Manufacture nationale de Sèvres
Coordinates: 48°49′43″N 2°13′21″E / 48.82861°N 2.22250°E
| French porcelain |
|---|
 Clodion vase. Hard-paste porcelain and gilt bronze, 1817. Manufacture nationale de Sèvres. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Manufacture nationale de Sèvres. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Sèvres porcelain. |
The manufacture nationale de Sèvres is one of the principal European porcelain manufacturies. It is located in Sèvres, Hauts-de-Seine, France.
The manufactury was continuously part of the political order, first royal, then imperial and finally national. Continuously in operation, the manufactury has been creating objects since 1740. Its production is still largely based around the creation of contemporary objects today. It became part of the Cité de la céramique with the Musée national de Céramique-Sèvres in 2010 and since 2012 with the Musée national Adrien Dubouché in Limoges.
History
Origins

In 1738, the Manufacture de Vincennes was founded, thanks to the support of Louis XV and Madame de Pompadour, in order to compete with the manufacturies at Chantilly and Meissen.[1] In 1756, the manufactury was moved to a building in Sèvres, built at the initiative of Madame de Pompadour, near her château.
130 metres long and four stories high, the building was erected between 1753 and 1756 by the architect Laurent Lindet on the site of a farm called "de la Guyarde." There was a central pavilion surmounted by a pediment with a clock from the old royal glass-makers on the fourth level, with two long wings terminating in corner pavilions at each end. In front of the pavilion was a "public" courtyard, enclosed by a wrought iron fence. This front area was decorated twice a month in order to hold parties for visitors.
The ground floor of the building contained clay reserves, books and storerooms of raw materials. The first floor contained the workshops of the moulders, plasterers, sculptors, engravers and the ovens. On the second floor were the sculptors, turners, repairers and packers. Finally, the painters, gilders and makers of animals and figures worked in the loft
Jean-Claude Chambellan Duplessis served as artistic director of the Vincennes porcelain manufactory and its successor at Sèvres from 1748 to his death in 1774. The manufactury was brought under the Crown in 1759.
Development of hard-paste porcelain

Initially, the manufactury produced a Soft-paste porcelain. In 1768, the Bordeaux chemist, Vilaris and his friend Jean-Baptiste Darnet discovered the first deposit of kaolin on French soil at Saint-Yrieix-la-Perche to the south of Limoges. On 13 February 1771, the Comte de Thy de Milly of the Royal Academy sent the academy a report on the creation of Hard-paste porcelain. This report was published in 1777 in volume 7 of the encyclopedia, Art de la porcelaine. This work derived from his observations of the different manufacturies of Germany, especially Meissen. "Up to this time, the manufacturies of France - Sèvres not excepted - have only produced glass porcelain, which only has some qualities of the real thing...".[2]
Hard-paste porcelain began to be manufactured in Sèvres after 1770.
Louis-Simon Boizot was director between 1774 and 1800; Alexandre Brogniart director between 1800 and 1847; and Henri Victor Regnault director beginning in 1854.
In 1875, the manufactury was transferred to buildings which had been specially built by the French state next to the Parc de Saint-Cloud. It is still on this site today, classed as a Monument historique, but still in operation.
In 1920, the Treaty of Sèvres, the peace treaty between the Ottoman Empire and Allies at the end of World War I, was signed at the factory.
Women at the royal manufactury
At the Manufacture de Vincennes, in 1748, a "floristry" composed of twenty young girls was established under the direction of Madame Gravant. It continued its activities until 1753, when women were banned from the manufactury. In 1756 Sèvres employed two hundred male workers.
"... The few women who continued to work at Vincennes and then at Sèvres, after this [the floristry], henceforth worked from home, picking up the wares, taking them home and bringing them back each day, despite the risk of breaking the delicate objects which they painted and burnished.".[3]
Production of porcelain

The kaolin was brought, traditionally, from Saint-Yrieix near Limoges. Nowadays there are many sources. The glaze, applied as enamel over the kaolin paste after firing is made mainly of Marcognac pegmatite, mixed with feldspath and quart.[4]
The blue of Sèvres is a characteristic colour of the manufactury. It is made from a cobalt oxide which is incorporated into the glaze.
The 19th century kilns
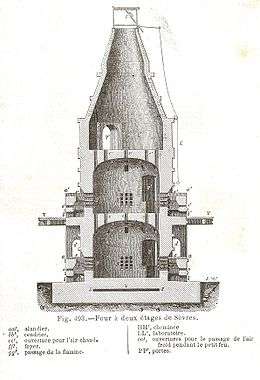
Dictionnaire de chimie industriel (Barreswil, A. Girard) 1864
The ceramist Ambroise Milet was Director of the Paste Kilns and Chief of Manufacture at the manufactury before he left it in 1883 at the age of 53. One of the key tasks of Ambroise Milet was the construction of six great Anagama kilns in 1877. These kilns are today classed as French monuments historiques.
The kilns consist of a cylindrical body separated into three levels. The lowest is called the "first laboratoire" and is 2.6 m in diameter and 3 m tall. The middle level is called the "second laboratoire" and is 2.6 metres in diameter and 2 metres high. The top level is the 2 metre high chimney cone. The firebox is an opening at the bottom of the first laboratoire, 1 metre high, 0.58 metres wide and 0.29 metres deep.[5] In the vault between the first and second laboratoires, is a large flue at the centre and 9 small ones around the edge. These flues serve to guide the flames and release the heated gas. Grills, called "flue-guards" are arranged to divide the flames. At the base of the second laboratoire, a little fire box helps to increase the temperature further. The oven contains four fireboxes for distributing the heat effectively.
Only birch wood is used to heat the oven. Its strong and quick combustion is uniform, its flames are long and it releases few cinders. Only this wood can bring the oven to the high temperatures required (800 °C in the small fires, nearly 1300 °C in the main one. The logs of wood are 73 cm long. The oven can fire Bisque porcelain in 15–16 hours and glass or glazed porcelain in 11–12 hours. One firing requires 25 cubic metres of wood, which is burnt over 48 hours using a specialised technique in order to raise the temperature. The oven then takes between fifteen and twenty days to cool down. The wall which blocks the oven door is dismantled in order to empty the oven. A hundred pieces are fired at once, depending on their exact size.
The firing process gives the incomparable enamel quality to the porcelain which cannot be obtained by other techniques. The cause of this is the high uniformity of heat in the oven and the extremely gradual cooling process. Among other things, these ovens are uniquely capable of producing large pieces, which Sèvres has made a specialty.
The last large firing with wood took place in October 2006. Nearly 180 pieces were produced for l'Epreuve du Feu ("the trial by flame"), the name of the exhibition which these pieces were displayed in at the Parisian gallery of the manufactury, before they were dispersed. The opening of the oven, as it began to burn, was broadcast live on television. The next firing will be announced on the official website of the manufactury.
Aside from these exceptional firings, the manufactury uses electric ovens for all contemporary production.
The manufactury today

Until 2009, the Manufacture nationale de Sèvres was a Service à compétence nationale (national service) administered by the French ministry of culture and communication.
As a result of a decree of 26 December 2009, from 1 January 2010, the manufactory has formed the public organisation Sèvres - Cité de la céramique, (Sèvres - Ceramic City), along with the Musée national de la céramique.[6] On 1 May 2012, the musée national de la porcelaine Adrien-Dubouché was also made part of this public organisation, whose name was changed to Cité de la céramique - Sèvres et Limoges.[7]
Since becoming a public organisation, its mission, in accordance with its origins in 1740, is to produce ceramic works of art using artisanal techniques, including both reproductions of old models and contemporary creations. It produces good both for state needs and commercial sale and is charged with promoting technological and artistic research in ceramics. Its work is concentrated on the upmarket pieces, maintaining a high quality of artisanry, while neglecting industrial scale mass production.
The creations of the manufactory are displayed in only two galleries: one in Sèvres and the other in the heart of Paris, in the 1st arrondissement, between the Louvre and the Comédie Française. The manufactory also organises numerous exhibitions around the world and participates in a number of contemporary art festivals.
Notable artists


On account of its reputation for excellence and its prestige, the manufactory has always attracted some of the best ceramists. Among the most well-known are:
- Pierre Alechinsky
- Arman
- Jean Arp
- Louttre B.
- Charles-François Becquet
- Antoine Béranger
- Louis-Simon Boizot
- François Boucher
- Louise Bourgeois
- Pierre Buraglio
- Félix Bracquemond
- Alexander Calder
- Albert-Ernest Carrier-Belleuse (artistic director)
- Ernest Chaplet
- Albert Dammouse
- Hermine David
- Théodore Deck, director of the manufactory from 1887
- Émile Decoeur
- Marcel Derny
- Jean-Charles Develly
- Erik Dietman
- Charles-Nicolas Dodin
- Martin Drolling, director of painting 1802-1813.
- Jean-Claude Duplessis (or Duplessis père),
- Étienne Maurice Falconet
- Alexandre-Évariste Fragonard, son of Jean-Honoré Fragonard
- Théophile Fragonard, son of Alexandre-Évariste Fragonard
- Viola Frey[8]
- Hector Guimard
- Étienne Hajdu
- François-Xavier Lalanne
- Espérance Langlois
- Polyclès Langlois
- François Levavasseur
- Louis Prosper Levavasseur, l'aîné
- Clément Massier
- Roberto Matta
- Jean Mayodon
- Félix Optat Milet
- Jean-Louis Morin
- Guillaume Noël[9]
- Richard Peduzzi
- Charles Percier
- Arthur-Luiz Piza
- Serge Poliakoff
- Henri Rapin
- Auguste Rodin
- Dana Roman
- Jacques-Émile Ruhlmann
- Alexandre Sandier
- Adrian Saxe
- Ettore Sottsass
- Vincent Taillandier
- Louis Jean Thévenet, père
- Giovanni Battista Tiepolo
- Betty Woodman
- Philippe Xhrouet (or "Xhrowet, Secroix") and Marie-Claude-Sophie Xhrouet[10]
- Yayoi Kusama
Gallery
 Elephant vases, painted by Charles Nicolas Dodin, c 1760 (Walters Art Museum)
Elephant vases, painted by Charles Nicolas Dodin, c 1760 (Walters Art Museum)_-_Walters_48559.jpg) Sèvres pot-pourri vase in the shape of a ship, or Vase à vaisseau, 1764. one of the most famous shapes, of which only 10 examples survive.
Sèvres pot-pourri vase in the shape of a ship, or Vase à vaisseau, 1764. one of the most famous shapes, of which only 10 examples survive.- Sèvres sucrier and cover - sugar pot, Bouret shape - c. 1770
_-_Walters_48635_-_Back.jpg) Potpourri vase ovale Mercure in early Neoclassical taste, c. 1770 (Walters Art Museum)
Potpourri vase ovale Mercure in early Neoclassical taste, c. 1770 (Walters Art Museum) One of a series of vases made for Louis XVI.
One of a series of vases made for Louis XVI. The Toilet of Madame: Hard-paste porcelain, marble, gilt on bronze. Portraying a domestic scene from upper-class life.
The Toilet of Madame: Hard-paste porcelain, marble, gilt on bronze. Portraying a domestic scene from upper-class life.- Writing table (Museu Calouste Gulbenkian, 1772)
- Tureen by Jacques-François Micaud (1732/1735-1811), national Gallery of Victoria, Australia.

- Vase in the shape of an egg, depicting Louis-Philippe I (Louvre, 1837)
 Vase Clodion, offered by Louis XVIII to his brother, Monsieur, the future Charles X (1817)
Vase Clodion, offered by Louis XVIII to his brother, Monsieur, the future Charles X (1817) Sèvres porcelain vase. Museu Calouste Gulbenkian
Sèvres porcelain vase. Museu Calouste Gulbenkian Annette and Lubin, c. 1764 at Waddesdon Manor
Annette and Lubin, c. 1764 at Waddesdon Manor Vase with candleholders, c. 1760 at Waddesdon Manor
Vase with candleholders, c. 1760 at Waddesdon Manor Pot-pourri vase, 1763 at Waddesdon Manor
Pot-pourri vase, 1763 at Waddesdon Manor Three pop-pourri vase in the shape of a ship, all at Waddesdon Manor
Three pop-pourri vase in the shape of a ship, all at Waddesdon Manor Plate from the Marie-Antoinette service, 1781 at Waddesdon Manor
Plate from the Marie-Antoinette service, 1781 at Waddesdon Manor Fan-shaped jardiniere and stand, 1758 at Waddesdon Manor
Fan-shaped jardiniere and stand, 1758 at Waddesdon Manor
See also
References
- ↑ Sèvres Porcelain Manufactory | People | Collection of Smithsonian Cooper-Hewitt, National Design Museum
- ↑ « Jusqu'à cette époque, on n’avait fait dans les manufactures de porcelaine établies en France, sans excepter celle de Sèvres, que des porcelaines vitreuses, qui n’avaient aucune des qualités réelles…. », Art de la porcelaine page 147
- ↑ Bleu de Sèvres (1759-1769), Jean-Paul Desprat, ed. du Seuil, Paris, juin 2006
- ↑ D'Albis A, La verseuse du Déjeuner égyptien de la duchesse de Montebello, étapes d'une fabrication, L'objet d'art, mars 2008 No. 36, p 29-9
- ↑ Page 469 Volume two - Second edition -Traité des arts céramiques, ou des poteries, considérées dans leur histoire by Alexandre Brongniart, Louis-Alphonse Savétat - Chez Béchet jeune, libraire éditeur 22 Rue Monsieur-le -prince à Paris - janvier 184 - Archive of the Ashmolean museum library - accessed on Google Books
- ↑ Décret n° 2009-1643 du 24 décembre 2009 portant création de l’Établissement public Sèvres - Cité de la céramique.
- ↑ Décret n° 2012-462 du 6 avril 2012 relatif à l'établissement public Cité de la céramique – Sèvres et Limoges.
- ↑
- ↑ Gobelet litron et soucoupe in The Fitzwilliam Museum
- ↑ Jardinière in The British Museum
Bibliography
- Georges Lechevallier-Chevignard, La Manufacture de porcelaine de Sèvres : histoire, organisation, ateliers, musée céramique, répertoire des marques et monogrammes d'artistes,Paris, le Livre d'histoire, 2013, Online at
- Tamara Préaud et Guilhem Scherf (ed.), La manufacture des lumières. La sculpture à Sèvres de Louis XV à la Révolution, [Exhibition Catalogue], Éditions Faton, 2015, ISBN 978-287844-206-9

