Santa Maria della Pace
| Santa Maria della Pace Our Lady of Peace (in English) S. Mariæ de Pace (in Latin) | |
|---|---|
 Santa Maria della Pace façade | |
| Basic information | |
| Location |
|
| Affiliation | Roman Catholic |
| District | Lazio |
| Province | Rome |
| Country | Italy |
| Ecclesiastical or organizational status | Titular church |
| Leadership | Francisco Javier Errazuriz Ossa, P. Schonstatt |
| Architectural type | Church |
Santa Maria della Pace is a church in Rome, central Italy, not far from Piazza Navona. The building lies in rione Ponte.
History
The current building was built on the foundations of the pre-existing church of Sant'Andrea de Aquarizariis[1] in 1482, commissioned by Pope Sixtus IV. The church was rededicated to the Virgin Mary to remember a miraculous bleeding of a Madonna image there in 1480. The author of the original design is not known, though Baccio Pontelli has been proposed.

In 1656–67 Pope Alexander VII had the edifice restored by Pietro da Cortona, who also added the famous Baroque façade projecting from its concave wings: this, devised to simulate a theatrical set, has two orders and is entered by a semi-circular pronaos with paired Tuscan columns. The church presses forward almost to fill its tiny piazza; several houses had to be demolished by Pietro da Cortona to create even this miniature trapezoidal space. This newly formed piazza, focussed on the church facade even in its architectural detailing, had the additional benefits of facilitating the turning of coaches which had become so fashionable with the Roman nobility of the time and creating an ingenious unified ensemble of the church in its urban setting.[2] The play of concave and convex forms at varying scales in and around the predominant main facade masks the neighbouring buildings, extends the apparent breadth of the facade and so increases the visual impact on the spectator physically confined by the small trapezoidal piazza. The monumental effect of the plasticity of forms, spatial layering and chiarascuro lighting effects belies the actual scale of this urban intervention.
The inscription around the porch architrave is taken from Psalm 72: SUSCIPIANT MONTES PACEM POPULO ET COLLES IUSTITIAM ("The mountains shall bring peace to the people; and the hills, justice"). This reference to the 'mountains' of the coat of arms of the Chigi family, to which Alexander VII belonged, is presumably an allusion to the benefits of his papal reign. Oak leaf motifs, another Chigi family emblem, can also be found on the facade. On the upper facade, Cortona had the curved travertine panels cut to make grained matching patterns, in an unusual use of this particular material. Through the tall central window, the circular window of the Quattrocento church facade is visible.
Cardinalatial Titulus
The Church of Santa Maria della Pace was designated as a titulus for a Cardinal-Priest on 13 April 1587 by Pope Sixtus V.[3] The holders of the title were:[4]
Cardinal Priests
- Antonmaria Salviati (20 April 1587 - 23 April 1600)
- Flaminio Piatti (24 April 1600 - 1 November 1613)
- Giacomo Serra (28 September 1615 - 19 August - 19 August 1623)
- Alessandro d'Este (2 October 1623 - 13 May 1624).
- Melchior Klesl (1 July 1624 - 18 September 1630)
- Fabrizio Verospi (5 September 1633 - 27 January 1639)
- Marcantonio Franciotti (19 December 1639 - 8 February 1666)
- Giacomo Filippo Nini (15 March 1666 - 11 August 1680)
- Stefano Brancaccio (22 September 1681 - 8 September 1682)
- Carlo Barberini (27 September 1683 - 30 April 1685)
- Giacomo Franzoni (30 April 1685 - 10 November 1687)
- Augustyn Michal Stefan Radziejowski (14 November 1689 - 11 October 1705)
- Lorenzo Maria Fieschi (25 June 1706 - 1 May 1726)
- Carlo Alberto Guidobono Cavalchini (23 September 1743 - 12 February 1759)
- Antonio Maria Priuli (13 July 1759 - 19 April 1762)
- Marcantonio Colonna (cardinal) (19 April 1762 - 25 June 1784)
- Ignazio Busca (3 August 1789 - 18 December 1795)
- Carlo Bellisomi (18 December 1795 - 18 September 1807)
- Antonio Gabriele Severoli (1 October 1817 - 8 September 1824)
- Carlo Maria Pedicini (15 December 1828 - 5 July 1830)
- Giuseppe Antonio Sala (30 September 1831 - 23 June 1839)
- Charles Januarius Acton (24 January 1842 - 21 December 1846)
- Pierre Giraud (4 October 1847 - 17 April 1850)
- Juan Jose Bonel y Orbe (30 November 1854 - 11 February 1857)
- Fernando de la Puente y Primo de Rivera (21 May 1862 - 12 March 1867)
- Juan de la Cruz Ignacio Moreno y Maisanove (22 November 1869 - 28 August 1884)
- Domenico Agostini (7 June 1886 - 31 December 1891)
- Michael Logue (19 January 1893 - 19 November 1924)
- Patrick Joseph O'Donnell (17 December 1925 - 22 October 1927)
- August Hlond, SDB (20 June 1927 - 22 October 1948)
- Maurice Feltin (12 January 1953 - 27 September 1975)
- Joseph Asjiro Satowaki (30 June 1979 - 8 August 1996)
- Francisco Javier Errázuriz Ossa (21 February 2001 - incumbent)
Interior
The interior, which can be reached from the original fifteenth-century door, has a short nave with cruciform vaulting and a tribune surmounted by a cupola. Cortona articulated the interior of the dome with octagonal coffering and a series of ribs radiating from the lantern. This is an early example of combining these two forms of dome decoration and was employed by Gianlorenzo Bernini in his later churches at Ariccia and Castelgandolfo.[5]
Carlo Maderno designed the high altar (1614) to enframe the venerable icon of the Madonna and Child.
Chigi Chapel

Raphael began to fresco the Sibyls receiving angelic instruction (1514) above the arch of the Chigi Chapel, commissioned by Agostino Chigi, the papal banker.[6] The Deposition over the altar is by Cosimo Fancelli.
Cesi and Ponzetti Chapels
The second chapel on the right, the Cesi Chapel, was designed by Antonio da Sangallo the Younger, and has a very fine Renaissance decoration on the external arch by Simone Mosca, as well as two small frescoes, the Creation of Eve and the Original Sin by Rosso Fiorentino.
The first chapel on the left (Ponzetti Chapel) has noteworthy Renaissance frescoes by Baldassarre Peruzzi, who is better known as an architect. The second chapel has marble taken from the ruins of the Temple of Jupiter Capitolinus.
The tribune has paintings by Carlo Maratta, Peruzzi, Orazio Gentileschi, Francesco Albani and others.
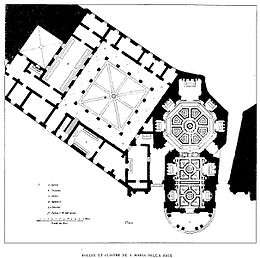
A main feature of the church and monastery complex is the Bramante cloister. Built in 1500-1504 for Cardinal Oliviero Carafa, it was the first work of Donato Bramante in the city. It has two levels: the first is articulated by shallow pilasters set against an arcade; the second also has pilasters set against an arcade which is vertically continuous with the lower storey, but with columns located in between each arch span.
Gallery
- Dome
 Bramante cloister
Bramante cloister- Bramante cloister
See also
Bibliography
- Mariano Armellini, Le chiese di Roma dalle loro origini sino al secolo XIX (Roma: Editrice Romana, 1878), pp. 433-434.
- Nunzia Di Girolamo, Santa Maria della Pace : saggio monografico (Montreal: K-Editrice Internazionale, 1985).
- Gizzi, Federico (1994). Le chiese rinascimentali di Roma. Rome: Newton Compton.
References
- ↑ Aquarizariis: "of the water carriers" on whom Rome depended after the aqueducts were broken.
- ↑ Anthony Blunt, Guide to Baroque Rome, Granada, 1982, p. 103
- ↑ David Cheney, GCatholic Santa Maria della Pace. Retrieved: 03/09/1216.
- ↑ Patrice Gauchat, Hierarchia catholica medii et recentioris aevi Volumen Quartum (Monasterii 1935), p. 45.
- ↑ A. Blunt, 1982, p. 104
- ↑ Unfinished by Raphael at his death (1520), the frescoes were completed based on his drawings by Sebastiano del Piombo. Raphael's assistant Timoteo Viti painted the four Prophets.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Santa Maria della Pace (Rome). |
Coordinates: 41°54′00″N 12°28′18″E / 41.89987°N 12.47164°E