Süleymaniye Mosque
| Süleymaniye Mosque | |
|---|---|
|
View of the mosque from Galata Tower | |
| Basic information | |
| Location | Istanbul, Turkey |
| Geographic coordinates | 41°00′58″N 28°57′50″E / 41.01611°N 28.96389°ECoordinates: 41°00′58″N 28°57′50″E / 41.01611°N 28.96389°E |
| Affiliation | Islam |
| Country | Turkey |
| Architectural description | |
| Architect(s) | Mimar Sinan |
| Architectural type | Mosque |
| Architectural style | Ottoman architecture |
| Groundbreaking | 1550 |
| Completed | 1558 |
| Specifications | |
| Height (max) | 53 m (174 ft) |
| Dome dia. (inner) | 26 m (85 ft) |
| Minaret(s) | 4 |
| Minaret height | 72 m (236 ft) |
The Süleymaniye Mosque (Turkish: Süleymaniye Camii, Turkish pronunciation: [sylejˈmaːnije]) is an Ottoman imperial mosque located on the Third Hill of Istanbul, Turkey. It is the second largest mosque in the city, and one of the best-known sights of Istanbul.
History

The Süleymaniye Mosque, built on the order of Sultan Süleyman (Süleyman the Magnificent), "was fortunate to be able to draw on the talents of the architectural genius of Mimar Sinan" (481 Traditions and Encounters: Brief Global History). The construction work began in 1550 and the mosque was finished in 1557.
This "vast religious complex called the Süleymaniye...blended Islamic and Byzantine architectural elements. It combines tall, slender minarets with large domed buildings supported by half domes in the style of the Byzantine church Hagia Sophia (which the Ottomans converted into the mosque of Aya Sofya)" (481 Traditions and Encounters: Brief Global History).
The design of the Süleymaniye also plays on Suleyman's self-conscious representation of himself as a 'second Solomon.' It references the Dome of the Rock, which was built on the site of the Temple of Solomon, as well as Justinian's boast upon the completion of the Hagia Sophia: "Solomon, I have surpassed thee!"[1] The Süleymaniye, similar in magnificence to the preceding structures, asserts Suleyman's historical importance. The structure is nevertheless smaller in size than its older archetype, the Hagia Sophia.

The Süleymaniye was ravaged by a fire in 1660 and was restored by Sultan Mehmed IV. Part of the dome collapsed again during the earthquake of 1766. Subsequent repairs damaged what was left of the original decoration of Sinan (recent cleaning has shown that Sinan experimented first with blue, before turning red the dominant color of the dome).
During World War I the courtyard was used as a weapons depot, and when some of the ammunition ignited, the mosque suffered another fire. Not until 1956 was it fully restored again.
The construction of the Halic metro bridge in 2013 has irreparably altered the view of the mosque from north.[2]
Architecture

Exterior

Like the other imperial mosques in Istanbul, the mosque itself is preceded by a monumental courtyard (avlu) on its west side. The courtyard at the Süleymaniye is of exceptional grandeur with a colonnaded peristyle with columns of marble, granite and porphyry. At the four corners of the courtyard are the four minarets, a number only allowable to mosques endowed by a sultan (princes and princesses could construct two minarets; others only one). The minarets have a total of 10 galleries (serifes), which by tradition indicates that Suleiman I was the 10th Ottoman sultan.
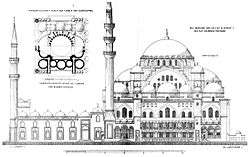
The main dome is 53 metres (174 feet) high and has a diameter of 27.5 metres (90.2 feet). At the time it was built, the dome was the highest in the Ottoman Empire, when measured from sea level, but still lower from its base and smaller in diameter than that of Hagia Sophia.
Interior

The interior of the mosque is almost a square, 59 metres (194 feet) in length and 58 metres (190 feet) in width, forming a single vast space. The dome is flanked by semi-domes, and to the north and south arches with tympana-filled windows, supported by enormous porphyry monoliths. Sinan decided to make a radical architectural innovation to mask the huge north-south buttresses needed to support these central piers. He incorporated the buttresses into the walls of the building, with half projecting inside and half projecting outside, and then hid the projections by building colonnaded galleries. There is a single gallery inside the structure, and a two-story gallery outside.
The interior decoration is subtle, with very restrained use of Iznik tiles. The white marble mihrab and mimbar are also simple in design, and woodwork is restrained, with simple designs in ivory and mother of pearl.
Complex

As with other imperial mosques in Istanbul, the Süleymaniye Mosque was designed as a külliye, or complex with adjacent structures to service both religious and cultural needs. The original complex consisted of the mosque itself, a hospital (darüşşifa), primary school, public baths (hamam), a Caravanserai, four Qur'an schools (medrese), a specialized school for the learning of hadith, a medical college, and a public kitchen (imaret) which served food to the poor. Many of these structures are still in existence, and the former imaret is now a noted restaurant. The former hospital is now a printing factory owned by the Turkish Army.
In the garden behind the main mosque there are two mausoleums (türbe) including the tombs of Sultan Suleiman I, his wife Hürrem Sultan (Roxelana) and their daughter Mihrimah Sultan. The sultans Suleiman II, Ahmed II and also Saliha Dilaşub Sultan and Safiye Sultan (died in 1777), the daughter of Mustafa II, are buried here.
Just outside the mosque walls, to the north is the tomb of architect Sinan.
Gallery
See also
- Mosques commissioned by the Ottoman dynasty
- Ottoman architecture
- Suleymaniye hamam
- Suleymaniye Mosque (London)
- Islam in Turkey
- Ottoman architecture
- List of mosques in Istanbul
- List of mosques in Turkey
- List of mosques
- Sultan Ahmed Mosque
- Hagia Sophia
- Çamlıca Mosque
References
- ↑ Necipoglu-Kafadar, Gulru (1985). "The Süleymaniye Complex in Istanbul: An Interpretation". Brill. doi:10.2307/1523086.
- ↑ Hartmann, Veronika. "Wem gehört die Stadt?". NZZ. Retrieved 6 July 2013.
Sources
- Goodwin, Godfrey (May 2003). A History of Ottoman Architecture. London: Thames & Hudson Ltd. ISBN 0-500-27429-0.
- Faroqhi, Suraiyah (2005). Subjects of the Sultan: Culture and Daily Life in the Ottoman Empire. I B Tauris. ISBN 1-85043-760-2.
- Freely, John (2000). Blue Guide Istanbul. W. W. Norton & Company. ISBN 0-393-32014-6.
- Rogers, J.M. (2007). Sinan: Makers of Islamic Civilization. I B Tauris. ISBN 1-84511-096-X.
Further reading
- Necipoğlu, Gülru (2005). The Age of Sinan: Architectural Culture in the Ottoman Empire. London: Reaktion Books. ISBN 978-1-86189-253-9.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to: |
- Süleymaniye Külliyesi, Archnet
- Süleymaniye Mosque ve Mimar Sinan (in Turkish)
- Suleymaniye Mosque Virtual Walking Tour, Saudi Aramco World.
- Photographs by Dick Osseman







.jpg)


.jpg)
.jpg)







