Raman spectroscopy
Raman spectroscopy (/ˈrɑːmən/; named after Sir C. V. Raman) is a spectroscopic technique used to observe vibrational, rotational, and other low-frequency modes in a system.[1] Raman spectroscopy is commonly used in chemistry to provide a structural fingerprint by which molecules can be identified.
It relies on inelastic scattering, or Raman scattering, of monochromatic light, usually from a laser in the visible, near infrared, or near ultraviolet range. The laser light interacts with molecular vibrations, photons or other excitations in the system, resulting in the energy of the laser photons being shifted up or down. The shift in energy gives information about the vibrational modes in the system. Infrared spectroscopy yields similar, but complementary, information.
Typically, a sample is illuminated with a laser beam. Electromagnetic radiation from the illuminated spot is collected with a lens and sent through a monochromator. Elastic scattered radiation at the wavelength corresponding to the laser line (Rayleigh scattering) is filtered out by either a notch filter, edge pass filter, or a band pass filter, while the rest of the collected light is dispersed onto a detector.
Spontaneous Raman scattering is typically very weak, and as a result the main difficulty of Raman spectroscopy is separating the weak inelastically scattered light from the intense Rayleigh scattered laser light. Historically, Raman spectrometers used holographic gratings and multiple dispersion stages to achieve a high degree of laser rejection. In the past, photomultipliers were the detectors of choice for dispersive Raman setups, which resulted in long acquisition times. However, modern instrumentation almost universally employs notch or edge filters for laser rejection and spectrographs either axial transmissive (AT), Czerny–Turner (CT) monochromator, or FT (Fourier transform spectroscopy based), and CCD detectors.
The advanced types of Raman spectroscopy include surface-enhanced Raman, resonance Raman, tip-enhanced Raman, polarized Raman, stimulated Raman (analogous to stimulated emission), transmission Raman, spatially offset Raman, and hyper Raman.
Theoretical basis
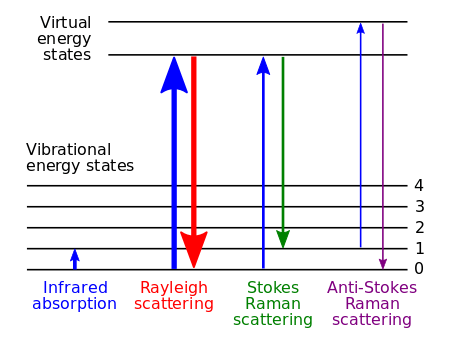
The Raman effect occurs when electromagnetic radiation interacts with a solid, liquid, or gaseous molecule’s polarizable electron density and bonds. The spontaneous effect is a form of inelastic light scattering, where a photon excites the molecule in either the ground (lowest energy) or excited rovibronic state (a rotational and vibrational energy level within an electronic state). This excitation puts the molecule into a virtual energy state for a short time before the photon scatters inelastically. Inelastic scattering means that the scattered photon can be of either lower or higher energy than the incoming photon, compared to elastic, or Rayleigh, scattering where the scattered photon has the same energy as the incoming photon. After interacting with the photon, the molecule is in a different rotational or vibrational state. This change in energy between the initial and final rovibronic states causes the scattered photon's frequency to shift away from the excitation wavelength (that of the incoming photon), called the Rayleigh line.
For the total energy of the system to remain constant after the molecule moves to a new rovibronic state, the scattered photon shifts to a different energy, and therefore a different frequency. This energy difference is equal to that between the initial and final rovibronic states of the molecule. If the final state is higher in energy than the initial state, the scattered photon will be shifted to a lower frequency (lower energy) so that the total energy remains the same. This shift in frequency is called a Stokes shift, or downshift. If the final state is lower in energy, the scattered photon will be shifted to a higher frequency, which is called an anti-Stokes shift, or upshift.
For a molecule to exhibit a Raman effect, there must be a change in its electric dipole-electric dipole polarizability with respect to the vibrational coordinate corresponding to the rovibronic state. The intensity of the Raman scattering is proportional to this polarizability change. Therefore, the Raman spectrum, scattering intensity as a function of the frequency shifts, depends on the rovibronic states of the molecule.
The Raman effect is based on the interaction between the electron cloud of a sample and the external electrical field of the monochromatic light, which can create an induced dipole moment within the molecule based on its polarizability. Because the laser light does not excite the molecule there can be no real transition between energy levels.[2] The Raman effect should not be confused with emission (fluorescence or phosphorescence), where a molecule in an excited electronic state emits a photon and returns to the ground electronic state, in many cases to a vibrationally excited state on the ground electronic state potential energy surface. Raman scattering also contrasts with infrared (IR) absorption, where the energy of the absorbed photon matches the difference in energy between the initial and final rovibronic states. The dependence of Raman on the electric dipole-electric dipole polarizability derivative also differs from IR spectroscopy, which depends on the electric dipole moment derivative, the atomic polar tensor (APT). This contrasting feature allows rovibronic transitions that might not be active in IR to be analyzed using Raman spectroscopy, as exemplified by the rule of mutual exclusion in centrosymmetric molecules. Transitions which have large Raman intensities often have weak IR intensities and vice versa. A third vibrational spectroscopy technique, inelastic incoherent neutron scattering (IINS), can be used to determine the frequencies of vibrations in highly symmetric molecules that may be both IR and Raman inactive. The IINS selection rules, or allowed transitions, differ from those of IR and Raman, so the three techniques are complementary. They all give the same frequency for a given vibrational transition, but the relative intensities provide different information due to the different types of interaction between the molecule and the incoming particles, photons for IR and Raman, and neutrons for IINS.
History
Although the inelastic scattering of light was predicted by Adolf Smekal in 1923,[3] it was not observed in practice until 1928. The Raman effect was named after one of its discoverers, the Indian scientist Sir C. V. Raman, who observed the effect by means of sunlight (1928, together with K. S. Krishnan and independently by Grigory Landsberg and Leonid Mandelstam).[1] Raman won the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1930 for this discovery accomplished using sunlight, a narrow-band photographic filter to create monochromatic light, and a "crossed filter" to block this monochromatic light. He found that a small amount of light had changed frequency and passed through the "crossed" filter.
Systematic pioneering theory of the Raman effect was developed by Czechoslovak physicist George Placzek between 1930 and 1934.[4] The mercury arc became the principal light source, first with photographic detection and then with spectrophotometric detection.
In the years following its discovery, Raman spectroscopy was used to provide the first catalog of molecular vibrational frequencies. Originally, heroic measures were required to obtain Raman spectra due to the low sensitivity of the technique. Typically, the sample was held in a long tube and illuminated along its length with a beam of filtered monochromatic light generated by a gas discharge lamp. The photons that were scattered by the sample were collected through an optical flat at the end of the tube. To maximize the sensitivity, the sample was highly concentrated (1 M or more) and relatively large volumes (5 mL or more) were used. Consequently, the use of Raman spectroscopy dwindled when commercial IR spectrophotometers became available in the 1940s. However, the advent of the laser in the 1960s resulted in simplified Raman spectroscopy instruments and also boosted the sensitivity of the technique. This has revived the use of Raman spectroscopy as a common analytical technique.
Raman shift
Raman shifts are typically reported in wavenumbers, which have units of inverse length, as this value is directly related to energy. In order to convert between spectral wavelength and wavenumbers of shift in the Raman spectrum, the following formula can be used:
where is the Raman shift expressed in wavenumber, λ0 is the excitation wavelength, and λ1 is the Raman spectrum wavelength. Most commonly, the unit chosen for expressing wavenumber in Raman spectra is inverse centimeters (cm−1). Since wavelength is often expressed in units of nanometers (nm), the formula above can scale for this unit conversion explicitly, giving
Applications
Raman spectroscopy is used in chemistry to identify molecules and study chemical bonding. Because vibrational frequencies are specific to a molecule’s chemical bonds and symmetry (the fingerprint region of organic molecules is in the wavenumber range 500–1500 cm−1,[5] Raman provides a fingerprint to identify molecules. For instance, Raman and IR spectra were used to determine the vibrational frequencies of SiO, Si2O2, and Si3O3 on the basis of normal coordinate analyses.[6] Raman is also used to study the addition of a substrate to an enzyme.
In solid-state physics, Raman spectroscopy is used to characterize materials, measure temperature, and find the crystallographic orientation of a sample. As with single molecules, a solid material can be identified by characteristic phonon modes. Information on the population of a phonon mode is given by the ratio of the Stokes and anti-Stokes intensity of the spontaneous Raman signal. Raman spectroscopy can also be used to observe other low frequency excitations of a solid, such as plasmons, magnons, and superconducting gap excitations. Distributed temperature sensing (DTS) uses the Raman-shifted backscatter from laser pulses to determine the temperature along optical fibers. The orientation of an anisotropic crystal can be found from the polarization of Raman-scattered light with respect to the crystal and the polarization of the laser light, if the crystal structure’s point group is known.
In nanotechnology, a Raman microscope can be used to analyze nanowires to better understand their structures, and the radial breathing mode of carbon nanotubes is commonly used to evaluate their diameter.
Raman active fibers, such as aramid and carbon, have vibrational modes that show a shift in Raman frequency with applied stress. Polypropylene fibers exhibit similar shifts.
In solid state chemistry and the bio-pharmaceutical industry, Raman spectroscopy can be used to not only identify active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), but to identify their polymorphic forms, if more than one exist. For example, the drug Cayston (aztreonam), marketed by Gilead Sciences for cystic fibrosis,[7] can be identified and characterized by IR and Raman spectroscopy. Using the correct polymorphic form in bio-pharmaceutical formulations is critical, since different forms have different physical properties, like solubility and melting point.
Raman spectroscopy has a wide variety of applications in biology and medicine. It has helped confirm the existence of low-frequency phonons[8] in proteins and DNA,[9][10][11][12] promoting studies of low-frequency collective motion in proteins and DNA and their biological functions.[13][14] Raman reporter molecules with olefin or alkyne moieties are being developed for tissue imaging with SERS-labeled antibodies.[15] Raman spectroscopy has also been used as a noninvasive technique for real-time, in situ biochemical characterization of wounds. Multivariate analysis of Raman spectra has enabled development of a quantitative measure for wound healing progress.[16] Spatially offset Raman spectroscopy (SORS), which is less sensitive to surface layers than conventional Raman, can be used to discover counterfeit drugs without opening their packaging, and to non-invasively study biological tissue.[17] A huge reason why Raman spectroscopy is so useful in biological applications is because its results often do not face interference from water molecules, due to the fact that they have permanent dipole moments, and as a result, the Raman scattering cannot be picked up on. This is a large advantage, specifically in biological applications.[18] Raman spectroscopy also has a wide usage for studying biominerals.[19] Lastly, Raman gas analyzers have many practical applications, including real-time monitoring of anesthetic and respiratory gas mixtures during surgery.
Raman spectroscopy is an efficient and non-destructive way to investigate works of art.[20] Identifying individual pigments in paintings and their degradation products provides insight into the working method of the artist. It also gives information about the original state of the painting in cases where the pigments degraded with age.[21] In addition to paintings, Raman spectroscopy can be used to investigate the chemical composition of historical documents (such as the Book of Kells), which can provide insight about the social and economic conditions when they were created.[22] It also offers a noninvasive way to determine the best method of preservation or conservation of such materials.
Raman spectroscopy has been used in several research projects as a means to detect explosives from a safe distance using laser beams.[23][24][25]
Raman Spectroscopy is being further developed so it could be used in the clinical setting. Raman4Clinic is a European organization that is working on incorporating Raman Spectroscopy techniques in the medical field. They are currently working on different projects, one of them being monitoring cancer using bodily fluids such as urine and blood samples which are easily accessible. This technique would be less stressful on the patients than constantly having to take biopsies which are not always risk free. [26]
Microspectroscopy
Raman spectroscopy offers several advantages for microscopic analysis. Since it is a scattering technique, specimens do not need to be fixed or sectioned. Raman spectra can be collected from a very small volume (< 1 µm in diameter); these spectra allow the identification of species present in that volume. Water does not generally interfere with Raman spectral analysis. Thus, Raman spectroscopy is suitable for the microscopic examination of minerals, materials such as polymers and ceramics, cells, proteins and forensic trace evidence. A Raman microscope begins with a standard optical microscope, and adds an excitation laser, a monochromator, and a sensitive detector (such as a charge-coupled device (CCD), or photomultiplier tube (PMT)). FT-Raman has also been used with microscopes. Ultraviolet microscopes and UV enhanced optics must be used when a UV laser source is used for Raman microspectroscopy.
In direct imaging, the whole field of view is examined for scattering over a small range of wavenumbers (Raman shifts). For instance, a wavenumber characteristic for cholesterol could be used to record the distribution of cholesterol within a cell culture.
The other approach is hyperspectral imaging or chemical imaging, in which thousands of Raman spectra are acquired from all over the field of view. The data can then be used to generate images showing the location and amount of different components. Taking the cell culture example, a hyperspectral image could show the distribution of cholesterol, as well as proteins, nucleic acids, and fatty acids. Sophisticated signal- and image-processing techniques can be used to ignore the presence of water, culture media, buffers, and other interference.
Raman microscopy, and in particular confocal microscopy, has very high spatial resolution. For example, the lateral and depth resolutions were 250 nm and 1.7 µm, respectively, using a confocal Raman microspectrometer with the 632.8 nm line from a helium–neon laser with a pinhole of 100 µm diameter. Since the objective lenses of microscopes focus the laser beam to several micrometres in diameter, the resulting photon flux is much higher than achieved in conventional Raman setups. This has the added benefit of enhanced fluorescence quenching. However, the high photon flux can also cause sample degradation, and for this reason some setups require a thermally conducting substrate (which acts as a heat sink) in order to mitigate this process.
Another approach called global Raman imaging[28] uses complete monochromatic images instead of reconstruction of images from acquired spectra. This technique is being used for the characterization of large scale devices, mapping of different compounds and dynamics study. It has already been use for the characterization of graphene layers,[29] J-aggregated dyes inside carbon nanotubes[30] and multiple other 2D materials such as MoS2 and WSe2. Since the excitation beam is dispersed over the whole field of view, those measurements can be done without damaging the sample.
By using Raman microspectroscopy, in vivo time- and space-resolved Raman spectra of microscopic regions of samples can be measured. As a result, the fluorescence of water, media, and buffers can be removed. Consequently, in vivo time- and space-resolved Raman spectroscopy is suitable to examine proteins, cells and organs.
Raman microscopy for biological and medical specimens generally uses near-infrared (NIR) lasers (785 nm diodes and 1064 nm Nd:YAG are especially common). The use of these lower energy wavelengths reduces the risk of damaging the specimen. However, the intensity of NIR Raman is low (owing to the ω4 dependence of Raman scattering intensity), and most detectors require very long collection times. Recently advances were made which had no destructive effect on mitochondria in the observation of changes in cytochrome c structure that occur in the process of electron transport and ATP synthesis.[31]
Sensitive detectors have become available, making the technique better suited to general use. Raman microscopy of inorganic specimens, such as rocks and ceramics and polymers, can use a broader range of excitation wavelengths.[32]
Polarized analysis
The polarization of the Raman scattered light also contains useful information. This property can be measured using (plane) polarized laser excitation and a polarization analyzer. Spectra acquired with the analyzer set at both perpendicular and parallel to the excitation plane can be used to calculate the depolarization ratio. Study of the technique is useful in teaching the connections between group theory, symmetry, Raman activity, and peaks in the corresponding Raman spectra.[33] Polarized light only gives access to some of the Raman active modes. By rotating the polarization you can gain access to the other modes. Each mode is separated according to its symmetry.[34]
The spectral information arising from this analysis gives insight into molecular orientation and vibrational symmetry. In essence, it allows the user to obtain valuable information relating to the molecular shape, for example in synthetic chemistry or polymorph analysis. It is often used to understand macromolecular orientation in crystal lattices, liquid crystals or polymer samples.[35]
It is convenient in polarised Raman spectroscopy to describe the propagation and polarisation directions using Porto's notation,[36] described by and named after Brazilian physicist Sergio Pereira da Silva Porto.
Variants
Several variations of Raman spectroscopy have been developed. The usual purpose is to enhance the sensitivity (e.g., surface-enhanced Raman), to improve the spatial resolution (Raman microscopy), or to acquire very specific information (resonance Raman).
- Spontaneous Raman spectroscopy – Term used to describe Raman spectroscopy without enhancement of sensitivity.
- Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) – Normally done in a silver or gold colloid or a substrate containing silver or gold. Surface plasmons of silver and gold are excited by the laser, resulting in an increase in the electric fields surrounding the metal. Given that Raman intensities are proportional to the electric field, there is large increase in the measured signal (by up to 1011). This effect was originally observed by Martin Fleischmann but the prevailing explanation was proposed by Van Duyne in 1977.[37] A comprehensive theory of the effect was given by Lombardi and Birke.[38]
- Resonance Raman spectroscopy – The excitation wavelength is matched to an electronic transition of the molecule or crystal, so that vibrational modes associated with the excited electronic state are greatly enhanced. This is useful for studying large molecules such as polypeptides, which might show hundreds of bands in "conventional" Raman spectra. It is also useful for associating normal modes with their observed frequency shifts.[39]
- Surface-enhanced resonance Raman spectroscopy (SERRS) – A combination of SERS and resonance Raman spectroscopy that uses proximity to a surface to increase Raman intensity, and excitation wavelength matched to the maximum absorbance of the molecule being analysed.
- Angle-resolved Raman spectroscopy – Not only are standard Raman results recorded but also the angle with respect to the incident laser. If the orientation of the sample is known then detailed information about the phonon dispersion relation can also be gleaned from a single test.[40]
- Hyper Raman – A non-linear effect in which the vibrational modes interact with the second harmonic of the excitation beam. This requires very high power, but allows the observation of vibrational modes that are normally "silent". It frequently relies on SERS-type enhancement to boost the sensitivity.[41]
- Optical tweezers Raman spectroscopy (OTRS) – Used to study individual particles, and even biochemical processes in single cells trapped by optical tweezers.
- Stimulated Raman scattering (SRS) – A pump-probe technique, where a spatially coincident, two color pulse (with polarization either parallel or perpendicular) transfers the population from ground to a rovibrationally excited state. If the difference in energy corresponds to an allowed Raman transition, scattered light will correspond to loss or gain in the pump beam.
- Spatially offset Raman spectroscopy (SORS) – The Raman scattering beneath an obscuring surface is retrieved from a scaled subtraction of two spectra taken at two spatially offset points
- Coherent anti-Stokes Raman spectroscopy (CARS) – Two laser beams are used to generate a coherent anti-Stokes frequency beam, which can be enhanced by resonance.
- Raman optical activity (ROA) – Measures vibrational optical activity by means of a small difference in the intensity of Raman scattering from chiral molecules in right- and left-circularly polarized incident light or, equivalently, a small circularly polarized component in the scattered light.[42]
- Transmission Raman – Allows probing of a significant bulk of a turbid material, such as powders, capsules, living tissue, etc. It was largely ignored following investigations in the late 1960s (Schrader and Bergmann, 1967)[43] but was rediscovered in 2006 as a means of rapid assay of pharmaceutical dosage forms.[44] There are medical diagnostic applications particularly in the detection of cancer.[25][45][46]
- Inverse Raman spectroscopy.
- Tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (TERS) – Uses a metallic (usually silver-/gold-coated AFM or STM) tip to enhance the Raman signals of molecules situated in its vicinity. The spatial resolution is approximately the size of the tip apex (20–30 nm). TERS has been shown to have sensitivity down to the single molecule level and holds some promise for bioanalysis applications.[47]
- Surface plasmon polariton enhanced Raman scattering (SPPERS) – This approach exploits apertureless metallic conical tips for near field excitation of molecules. This technique differs from the TERS approach due to its inherent capability of suppressing the background field. In fact, when an appropriate laser source impinges on the base of the cone, a TM0 mode[48] (polaritonic mode) can be locally created, namely far away from the excitation spot (apex of the tip). The mode can propagate along the tip without producing any radiation field up to the tip apex where it interacts with the molecule. In this way, the focal plane is separated from the excitation plane by a distance given by the tip length, and no background plays any role in the Raman excitation of the molecule.[49][50][51][52]
- Micro-cavity substrates – A method that improves the detection limit of conventional Raman spectra using micro-Raman in a micro-cavity coated with reflective Au or Ag. The micro-cavity has a radius of several micrometers and enhances the entire Raman signal by providing multiple excitations of the sample and couples the forward-scattered Raman photons toward the collection optics in the back-scattered Raman geometry.[53]
- Stand-off remote Raman. In standoff Raman, the sample is measured at a distance from the Raman spectrometer, usually by using a telescope for light collection. Remote Raman spectroscopy was proposed in the 1960s[54] and initially developed for the measurement of atmospheric gases.[55] The technique was extended In 1992 by Angel et al. for standoff Raman detection of hazardous inorganic and organic compounds.[56] Standoff Raman detection offers a fast-Raman mode of analyzing large areas such as a football field in minutes. A pulsed laser source and gated detector allow Raman spectra measurements in the daylight[57] and reduces the long-lived fluorescent background generated by transition ions and rare earth ions. Another way to avoid fluorescence, first demonstrated by Sandy Asher in 1984, is to use a UV laser probe beam. At wavelengths of 260 nm, there is effectively no fluorescence interference and the UV signal is inherently strong.[25][58][59] A 10X beam expander mounted in front of the laser allows focusing of the beam and a telescope is directly coupled through the camera lens for signal collection. With the system's time-gating capability it is possible to measure remote Raman of your distant target and the atmosphere between the laser and target.[25]
See also
References
- 1 2 Gardiner, D.J. (1989). Practical Raman spectroscopy. Springer-Verlag. ISBN 978-0-387-50254-0.
- ↑ G., Hammes, Gordon (2005). Spectroscopy for the biological sciences. Wiley. ISBN 9780471733546. OCLC 850776164.
- ↑ Smekal, A. (1923). "Zur Quantentheorie der Dispersion". Die Naturwissenschaften. 11 (43): 873–875. doi:10.1007/BF01576902.
- ↑ Placzek G. (1934) "Rayleigh Streuung und Raman Effekt", In: Hdb. der Radiologie, Vol. VI., 2, p. 209
- ↑ THE FINGERPRINT REGION OF AN INFRA-RED SPECTRUM Chemguide, Jim Clark 2000
- ↑ Khanna, R.K. (1981). "Raman-spectroscopy of oligomeric SiO species isolated in solid methane". Journal of Chemical Physics. 74 (4): 2108. Bibcode:1981JChPh..74.2108K. doi:10.1063/1.441393.
- ↑ "FDA approves Gilead cystic fibrosis drug Cayston". BusinessWeek. February 23, 2010. Retrieved 2010-03-05.
- ↑ Chou, Kuo-Chen; Chen, Nian-Yi (1977). "The biological functions of low-frequency phonons". Scientia Sinica. 20 (3): 447–457.
- ↑ Urabe, H.; Tominaga, Y.; Kubota, K. (1983). "Experimental evidence of collective vibrations in DNA double helix Raman spectroscopy". Journal of Chemical Physics. 78 (10): 5937–5939. Bibcode:1983JChPh..78.5937U. doi:10.1063/1.444600.
- ↑ Chou, K.C. (1983). "Identification of low-frequency modes in protein molecules". Biochemical Journal. 215 (3): 465–469. PMC 1152424
 . PMID 6362659. doi:10.1042/bj2150465.
. PMID 6362659. doi:10.1042/bj2150465. - ↑ Chou, K.C. (1984). "Low-frequency vibration of DNA molecules". Biochemical Journal. 221 (1): 27–31. PMC 1143999
 . PMID 6466317. doi:10.1042/bj2210027.
. PMID 6466317. doi:10.1042/bj2210027. - ↑ Urabe, H.; Sugawara, Y.; Ataka, M.; Rupprecht, A. (1998). "Low-frequency Raman spectra of lysozyme crystals and oriented DNA films: dynamics of crystal water". Biophys J. 74 (3): 1533–1540. PMC 1299499
 . PMID 9512049. doi:10.1016/s0006-3495(98)77865-8.
. PMID 9512049. doi:10.1016/s0006-3495(98)77865-8. - ↑ Chou, Kuo-Chen (1988). "Review: Low-frequency collective motion in biomacromolecules and its biological functions". Biophysical Chemistry. 30 (1): 3–48. PMID 3046672. doi:10.1016/0301-4622(88)85002-6.
- ↑ Chou, K.C. (1989). "Low-frequency resonance and cooperativity of hemoglobin". Trends in Biochemical Sciences. 14 (6): 212–3. PMID 2763333. doi:10.1016/0968-0004(89)90026-1.
- ↑ Schlücker, S.; et al. (2011). "Design and synthesis of Raman reporter molecules for tissue imaging by immuno-SERS microscopy". Journal of Biophotonics. 4 (6): 453–463. PMID 21298811. doi:10.1002/jbio.201000116.
- ↑ Jain, R.; et al. (2014). "Raman Spectroscopy Enables Noninvasive Biochemical Characterization and Identification of the Stage of Healing of a Wound". Analytical Chemistry. 86 (8): 3764–3772. PMC 4004186
 . PMID 24559115. doi:10.1021/ac500513t.
. PMID 24559115. doi:10.1021/ac500513t. - ↑ "Fake drugs caught inside the pack". BBC News. 2007-01-31. Retrieved 2008-12-08.
- ↑ "Using Raman spectroscopy to characterize biological materials : Nature Protocols". www.nature.com. Retrieved 2017-05-22.
- ↑ Taylor, P.D.; Vinn, O.; Kudryavtsev, A.; Schopf, J.W. (2010). "Raman spectroscopic study of the mineral composition of cirratulid tubes (Annelida, Polychaeta)". Journal of Structural Biology. 171 (3): 402–405. PMID 20566380. doi:10.1016/j.jsb.2010.05.010. Retrieved 2014-06-10.
- ↑ Howell G. M. Edwards, John M. Chalmers, Raman Spectroscopy in Archaeology and Art History, Royal Society of Chemistry, 2005
- ↑ Raman Spectroscopy at ColourLex
- ↑ Quinn, Eamon (May 28, 2007) Irish classic is still a hit (in calfskin, not paperback). New York Times
- ↑ Ben Vogel (29 August 2008). "Raman spectroscopy portends well for standoff explosives detection". Jane's. Archived from the original on 2008-12-03. Retrieved 2008-08-29.
- ↑ "Finding explosives with laser beams", a TU Vienna press-release
- 1 2 3 4 Misra, Anupam K.; Sharma, Shiv K.; Acosta, Tayro E.; Porter, John N.; et al. (2012). "Single-Pulse Standoff Raman Detection of Chemicals from 120 m Distance During Daytime". Applied Spectroscopy. 66 (11): 1279–85. PMID 23146183. doi:10.1366/12-06617.
- ↑ "Working Groups | raman4clinics.eu". www.raman4clinics.eu. Retrieved 2017-05-22.
- ↑ Li, Xufan; Lin, Ming-Wei; Puretzky, Alexander A.; Idrobo, Juan C.; Ma, Cheng; Chi, Miaofang; Yoon, Mina; Rouleau, Christopher M.; Kravchenko, Ivan I.; Geohegan, David B.; Xiao, Kai (2014). "Controlled Vapor Phase Growth of Single Crystalline, Two-Dimensional Ga Se Crystals with High Photoresponse". Scientific Reports. 4. doi:10.1038/srep05497.
- ↑ Marcet, S.; Verhaegen, M.; Blais-Ouellette, S.; Martel, R. (2012). "Raman Spectroscopy hyperspectral imager based on Bragg Tunable Filters". SPIE Photonics North. Photonics North 2012. 8412: 84121J. doi:10.1117/12.2000479.
- ↑ Robin W. Havener; et al. (December 2011). "High-Throughput Graphene Imaging on Arbitrary Substrates with Widefield Raman Spectroscopy". ACS Nano. 6 (1): 373–80. PMID 22206260. doi:10.1021/nn2037169.
- ↑ Gaufrès, E.; Tang, N. Y.-Wa; Lapointe, F.; Cabana, J.; Nadon, M.-A.; Cottenye, N.; Raymond, F.; Szkopek, T.; Martel, R. (2014). "Giant Raman scattering from J-aggregated dyes inside carbon nanotubes for multispectral imaging". Nature Photonics. 8: 72–78. doi:10.1038/nphoton.2013.309.
- ↑ "Mitochondria on guard of human life", Lomonosov Moscow State University. Phys. November 18, 2015. Retrieved 10 feb 2017
- ↑ Ellis DI; Goodacre R (August 2006). "Metabolic fingerprinting in disease diagnosis: biomedical applications of infrared and Raman spectroscopy". Analyst. 131 (8): 875–85. Bibcode:2006Ana...131..875E. PMID 17028718. doi:10.1039/b602376m.
- ↑ Itoh, Yuki; Hasegawa, Takeshi (May 2, 2012). "Polarization Dependence of Raman Scattering from a Thin Film Involving Optical Anisotropy Theorized for Molecular Orientation Analysis". The Journal of Physical Chemistry A. 116 (23): 5560–5570. PMID 22551093. doi:10.1021/jp301070a.
- ↑ Iliev, M. N.; Abrashev, M. V.; Laverdiere, J.; Jandi, S.; et al. (February 16, 2006). "Distortion-dependent Raman spectra and mode mixing in RMnO3 perovskites (R=La,Pr,Nd,Sm,Eu,Gd,Tb,Dy,Ho,Y)". Physical Review B. doi:10.1103/physrevb.73.064302.
- ↑ Khanna, R.K. (1957). Evidence of ion-pairing in the polarized Raman spectra of a Ba2+CrO doped KI single crystal. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. doi:10.1002/jrs.1250040104.
- ↑ Porto's notation Bilbao Crystallographic → Raman scattering
- ↑ Jeanmaire DL; van Duyne RP (1977). "Surface Raman Electrochemistry Part I. Heterocyclic, Aromatic and Aliphatic Amines Adsorbed on the Anodized Silver Electrode". Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry. Elsevier Sequouia S.A. 84: 1–20. doi:10.1016/S0022-0728(77)80224-6.
- ↑ Lombardi JR; Birke RL (2008). "A Unified Approach to Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy". [Journal of Physical Chemistry C]. American Chemical Society. 112 (14): 5605–5617. doi:10.1021/jp800167v.
- ↑ Chao RS; Khanna RK; Lippincott ER (1974). "Theoretical and experimental resonance Raman intensities for the manganate ion". J Raman Spectroscopy. 3 (2–3): 121–131. Bibcode:1975JRSp....3..121C. doi:10.1002/jrs.1250030203.
- ↑ Zachary J. Smith & Andrew J. Berger (2008). "Integrated Raman- and angular-scattering microscopy". Opt. Lett. 3 (7): 714–716. Bibcode:2008OptL...33..714S. doi:10.1364/OL.33.000714.
- ↑ Kneipp K; et al. (1999). "Surface-Enhanced Non-Linear Raman Scattering at the Single Molecule Level". Chem. Phys. 247: 155–162. Bibcode:1999CP....247..155K. doi:10.1016/S0301-0104(99)00165-2.
- ↑ Barron LD; Hecht L; McColl IH; Blanch EW (2004). "Raman optical activity comes of age". Molec. Phys. 102 (8): 731–744. Bibcode:2004MolPh.102..731B. doi:10.1080/00268970410001704399.
- ↑ Schrader, Bernhard; Bergmann, Gerhard (1967). "Die Intensität des Ramanspektrums polykristalliner Substanzen". Fresenius' Zeitschrift für Analytische Chemie. 225 (2): 230–247. ISSN 0016-1152. doi:10.1007/BF00983673.
- ↑ Matousek, P.; Parker, A. W. (2006). "Bulk Raman Analysis of Pharmaceutical Tablets". Applied Spectroscopy. 60 (12): 1353–1357. Bibcode:2006ApSpe..60.1353M. PMID 17217583. doi:10.1366/000370206779321463.
- ↑ Matousek, P.; Stone, N. (2007). "Prospects for the diagnosis of breast cancer by noninvasive probing of calcifications using transmission Raman spectroscopy". Journal of Biomedical Optics. 12 (2): 024008. Bibcode:2007JBO....12b4008M. PMID 17477723. doi:10.1117/1.2718934.
- ↑ Kamemoto, Lori E.; Misra, Anupam K.; Sharma, Shiv K.; Goodman, Hugh Luk; et al. (December 4, 2009). "Near-Infrared Micro-Raman Spectroscopy for in Vitro Detection of Cervical Cancer". Applied Spectroscopy. 64 (3): 255–61. PMC 2880181
 . PMID 20223058. doi:10.1366/000370210790918364.
. PMID 20223058. doi:10.1366/000370210790918364. - ↑ Hermann, P; Hermeling, A; Lausch, V; Holland, G; Möller, L; Bannert, N; Naumann, D (2011). "Evaluation of tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for characterizing different virus strains". Analyst. 136 (2): 1148–1152. doi:10.1039/C0AN00531B.
- ↑ Novotny, L; Hafner, C (1994). "Light propagation in a cylindrical waveguide with a complex, metallic, dielectric function". Physical Review E. 50 (5): 4094–4106. Bibcode:1994PhRvE..50.4094N. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.50.4094.
- ↑ De Angelis, F; Das, G; Candeloro, P; Patrini, M; et al. (2010). "Nanoscale chemical mapping using three-dimensional adiabatic compression of surface plasmon polaritons". Nature Nanotechnology. 5 (1): 67–72. Bibcode:2010NatNa...5...67D. PMID 19935647. doi:10.1038/nnano.2009.348.
- ↑ De Angelis, F; Proietti Zaccaria, R; Francardi, M; Liberale, C; et al. (2011). "Multi-scheme approach for efficient surface plasmon polariton generation in metallic conical tips on AFM-based cantilevers". Optics Express. 19 (22): 22268. Bibcode:2011OExpr..1922268D. doi:10.1364/OE.19.022268.
- ↑ Proietti Zaccaria, R; Alabastri, A; De Angelis, F; Das, G; et al. (2012). "Fully analytical description of adiabatic compression in dissipative polaritonic structures". Physical Review B. 86 (3): 035410. Bibcode:2012PhRvB..86c5410P. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.86.035410.
- ↑ Proietti Zaccaria, R; De Angelis, F; Toma, A; Razzari, L; et al. (2012). "Surface plasmon polariton compression through radially and linearly polarized source". Optics Letters. 37 (4): 545. Bibcode:2012OptL...37..545Z. doi:10.1364/OL.37.000545.
- ↑ Misra, Anupam K.; Sharma, Shiv K.; Kamemoto, Lori; Zinin, Pavel V.; et al. (December 8, 2008). "Novel Micro-Cavity Substrates for Improving the Raman Signal from Submicrometer Size Materials". Applied Spectroscopy. 63 (3): 373–7. PMID 19281655. doi:10.1366/000370209787598988.
- ↑ Cooney, J. (1965). Proceedings of the MRI Symposium on Electromagnetic Sensing of the Earth from Satellites, J. Fox, Ed. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑ Leonard, Donald A. (1967). "Observation of Raman Scattering from the Atmosphere using a Pulsed Nitrogen Ultraviolet Laser". Nature. 216 (5111): 142–143. doi:10.1038/216142a0.
- ↑ Angel, S. M.; Kulp, Thomas J.; Vess, Thomas M. (1992). "Remote-Raman Spectroscopy at Intermediate Ranges Using Low-Power cw Lasers". Applied Spectroscopy. 46 (7): 1085–1091. doi:10.1366/0003702924124132.
- ↑ Carter, J. C.; Angel, S. M.; Lawrence-Snyder, M; Scaffidi, J; Whipple, R. E.; Reynolds, J. G. (2005). "Standoff detection of high explosive materials at 50 meters in ambient light conditions using a small Raman instrument". Applied Spectroscopy. 59 (6): 769–75. PMID 16053543. doi:10.1366/0003702054280612.
- ↑ Gaft, M.; Panczer, M.G.; Reisfeld, R.; Uspensky, E. (2001). "Laser-induced timeresolved luminescence as a tool for rare-earth element identification in minerals". Phys. Chem. Minerals. 28 (5): 347–363. doi:10.1007/s002690100163.
- ↑ Waychunas, G.A. (1988). "Luminescence, x-ray emission and new spectroscopies". Reviews in Mineralogy Mineralogical Society of America. 18.
External links
- DoITPoMS Teaching and Learning Package – Raman Spectroscopy – an introduction to Raman spectroscopy, aimed at undergraduate level.
- Raman spectroscopy in analysis of paintings, ColourLex