Solar eclipse of April 25, 1865
| Solar eclipse of April 25, 1865 | |
|---|---|
 Map | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Total |
| Gamma | -0.4826 |
| Magnitude | 1.0584 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 323 sec (5 m 23 s) |
| Coordinates | 14°48′S 25°48′W / 14.8°S 25.8°W |
| Max. width of band | 219 km (136 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 14:08:34 |
| References | |
| Saros | 136 (29 of 71) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9199 |
A total solar eclipse occurred on April 25, 1865. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide.
Observations

Related eclipses
Solar eclipses 1916–1920
Each member in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.
| Solar eclipse series sets from 1916–1920 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||
| 111 | December 24, 1916 Partial |
116 | June 19, 1917 Partial | |
| 121 | December 14, 1917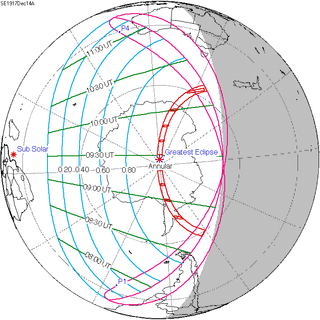 Annular |
126 | June 8, 1918 Total | |
| 131 | December 3, 1918 Annular |
136 | May 29, 1919 Total | |
| 141 | November 22, 1919 Annular |
146 | May 18, 1920 Partial | |
| 151 | November 10, 1920 Partial | |||
Saros 136
Solar Saros 136, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, contains 71 events. The series started with partial solar eclipse on June 14, 1360, and reached a first annular eclipse on September 8, 1504. It was a hybrid event from November 22, 1612, through January 17, 1703, and total eclipses from January 27, 1721 through May 13, 2496. The series ends at member 71 as a partial eclipse on July 30, 2622, with the entire series lasting 1262 years. The longest eclipse occurred on June 20, 1955, with a maximum duration of totality at 7 minutes, 8 seconds.[1]
| Series members 29–43 occur between 1865 and 2117 | ||
|---|---|---|
| 29 | 30 | 31 |
 Apr 25, 1865 |
 May 6, 1883 |
 May 18, 1901 |
| 32 | 33 | 34 |
 May 29, 1919 |
 Jun 8, 1937 |
 Jun 20, 1955 |
| 35 | 36 | 37 |
 Jun 30, 1973 |
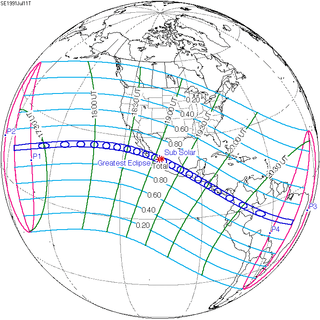 Jul 11, 1991 |
 Jul 22, 2009 |
| 38 | 39 | 40 |
 Aug 2, 2027 |
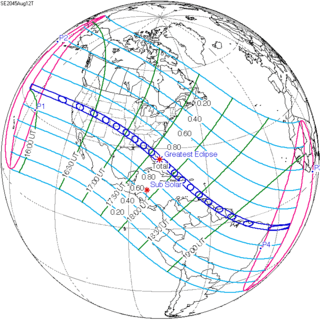 Aug 12, 2045 |
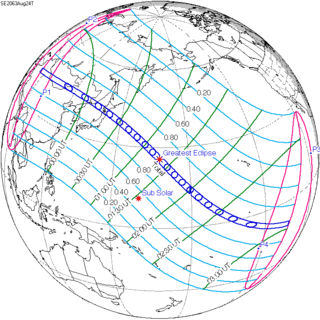 Aug 24, 2063 |
| 41 | 42 | 43 |
 Sep 3, 2081 |
 Sep 14, 2099 |
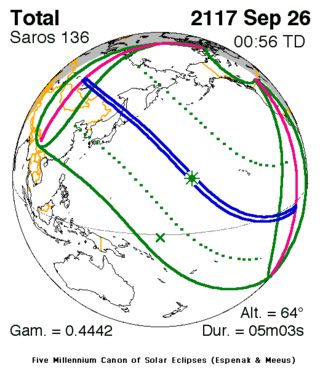 Sep 26, 2117 |
References
- NASA chart graphics
- Googlemap
- NASA Besselian elements
- Total Eclipses of the Sun by Mabel Loomis Todd, 1900
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Solar eclipse of 1865 April 25. |
