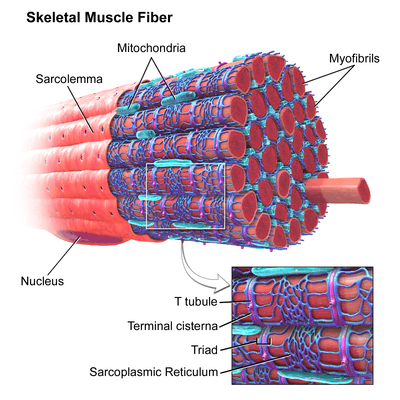
Sarcolemma
| Sarcolemma | |
|---|---|
 Skeletal muscle, with sarcolemma labeled at upper left. | |
| Identifiers | |
| Code | TH H2.00.05.0.00003 |
The sarcolemma (sarco (from sarx) from Greek; flesh, and lemma from Greek; sheath.) also called the myolemma, is the cell membrane of a striated muscle fiber cell.[1] It consists of a plasma membrane, which is a lipid bilayer, and an outer coat consisting of a thin layer of polysaccharide material (glycocalyx) that contacts the basement membrane, which contains numerous thin collagen fibrils and specialized proteins such as laminin[2] that provide a scaffold for the muscle fiber to adhere to. Through transmembrane proteins residing in the plasma membrane, the actin skeleton inside the cell is connected to the basement membrane and the cell's exterior. At each end of the muscle fiber, the surface layer of the sarcolemma fuses with a tendon fiber, and the tendon fibers in turn collect into bundles to form the muscle tendons that then adhere onto bones.
The sarcolemma generally maintains the same function in muscle cells as the plasma membrane does in other eukaryote cells.[3] It acts as a barrier between the extracellular and intracellular compartments, defining the individual muscle fiber from its surroundings. The lipid nature of the membrane allows it to separate the fluids of the intra- and extracellular compartments, since it is only selectively permeable to water through aquaporin channels. As in other cells this allows for the compositions of the compartments to be controlled by selective transport through the membrane. Membrane proteins, such as ion pumps, may create ion gradients with the consumption of ATP, that may later be used to drive transport of other substances through the membrane (Co-transport) or generate electrical impulses such as Action potentials.
A special feature of the sarcolemma is that it invaginates into the cytoplasm of the muscle cell, forming membranous tubules radially and longitudinally within the fiber called transverse tubules (T-tubules). On either side of the transverse tubules are Terminal cisterna enlargements of smooth endoplasmic reticulum termed sarcoplasmatic reticulum (SR) in muscle. A transverse tubule surrounded by two SR cisterna are known as triads, and the contact between these structures is located at the junction of the A and I bands.
See also
References
- ↑ Sarcolemma at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- ↑ Engvall, E.; Earwicker D; Haaparanta T; Ruoslahti E; Sanes JR. (September 1990). "Distribution and isolation of four laminin variants; tissue restricted distribution of heterotrimers assembled from five different subunits". Cell Regulation. 1 (10): 731–40. PMC 361653
 . PMID 2099832. doi:10.1091/mbc.1.10.731.
. PMID 2099832. doi:10.1091/mbc.1.10.731. - ↑ Boron, Walter F. (2009). Medical Physiology 2nd edition. Philadelphia: Saunders. pp. 9–21.