Regisaurus
| Regisaurus Temporal range: Late Permian–Early Triassic | |
|---|---|
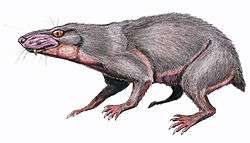 | |
| Restoration of R. jacobi | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Synapsida |
| Order: | Therapsida |
| Suborder: | Therocephalia |
| Family: | Regisauridae |
| Genus: | Regisaurus |
| Species | |
| |
Regisaurus ("Rex's lizard", named after its discoverer Francis Rex Parrington) is an extinct Genus of small carnivorous therocephalian. It is known from a single described species, the type species Regisaurus jacobi, from the Early Triassic Lystrosaurus Assemblage Zone of South Africa, although at least one undescribed species is also known.[1]
Description
It was a rather derived baurioid, with a robust skull, short tail, long limbs and relatively large canines. It was apparently related to Urumchia and like Urumchia, it had vomer bones, which form the secondary palate, but they do not narrow to a tip like in Urumchia. However it retained some primitive characteristics. It had six incisor teeth in each side of the jaw, whereas other baurioids had less.[2] It was probably carnivorous, and ate insects and small vertebrates
Discovery and Species
Regisaurus was discovered in 1964 by Francis Rex Parrington and it was named in 1972 by C. H. Mendrez. Two species are known, the type species Regisaurus jacobi and an additional undescribed species. R. jacobi is known from the holotype FRP 1964/27 and the referred specimen BP/1/3973,[3] while the undescribed species is known only from the Holotype T837.[4][5]
Classification
Below is a cladogram modified from Sidor (2001) and Huttenlocker (2009):[6][7]
| Baurioidea |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See also
References
- ↑ C. H. Mendrez (1972). "On the skull of Regisaurus jacobi, a new genus and species of Bauriamorpha Watson and Romer 1956 (=Scaloposauria Boonstra 1953), from the Lystrosaurus-zone of South Africa". In K.A. Joysey, T.S. Kemp. Studies in Vertebrate Evolution. Edinburgh: Oliver & Boyd. pp. 191–212. ISBN 9780050021316.
- ↑ http://wiredspace.wits.ac.za/bitstream/handle/10539/16101/2007.v.42.Fourie_%26_Rubidge_Postcranial_anatomy_therocephalian.pdf?sequence=1
- ↑ http://www.paleofile.com/Theriodontia/Regisaurus.asp
- ↑ Kemp, T.S. (1986). "The skeleton of a baurioid therocephalian therapsid from the Lower Triassic (Lystrosaurus Zone) of South Africa" (PDF). Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 6 (3): 215–232. JSTOR 4523096. doi:10.1080/02724634.1986.10011617. Retrieved 26 March 2011.
- ↑ http://www.paleofile.com/Theriodontia/Regisaurussp.asp
- ↑ Sidor, C.A. (2001). "Simplification as a trend in synapsid cranial evolution". Evolution. 55 (7): 1419–1442. PMID 11525465. doi:10.1554/0014-3820(2001)055[1419:saatis]2.0.co;2. External link in
|title=(help) - ↑ Huttenlocker, A. (2009). "An investigation into the cladistic relationships and monophyly of therocephalian therapsids (Amniota: Synapsida)". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. 157 (4): 865–891. doi:10.1111/j.1096-3642.2009.00538.x.