Software house
A software house is a company whose primary products are various forms of software, software technology, distribution, and software product development.[1] Software houses are companies in the software industry.
Types
There are a number of different types of software houses:
- Large and well-known companies producing Commercial off-the-shelf (COTS), such as Microsoft, SAP AG, Oracle Corporation, HP, Adobe Systems and Red Hat[2]
- Smaller companies that produce custom software for other companies and entrepreneurs, such as RIKSOF
- Companies producing specialized Commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) software, such as Panorama, Hyperion, Siebel Systems, GazitIT, Enigma Technologies
- Companies producing Software as a Service SaaS, such as Google, Facebook, LinkedIn
- Companies producing software components, such as Developer Express, Dundas, ComponentOne and Sohn Software
- Application Service Provider such as Salesforce
- Companies focused on delivering bespoke software solutions for vertical industries or particular geographical regions
All of these may be categorized in one or many of the following:[3]
- contractual - when the software house is contracted to deliver some particular software from outside (software outsourcing)
- product development - when it produces ready to use, packaged software; Commercial off-the-shelf
Common roles in a software house
Organizing a software house is very specialized type of management skill, where experienced persons can turn the organizational problem into a unique benefit. For example, having sub-teams spread in different time zones may allow a 24-hour company working day, if the teams, systems and procedures are well established. A good example is the test team in time zone 8 hours ahead or behind the development team, who fix software bugs found by the testers.
A professional software house normally consists of at least three dedicated sub-teams :
- Business analysts who define the business needs of the market
- Software developers who create the technical specification and write the software
- Software testers who are responsible for the whole process of quality management
In bigger software houses, greater specialization is employed, and quite often there are also:
- Technical writers who write all the documentation such as user guides
- Release specialists who are responsible for building the whole product and software versioning
- Graphic designers who are normally responsible for the design of the graphical user interface.
- Maintenance engineers who are behind two, three or more lines of support
- Consultants responsible for making the solution operational, especially if some specialist knowledge is necessary. Examples of this include: building multidimensional cubes in business intelligence software, integrating with existing solutions, and implementing business scenarios in Business Process Management software.
Structure
The manager of a software house is usually called the Head Of Development (HOD),[4] and reports to the stakeholders. He or she leads the sub-teams directly or via the managers/leaders depending on the size of the organization. Usually teams of up to 10 person are the most operational. In bigger organizations, there are in general two models of the hierarchy:
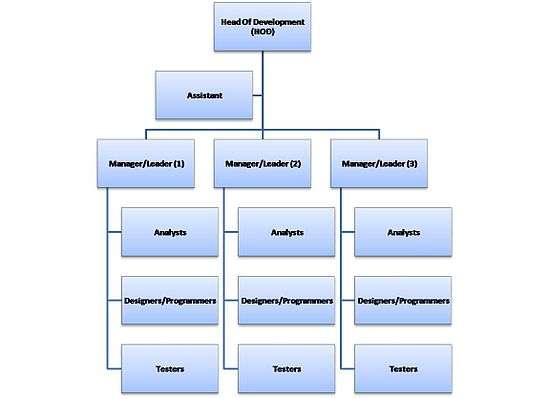
All the teams are fully independent and they work separately on the different projects. The structure is quite simple and all the employees reports to one person, what make the situation quite clear however it is not a good solution in terms of knowledge exchange and optimal usage of human resources.

In this model there are dedicated managers/leaders for each main specialization, "renting" their people for particular projects led by product/project managers, who formally or informally buy the people and pay for their time. This leads to each private employee having two bosses – the product/project manager and the specialized "resource" manager. On one hand it optimizes the usage of human resources, on the other hand it may give rise to conflicts about which one manager has priority in the structure.
There are also a number of variants of these structures, and a number of organizations have this structure spread and split within various departments and units.
Methodologies
Software house may use a number of various methodologies to produce the code. These can include:
- the waterfall model, including project management methodologies like PRINCE2[5] or PMBoK[6]
- agile software development, such as Extreme Programming[7] and SCRUM[8]
There are also some methodologies which combine both, such as the spiral model, Rational Unified Process (RUP)[9] or MSF.[10]
Product life cycle
Regardless of the methodology used, the product life cycle always consists of at least three stages:
- Design – including both the business and technical specification
- Coding – the development itself
- Testing – the quality management
Each stage ideally takes 30% of the total time, with the remaining 10% in reserve.
The UML sequence diagram of interaction between these groups may look like:

At each stage a different group plays a key role, however each type of role must be involved throughout the whole development process:
- Analysts, after completing the business specification, manage the changing business situation to minimize the possibility of change over time. They also support both programmers and testers during the whole development process to ensure that the final product fulfills the business needs specified at the start. The process ideally puts business analysts as the key players during final delivery of the solution to the customer, as they are best placed to provide the best business layer.
- Programmers do the technical specification during the design phase, which is why they are called programmers/designers, and during testing time they fix bugs.
- Testers complete the test scenarios during the design phase, and evaluate them during the coding phase
Systems and procedures
Well-run software houses possess various systems and procedures implemented and working internally across all the sub-teams. These include:
Business Analysts
- Modeling tools like Sparx Systems Enterprise Architect or IBM Rational Rose
Programmers
- Version Control Systems and software versioning procedures
- Code analysis tools and coding standards, validated manually or automatically
- Deployment mechanisms
Testers
- Bug tracking systems
- Test automation tools
- Performance and stress test tools
Project/Product managers
- Enterprise Project Management (EPM) systems and procedures
- Product Portfolio Management (PPM)
- Change management systems and procedures
There are also Application Lifecycle Management (ALM), which embed some of these functionalities in one package and are used across the groups. They are delivered from various vendors like Borland, ECM or Compuware.
Efficiency audits
Well-established software houses typically have some way of measuring their own efficiency. This is usually done by defining the set of key performance indicators (KPI), such as
- The average number of bugs done by the developer per unit of time or source lines of code
- The number of bugs found by tester per test cycle
- The average number of test cycles until Zero Bug Bounce (ZBB)
- The average time of test cycle
- Estimated time of task comparing to the real time of the task (exactitude of planning)
- Number of corrections to the baseline
A number of organizations are focused on reaching the optimum level of the Capability Maturity Model (CMM), where "optimum" does not necessarily mean the highest. There are also other systems such as Carnegie-Mellon University's SEMA, or particular ISO standards. Small software houses will sometimes use less formalized approaches, such as the Joel Test : 12 steps to better code. Each organization works out its own style, which lies somewhere between total technocracy (where all is defined by numbers) and total anarchy (where there are no numbers at all). Whichever way the organization goes, they consider the pyramid describing the cost and risk of introducing change to already-begun development processes:

See also
References
- ↑ "What is a Software Company Today?". RedMonk. 2014. Retrieved June 2, 2017.
- ↑ "Types of Software Companies". Adnan Chohdry. 2011. Retrieved June 2, 2017.
- ↑ Software Process: Principles, Methodology, and Technology Author: Jean Claude Derniame, Badara Ali Kaba, David Wastell p.166
- ↑ Greenlit: Developing Factual/Reality TV Ideas from Concept to Pitch p.12
- ↑ Managing successful projects with PRINCE2
- ↑ A User's Manual to the PMBOK Guide
- ↑ Planning extreme programming
- ↑ Agile Project Management with Scrum
- ↑ The rational unified process made easy: a practitioner's guide to the RUP
- ↑ Microsoft Solutions Framework (MSF): A Pocket Guide