Saudi Arabian Army
| Royal Saudi Arabian Army | |
|---|---|
| Arabic: القُوّات البَرِيَة المَلَكيَّة السُّـعُوديَّة | |
|
Seal | |
| Active | As early as January 1745;[1] |
| Country |
|
| Allegiance | Custodian of the Two Holy Mosques |
| Branch | Saudi Armed Forces (as of 1902) |
| Type | Army |
| Role | Ground-based warfare |
| Size |
300,000+[2] full-time personnel (2012 est.) 325,000[3] reserve and National Guard 625,000+ total personnel (2015 est.) |
| Part of | |
| Headquarters | King Rd, Al Wazarat, Riyadh |
| Anniversaries | January 13; (115 years ago) |
| Decorations |
|
| Website | Official Website |
| Commanders | |
| Minister of Defense | Crown Prince Mohammad Al Saud |
| Chief of Joint Staff | General Abdul Rahman Al Banyan |
| Commander of Royal Land Forces | Lt. General Prince Fahd Al Saud |
| Insignia | |
| Battle flag |
 |
| Flag |
 |
The Royal Saudi Land Forces (KSA) (Arabic: القوات البرية الملكية السعودية), also called Saudi Arabian Army (Arabic: الجيش العربي السعودي Al-Jai? al-?Arab?yat al-Su??d?yah), are the largest branch of the Saudi Arabia Armed Forces. The Saudi Arabia Ground Armed Forces (SAAF) divide its manpower between two main entities, the National Guard (SANG) and the Army [RSLF]. The Chief of the Saudi General Staff until 2011 was Field Marshal Saleh Al-Muhaya.[4]
History
The modern Saudi Army has its roots in the first Saudi State, which was formed as early as 1745, and is considered to be the birth year of the Saudi Army. As of 13 January 1902 was founded as the Royal Saudi Land Forces, and is the oldest branch of the KSA military.[1]
Other events that led to an expansion of the Saudi Army were the Arab–Israeli conflict in 1948, the fall of Shah Mohammad Reza Pahlavi in the Iranian Revolution in 1979 and the subsequent fears of possible Shia's actions, and in the last years the first Gulf War in 1990. In the year 2000, Saudi Arabia's government spent billions of dollars to expand the Saudi Forces including the Saudi Army.
Fahad Al-Eissa, Director general of the defense minister’s office stated that “We are the fourth-largest military spender in the world, yet when it comes to the quality of our arms, we are barely in the top 20,”. Mohammad bin Salman was appointed Defense Minister to correct these defficiencies.[5]
Wars involved

First Saudi State (1745–1818)
- Battle of Riyadh (1746)
- Battle of Al-Hayer (1764)
- Battle of ghrimeel (1789)
- Ibn Ufaisan's Invasion (1793)
- Invasion of Qatar (1793–1798)
- Battle of Khakeekera (1801)
- Ottoman–Saudi War (1811–1818)
Saudi State (1818–1891)
- Rebellion against Egypt Eyalet (1821–1824)
- Saudi Civil War (1865–1875)
- Al-Hasa Expedition (1870–1871)
- Battle of Arwa (1883) (1883)
- Battle of Mulayda (1891)
The Unification of Saudi Arabia (1902–1933)
- Battle of Riyadh (1902)
- Battle of Dilam (1903)
- First Saudi–Rashidi War (1903–1907)
- Battle of Hadia (1910)
- Conquest of al-Hasa (1913)
- Battle of Jarrab (1915)
Battle of Kinzaan (1915) - First Saudi–Hashemite War (1918–1919)
- Kuwait-Saudi War (1919–1920)
- Second Saudi–Rashidi War (1921)
- Saudi-Transjordan War (1922)
- Second Saudi-Hashemite War (1924–1925)
- Ikhwan Revolt (1927–1930)
Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (1933–present)
- Saudi–Yemeni War (1934)
- 1948 Arab–Israeli War more than 3,000 Saudi troops participated in combat against Israel.
- 1967 RSLF deployed over 20,000 troops in Jordan.
- 1969 Al-Wadiah War. South Yemeni Forces invaded Al-Wadiah, a Saudi town, but later were defeated by the Saudi Army.
- 1973 during the Yom Kippur War Saudi Arabia, along with other Persian Gulf nations, protested American intervention by raising oil prices, Saudi Arabia sent 3,000 troops stationed in Jordan to Syria four days after the war began, though they did not engage in the fighting.[6]
- Gulf War (1990–91) Together with the allied forces, the Saudi Armed Forces and SANG played a major part in the Battle of Khafji and the Liberation of Kuwait.
- 2007–10 Houthi Insurgency. Yemeni Houthis attacked southern Saudi Arabia and were defeated by the Saudi army.
- 2015 Saudi Arabian-led intervention in Yemen at the request of the Yemeni president to repel Houthi rebels allied with the deposed Ali Abdullah Saleh, as part of the Yemeni Civil War (2015).
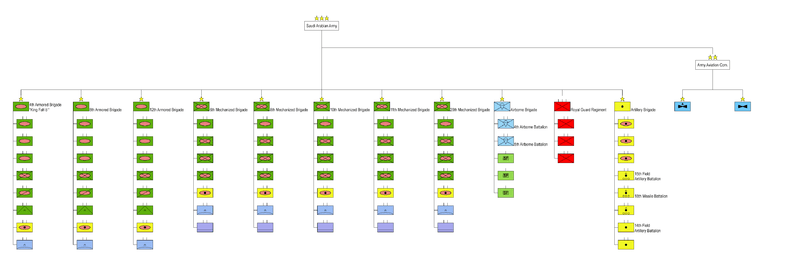
Structure

The combat strength of the Saudi Army consists of 4 Armoured, 5 Mechanized, 2 Light Infantry (1 Royal Guards, 1 Special Forces) Brigades. The Saudi Army deployed the 12th Armoured Brigade and 6th Mechanized Brigade at King Faisal Military City in the Tabuk area. It deployed the 4th Armoured Brigade, and 11th Mechanized Brigade at King Abdul Aziz Military City in the Khamis Mushayt area. It deployed the 20th Mechanized Brigade and 8th Mechanized Brigade at King Khalid Military City near Hafr al Batin. The 10th Mechanized Brigade is deployed at Sharawrah, which is near the border with Yemen and about 150 kilometers from Zamak.[7]
Despite the addition of a number of units and increased mobility achieved during the 1970s and 1980s, the army's personnel complement has expanded only moderately since a major buildup was launched in the late 1960s. The army has been chronically understrength, in the case of some units by an estimated 30 to 50 percent. These shortages have been aggravated by a relaxed policy that permitted considerable absenteeism and by a serious problem of retaining experienced technicians and noncommissioned officers (NCOs). The continued existence of a separate national guard also limited the pool of potential army recruits.[7]
Armor
- 4th (King Khaled) Armoured Brigade
- 6th (King Fah'd) Armoured Brigade
- 7th (Prince Sultan)Armoured Brigade
- 8th (King Fah'd)Armoured Brigade
- 10th (King Faisal)Armoured Brigade
- 12th (Khalid ibn al-Walid)Armoured Brigade
A typical Saudi armoured brigade has an armoured reconnaissance company, three tank battalions with 35 tanks each, a mechanized infantry battalion with AIFVs/APCs, and an artillery battalion with 18 self-propelled guns. It also has an army aviation company, an engineer company, a logistic battalion, a field workshop, and a medical company.[8]
Mechanized
- 11th Mechanized Brigade
- 12th Mechanized Brigade
- 13th Mechanized Brigade
- 14th Mechanized Brigade
- 20th Mechanized Brigade
A typical Saudi mechanized brigade has an armoured reconnaissance company, one tank battalion with 40 tanks, three mechanized infantry battalions with AIFVs/APCs, and an artillery battalion with 18 self-propelled guns. It also has an army aviation company, an engineer company, a logistic battalion, a field workshop, and a medical company. It has 24 anti-tank guided weapons launchers and four mortar sections with a total of eight 81 mm (3 in) mortars.[8]
Infantry
- 16th (King Saud) Light motorized infantry brigade
- 17th (Abu Bakr Assiddeeq) Light motorized infantry brigade
- 18th (King Abdullah) Light motorized infantry brigade
- 19th (?Umar ibn Al-Khatt?b) Light motorized infantry brigade
Each infantry brigade consists of three motorized battalions, an artillery battalion, and a support battalion. Army brigades should not be confused with Saudi Arabian National Guard brigades.
Airborne
- The 1st Airborne Brigade
- 4th Airborne Battalion
- 5th Airborne Battalion
The Airborne Brigade is normally deployed near Tabuk. The Airborne Brigade has two parachute battalions and three Special Forces companies. Saudi Arabia is expanding its Special Forces and improving their equipment and training to help deal with the threat of terrorism. The Special Forces have been turned into independent fighting units to help deal with terrorists, and report directly to Prince Sultan.
Artillery Battalions
- five artillery battalions
Aviation
- 1st Aviation Group
- 2nd Aviation Group
- 3rd Aviation Group
- 4th Aviation Group
The separate Royal Guard Regiment consists of four light infantry battalions.
Main equipment
Note that figures below do not include war losses due to the ongoing conflict in Yemen.
Infantry weapons
Small arms
| Model | Image | Type | Quantity | Acquired | Origin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Browning Hi-Power |  | Semi-automatic pistol | | |||
| Glock 17 |  | Semi-automatic pistol | | |||
| FN P90 |  | Submachine gun | | |||
| HK33A2 | .jpg) | Assault rifle | | |||
| H&K MP5 |  | Submachine gun | | Manufactured by Military Industries Corporation. MP5A2, MP5A3 & MP5K variants.[9] | ||
| Heckler & Koch G3 |  | Battle Rifle | | Manufactured by Military Industries Corporation[10] | ||
| Heckler & Koch G36 | .jpg) | Assault Rifle | | Manufactured by Military Industries Corporation[11] | ||
| M4 carbine |  | Assault Rifle | | |||
| Steyr AUG |  | Assault Rifle | | |||
| AK-103 | | Assault Rifle | | |||
| AUG A1 HBAR |  | Squad automatic weapon | | |||
| FN MAG |  | General purpose machine gun | | |||
| M2 Browning |  | Heavy machine gun | | |||
Grenade, rocket, anti-tank, and missile systems
| Model | Type | Quantity | Acquired | Origin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M203 | Single shot grenade launcher | | |||
| FGM-148 Javelin | Anti-tank guided missile | | |||
| MBT LAW | Anti-tank guided missile | | |||
| Swingfire | Anti-tank guided missile | | |||
| Vickers Vigilant | Anti-tank missile | 500 | | ||
| M47 Dragon | Anti-tank missile | 4,692 | | ||
| AGM-114 Hellfire | Anti-tank guided missile | 2,954 | | ||
| MILAN | Anti-tank guided missile | | |||
| HOT | Anti-tank guided missile | 3,500 | | ||
| HOT 2 | Anti-tank guided missile | 249 | | ||
| Bill 2 | SACLOS Anti-tank missile | 200 | | ||
| SS.11 | Anti-tank guided missile | 2,000 | | ||
| BGM-71 TOW | Anti-tank guided missile | 10,738 | | ||
| BGM-71C ITOW | Anti-tank guided missile | 2,538 | | ||
| BGM-71D TOW-2 | Anti-tank guided missile | 6,210 | | ||
| BGM-71E TOW-2A | Anti-tank guided missile | 5,131 | |
Mortars
| Model | Type | Quantity | Acquired | Origin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M224 Mortar | Mortar | N/A | N/A | | |
| Brandt Mle CM60A1 | Mortar | N/A | N/A | | |
| MO-120-RT-61 120mm | Mortar | 200 | 200 | | |
| 2R2M 120MM | Mortar | 28 | 28 | | |
| M30 107 mm Mortar | Mortar | N/A | | ||
Vehicles
Tanks
| Model | Image | Origin | Variant | Quantity | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 Abrams | | | M1A2S | 442
+ 153 on order |
Saudi Arabia bought 373 M1A2 tanks,[12] with further 69 more M1A2S tanks ordered on 8 January 2013 and delivered by 31 July 2014.[13] Later Saudi Arabia decided to upgrade all of M1A2 variants to M1A2S configuration. 153 M1A2S on order since Aug 9, 2016[12] |
| M60 Patton | .jpg) | | M60A3 | 450[14] | 485 were acquired, currently in reserve. |
| AMX-30 |  |
AMX-30SA | 250 | in reserve |
Infantry fighting vehicles
| Model | Image | Origin | Variant | Quantity | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M2 Bradley |  | | M2A2 | 400[14] | Principal IFV of the Saudi Army.[15] |
| AMX-10P |  | | 500[14] | 500[16] were bought from France in 1974; most are now stored as a reserve. | |
Armored personnel carriers
| Model | Image | Origin | Variant | Quantity | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M113 |  | | Many | 1,112 | 364 had been upgraded in Turkey.[15] |
| Al-Masmak | | 2,750 | x[17][18] |
Utility vehicles
| Model | Image | Origin | Variant | Quantity | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HMMWV |  | | various configurations | 15,000+ | |
| Oshkosh M-ATV |  | | Many | 1859 | Saudi Arabia began negotiations for an order for an undisclosed number of M-ATVs Saudi Arabia received an estimated 1859 |
| URO VAMTAC |  | | 300 | [19] | |
| CUCV II[20] |  | | 2,000+ | ||
Artillery and missile systems
| Model | Image | Origin | Type | Variant | Quantity | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M270 | _Vehicles_at_Camp_Bastion%2C_Afghanistan_MOD_45148148.jpg) | | MRL 270mm | 50 | ||
| Astros II MLRS | | | MRL 127mm | SS-30 | 72 | |
| PLZ-45 |  | | Self-propelled howitzer 155mm | 54[21] | ||
| M109 howitzer | | | Self-propelled howitzer 155mm | M109A5 M109A2 | 48 110 | |
| AMX-GCT | | | Self-propelled howitzer 155mm | 51 | ||
| M198 howitzer |  | | Towed Howitzer 155mm | 42 | ||
| FH-70 | .jpg) | | Towed Howitzer 155mm | 40 | ||
| M114 howitzer |  | | Towed Howitzer 155mm | M114A1 | 50 | All are stored in reserve. |
| M102 howitzer |  | | Towed Howitzer 105mm | 140[15] | ||
| M101 howitzer |  | | Towed Howitzer 105mm | M101A1 | 100 | All are stored in reserve. |
Army aviation
| Model | Image | Origin | Type | Variant | Quantity | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AH-64 Apache |  | | Attack Helicopter | AH-64D | 94 | A further 29 AH-64D Longbow III requested for more than $1.2bn. |
| Boeing AH-6 | | | Armed Scout Helicopter | 0 | 36 on order for Saudi Arabian National Guard | |
| Bell 406 |  | | Scout Helicopter | Bell 406CS | 13 | |
| Sikorsky UH-60 Black Hawk |  | | Transport Helicopter | UH-60L | 37 | A further 24 UH-60L requested for $350m. |
| Sikorsky S-70 |  | | Medevac Helicopter | S-70A1L | 8 | |
| Boeing CH-47F Chinook |  | | Cargo Helicopter | CH-47F | 48 | Ordered in December 2016. |
| Aeryon Scout[22] |  | | Miniature UAV | 10 | ||
| Saqr,2,3,4[23] | | Unmanned aerial vehicle | ? | ? | ||
| CAIG Wing Loong [24][25] |  | | MALE UCAV | Pterodactyl Wing Loong II | 300[26] | |
| Denel Dynamics Seeker [27][28] |  | | UCAV | Seeker 400 | ? | |
| EMT Luna X-2000[30] |  | | Unmanned aerial vehicle | ? | ? | |
| Selex ES Falco[32] |  | | Unmanned aerial vehicle | ? | ? | |
- (Anti-Air systems belong to Air Defense Force)
Royal Saudi Land Forces Ranks
Land Officer Corps
| Equivalent NATO Code | OF-10 | OF-9 | OF-8 | OF-7 | OF-6 | OF-5 | OF-4 | OF-3 | OF-2 | OF-1 | OF(D) & Student officer | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Edit) |
No equivalent | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Unknown | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fariq Awwal (فريق أول) |
Fariq (فريق) |
Liwa (لواء) |
Amid (عميد) |
Aqid (عقيد) |
Muqaddam (مقدم) |
Raid (رائد) |
Naqib (نقيب) |
Mulazim Awwal (ملازم أول) |
Mulazim (ملازم) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Land Enlisted Corps
| Junior enlisted | Non-commissioned Officers (NCOs) | Warrant Officers (WOs) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Private (PVT) |
First Class Private (FCS) |
Corporal (CPL) |
Vice Sergeant (VS) |
Sergeant (S) |
First Class sergeant (FCS) |
Sergeant Major (SGM) | |||||
| E-1 | E-2 | E-3 | E-4/5 | E-7 | E-8 | E-9 | |||||
| No Chevron (Arabic: جندي Jundi) |
One Chevron (Arabic: جندي أول Jundi Awaal) |
Two Chevrons (Arabic: عريف Areef) |
Three Chevrons (Arabic: وكيل رقيب Wakil Raqib) |
Four Chevrons (Arabic: رقيب Raqib) |
Four Chevrons with stripe (Arabic: رقيب أول Raqib Awaal ) |
stripe (Arabic: رئيس رقباء Rais Ruquba) | |||||
See also
- Military of Saudi Arabia
- Royal Saudi Air Force
- Royal Saudi Navy
- Royal Saudi Air Defense
- Royal Saudi Strategic Missile Force
- Saudi Arabian National Guard
- Saudi Royal Guard Regiment
- King Khalid Military City
- Saudi Arabia
Notes
- ↑
- Saudi State (first) Jan 1745– Sep 1818
- Emirate of Nejd(second) Sep 1818– Jan 1891
- Modern State(third) Jan 1902– present
References
- 1 2 Wynbrandt, James (2004). A Brief History of Saudi Arabia (1st ed.). p. 353. Retrieved Oct 10, 2016.
- ↑ "Political Regimes in the Arab World: Society and the Exercise of Power". September 4, 2012.
- ↑ "Saudi King Salman cements hold on power". aljazeera.net. 30 January 2015. Retrieved 30 January 2015.
- ↑ Royal Saudi Land Forces.
- ↑ https://www.bloomberg.com/news/features/2016-04-21/the-2-trillion-project-to-get-saudi-arabia-s-economy-off-oil
- ↑
- 1 2 Royal Saudi Land Forces
- 1 2 Accéder Google Francais
- ↑ "MP5 Sub Machine Gun". mic.org.sa. Retrieved 2017-04-25.
- ↑ "G3 Semi-Automatic Rifle". mic.org.sa. Retrieved 2017-04-25.
- ↑ "Rifle G36". mic.org.sa. Retrieved 2017-04-25.
- 1 2 "The 2006 Saudi Shopping Spree: $2.9B to Upgrade M1 Abrams Tank Fleet". DefenseIndustryDaily.com. 4 January 2011. Archived from the original on October 25, 2006. Retrieved 28 July 2011.
- ↑ "Saudi Arabia Orders 69 More M1A2S Abrams Heavy Tanks". Deagel.com, 8 January 2013.
- 1 2 3 "Royal Saudi Land Forces Equipment". Global Security. Retrieved 2015-04-09.
- 1 2 3 Military Balance 2005- page 135
- ↑
- ↑ "Al-Masmak Masmak Nyoka Mk2 MRAP Mine Resistant Armored Personnel Carrier technical data sheet - Army Recognition - Army Recognition". Retrieved 25 December 2014.
- ↑ "Saudi Al-Masmak Achieves the Highest Protection Level Recorded for MRAP". Retrieved 25 December 2014.
- ↑ Administrator. "30 VAMTAC's to Saudi Arabia". Retrieved 25 December 2014.
- ↑ "Commercial Utility Cargo Vehicle: CUCV II". Olive-drab.com. Retrieved 2013-03-15.
- ↑ Chinese Guns Conquer Arabia
- ↑ "picture of Saudi Army with Aeryon Scout".
- ↑
- ↑ Fischer Junior, Richard. "Kazakhstan purchases two Chinese Wing-Loong UCAVs" (7 June 2016). IHS Jane's 360. Retrieved 7 November 2016.
- ↑ Atherton, Kelsey (22 June 2016). "Chinese-made drone crashes in Pakistan". Popular Science. Retrieved 7 November 2016.
- ↑ "??300?????????????????".
- ↑ "After Obama snub, Saudis tap up South Africa for armed drone" (2 April 2013). the Commentator.
- ↑ Gertz, Bill (2 April 2013). "Saudi Arabia buying South African armed drone". Free Beacon.
- ↑ "Riyadh's secret armed drone programme". Intelligence Online. 2013-03-27.
- ↑ Amnesty International. "Der Kunde ist K?nig" (in German). Retrieved 2012-04-05.
- ↑ Lake, Jon. "Saudi Arabia shows Luna [IDX15D4]" (26 February 2015). janes.
- ↑ http://www.ainonline.com/aviation-news/farnborough-air-show/2012-07-13/falco-gains-mystery-customer-evo-prepped-flight
External links
- RSLF official website
- CIA World Factbook
- Pakistani tanks deal
- 2006 Military spending of Saudi Forces
- latest French tanks deal
.png)

