Metribuzin
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
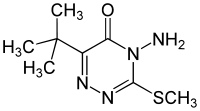
| IUPAC name
4-Amino-6-tert-butyl-3-methylsulfanyl-1,2,4-triazin-5-one | |
| Other names
4-Amino-6-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-3-(methylthio)-1,2,4-triazin-5(4H)-one | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.040.175 |
| PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H14N4OS | |
| Molar mass | 214.29 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless, crystalline solid[1] |
| Density | 1.31 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 125 °C (257 °F; 398 K) |
| 0.1% (20 °C)[1] | |
| Vapor pressure | 0.0000004 mmHg (20 °C)[1] |
| Hazards | |
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |
| PEL (Permissible) |
none[1] |
| REL (Recommended) |
5 mg/m3[1] |
| IDLH (Immediate danger) |
N.D.[1] |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Metribuzin (4-amino-6-tert-butyl-3-(methylthio)-as-triazin-5(4H)-one) is an herbicide used both pre- and post-emergence in crops including soy bean, potatoes, tomatoes and sugar cane. It acts by inhibiting photosynthesis by disrupting photosystem II.[2] It is widely used in agriculture and has been found to contaminate groundwater.[3]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards #0430". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ↑ Terence Robert Roberts; David Herd Hutson (17 July 1998). Metabolic Pathways of Agrochemicals: Herbicides and plant growth regulators. Royal Society of Chemistry. pp. 662–. ISBN 978-0-85404-494-8. Retrieved 25 May 2012.
- ↑ Undabeytia, T. S.; Recio, E.; Maqueda, C.; Morillo, E.; Gómez-Pantoja, E.; Sánchez-Verdejo, T. (2011). "Reduced metribuzin pollution with phosphatidylcholine-clay formulations". Pest Management Science. 67 (3): 271–278. PMID 21308953. doi:10.1002/ps.2060.
External links
- Metribuzin in the Pesticide Properties DataBase (PPDB)
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.