Sheeppox
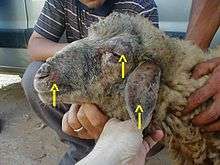
Vaccinal disease due to poorly inactivated vaccine
Sheeppox (or sheep pox, known as variola ovina in Latin, clavelée in French, Pockenseuche in German) is a highly contagious disease of sheep caused by a poxvirus different from the benign orf (or contagious ecthyma).
Sheep pox is the most severe of all the pox diseases of animals.[1]
Goatpox is a similar disease of goats, caused by a virus antigenically distinct from sheeppox virus.
Geographical distribution
Sheep pox is present in Mediterranean area, and the Middle East to Pakistan.[2]
Clinical findings
 Lesions around lips (orf is on lips)
Lesions around lips (orf is on lips)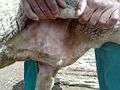 Starting lesions (reddening) in axilla
Starting lesions (reddening) in axilla Crusty lesions in axilla
Crusty lesions in axilla Crusty lesions on tail
Crusty lesions on tail Crusty lesions on tail (lamb)
Crusty lesions on tail (lamb)
Vaccination
In most countries, large scale state vaccination programs are implemented against the disease. But, so far, few have succeeded in eradicating it.It is carried out by different type of vaccines. 1.Tissue Vaccine 2.Attenuated Vaccine 3.Killed Vaccine 4.Freeze dried Live Vaccine
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Sheep pox. |
References
- ↑ D.C. Blood; J.A. Henderson; O.M. Radostits (1979). Veterinary Medicine (5th ed.). London: Baillière Tindall. pp. 708–709 (Sheeppox and goatpox). ISBN 0-7020-0718-8.
- ↑ Jensen, Rue & Brinton L. (1982) Diseases of Sheep Philadelphia, Lea & Febiger ISBN 0-8121-0836-1, pp. 235-238
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.