Reye syndrome
| Reye syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Reye's syndrome |
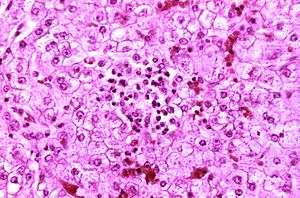 | |
| Appearance of a liver from a child who died of Reye syndrome as seen with a microscope. Hepatocytes are pale-staining due to intracellular fat droplets. | |
| Pronunciation |
|
| Specialty | Pediatrics |
| Symptoms | Vomiting, personality changes, confusion, seizures, loss of consciousness[1] |
| Causes | Unknown[2] |
| Risk factors | Aspirin use in children, viral infection[2][1] |
| Treatment | Supportive care[1] |
| Medication | Mannitol[2] |
| Prognosis | 1/3rd long term disability[2][3] |
| Frequency | Less than one in a million children a year[2] |
| Deaths | ~30% chance of death[2][3] |
Reye syndrome is a rapidly progressive encephalopathy.[2] Symptoms may include vomiting, personality changes, confusion, seizures, and loss of consciousness.[1] Even though liver toxicity typically occurs, yellowish skin usually does not.[2] Death occurs in 20–40% of those affected and about a third of those who survive are left with a significant degree of brain damage.[2][3]
The cause of Reye syndrome is unknown.[2] It usually begins shortly after recovery from a viral infection, such as influenza or chickenpox.[1] About 90% of cases are associated with aspirin (salicylate) use in children.[2] Inborn errors of metabolism are also a risk factor.[3] Changes on blood tests may include a high blood ammonia level, low blood sugar level, and prolonged prothrombin time. Often the liver is enlarged.[2]
Prevention is typically by avoiding the use of aspirin in children.[1] When aspirin was withdrawn for use in children a decrease of more than 90% in rates of Reye syndrome was seen.[2] Early diagnosis improves outcomes. Treatment is supportive.[1] Mannitol may be used to help with the brain swelling.[2]
The first detailed description of Reye syndrome was in 1963 by Douglas Reye.[4] Children are most commonly affected. It affects less than one in a million children a year.[2] The general recommendation to use aspirin in children was withdrawn because of Reye syndrome, with use of aspirin only recommended in Kawasaki disease.[3]
Signs and symptoms
Reye syndrome progresses through five stages:[5][6][7]
- Stage I
- Stage II
- Stupor
- Hyperventilation
- Fatty liver (found by biopsy)
- Hyperactive reflexes
- Stage III
- Continuation of Stage I and II symptoms
- Possible coma
- Possible cerebral edema
- Rarely, respiratory arrest
- Stage IV
- Deepening coma
- Dilated pupils with minimal response to light
- Minimal but still present liver dysfunction
- Stage V
- Very rapid onset following stage IV
- Deep coma
- Seizures
- Multiple organ failure[9]
- Flaccidity
- Hyperammonemia (above 300 mg/dL of blood)
- Death
Causes
The precise mechanism by which Reye syndrome occurs is unknown. This serious condition is described as a "syndrome" rather than a disease as the clinical features that physicians use to diagnose it are quite broad.
Aspirin
There is an association between taking aspirin for viral illnesses and the development of Reye syndrome,[10] but no animal model of Reye syndrome has been developed in which aspirin causes the condition.[11]
The serious symptoms of Reye syndrome appear to result from damage to cellular mitochondria,[12] at least in the liver, and there are a number of ways that aspirin could cause or exacerbate mitochondrial damage. A potential increased risk of developing Reye syndrome is one of the main reasons that aspirin has not been recommended for use in children and teenagers, the age group for which the risk of lasting serious effects is highest.
No research has found a definitive cause of Reye syndrome, and association with aspirin has been shown through epidemiological studies. The diagnosis of "Reye Syndrome" greatly decreased in the 1980s, when genetic testing for inborn errors of metabolism was becoming available in developed countries.[11] A retrospective study of 49 survivors of cases diagnosed as "Reye's Syndrome" showed that the majority of the surviving patients had various metabolic disorders, particularly a fatty-acid oxidation disorder medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency.[13]
In some countries, oral mouthcare product Bonjela (not the form specifically designed for teething) has labeling cautioning against its use in children, given its salicylate content. There have been no cases of Reye syndrome following its use, and the measure is a precaution.[14] Other medications containing salicylates are often similarly labeled as a precaution.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the U.S. Surgeon General, the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recommend that aspirin and combination products containing aspirin not be given to children under 19 years of age during episodes of fever-causing illnesses. Hence, in the United States, it is advised that the opinion of a doctor or pharmacist should be obtained before anyone under 19 years of age is given any medication containing aspirin (also known on some medicine labels as acetylsalicylate, salicylate, acetylsalicylic acid, ASA, or salicylic acid).
Current advice in the United Kingdom by the Committee on Safety of Medicines is that aspirin should not be given to those under the age of 16 years, unless specifically indicated in Kawasaki disease or in the prevention of blood clot formation.[15]
Differential diagnosis
Causes for similar symptoms include
- Various inborn metabolic disorders
- Viral encephalitis
- Drug overdose or poisoning
- Head trauma
- Liver failure due to other causes
- Meningitis
- Kidney failure
- Shaken baby syndrome
Prognosis
Documented cases of Reye syndrome in adults are rare. The recovery of adults with the syndrome is generally complete, with liver and brain function returning to normal within two weeks of onset. In children, however, mild to severe permanent brain damage is possible, especially in infants. Over thirty percent of the cases reported in the United States from 1981 through 1997 resulted in fatality.
Epidemiology
Reye syndrome occurs almost exclusively in children. While a few adult cases have been reported over the years, these cases do not typically show permanent neural or liver damage. Unlike in the UK, the surveillance for Reye syndrome in the US is focused on patients under 18 years of age.
In 1980, after the CDC began cautioning physicians and parents about the association between Reye syndrome and the use of salicylates in children with chickenpox or virus-like illnesses, the incidence of Reye syndrome in the United States began to decline. However, the decline began prior to the FDA's issue of warning labels on aspirin in 1986.[11] In the United States between 1980 and 1997, the number of reported cases of Reye syndrome decreased from 555 cases in 1980 to about 2 cases per year since 1994. During this time period 93% of reported cases for which racial data were available occurred in whites and the median age was six years. In 93% of cases a viral illness had occurred in the preceding three-week period. For the period 1991-1994, the annual rate of hospitalizations due to Reye syndrome in the US was estimated to be between 0.2 and 1.1 per million population less than 18 years of age.
During the 1980s, a case-control study carried out in the United Kingdom also demonstrated an association between Reye syndrome and aspirin exposure.[16] In June 1986, the United Kingdom Committee on Safety of Medicines issued warnings against the use of aspirin in children under 12 years of age and warning labels on aspirin-containing medications were introduced. UK surveillance for Reye syndrome documented a decline in the incidence of the illness after 1986. The reported incidence rate of Reye syndrome decreased from a high of 0.63 per 100,000 population less than 12 years of age in 1983/84 to 0.11 in 1990/91.
From November 1995 to November 1996 in France, a national survey of pediatric departments for children under 15 years of age with unexplained encephalopathy and a threefold (or greater) increase in serum aminotransferase and/or ammonia led to the identification of nine definite cases of Reye syndrome (0.79 cases per million children). Eight of the nine children with Reye syndrome were found to have been exposed to aspirin. In part because of this survey result, the French Medicines Agency reinforced the international attention to the relationship between aspirin and Reye syndrome by issuing its own public and professional warnings about this relationship.[17]
History
The syndrome is named after Dr. Douglas Reye, who, along with fellow physicians Drs. Graeme Morgan and Jim Baral, published the first study of the syndrome in 1963 in The Lancet.[18] In retrospect, the occurrence of the syndrome may have first been reported in 1929. Also in 1964, Dr. George Johnson and colleagues published an investigation of an outbreak of influenza B that described 16 children who developed neurological problems, four of whom had a profile remarkably similar to Reye syndrome. Some investigators refer to this disorder as Reye-Johnson syndrome, although it is more commonly called Reye syndrome. In 1979, Dr. Karen Starko and colleagues conducted a case-control study in Phoenix, Arizona and found the first statistically significant link between aspirin use and Reye syndrome.[19] Studies in Ohio and Michigan soon confirmed her findings [20] pointing to the use of aspirin during an upper respiratory tract or chickenpox infection as a possible trigger of the syndrome. Beginning in 1980, the CDC cautioned physicians and parents about the association between Reye syndrome and the use of salicylates in children and teenagers with chickenpox or virus-like illnesses. In 1982 the U.S. Surgeon General issued an advisory, and in 1986 the Food and Drug Administration required a Reye syndrome-related warning label for all aspirin-containing medications.[21]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 "NINDS Reye's Syndrome Information Page". NINDS. September 25, 2009. Archived from the original on August 1, 2016. Retrieved August 8, 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Pugliese, A; Beltramo, T; Torre, D (October 2008). "Reye's and Reye's-like syndromes.". Cell biochemistry and function. 26 (7): 741–6. PMID 18711704. doi:10.1002/cbf.1465.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Schrör, K (2007). "Aspirin and Reye syndrome: a review of the evidence.". Paediatric drugs. 9 (3): 195–204. PMID 17523700. doi:10.2165/00148581-200709030-00008.
- ↑ McMillan, Julia A.; Feigin, Ralph D.; DeAngelis, Catherine; Jones, M. Douglas (2006). Oski's Pediatrics: Principles & Practice. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 2306. ISBN 9780781738941.
- ↑ Knight, J. (2009). "Reye's Syndrome". Healthy Child Care. 12 (4).
- ↑ Boldt, D.W. (February 2003). "Reye Syndrome". University of Hawaii John A. Burns School of Medicine.
- ↑ "What is Reye's Syndrome?". National Reye's Syndrome Foundation.
- ↑ "Reye's Syndrome". KidsHealth.org. Nemour Foundation. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ↑ Ku AS, Chan LT (April 1999). "The first case of H5N1 avian influenza infection in a human with complications of adult respiratory distress syndrome and Reye's syndrome". Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health. 35 (2): 207–9. PMID 10365363. doi:10.1046/j.1440-1754.1999.t01-1-00329.x.
- ↑ Hurwitz, E. S. (1989). "Reye's syndrome". Epidemiologic reviews. 11: 249–253. PMID 2680560.
- 1 2 3 Orlowski JP, Hanhan UA, Fiallos MR (2002). "Is aspirin a cause of Reye's syndrome? A case against". Drug Safety. 25 (4): 225–31. PMID 11994026. doi:10.2165/00002018-200225040-00001.
- ↑ Gosalakkal JA, Kamoji V (September 2008). "Reye syndrome and reye-like syndrome". Pediatric Neurology. 39 (3): 198–200. PMID 18725066. doi:10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2008.06.003.
- ↑ Orlowski JP (August 1999). "Whatever happened to Reye's syndrome? Did it ever really exist?". Critical Care Medicine. 27 (8): 1582–7. PMID 10470768. doi:10.1097/00003246-199908000-00032.
- ↑ "New advice on oral salicylate gels in under 16s" (Press release). Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency. April 23, 2009. Retrieved May 1, 2009.
- ↑ "2.9 Antiplatelet drugs". British National Formulary for Children. British Medical Association and Royal Pharmaceutical Society of Great Britain. 2007. p. 151.
- ↑ Hall SM, Plaster PA, Glasgow JF, Hancock P (1988). "Preadmission antipyretics in Reye's syndrome". Arch. Dis. Child. 63 (7): 857–66. PMC 1779086
 . PMID 3415311. doi:10.1136/adc.63.7.857.
. PMID 3415311. doi:10.1136/adc.63.7.857. - ↑ Autret-Leca E, Jonville-Béra AP, Llau ME, et al. (2001). "Incidence of Reye's syndrome in France: a hospital-based survey". Journal of Clinical Epidemiology. 54 (8): 857–62. PMID 11470397. doi:10.1016/S0895-4356(00)00366-8.
- ↑ Reye RD, Morgan G, Baral J (1963). "Encephalopathy and fatty degeneration of the viscera. A Disease entity in childhood". Lancet. 2 (7311): 749–52. PMID 14055046. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(63)90554-3.
- ↑ Starko KM, Ray CG, Dominguez LB, Stromberg WL, Woodall DF (December 1980). "Reye's syndrome and salicylate use". Pediatrics. 66 (6): 859–864. PMID 7454476.
- ↑ Mortimor, Edward A., Jr.; et al. (June 1, 1980). "Reye Syndrome-Ohio, Michigan". Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. 69 (29): 532, 810–2. PMID 7079050.
- ↑ Associated Press (March 8, 1986). "Aspirin Labels to Warn About Reye Syndrome". The New York Times.
External links
| Classification |
V · T · D |
|---|---|
| External resources |