Short ciliary nerves
| Short ciliary nerves | |
|---|---|
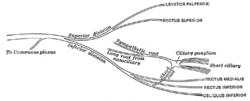 Plan of oculomotor nerve. (Short ciliary labeled at center right.) | |
| Details | |
| From | ciliary ganglion |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nervi ciliares breves |
| Dorlands /Elsevier | n_05/12565369 |
| TA | A14.3.02.005 |
| FMA | 75474 |
The branches of the ciliary ganglion are the short ciliary nerves.
These are delicate filaments, from six to ten in number, which arise from the forepart of the ganglion in two bundles connected with its superior and inferior angles; the lower bundle is the larger.
They run forward with the ciliary arteries in a wavy course, one set above and the other below the optic nerve, and are accompanied by the long ciliary nerves from the nasociliary.
They pierce the sclera at the back part of the bulb of the eye, pass forward in delicate grooves on the inner surface of the sclera, and are distributed to the ciliary muscle, iris, and cornea.
The short ciliary nerve contains parasympathetic and sympathetic nerve fibers. The parasympathetics arise from the Edinger-Westphal nucleus and synapse in the ciliary ganglion via the oculomotor nerve, the postganglionic parasympathetics leave the ciliary ganglion in the short ciliary nerve and supply the ciliary body and iris. Sympathetics are provided by the superior cervical ganglion and they reach the ganglion either as branches of the nasociliary nerve or directly from the extension of the plexus on the ophthalmic artery (sympathetic branch to ciliary ganglion).
Damage to the short ciliary nerve may result in loss of the pupillary light reflex, or mydriasis.
Additional images
 Scheme showing sympathetic and parasympathetic innervation of the pupil and sites of lesion in a Horner's syndrome.
Scheme showing sympathetic and parasympathetic innervation of the pupil and sites of lesion in a Horner's syndrome. Sympathetic connections of the ciliary and superior cervical ganglia.
Sympathetic connections of the ciliary and superior cervical ganglia. Pathways in the Ciliary Ganglion.
Pathways in the Ciliary Ganglion.
See also
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- "3-11". Cranial Nerves. Yale School of Medicine. Archived from the original on 2016-03-03.
- lesson3 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (orbit4)
- cranialnerves at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (III)