Regions Financial Corporation
|
| |
| Public company | |
| Traded as |
NYSE: RF S&P 500 Component |
| Industry | Financial services |
| Founded | 1971 (as First Alabama Bancshares) |
| Headquarters |
Regions Center Birmingham, Alabama, United States |
Number of locations | 1,906 ATMs and 1,527 banking offices[1] |
Key people |
O. B. Grayson Hall, Jr., President and CEO David J. Turner, Jr., CFO[1] |
| Products |
Commercial banking Retail banking Mortgage banking Investment banking Asset management Insurance |
| Revenue |
|
|
| |
|
| |
| Total assets |
|
| Total equity |
|
Number of employees | 22,166 (2016)[1] |
| Capital ratio | 11.05%[1] |
| Website | Regions.com |
Regions Financial Corporation is a bank and financial services company headquartered in the Regions Center in Birmingham, Alabama. The company provides retail and commercial banking, trust, securities brokerage, mortgage and insurance products and services.
Regions is the only member of the Fortune 500 headquartered in Alabama, and was ranked #436 in 2017.[2] Regions is also on the list of largest banks in the United States
Its banking subsidiary, Regions Bank, operates 1,906 automated teller machines and 1,527 banking offices across 15 states in the southern United States.
Current operations

As of June 30, 2016, Regions was the largest deposit holder in Alabama, with $22.586 billion in local deposits, or 23.26% of all local deposits. In Tennessee, Regions is also the largest deposit holder with $17.3 billion in total deposits, or 14.1% of all local deposits. Regions has $4 billion in deposits (7.5% of local deposits) in Arkansas, $7.2 billion in deposits (7.6% of local deposits) in Louisiana, $6.6 billion in deposits (13.8% of local deposits) in Mississippi, and $19.1 billion in deposits (4.2% of local deposits) in Florida.[3]
The company's headquarters is in the Regions Center in Birmingham, Alabama.
History
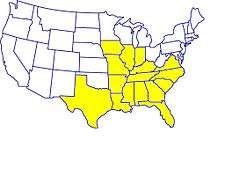
Regions Geographic Footprint
Regions Financial Corporation, formerly known as First Alabama Bancshares, was founded on July 13, 1971 with the merger of three Alabama banks: First National Bank of Montgomery, Alabama (opened 1871), Exchange Security Bank of Birmingham, Alabama (opened 1928), and First National Bank of Huntsville, Alabama (opened 1856).[4][5] The headquarters of First National Bank of Huntsville was a historic building built in 1835.[6] It served as a hospital for Union soldiers during the American Civil War, and once held a rifle owned by Frank James as collateral for bail money when he was incarcerated across the street in the Madison County Jail.
Until their formal merger in March 1985, under revised banking regulations, the banks continued to operate independently.
In 1986, changes in the Interstate Banking Bill allowed bank holding companies to purchase bank branches outside the state in which they were chartered. First Alabama Bancshares expanded its operations first into Florida, continuing into Georgia, Tennessee, and Arkansas. In 1992, to reflect its growth into a regional company, First Alabama Bancshares changed its name to Regions Financial Corporation and the name of its banking subsidiary to Regions Bank.[4]
Regions added banking branches in Alabama, Georgia, Tennessee, Florida, South Carolina, Texas, Louisiana, and Arkansas. The name "Regions" was purchased from First Commercial Corporation, the Arkansas Bank that Regions subsequently purchased in 1998. The Louisiana Regions Banks were established in Monroe (Ouachita Parish) by two former members of the Louisiana State Legislature, Jamar Adcock and Billy Boles.
In 2001, Regions acquired Rebsamen Insurance Company, which was renamed Regions Insurance Group.[7]


In 2001, Regions acquired Morgan Keegan & Company for $789 million.[8] In January 2012, Regions sold Morgan Keegan to Raymond James for $930 million. The trust department was retained by Regions and now operates as Regions Trust.[9]
In 2002, the company announced that it will list its common stock on the New York Stock Exchange.[10]
In 2002, Regions acquired Independence Bank for approximately $20 million in cash.[11][12]

On January 24, 2004, Regions merged with Memphis, Tennessee based Union Planters Bank in a $5.9 billion transaction. Jackson W. Moore, the former CEO of Union Planters, became CEO of the merged company. He suffered a stroke after the merger closed, but was still able to assume his new post upon recovery. After the merger, Regions adopted Union Planters' former logo of a young cotton plant and used it until the AmSouth conversion. The merger significantly increased Regions' footprint in Tennessee; Union Planters had been the largest Tennessee-based bank.[13][14]
In 2006, Regions acquired AmSouth Bancorporation, another Birmingham based bank, in a $10 billion transaction. While Regions was surviving company, the merged entity adopted AmSouth's corporate structure.[15][16]
In 2008, Regions Bank received a $3.5 billion loan as part of the Troubled Asset Relief Program. On April 4, 2012 Regions repaid the $3.5 billion loan.[17]
On August 29, 2008, as a result of the 2007-2008 financial crisis, Integrity Bank of Alpharetta, Georgia was placed into receivership by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation and Regions Bank assumed its operations.[18][19]
In February 2009, FirstBank Financial Services of McDonough, Georgia, was also placed into receivership by the FDIC and Regions Bank assumed its operations.[20][21]
Customer satisfaction
In J. D. Power and Associates 2008 Retail Banking Satisfaction Study, Regions came in last in customer satisfaction in the Southeastern region.[22] In the 2011 Retail Banking Satisfaction Study, Regions came in 4th in customer satisfaction in the Southeastern region.[23]
In April 2011, Regions Bank scored the highest marks for retail banks in Florida, according to J.D. Power & Associates.[24]
Criticism
Customer fraud
In 2011, Regions paid $200 million to settle with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission over mispricing risky mortgage-backed bonds in its conservative mutual funds in its Morgan Keegan subsidiary.[25][26]
Overdraft fees
In April 2015, Regions was fined $7.5 million by the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau for charging consumers with inappropriate or illegal overdraft fees.[27] Regions did not obtain affirmative opt-ins from charging overdraft fees on ATM and point of sale transactions.[28] The CFPB also found that Regions misrepresented overdraft and non-sufficient fund fees related to the bank's short-term loan program.[29]
See also
- Regions Center - the headquarters of Regions Financial
- Regions Charity Classic - a former golf tournament sponsored by Regions Financial in 2009-2010
- Regions Field - a minor league baseball stadium in Birmingham, Alabama sponsored by Regions Financial
- The Tradition - a golf tournament sponsored by Regions Financial
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Regions Financial Corporation 2016 Form 10-K Annual Report
- ↑ Fortune 500: Regions Financial
- ↑ FDIC: Deposit Market Share Reports - Summary of Deposits
- 1 2 Regions History
- ↑ "Public Hearing on Preemption Petition: Regions Financial Corporation". Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation.
- ↑ Doyle, Steve (December 15, 2014). "Iconic First National Bank building in downtown Huntsville back open following extensive renovations". The Birmingham News.
- ↑ Mortiz, Gwen (February 7, 2001). "Regions Buys Rebsamen Insurance". Arkansas Business Publishing Group.(subscription required)
- ↑ "Regions buys Morgan Keegan". CNN. December 18, 2000.
- ↑ O'Daniel, Adam (January 11, 2012). "It's final: Regions to sell Morgan Keegan to Raymond James". American City Business Journals.
- ↑ "Regions to List Common Shares on NYSE". Arkansas Business Publishing Group. April 10, 2002.(subscription required)
- ↑ "Regions to acquire Independence Bank". American City Business Journals. December 21, 2001.
- ↑ "Regions to Acquire Independence Bank". Arkansas Business Publishing Group. December 27, 2001.(subscription required)
- ↑ MOLLENKAMP, CARRICK; SIDEL, ROBIN (January 26, 2004). "Regions Financial, Union Planters Get Support in $6.1 Billion Merger". Wall Street Journal.
- ↑ "Initial Regions-Union Planters Bank Conversions Successful; Second Phase Set for August" (Press release). Business Wire. May 3, 2005.
- ↑ "Regions Financial Corp. and AmSouth Bancorporation to Merge" (Press release). Business Wire. May 25, 2006.
- ↑ "JUSTICE DEPARTMENT REACHES AGREEMENT REQUIRING DIVESTITURES IN MERGER OF REGIONS FINANCIAL CORP. AND AMSOUTH BANCORPORATION" (Press release). U.S. Department of Justice. October 19, 2006.
- ↑ SPARSHOTT, JEFFREY (April 4, 2012). "Regions Returns TARP Money". Wall Street Journal.(subscription required)
- ↑ FDIC: Failed Bank Information: Integrity Bank, Alpharetta, GA Closing Information
- ↑ Rauch, Joe (September 2, 2008). "Integrity Bank fails, bought by Regions Financial". American City Business Journals.
- ↑ FDIC: Failed Bank Information: FirstBank Financial Services, McDonough, GA Closing Information
- ↑ Rauch, Joe (February 6, 2009). "FirstBank seized by feds, Regions to take over". American City Business Journals.
- ↑ "J.D. Power: BancorpSouth best in customer service, Regions last". American City Business Journals. May 28, 2008.
- ↑ "J.D. Power: 2012 Retail Banking Survey" (Press release). J. D. Power and Associates. April 19, 2012.
- ↑ "Regions ranks first on J.D. Power list". American City Business Journals. April 22, 2011.
- ↑ LATTMAN, PETER (June 22, 2011). "Regions Settles S.E.C. Case Over Former Morgan Keegan Funds". The New York Times.
- ↑ "Morgan Keegan to Pay $200 Million to Settle Fraud Charges Related to Subprime Mortgage-Backed Securities" (Press release). U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. June 22, 2011.
- ↑ Holland, Kelley (October 28, 2015). "CFPB fines Regions Bank for illegal overdraft fees". CNBC.
- ↑ Lewis, Truman (October 20, 2015). "Feds fine Regions Bank for gouging customers with illegal overdraft fees". ConsumerAffairs.com.
- ↑ McCoy, Kevin (April 28, 2015). "Regions Bank fined $7.5M for overdraft fees". USA Today.
External links
-
- Business data for Regions Financial Corporation: Google Finance
- Yahoo! Finance
- Reuters
- SEC filings