews.[7]
Trowbridge's shrew can be distinguished from closely related shrews by the third unicuspid being smaller than the fourth. Other distinguishing features include a post-mandibular foramen, more posterior positioning of the orbit, and orientation of lacrimal and infraorbital foramina relative to the molars.[7]
| total length (mm) | tail length (mm) | hind foot length (mm) | condylobasal length (mm) | cranial breadth (mm) | interorbital width (mm) | maxillary width (mm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Canadian S. t. Trowbridgii | 113 | 54 | 13 | 17.2 | 8.6 | 3.8 | 4.9 |
| American S. t. Trowbridgii | 119 | 56 | 14 | 17.4 | 8.7 | 3.8 | 4.9 |
| S. t. humboldtensis | 131 | 61 | 15 | 18.1 | 9 | 4 | 5.3 |
| S. t. monteneretensis | 123 | 52 | 14 | 18.2 | 9 | 4.2 | 5.6 |
| S. t. mariposae | 119 | 51 | 14 | 18.6 | 9.3 | 4.2 | 5.6 |
Fossil record
Fossilized remains of Trowbridge's shrew have been obtained from the Carpinteria Tar Pits. These dated from the Wisconsonian (late Ranchlabrean) epoch. These remains were obtained from a site at the extreme south end of the range of distribution. Scientists suspect that the shrew developed earlier, but that no fossils have been found due to a lack of such fossil sites of suitable age along the west coast north of San Francisco.[7]
Distribution and habitat
Trowbridge's shrew is found along the western coast of North America. They occur in the extreme southwest of British Columbia, south of Burrard Inlet. They are found in the western part of the states of Washington and Oregon. In northern California, the distribution forks. In the west, the population continues south through the coast range to Santa Barbara County. Through eastern California, the population extends south through the Warner Mountains and the Sierra Nevada Mountains to Kern County.[7] Different subspecies are found in different regions of the geographic range.[8] They are found from sea level up to an elevation of 1,820 m (5,970 ft).[1]
Trowbridge's shrew resides in forested areas where the ground may be littered with debris for cover.[10] After logging in an area, they may remain, if sufficient ground cover is present. They are found in both dry and moist forests, as well as in swampy woodlands. Populations on Destruction Island off the Washington coast live in deep rank grass near salmonberry patches.[10] They are less likely to be found near streams. In the southern reaches of their range, they may be found in chaparral.[10]
Behavior and ecology
Trowbridge's shrews occupy an important ecological niche. They are preyed upon by raptors including the barred owl (Stirix varia).[8] The Pacific giant salamander (Dicamptodon sp.) is another known predator. While domestic cats are known to kill them, they usually do not eat them.[8] Known parasites include a number of ticks, mites, chiggers, fleas, worms, and single-celled organisms.[8]
Since they are the most frequently captured shrews within their range, it is presumed that they are the most abundant.[1]
The life-span of Trowbridge's shrews is around 1.5 years.[10] They do not hibernate, but remain active year-round. They are roughly twice as abundant in the fall as in the spring.[1] Insects are a primary food source for the shrews, but they also will eat spiders, worms, and centipedes. They also eat plants. Compared to other shrews in the genus Sorex, Trowbridge's shrews eat more vegetable matter.[1] During winter months, they may feed on conifer seeds, such as Douglas-fir and pine, as well as other plant seeds.[10]
Although some shrews are known to be strong swimmers, it is not clear if this is true for Trowbridge's shrew. Thus, rivers may present a barrier to dispersal of the species.[10] Additional comments about the range of Trowbdridge's shrew are extrapolated from studies on other species.[10]
Reproduction
As they reach sexual maturity, Trowbridge shrews gain whole body mass. Non-breeding shrews weigh around 3.8 g (0.13 oz) while breeding shrews average around 5 g (0.18 oz). The size of the testes in males increases, while the uterine horns widen in females. Once the breeding season has concluded, these structures atrophy.[8] The time of onset of sexual maturity may be earlier or later, depending on local climate conditions, with an earlier age of onset in warmer areas.[10] Males apparently reach sexual maturity two weeks earlier than females.[8]
Since pregnant females have been found, which are still lactating, it is suspected that they became pregnant while nursing the young from prior broods. The average brood size is around 3-5.[7] In northern areas, the number of embryos found in pregnant females was fewer and the breeding season appears to be shorter. The breeding season runs from March to May in Washington, but from February to June in California.[8]
Human interactions
Effects of logging on Trowbridge's shrew populations has been studied, but the results were inconclusive, since one study showed and increase and the other a decrease.[1]
Conservation status
The IUCN lists Trowbridge's shrew as "Least Concern" based on a 2008 assessment. The rationale for the listing includes an overall stable population, lack of major threats, and a widespread geographic distribution. In addition, there are protected areas throughout the area of distribution.[1]
References
Footnotes:
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 IUCN Red List 2008.
- ↑ Hutterer 2005, p. 298.
- ↑ Baird 1860.
- 1 2 George 1989, p. 4.
- ↑ Baird 1860, p. 14.
- ↑ Baird 1860, p. 15.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 George 1989, p. 1.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 George 1989, p. 2.
- ↑ Jameson & Peeters 1988, p. 104.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 NatureServe 2014.
Sources:
- Baird, Spencer Fullerton, 1823-1887 (1860). Reports of explorations and surveys, to ascertain the most practicable and economical route for a railroad from the Mississippi River to the Pacific Ocean. Washington, A.O.P. Nicholson, Printer [etc.] Retrieved 21 December 2014.
- "Comprehensive Report Species - Sorex trowbridgii". NatureServe Explorer: An online encyclopedia of life [web application]. Version 7.1. NatureServe, Arlington, Virginia. 2014. Retrieved 21 December 2014.
- George, Sarah B. (12 May 1989). "Sorex trowbridgii" (PDF). Mammalian Species. 337: 1–5. doi:10.2307/3504159. Retrieved 21 December 2014.
- Hammerson, G. (NatureServe) (2008). "Sorex trowbridgii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2014.2. International Union for Conservation of Nature. Retrieved 31 December 2014.
- Hutterer, R. (2005). "Order Soricomorpha". In Wilson, D.E.; Reeder, D.M. Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 298. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.
- Jameson, Everett Williams; Peeters, Hans J. (1988). California Mammals. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-05391-5.
External links
-
 Media related to Sorex trowbridgii at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Sorex trowbridgii at Wikimedia Commons -
 Data related to Sorex trowbridgii at Wikispecies
Data related to Sorex trowbridgii at Wikispecies
