Ramer–Douglas–Peucker algorithm
This algorithm is also known under the names Douglas–Peucker algorithm and iterative end-point fit algorithm.
Idea
The purpose of the algorithm is, given a curve composed of line segments (which is also called a Polyline in some contexts), to find a similar curve with fewer points. The algorithm defines 'dissimilar' based on the maximum distance between the original curve and the simplified curve (i.e., the Hausdorff distance between the curves). The simplified curve consists of a subset of the points that defined the original curve.
Algorithm
The starting curve is an ordered set of points or lines and the distance dimension ε > 0.
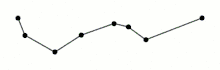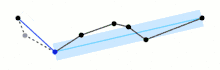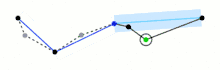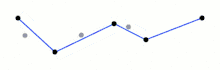
The algorithm recursively divides the line. Initially it is given all the points between the first and last point. It automatically marks the first and last point to be kept. It then finds the point that is furthest from the line segment with the first and last points as end points; this point is obviously furthest on the curve from the approximating line segment between the end points. If the point is closer than ε to the line segment, then any points not currently marked to be kept can be discarded without the simplified curve being worse than ε.
If the point furthest from the line segment is greater than ε from the approximation then that point must be kept. The algorithm recursively calls itself with the first point and the furthest point and then with the furthest point and the last point, which includes the furthest point being marked as kept.
When the recursion is completed a new output curve can be generated consisting of all and only those points that have been marked as kept.

Non-parametric Ramer-Douglas-Peucker
The choice of ε is usually user-defined. Like most line fitting / polygonal approximation / dominant point detection methods, it can be made non-parametric by using the error bound due to digitization / quantization as a termination condition.[1] MATLAB code for such a non-parametric RDP algorithm[2] is available here.[3]
Pseudocode
(Assumes the input is a one-based array)
function DouglasPeucker(PointList[], epsilon)
// Find the point with the maximum distance
dmax = 0
index = 0
end = length(PointList)
for i = 2 to ( end - 1) {
d = perpendicularDistance(PointList[i], Line(PointList[1], PointList[end]))
if ( d > dmax ) {
index = i
dmax = d
}
}
// If max distance is greater than epsilon, recursively simplify
if ( dmax > epsilon ) {
// Recursive call
recResults1[] = DouglasPeucker(PointList[1...index], epsilon)
recResults2[] = DouglasPeucker(PointList[index...end], epsilon)
// Build the result list
ResultList[] = {recResults1[1...length(recResults1)-1], recResults2[1...length(recResults2)]}
} else {
ResultList[] = {PointList[1], PointList[end]}
}
// Return the result
return ResultList[]
end
Application
The algorithm is used for the processing of vector graphics and cartographic generalization.
The algorithm is widely used in robotics[4] to perform simplification and denoising of range data acquired by a rotating range scanner; in this field it is known as the split-and-merge algorithm and is attributed to Duda and Hart.
Complexity
The expected complexity of this algorithm can be described by the linear recurrence T(n) = 2T( n⁄2) + O(n), which has the well-known solution (via the master theorem) of T(n) ∈ Θ(n log n). However, the worst-case complexity is Θ(n2).
Other line simplification algorithms
Alternative algorithms for line simplification include:
- Visvalingam–Whyatt
- Reumann–Witkam
- Opheim simplification
- Lang simplification
- Zhao-Saalfeld
Further reading
- Urs Ramer, "An iterative procedure for the polygonal approximation of plane curves", Computer Graphics and Image Processing, 1(3), 244–256 (1972) doi:10.1016/S0146-664X(72)80017-0
- David Douglas & Thomas Peucker, "Algorithms for the reduction of the number of points required to represent a digitized line or its caricature", The Canadian Cartographer 10(2), 112–122 (1973) doi:10.3138/FM57-6770-U75U-7727
- John Hershberger & Jack Snoeyink, "Speeding Up the Douglas–Peucker Line-Simplification Algorithm", Proc 5th Symp on Data Handling, 134–143 (1992). UBC Tech Report TR-92-07 available at http://www.cs.ubc.ca/cgi-bin/tr/1992/TR-92-07
- R.O. Duda and P.E. Hart, "Pattern classification and scene analysis", (1973), Wiley, New York (http://rii.ricoh.com/~stork/DHS.html)
- Visvalingam, M; Whyatt, JD (1992). Line Generalisation by Repeated Elimination of the Smallest Area (Technical report). Discussion Paper. Cartographic Information Systems Research Group (CISRG), The University of Hull. 10.
References
- ↑ Prasad, Dilip K.; Leung, Maylor K.H.; Quek, Chai; Cho, Siu-Yeung (2012). "A novel framework for making dominant point detection methods non-parametric". Image and Vision Computing. 30 (11): 843–859. doi:10.1016/j.imavis.2012.06.010.
- ↑ Prasad, Dilip K.; Quek, Chai; Leung, Maylor K.H.; Cho, Siu-Yeung (2011). A parameter independent line fitting method. 1st IAPR Asian Conference on Pattern Recognition (ACPR 2011), Beijing, China, 28-30 Nov. doi:10.1109/ACPR.2011.6166585.
- ↑ Prasad, Dilip K. "Matlab source code for non-parametric RDP". Retrieved 15 October 2013.
- ↑ Nguyen, Viet; Gächter, Stefan; Martinelli, Agostino; Tomatis, Nicola; Siegwart, Roland (2007). "A comparison of line extraction algorithms using 2D range data for indoor mobile robotics" (PDF). Autonomous Robots. 23 (2): 97. doi:10.1007/s10514-007-9034-y.
External links
- Implementation of Ramer–Douglas–Peucker and many other simplification algorithms with open source licence in C++
- XSLT implementation of the algorithm for use with KML data.
- You can see the algorithm applied to a GPS log from a bike ride at the bottom of this page
- Interactive visualization of the algorithm
- Implementation in F#
- Ruby gem implementation
- JTS, Java Tolopogy Suite, contains Java implementation of many algorithms, including javadoc/com/vividsolutions/jts/simplify/DouglasPeuckerLineSimplifier.html javadoc for Douglas-Peucker algorithm