New Zealand House of Representatives
| New Zealand House of Representatives | |
|---|---|
| 51st New Zealand Parliament | |
 | |
| Type | |
| Type |
Sole house of the New Zealand Parliament |
| Leadership | |
Leader | |
| Structure | |
| Seats | 121 (119 currently) |
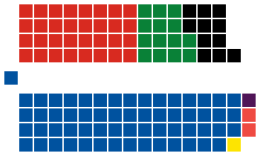 | |
Political groups |
Government[a] Supported by (4)
Opposition (58) |
| Elections | |
| Closed list Mixed-member proportional representation | |
Last election | 20 September 2014 |
Next election | 23 September 2017 |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| Parliament House, Wellington | |
| Website | |
| www.parliament.nz | |
| Footnotes | |
|
^ a. The National Government has confidence and supply agreements with ACT, the Māori Party and United Future.[2] ^ b. Due to electorate vacancies these parties have fewer seats than their share of the vote entitles them to. | |
The New Zealand House of Representatives is a component of the New Zealand Parliament, along with the Sovereign (represented by the Governor-General). The House passes all laws, provides ministers to form a Cabinet, and supervises the work of the Government. It is also responsible for adopting the state's budgets and approving the state's accounts.
The House of Representatives is a democratically elected body whose members are known as Members of Parliament (MPs). There are usually 120 members, though this number can be higher if there is an overhang.[3] MPs are elected for limited terms, holding office until Parliament is dissolved (a maximum of three years). A government is formed from the party or coalition with the majority of MPs.[3] If no majority is possible then a minority government can be formed with a confidence and supply arrangement.
The House of Representatives was created by the British New Zealand Constitution Act 1852, which established a bicameral legislature; however the upper chamber, the Legislative Council, was abolished in 1951.[3] Parliament received full control over all New Zealand affairs in 1947 with the passage of the Statute of Westminster Adoption Act.
The debating chamber of the House of Representatives is located inside Parliament House in Wellington, the capital city. Sittings of the House are usually open to the public, but the House may at any time vote to sit in private. Proceedings are also broadcast through Parliament TV, AM Network and Parliament Today.
Constitutional function
The House of Representatives takes the House of Commons of the United Kingdom as its model. The New Zealand Parliament is based on the Westminster system (that is, the model of the Parliament of the United Kingdom).[4] As a democratic institution, the primary role of the House of Representatives is to provide representation for the people and to pass legislation on behalf of the people (see below).[4]
The House of Representatives plays an important role in responsible government. The Government of New Zealand (the executive branch, headed by the Cabinet)[5] draws its membership exclusively from the House of Representatives.[6] A government is formed when a single party or group of parties can show that they have the "confidence" (support) of the House. This can involve making agreements among several parties. Some may join a coalition government, while others may stay outside the Government but agree to support it on confidence votes. The Prime Minister is answerable to, and must maintain the support of, the House of Representatives. Thus, whenever the office of prime minister falls vacant, the Governor-General appoints the person most likely to command the support of the House—that is, the leader of the Government.
The current Government is a minority government consisting of the National Party with agreements of confidence and supply from the ACT Party, United Future, and the Māori Party;[7] the current Prime Minister is Bill English.
Members and elections
The House of Representatives normally consists of 120 members, known as Members of Parliament (MPs). They were previously known as "Members of the House of Representatives" (MHRs) until the passing of the Parliamentary and Executive Titles Act 1907 when New Zealand became a Dominion, and prior to that as "Members of the General Assembly" (MGAs).
Members of Parliament are directly elected to three-year terms, subject to calls for early elections. These elected members represent the voters of New Zealand in the House of Representatives. Members represent the people to the House and the Government; they, in turn, represent the actions of the House and the Government to the people.
Current Parliament
The 51st New Zealand Parliament is the current sitting of the House. Its membership was elected at the 2014 general election and, so far, one subsequent by-election. It consists of 121 MPs; the number of geographical electorates was increased from 70 at the previous election, to account for New Zealand's increasing population.[8]

Based on British traditions, the longest continuously serving member in the households the unofficial title "Father (or Mother) of the House". The current Father of the House in the is Peter Dunne, the leader of the United Future party, having served continuously since the 1984 general election.[9]
- Oldest former MPs
The following members of parliament who were first elected more than 40 years ago are still alive:
Number of members

The House started with 37 members in 1854, with numbers progressively increasing to 95 by 1882, before being reduced to 74 in 1891. Numbers slowly increased again to 99 by 1993. In 1996 numbers increased to at least 120 with the introduction of MMP elections (i.e. 120 plus any overhang seats; there has been at least one overhang seat in four of the seven MMP elections held since 1996). The year in which each change in the number of members took effect is shown in the following table.
| Year | Number of seats |
| 1854 | 37[37] |
| 1860 | 41[38] |
| 1861 | 53[39] |
| 1863 | 57[40] |
| 1866 | 70[41] |
| 1868 | 74[42] |
| 1871 | 78[43] |
| 1876 | 88[44] |
| 1882 | 95[45] |
| 1891 | 74[46] |
| 1902 | 80[47] |
| 1970 | 841 |
| 1973 | 871 |
| 1976 | 922 |
| 1984 | 952 |
| 1987 | 972 |
| 1993 | 992 |
| 1996 | 120 + any overhang seats[48] |
| Table notes
1 The total number of seats from 1969 to 1975 was calculated by the formula stated in the Electoral Amendment Act 1965: 4M+(PN/(PS/25)) where: 4M = 4 Maori seats; PN = European population of North Island; PS = European population of South Island.[49] 2 The total number of seats from 1976 to 1995 was calculated by the formula stated in the Electoral Amendment Act 1975: (PM/(PS/25))+(PN/(PS/25)) where: PM = Maori population; PN = European population of North Island; PS = European population of South Island.[50] |
Electoral system

All New Zealand citizens 18 years or older may vote in general elections, which are conducted by secret ballot. New Zealand was the first self-governing territory to enfranchise women, starting from the 1893 election.
Since the 1996 election, a form of proportional representation called mixed-member proportional (MMP) has been used.[51] Under the MMP system each person has two votes; one is for electoral seats (including some reserved for Māori),[52] and the other is for a party. Since the 2014 election, there have been 71 electorate seats (which includes 7 Māori electorates), and the remaining 49 seats are assigned so that representation in parliament reflects the party vote, although a party has to win one electoral seat or 5 percent of the total party vote before it is eligible for these seats.[53]
Last election results
| Party | Votes | % of Votes | Seats | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | Change | Electorate | List | Total | Change | |||
| National | 1,131,501 | 47.04 | −0.28 | 41 | 19 | 60 | +1 | |
| Labour | 604,534 | 25.13 | −2.35 | 27 | 5 | 32 | −2 | |
| Green | 257,356 | 10.70 | −0.36 | 0 | 14 | 14 | 0 | |
| NZ First | 208,300 | 8.66 | +2.06 | 0 | 11 | 11 | +3 | |
| Māori | 31,850 | 1.32 | −0.11 | 1 | 1 | 2 | −1 | |
| ACT | 16,689 | 0.69 | −0.37 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |
| United Future | 5,286 | 0.22 | −0.38 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |
| other parties | 150,104 | 6.24 | +2.87 | 0 | 0 | 0 | −1[lower-alpha 1] | |
| total | 2,405,620 | 100.00 | 71 | 50 | 121 | 0 | ||
| National minority government | 1,185,326 | 49.27 | −1.14 | 44 | 20 | 64 | 0 | |
| Opposition parties | 1,070,190 | 44.49 | −1.73 | 27 | 30 | 57 | 0 | |
| party informal votes | 10,681 | |||||||
| disallowed votes | ||||||||
| total votes cast | 2,416,481 | |||||||
| turnout | 76.95% | |||||||
| total electorate | 3,140,417[55] | |||||||
- ↑ The loss of one MP is due to sole Mana Party MP Hone Harawira losing his Te Tai Tokerau seat.
Note
Officials and officers
The Speaker of the House presides over sittings.[56] It is the Speaker's role to apply the rules of the House (Standing Orders),[57] and oversee procedures and the day-to-day operation of the House. The House appoints a Deputy Speaker from amongst its members. The Deputy Speaker may perform the Speaker’s role when the Speaker is absent. Up to two Assistant Speakers are also appointed from amongst the members of the House.[58]
Several partisan roles are filled by elected members.[59] The Prime Minister is the head of government. The Leader of the Official Opposition is the member of Parliament who leads the largest opposition party (which is usually second-largest caucus in the House). The Leader of the House is a member appointed by the Prime Minister to arrange government business and the legislative programme of Parliament.[59] Whips are organisers and administrators of the members in each of the political parties in the House. The whips make sure that members of their party are in the House during crucial votes.[59]
A Clerk is responsible for several key administrative tasks, such as "advising members on the rules, practices and customs of the House".[59] The Clerk is a non-political appointee.[60]
The Serjeant-at-Arms is the officer who has the duty of maintaining order in the precincts of the House.[59] The Serjeant-at-Arms sits in the debating chamber opposite the Speaker at the visitors door for each House sitting session.[61] The Serjeant-at-Arms is also the custodian of the mace, and bears the mace into and out of the chamber of the House at the beginning and end of each sitting day.[62]
Procedure

The House of Representatives usually sits Tuesday to Thursday when in session.[63] The House meets in a debating chamber located inside Parliament House, Wellington. The arrangement is similar to the design of the chamber of the British House of Commons.[64] The seats and desks are arranged in rows in a horseshoe pattern.[61] The Speaker of the House sits in a raised chair at the open end of the horseshoe, giving them a clear view of proceedings. In front of the chair is the Table of the House, on which rests the ceremonial mace. The House of Representatives cannot lawfully meet without the mace—representing the monarch's authority—being present in the chamber.[62]
Various officers—clerks and other officials—sit at the Table, ready to advise the Speaker on procedure when necessary.[59] Members of the Government sit on the benches on the Speaker's right, while members of the Official Opposition occupy the benches on the Speaker's left. Members are assigned seating on the basis of the seniority in a party caucus; Government ministers sit around the Prime Minister, who is traditionally assigned the fourth seat along the front row on the Speaker's right-hand side.[61] The Opposition leader sits directly across from the Prime Minister and is surrounded by Opposition spokespersons. The remaining party leaders sit in the front rows. A member who is not a Government minister or a leading member of an Opposition party is referred to as a "backbencher".[5] A backbencher may still subject to party discipline (called "whipping").
Debates and votes
Speeches may be delivered in English or te reo Māori (with an interpreter provided).[65] Speeches are addressed to the presiding officer, using the words "Mister Speaker"', if a man, or 'Madam Speaker', if a woman. Only the Speaker may be directly addressed in debate; other members must be referred to in the third person. Traditionally, members do not refer to each other by name, but by electorate or ministerial post, using forms such as "the honourable member for [electoral district]" or "the Minister of [portfolio]". The Prime Minister is addressed as "the Right Honourable".[66] The Speaker may name a member who he believes has broken the rules of conduct of the House; following a vote this will usually result in the expulsion of said member from the chamber.[67]
No member may speak more than once on the same question (except that the mover of a motion is entitled to make one speech at the beginning of the debate and another at the end). The Standing Orders of the House of Representatives prescribe time limits for speeches. The limits depend on the nature of the motion, but are most commonly between ten and twenty minutes. However, under certain circumstances, the Prime Minister, the Leader of the Official Opposition, and others are entitled to make longer speeches. Debate may be further restricted by the passage of "time allocation" motions. Alternatively, the House may end debate more quickly by passing a motion for "closure".
A vote is held to resolve a question when it is put to the House of Representatives. The House first votes by voice vote; the Speaker or Deputy Speaker puts the question, and members respond either "Aye" (in favour of the motion) or "No" (against the motion).[60] The presiding officer then announces the result of the voice vote, but if his or her assessment is challenged by any Member, a recorded vote known as a division follows. If a division does occur, members enter one of two lobbies (the "Aye" lobby or the "No" lobby) on either side of the chamber, where their names are recorded by clerks. At each lobby are two tellers (themselves members of Parliament) who count the votes of the Members. Once the division concludes, the tellers provide the results to the Speaker or Deputy Speaker, who then announces them to the House. If there is an equality of votes, the Speaker or Deputy Speaker has a casting vote.
Every sitting day a period of time is set aside for questions to be asked of ministers and select committee chairs.[68] Questions to a minister must related to their official ministerial activities, not to his or her activities as a party leader or as a private Member of Parliament. In addition to questions asked orally during Question Time, Members of Parliament may also make inquiries in writing.
Passage of legislation
Most parliamentary business is about making new laws and amending old laws. The House examines and amends bills (proposed laws) in several formal stages. Once a bill has passed through all its parliamentary stages it becomes an Act of Parliament, forming part of New Zealand's law.
Bills become Acts after being approved three times by House votes and then receiving the Royal Assent from the Governor-General. The majority of bills are promulgated by the Government of the day (that is, the party or parties that have a majority in the House). It is rare for government bills to be defeated, indeed the first to be defeated in the twentieth century was in 1998, when the Local Government Amendment Bill (No 5) was defeated on its second reading.[69] It is also possible for individual MPs to promote their own bills, called member's bills—these are usually put forward by opposition parties, or by MPs who wish to deal with a matter that parties do not take positions on. Local government and private individuals (for $2000 and only affecting themselves) may also bring forward legislation.
Proxy voting is allowed, in which members may designate a party or another member to vote on their behalf. An excuse is required.[70]
First Reading
The first stage of the process is the First Reading. The MP introducing the bill (often a minister) will give a detailed speech on the bill as a whole. Debate on the bill generally lasts two hours, with 12 MPs making ten-minute speeches (although they can split their speaking time with another MP) on the bill's general principles. Speaking slots are allocated based on the size of each party, with different parties using different methods to distribute their slots among their MPs.[63]
The MP introducing the bill will generally make a recommendation that the bill be considered by an appropriate Select Committee (see below). Sometimes, it will be recommended that a special Committee be formed, usually when the bill is particularly important or controversial. The House then votes as to whether the bill should be sent to the Committee for deliberation. It is not uncommon for a bill to be voted to the Select Committee stage even by parties which do not support it — since Select Committees can recommend amendments to bills, parties will often not make a final decision on whether to back a bill until the Second Reading.[63]
Prior to the First Reading, the Attorney-General will check the bill is consistent with the New Zealand Bill of Rights Act 1990 (NZBORA).[71] If the bill or part of the bill is inconsistent with NZBORA, they will present a report to the House of Representatives, known as a Section 7 report, highlighting the inconsistencies.
Select Committee stage
The Select Committee will scrutinise the bill, going over it in more detail than can be achieved by the whole membership of the House. The public can also make submissions to Select Committees, offering support, criticism, or merely comments. Written submissions from the public to the committee are normally due two months after the bill's first reading. Submitters can opt to also give an oral submission, which are heard by the committee in Wellington, and numbers permitting, Auckland and Christchurch. The Select Committee stage is seen as increasingly important today — in the past, the governing party generally dominated Select Committees, making the process something of a rubber stamp, but in the multi-party environment there is significant scope for real debate. Select Committees frequently recommend changes to bills, with prompts for change coming from the MPs on the Committee, officials who advise the Committee, and members of the public. When a majority of the Committee is satisfied with the bill, the Committee will report back to the House on it. Unless Parliament grants an extension, the time limit for Select Committee deliberations is six months or whatever deadline was set by the House when the bill was referred.[63]
Second Reading
The Second Reading, like the first, generally consists of a two-hour debate in which MPs make ten-minute speeches. Again, speaking slots are allocated to parties based on their size. In theory, speeches should relate to the principles and objects of the bill, and also to the consideration and recommendations of the Select Committee and issues raised in public submissions. Parties will usually have made their final decision on a bill after the Select Committee stage, and will make their views clear during the Second Reading debates. At the conclusion of the Second Reading debate, the House votes on whether to accept any amendments recommended by the Select Committee by majority (unanimous amendments are not subjected to this extra hurdle).[63]
The Government (usually through the Minister of Finance) has the power (given by the House's Standing Orders) to veto any bill (or amendment to a bill) that would have a major impact on the Government's budget and expenditure plans. This veto could be invoked at any stage of the process, but if applied to a bill as a whole would most likely be employed at the Second Reading stage. This has not occurred since the veto power was introduced in 1996, although many amendments have been vetoed at the Committee of the whole House stage (see below).
If a bill receives its Second Reading, it goes on to be considered by a Committee of the whole House.[63]
Committee of the whole House
When a bill reaches the Committee of the whole House stage, the House resolves itself "Into Committee", that is, it forms a committee consisting of all MPs (as distinct from a Select Committee, which consists only of a few members). When the House is "In Committee", it is able to operate in a slightly less formal way than usual.[63]
During the Committee of the whole House stage, a bill is debated in detail, usually "part by part" (a "part" is a grouping of clauses). MPs may make five-minute speeches on a particular part or provision of the bill and may propose further amendments, but theoretically should not make general speeches on the bill's overall goals or principles (that should have occurred at the Second Reading).
Sometimes a member may advertise his or her proposed amendments beforehand by having them printed on a "Supplementary Order Paper". This is common for amendments proposed by government Ministers. Some Supplementary Order Papers are very extensive, and, if agreed to, can result in major amendments to bills. On rare occasions, Supplementary Order Papers are referred to Select Committees for comment.
The extent to which a bill changes during this process varies. If the Select Committee that considered the bill did not have a government majority and made significant alterations, the Government may make significant "corrective" amendments. There is some criticism that bills may be amended to incorporate significant policy changes without the benefit of Select Committee scrutiny or public submissions, or even that such major changes can be made with little or no notice. However, under the MMP system when the Government is less likely to have an absolute majority, any amendments will usually need to be negotiated with other parties to obtain majority support.
The Opposition may also put forward wrecking amendments. These amendments are often just symbolic of their contrasting policy position, or simply intended to delay the passage of the bill through the sheer quantity of amendments for the Committee of the whole House to vote on.
Third Reading
The final Reading takes the same format as the First and Second Readings — a two-hour debate with MPs making ten-minute speeches. The speeches once again refer to the bill in general terms, and represent the final chance for debate. A final vote is taken. If a bill passes its third reading, it is passed on to the Governor-General, who may (assuming constitutional conventions are followed) give it Royal Assent as a matter of law. It then becomes law.
Select committees
Legislation is scrutinised by select committees. The committees can call for submissions from the public, thereby meaning that there is a degree of public consultation before a parliamentary bill proceeds into law. The strengthening of the committee system was in response to concerns that legislation was being forced through, without receiving due examination and revision. Each select committee has a chairperson and a deputy chairperson. MPs may be members of more than one select committee.
For the 51st Parliament, elected from the 2014 general election in September 2014, there were the following select committees in the House of Representatives, as follows:
| Select committee | Portfolios/Jurisdictions | Members (Roles) |
|---|---|---|
| Business | Administration of the House of Representatives (sitting programmes, order of business, speaking allocations, select committee membership, etc.) |
|
| Commerce | Business development, commerce, communications, consumer affairs, energy, information technology, insurance, superannuation |
|
| Education and Science | Education, education review, industry training, research, science, technology |
|
| Finance and Expenditure | Audit of the financial statements of the Government and departments, Government finance, revenue, taxation |
|
| Foreign Affairs, Defence and Trade | Customs, defence, disarmament and arms control, foreign affairs, immigration, trade. |
|
| Government Administration | Civil defence, cultural affairs, fitness, sport and leisure, internal affairs, Pacific Island affairs, Prime Minister and Cabinet, racing, services to Parliament, State services, statistics, tourism, women’s affairs, youth affairs. |
|
| Health | Health |
|
| Justice and Electoral | Crown legal and drafting services, electoral matters, human rights, justice |
|
| Law and Order | corrections, courts, criminal law, police, serious fraud |
|
| Local Government and Environment | Conservation, environment, local government. |
|
| Māori Affairs | Māori affairs |
|
| Primary Production | Agriculture, biosecurity, fisheries, forestry, lands, and land information. |
|
| Privileges | Parliamentary privilege |
|
| Officers of Parliament |
| |
| Regulations Review | Administration of government regulations |
|
| Social Services | Housing, senior citizens, social development, veterans’ affairs, and work and income support |
|
| Standing Orders |
| |
| Transport and Industrial Relations | Accident compensation, industrial relations, labour, occupational health and safety, transport, transport safety |
|
Occasionally a special Select Committee will be created on a temporary basis. An example was the Select Committee established to study the foreshore and seabed bill.
New Zealand Youth Parliament
Once in every term of Parliament a New Zealand Youth Parliament is held. This major national event is open to 16- to 18-year-olds who are appointed by individual MPs to represent them in their role for a few days in Wellington. The Youth MPs spend time debating a mock bill in the House and in select committees and asking questions of Cabinet Ministers. The previous New Zealand Youth Parliament was held in July 2013.[72]
Accredited news organisations
The following list is of news agencies which are accredited members of the New Zealand House of Representatives press gallery.[73]
- Agence France-Presse
- Aotearoa Student Press Association
- Asia Pacific Economic News Service
- Associated Press
- Bloomberg Television
- Business Wire
- Capital Chinese News
- Content Ltd
- Deutsche Presse-Agentur
- The Dominion Post
- Dow Jones Newswires
- ED Insider
- Fairfax Media Bureau
- Front Page
- Herald on Sunday
- InsideWellington
- Interest.co.nz
- Mana Māori Media
- Māori Television
- National Business Review
- Newsroom and New Zealand Farmers Weekly
- Newstalk ZB
- New Zealand Chinese Times
- The New Zealand Herald
- New Zealand Listener
- New Zealand Newswire
- Otago Daily Times
- Pacific Media Network
- The Press
- Prime
- Radio Live
- Radio New Zealand
- Reuters
- Scoop
- Select Committee News
- South Pacific News Service
- The Sunday Star-Times
- Synapsis.co.nz
- Television New Zealand
- Te Upoko o Te Ika (Torangapu)
- Trans Tasman
- TV3
- Waatea National Māori Radio
- Xinhua News Agency
See also
Notes
- ↑ http://www.radionz.co.nz/news/political/336718/watch-live-metiria-turei-on-two-green-mps-resignation
- ↑ "Parliamentary parties". New Zealand Parliament. Retrieved 8 February 2017.
- 1 2 3 "How Parliament works: What is Parliament?". New Zealand Parliament. 28 June 2010. Retrieved 31 May 2014.
- 1 2 "Parliament Brief: What is Parliament?". New Zealand Parliament. Retrieved 19 December 2016.
- 1 2 "Glossary of terms". New Zealand Parliament. Retrieved 13 May 2017.
- ↑ "Parliament Brief: Government Accountability to the House". New Zealand Parliament.
- ↑ "Confidence and Supply Agreement with ACT New Zealand". Parliament.nz. Retrieved 2016-06-24.
- ↑ "Reviewing electorate numbers and boundaries". Elections New Zealand. Retrieved 6 January 2012.
- ↑ Wilson 1985, p. 194.
- 1 2 Wilson 1985, p. 193.
- 1 2 Wilson 1985, p. 221.
- ↑ Wilson 1985, p. 214.
- ↑ Wilson 1985, p. 206.
- ↑ Wilson 1985, p. 223.
- ↑ Wilson 1985, p. 239.
- ↑ Wilson 1985, p. 245.
- ↑ Wilson 1985, p. 231.
- 1 2 Wilson 1985, p. 185.
- 1 2 Wilson 1985, p. 184.
- 1 2 Wilson 1985, p. 218.
- ↑ Wilson 1985, p. 222.
- ↑ Wilson 1985, p. 182.
- ↑ Wilson 1985, p. 219.
- ↑ Wilson 1985, p. 187.
- 1 2 Wilson 1985, p. 211.
- ↑ Wilson 1985, p. 181.
- ↑ Wilson 1985, p. 228.
- ↑ Wilson 1985, p. 190.
- ↑ Wilson 1985, p. 195.
- ↑ Wilson 1985, p. 234.
- ↑ Wilson 1985, p. 208.
- ↑ Wilson 1985, p. 198.
- ↑ Wilson 1985, p. 216.
- ↑ Wilson 1985, p. 227.
- ↑ Wilson 1985, p. 244.
- ↑ Wilson 1985, p. 191.
- ↑ Proclamation from Government Gazette of 10 March 1853, New Zealand Spectator and Cook's Strait Guardian, 12 March 1853, page 3
- ↑ Electoral Districts Act 1858
- ↑ Representation Act 1860
- ↑ Representation Act 1862
- ↑ Representation Act 1865
- ↑ Maori Representation Act 1867
- ↑ Representation Act 1870
- ↑ Representation Act 1875
- ↑ Representation Act 1881
- ↑ Representation Acts Amendment Act 1887
- ↑ Representation Act 1900
- ↑ Electoral Act 1993
- ↑ Electoral Amendment Act 1965
- ↑ Electoral Amendment Act 1975
- ↑ "New Zealand's Change to MMP —". aceproject.org. ACE Electoral Knowledge Network. Retrieved 24 June 2017.
- ↑ "Reviewing electorate numbers and boundaries". Electoral Commission. 8 May 2005. Archived from the original on 9 November 2011. Retrieved 23 January 2012.
- ↑ "Sainte-Laguë allocation formula". Electoral Commission. 4 February 2013. Retrieved 31 May 2014.
- ↑ "Official Count Results -- Overall Status". Electoral Commission. 4 October 2014. Retrieved 4 October 2014.
- ↑ "Enrolment statistics by electorate -- as at 20 September 2014". Electoral Commission. Retrieved 20 September 2014.
- ↑ "Office of the Speaker". New Zealand Parliament. Retrieved 19 December 2016.
- ↑ "Rules of the House". New Zealand Parliament. Retrieved 13 May 2017.
- ↑ "Supporting the Speaker". New Zealand Parliament. Retrieved 13 May 2017.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "People in Parliament". New Zealand Parliament. Retrieved 13 May 2017.
- 1 2 Martin, John E. "Parliament - How Parliament works". Te Ara: The Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Retrieved 14 May 2017.
- 1 2 3 "Where MPs sit in the House". New Zealand Parliament. 22 October 2014. Retrieved 20 December 2016.
- 1 2 "What is the significance of the mace?". New Zealand Parliament. Retrieved 13 May 2017.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 "Standing Order of the House of Representatives of New Zealand" (PDF). Retrieved 13 May 2017.
- ↑ "How Parliament works". New Zealand Parliament. Retrieved 13 May 2017.
- ↑ "Parliament in te reo". New Zealand Ministry for Culture and Heritage. Retrieved 13 May 2017.
- ↑ "“The Honourable” and “The Right Honourable”". New Zealand Parliament.
- ↑ "Naming and Suspension of Member". New Zealand Parliament. Retrieved 13 May 2017.
- ↑ "Question time in the House". New Zealand Parliament. 16 October 2012. Retrieved 3 July 2017.
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 15 January 2012. Retrieved 9 February 2012.
- ↑ "Standing Orders of the House of Representatives" (PDF). New Zealand House of Representatives. 12 August 2005. Retrieved 2008-02-19.
- ↑ "New Zealand Bill of Rights Act 1990 | The Legislation Design and Advisory Committee". New Zealand Legislation Design and Advisory Committee. Retrieved 13 May 2017.
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 22 May 2010. Retrieved 25 March 2010.
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 9 February 2007. Retrieved 26 April 2013.
References
- Wilson, James Oakley (1985) [First published in 1913]. New Zealand Parliamentary Record, 1840–1984 (4th ed.). Wellington: V.R. Ward, Govt. Printer. OCLC 154283103.
External links
- Parliament of New Zealand
- Images from around Parliament Buildings
- Digitised reports from selected volumes of the Appendix to the Journals of the House of Representatives
- Standing Orders of the House of Representatives, 2014 - New Zealand Parliament
