Radiation protection
Radiation protection, sometimes known as radiological protection, is defined by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) as "The protection of people from harmful effects of exposure to ionizing radiation, and the means for achieving this". The IAEA also states "The accepted understanding of the term radiation protection is restricted to protection of people. Suggestions to extend the definition to include the protection of non-human species or the protection of the environment are controversial".[1] Exposure can be from a radiation source external to the human body or due to an intake of radioactive material into the body.
Ionizing radiation is widely used in industry and medicine, and can present a significant health hazard by causing microscopic damage to living tissue. This can result in skin burns and radiation sickness at high exposures, known as "tissue" or "deterministic" effects (conventionally indicated by the gray), and statistically elevated risks of cancer at low exposures, known as "stochastic effects" (conventionally measured by the sievert ).
Fundamental to radiation protection is the reduction of expected dose and the measurement of human dose uptake. For radiation protection and dosimetry assessment the International Committee on Radiation Protection (ICRP) and International Commission on Radiation Units and Measurements (ICRU) have published recommendations and data which is used to calculate the biological effects on the human body, and thereby advise dose uptake limits. Supporting this is a necessary range of radiation protection instruments to indicate radiation hazards, and dosimeters to measure dose; assisted by preventative techniques such as radiation shielding.
Principles



The ICRP recommends, develops and maintains the International System of Radiological Protection, based on evaluation of the large body of scientific studies available to equate risk to received dose levels. The system's health objectives are "to manage and control exposures to ionising radiation so that deterministic effects are prevented, and the risks of stochastic effects are reduced to the extent reasonably achievable".[2]
The ICRP's recommendations flow down to national and regional regulators, which have the opportunity to incorporate them into their own law; this process is shown in the accompanying block diagram. In most countries a national regulatory authority works towards ensuring a secure radiation environment in society by setting dose limitation requirements that are generally based on the recommendations of the ICRP.
Exposure situations
The ICRP recognises planned, emergency, and existing exposure situations, as described below;[3]
- Planned exposure – defined as "...where radiological protection can be planned in advance, before exposures occur, and where the magnitude and extent of the exposures can be reasonably predicted." [4] These are such as in occupational exposure situations, where it is necessary for personnel to work in a known radiation environment.
- Emergency exposure – defined as "...unexpected situations that may require urgent protective actions".[5] This would be such as an emergency nuclear event.
- Existing exposure – defined as "...being those that already exist when a decision on control has to be taken".[6] These can be such as from naturally occurring radioactive materials which exist in the environment.
Regulation of dose uptake
The ICRP uses the following overall principles for all controllable exposure situations.[7]
- Justification: No unnecessary use of radiation is permitted, which means that the advantages must outweigh the disadvantages.
- Limitation: Each individual must be protected against risks that are far too large through individual radiation dose limits.
- Optimization: Radiation doses should all be kept as low as reasonably achievable (ALARA). This means that it is not enough to remain under the radiation dose limits, but that radiation doses are as low as reasonably achievable, which often means much lower than the permitted limit.
Factors in external dose uptake
There are three factors that control the amount, or dose, of radiation received from a source. Radiation exposure can be managed by a combination of these factors:
- Time: Reducing the time of an exposure reduces the effective dose proportionally. An example of reducing radiation doses by reducing the time of exposures might be improving operator training to reduce the time they take to handle a radioactive source.
- Distance: Increasing distance reduces dose due to the inverse square law. Distance can be as simple as handling a source with forceps rather than fingers.
- Shielding: Sources of radiation can be shielded with solid or liquid material, which absorbs the energy of the radiation. The term 'biological shield' is used for absorbing material placed around a nuclear reactor, or other source of radiation, to reduce the radiation to a level safe for humans.[8]
Internal dose uptake

Internal dose, due to the inhalation or ingestion of radioactive substances, can result in stochastic or deterministic effects, depending on the amount of radioactive material ingested and other biokinetic factors.
The risk from a low level internal source is represented by the dose quantity committed dose, which has the same risk as the same amount of external effective dose.
The intake of radioactive material can occur through four pathways:
- inhalation of airborne contaminants such as radon
- ingestion of radioactive contamination in food or liquids
- absorption of vapours such as tritium oxide through the skin
- injection of medical radioisotopes such as technetium-99m
The occupational hazards from airborne radioactive particles in nuclear and radio-chemical applications are greatly reduced by the extensive use of gloveboxes to contain such material. To protect against breathing in radioactive particles in ambient air, respirators with particulate filters are worn. To monitor the concentration of radioactive particles in ambient air, radioactive particulate monitoring instruments measure the concentration or presence of airborne materials.
For ingested radioactive materials in food and drink, specialist laboratory radiometric assay methods are used to measure the concentration of such materials.
Recommended limits on dose uptake

The ICRP recommends a number of limits for dose uptake in table 8 of ICRP report 103. These limits are "situational", for planned, emergency and existing situations. Within these situations, limits are given for certain exposed groups;[9]
- Planned exposure – limits given for occupational, medical and public exposure
- Emergency exposure – limits given for occupational and public exposure
- Existing exposure – reference levels for all persons exposed
Further detail of some of the limits can be found on the ICRPedia page [10]
ALARP & ALARA
ALARP is an acronym for an important principle in exposure to radiation and other occupational health risks and stands for "As Low As Reasonably Practicable".[11] The aim is to minimize the risk of radioactive exposure or other hazard while keeping in mind that some exposure may be acceptable in order to further the task at hand. The equivalent term ALARA, "As Low As Reasonably Achievable", is more commonly used outside the UK.
This compromise is well illustrated in radiology. The application of radiation can aid the patient by providing doctors and other health care professionals with a medical diagnosis, but the exposure should be reasonably low enough to keep the statistical probability of cancers or sarcomas (stochastic effects) below an acceptable level, and to eliminate deterministic effects (e.g. skin reddening or cataracts). An acceptable level of incidence of stochastic effects is considered to be equal for a worker to the risk in another work generally considered to be safe.
This policy is based on the principle that any amount of radiation exposure, no matter how small, can increase the chance of negative biological effects such as cancer. It is also based on the principle that the probability of the occurrence of negative effects of radiation exposure increases with cumulative lifetime dose. These ideas are combined to form the linear no-threshold model. At the same time, radiology and other practices that involve use of radiations bring benefits to population, so reducing radiation exposure can reduce the efficacy of a medical practice. The economic cost, for example of adding a barrier against radiation, must also be considered when applying the ALARP principle. Computed Tomography, better known as C.T. Scans or CAT Scans have made an enormous contribution to medicine, however not without some risk. They use ionizing radiation which can cause cancer, especially in children.[12] When caregivers follow proper indications for their use and child safe techniques rather than adult techniques, downstream cancer can be prevented.[12][13]
Personal radiation dosimeters
The radiation dosimeter is an important personal dose measuring instrument. It is worn by the person being monitored and is used to estimate the radiation dose deposited in the individual wearing the device. They are used for Gamma, X-ray, beta and other strongly penetrating radiation, but not for weakly penetrating radiation such as alpha particles. Traditionally film badges were used for long term monitoring, and quartz fibre dosimeters for short term monitoring. However, these are being superseded by such as thermoluminescent dosimetry badges and electronic dosimeters. Electronic dosimeters can give an alarm warning if a preset dose threshold has been reached, enabling safer working in potentially higher radiation levels, where the received dose must be continually monitored.
Workers exposed to radiation, such as radiographers, nuclear power plant workers, doctors using radiotherapy, those in laboratories using radionuclides, and HAZMAT teams are required to wear dosimeters so a record of occupational exposure can be made. Such devices are generally termed "legal dosimeters" if they have been approved for use in recording personnel dose for regulatory purposes.
Dosimeters can be worn to obtain a whole body dose and there are also specialist types that can be worn on the fingers or clipped to headgear, to measure the localised body irradiation for specific activities.
Common types of wearable dosimeters for ionizing radiation include:[14][15]
- Film badge dosimeter
- Quartz fiber dosimeter
- Solid state (MOSFET or silicon diode) dosimeter
- Thermoluminescent dosimeter
Radiation Shielding


Almost any material can act as a shield from gamma or x-rays if used in sufficient amounts. Different types of ionizing radiation interact in different ways with shielding material. The effectiveness of shielding is dependent on the Stopping power of radiation particles, which varies with the type and energy of radiation and the shielding material used. Different shielding techniques are therefore used dependent on the application and the type and energy of the radiation.
Shielding reduces the intensity of radiation depending on the thickness. This is an exponential relationship with gradually diminishing effect as equal slices of shielding material are added. A quantity known as the halving-thicknesses is used to calculate this. For example, a practical shield in a fallout shelter with ten halving-thicknesses of packed dirt, which is roughly 115 cm (3 ft 9 in) reduces gamma rays to 1/1024 of their original intensity (i.e. 1/210).
The effectiveness of a shielding material in general increases with its atomic number, called Z, except for neutron shielding which is more readily shielded by the likes of neutron absorbers and moderators such as compounds of boron e.g. boric acid, cadmium, carbon and hydrogen respectively.
Graded-Z shielding is a laminate of several materials with different Z values (atomic numbers) designed to protect against ionizing radiation. Compared to single-material shielding, the same mass of graded-Z shielding has been shown to reduce electron penetration over 60%.[16] It is commonly used in satellite-based particle detectors, offering several benefits:
- protection from radiation damage
- reduction of background noise for detectors
- lower mass compared to single-material shielding
Designs vary, but typically involve a gradient from high-Z (usually tantalum) through successively lower-Z elements such as tin, steel, and copper, usually ending with aluminium. Sometimes even lighter materials such as polypropylene or boron carbide are used. [17][18]
In a typical graded-Z shield, the high-Z layer effectively scatters protons and electrons. It also absorbs gamma rays, which produces X-ray fluorescence. Each subsequent layer absorbs the X-ray fluorescence of the previous material, eventually reducing the energy to a suitable level. Each decrease in energy produces bremsstrahlung and Auger electrons, which are below the detector's energy threshold. Some designs also include an outer layer of aluminium, which may simply be the skin of the satellite. The effectiveness of a material as a biological shield is related to its cross-section for scattering and absorption, and to a first approximation is proportional to the total mass of material per unit area interposed along the line of sight between the radiation source and the region to be protected. Hence, shielding strength or "thickness" is conventionally measured in units of g/cm2. The radiation that manages to get through falls exponentially with the thickness of the shield. In x-ray facilities, walls surrounding the room with the x-ray generator may contain lead sheets, or the plaster may contain barium sulfate. Operators view the target through a leaded glass screen, or if they must remain in the same room as the target, wear lead aprons.
Particle radiation
Particle radiation consists of a stream of charged or neutral particles, both charged ions and subatomic elementary particles. This includes solar wind, cosmic radiation, and neutron flux in nuclear reactors.
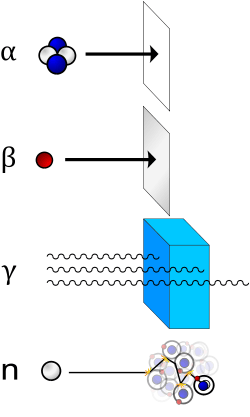
- Alpha particles (helium nuclei) are the least penetrating. Even very energetic alpha particles can be stopped by a single sheet of paper.
- Beta particles (electrons) are more penetrating, but still can be absorbed by a few millimeters of aluminum. However, in cases where high energy beta particles are emitted shielding must be accomplished with low atomic weight materials, e.g. plastic, wood, water, or acrylic glass (Plexiglas, Lucite).[19] This is to reduce generation of Bremsstrahlung X-rays. In the case of beta+ radiation (positrons), the gamma radiation from the electron-positron annihilation reaction poses additional concern.
- Neutron radiation is not as readily absorbed as charged particle radiation, which makes this type highly penetrating. Neutrons are absorbed by nuclei of atoms in a nuclear reaction. This most often creates a secondary radiation hazard, as the absorbing nuclei transmute to the next-heavier isotope, many of which are unstable.
- Cosmic radiation is not a common concern, as the Earth's atmosphere absorbs it and the magnetosphere acts as a shield, but it poses a problem for satellites and astronauts. Frequent fliers are also at a slight risk. Cosmic radiation is extremely high energy, and is very penetrating.
Electromagnetic radiation
Electromagnetic radiation consists of emissions of electromagnetic waves, the properties of which depend on the wavelength.
- X-ray and gamma radiation are best absorbed by atoms with heavy nuclei; the heavier the nucleus, the better the absorption. In some special applications, depleted uranium or thorium[20] are used, but lead is much more common; several centimeters are often required. Barium sulfate is used in some applications too. However, when cost is important, almost any material can be used, but it must be far thicker. Most nuclear reactors use thick concrete shields to create a bioshield with a thin water cooled layer of lead on the inside to protect the porous concrete from the coolant inside. The concrete is also made with heavy aggregates, such as Baryte or MagnaDense (Magnetite), to aid in the shielding properties of the concrete. Gamma rays are better absorbed by materials with high atomic numbers and high density, although neither effect is important compared to the total mass per area in the path of the gamma ray.
- Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is ionizing in its shortest wavelengths but it is not penetrating, so it can be shielded by thin opaque layers such as sunscreen, clothing, and protective eyewear. Protection from UV is simpler than for the other forms of radiation above, so it is often considered separately.
In some cases, improper shielding can actually make the situation worse, when the radiation interacts with the shielding material and creates secondary radiation that absorbs in the organisms more readily. For example, although high atomic number materials are very effective in shielding photons, using them to shield beta particles may cause higher radiation exposure due to the production of bremsstrahlung x-rays, and hence low atomic number materials are recommended. Also, using material with a high neutron activation cross section to shield neutrons will result in the shielding material itself becoming radioactive and hence more dangerous than if it were not present.
Radiation protection instruments
Practical radiation measurement using calibrated radiation protection instruments is essential in evaluating the effectiveness of protection measures, and in assessing the radiation dose likely to be received by individuals. The measuring instruments for radiation protection are both "installed" (in a fixed position) and portable (hand-held or transportable).
Installed instruments
Installed instruments are fixed in positions which are known to be important in assessing the general radiation hazard in an area. Examples are installed "area" radiation monitors, Gamma interlock monitors, personnel exit monitors, and airborne particulate monitors.
The area radiation monitor will measure the ambient radiation, usually X-Ray, Gamma or neutrons; these are radiations which can have significant radiation levels over a range in excess of tens of metres from their source, and thereby cover a wide area.
Gamma radiation "interlock monitors" are used in applications to prevent inadvertent exposure of workers to an excess dose by preventing personnel access to an area when a high radiation level is present. These interlock the process access directly.
Airborne contamination monitors measure the concentration of radioactive particles in the ambient air to guard against radioactive particles being ingested, or deposited in the lungs of personnel. These instruments will normally give a local alarm, but are often connected to an integrated safety system so that areas of plant can be evacuated and personnel are prevented from entering an air of high airborne contamination.
Personnel exit monitors (PEM) are used to monitor workers who are exiting a "contamination controlled" or potentially contaminated area. These can be in the form of hand monitors, clothing frisk probes, or whole body monitors. These monitor the surface of the workers body and clothing to check if any radioactive contamination has been deposited. These generally measure alpha or beta or gamma, or combinations of these.
The UK National Physical Laboratory publishes a good practice guide through its Ionising Radiation Metrology Forum concerning the provision of such equipment and the methodology of calculating the alarm levels to be used.[21]
Portable instruments

Portable instruments are hand-held or transportable. The hand-held instrument is generally used as a survey meter to check an object or person in detail, or assess an area where no installed instrumentation exists. They can also be used for personnel exit monitoring or personnel contamination checks in the field. These generally measure alpha, beta or gamma, or combinations of these.
Transportable instruments are generally instruments that would have been permanently installed, but are temporarily placed in an area to provide continuous monitoring where it is likely there will be a hazard. Such instruments are often installed on trolleys to allow easy deployment, and are associated with temporary operational situations.
In the United Kingdom the HSE has issued a user guidance note on selecting the correct radiation measurement instrument for the application concerned.[22] This covers all radiation instrument technologies, and is a useful comparative guide.
Instrument types
A number of commonly used detection instrument types are listed below, and are used for both fixed and survey monitoring.
- ionization chambers
- proportional counters
- Geiger counters
- Semiconductor detectors
- Scintillation detectors
- Airborne particulate radioactivity monitoring
The links should be followed for a fuller description of each.
Radiation related quantities
The following table shows the main radiation related quantities and units.
| Quantity | Name | Symbol | Unit | Year | SI Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Activity (A) | curie | Ci | 3.7×1010 s−1 | 1953 | 3.7×1010 Bq |
| becquerel | Bq | s−1 | 1974 | SI | |
| rutherford | Rd | 106s−1 | 1946 | 1,000,000 Bq | |
| Exposure (X) | röntgen | R | esu / 0.001293g of air | 1928 | 2.58×10−4 C/kg |
| Fluence (Φ) | (reciprocal area) | m−2 | 1962 | SI | |
| Absorbed dose (D) | erg·g−1 | 1950 | 1.0×10−4 Gy | ||
| rad | rad | 100 erg·g−1 | 1953 | 0.010 Gy | |
| gray | Gy | J·kg−1 | 1974 | SI | |
| Dose equivalent (H) | röntgen equivalent man | rem | 100 erg·g−1 | 1971 | 0.010 Sv |
| sievert | Sv | J·kg−1×WR | 1977 | SI |
Spacecraft radiation challenges
Spacecraft, both manned and unmanned, must cope with the high radiation environment of outerspace. Radiation emitted by the Sun and other galactic sources, and trapped in radiation "belts" is more dangerous and hundreds of times more intense than radiation sources such as medical X-rays or normal cosmic radiation usually experienced on Earth.[23] When the intensely ionizing particles found in space strike human tissue, it can result in cell damage and may eventually lead to cancer.
The usual method for radiation protection is material shielding by spacecraft and equipment structures (usually aluminium), possibly augmented by polyethylene in human spaceflight where the main concern is high energy protons and cosmic ray ions. On unmanned spacecraft in high electron dose environments such as Jupiter missions, or medium Earth orbit (MEO), additional shielding with materials of a high atomic number can be effective. On long duration manned missions, advantage can be taken of the good shielding characteristics of liquid hydrogen fuel and water.
The NASA Space Radiation Laboratory makes use of a particle accelerator that produces beams of protons or heavy ions. These ions are typical of those accelerated in cosmic sources and by the Sun. The beams of ions move through a 100-meter (328-foot) transport tunnel to the 37-square-meter (400-square-foot) shielded target hall. There, they hit the target, which may be a biological sample or shielding material.[23] In a 2002 NASA study, it was determined that materials that have high hydrogen contents, such as polyethylene, can reduce primary and secondary radiation to a greater extent than metals, such as aluminum.[24] The problem with this "passive shielding" method is that radiation interactions in the material generate secondary radiation.
Active Shielding, that is, using magnets, high voltages, or artificial magnetospheres to slow down or deflect radiation, has been considered to potentially combat radiation in a feasible way. So far, the cost of equipment, power and weight of active shielding equipment outweigh their benefits. For example, active radiation equipment would need a habitable volume size to house it, and magnetic and electrostatic configurations often are not homogenous in intensity, allowing high-energy particles to penetrate the magnetic and electric fields from low-intensity parts, like cusps in dipolar magnetic field of Earth. As of 2012, NASA is undergoing research in superconducting magnetic architecture for potential active shielding applications.[25]
Early radiation dangers

The dangers of radioactivity and radiation were not immediately recognized. The discovery of x‑rays in 1895 led to widespread experimentation by scientists, physicians, and inventors. Many people began recounting stories of burns, hair loss and worse in technical journals as early as 1896. In February of that year, Professor Daniel and Dr. Dudley of Vanderbilt University performed an experiment involving x-raying Dudley's head that resulted in his hair loss. A report by Dr. H.D. Hawks, a graduate of Columbia College, of his suffering severe hand and chest burns in an x-ray demonstration, was the first of many other reports in Electrical Review.[26]
Many experimenters including Elihu Thomson at Thomas Edison's lab, William J. Morton, and Nikola Tesla also reported burns. Elihu Thomson deliberately exposed a finger to an x-ray tube over a period of time and suffered pain, swelling, and blistering.[27] Other effects, including ultraviolet rays and ozone were sometimes blamed for the damage.[28] Many physicians claimed that there were no effects from x-ray exposure at all.[27]
As early as 1902 William Herbert Rollins wrote almost despairingly that his warnings about the dangers involved in careless use of x-rays was not being heeded, either by industry or by his colleagues. By this time Rollins had proved that x-rays could kill experimental animals, could cause a pregnant guinea pig to abort, and that they could kill a fetus.[29] He also stressed that "animals vary in susceptibility to the external action of X-light" and warned that these differences be considered when patients were treated by means of x-rays.
Before the biological effects of radiation were known, many physicians and corporations began marketing radioactive substances as patent medicine in the form of glow-in-the-dark pigments. Examples were radium enema treatments, and radium-containing waters to be drunk as tonics. Marie Curie protested against this sort of treatment, warning that the effects of radiation on the human body were not well understood. Curie later died from aplastic anaemia, likely caused by exposure to ionizing radiation. By the 1930s, after a number of cases of bone necrosis and death of radium treatment enthusiasts, radium-containing medicinal products had been largely removed from the market (radioactive quackery).
See also
- CBLB502, 'Protectan', a radioprotectant drug under development for its ability to protect cells during radiotherapy.
- Ex-Rad, a United States Department of Defense radioprotectant drug under development.
- Health physics
- Health threat from cosmic rays
- International Radiation Protection Association – (IRPA). The International body concerned with promoting the science and practice of radiation protection.
- Juno Radiation Vault
- Nuclear safety
- Potassium iodide
- Radiation monitoring
- Radiation Protection Convention, 1960
- Radiobiology
- Radiological protection of patients
- Radioresistance
- Society for Radiological Protection – The principal UK body concerned with promoting the science and practice of radiation protection. It is the UK national affiliated body to IRPA
Notes
- ↑ IAEA Safety Glossary - draft 2016 revision.
- ↑ ICRP. Report 103. pp. para 29.
- ↑ ICRP. "Report 103": Section 6.
- ↑ ICRP. "Report 103": para 253.
- ↑ ICRP. "Report 103": para 274.
- ↑ ICRP. "Report 103": para 284.
- ↑ ICRP. "Report 103": Introduction.
- ↑ "Biological shield". United States Nuclear Regulatory Commission. Retrieved 13 August 2010.
- ↑ ICRP. "Report 103": Table 8, section 6.5.
- ↑ ICRPedia on-line. "ICRP". Retrieved 28 July 2017.
- ↑ This is the wording used by the national regulatory authority that coined the term, in turn derived from its enabling legislation: Health and Safety at Work etc. Act 1974: "Risk management: ALARP at a glance". London: Health and Safety Executive. Retrieved 13 February 2011.
'ALARP' is short for 'as low as reasonably practicable'
- 1 2 Swensen, Stephen J.; Duncan, James R.; Gibson, Rosemary; Muething, Stephen E.; LeBuhn, Rebecca; Rexford, Jean; Wagner, Carol; Smith, Stephen R.; DeMers, Becky. "An Appeal for Safe and Appropriate Imaging of Children". Journal of Patient Safety. 10 (3): 121–124. doi:10.1097/pts.0000000000000116.
- ↑ "Image Gently". www.imagegently.org. Alliance for Radiation Safety in Pediatric Imaging (the Image Gently Alliance). Retrieved 2016-02-08.
- ↑ Advances in kilovoltage x-ray beam dosimetry by Hill et al in http://iopscience.iop.org/0031-9155/59/6/R183/article
- ↑ "Review on the characteristics of radiation detectors for dosimetry and imaging". Physics in Medicine and Biology. 59: R303–R347. Oct 2014. Bibcode:2014PMB....59R.303S. PMID 25229250. doi:10.1088/0031-9155/59/20/R303.
- ↑ Fan, W.C.; et al. (1996). "Shielding considerations for satellite microelectronics". IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science. 43 (6): 2790–2796. Bibcode:1996ITNS...43.2790F. doi:10.1109/23.556868.
- ↑ Smith, D.M.; et al. (2002). "The RHESSI Spectrometer". Solar Physics. 210: 33–60. Bibcode:2002SoPh..210...33S. doi:10.1023/A:1022400716414.
- ↑ Pia, Maria Grazia; et al. (2009). "PIXE Simulation with Geant4". IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science. 56 (6): 3614–3649. Bibcode:2009ITNS...56.3614P. doi:10.1109/TNS.2009.2033993.
- ↑ http://www.oseh.umich.edu/TrainP32.pdf
- ↑ Historical Use of Thorium at Hanford
- ↑ Operational Monitoring Good Practice Guide "The Selection of Alarm Levels for Personnel Exit Monitors" Dec 2009 - National Physical Laboratory, Teddington UK
- ↑ http://www.hse.gov.uk/pubns/irp7.pdf
- 1 2 "Behind the scenes - NASA's Space Radiation Laboratory". NASA. 2003. Retrieved 2012-07-25.
- ↑ "Understanding Space Radiation" (PDF). Lyndon B. Johnson Space Center. NASA. October 2002. Retrieved 2012-07-25.
FS-2002-10-080-JSC
- ↑ "Radiation Protection and Architecture Utilizing High Temperature Superconducting Magnets". NASA Johnson Space Center. Shayne Westover. 2012. Retrieved 2014-04-28.
- ↑ Sansare, K.; Khanna, V.; Karjodkar, F. (2011). "Early victims of X-rays: a tribute and current perception". Dentomaxillofacial Radiology. 40 (2): 123–125. ISSN 0250-832X. PMC 3520298
 . PMID 21239576. doi:10.1259/dmfr/73488299.
. PMID 21239576. doi:10.1259/dmfr/73488299. - 1 2 Ronald L. Kathern and Paul L. Ziemer, he First Fifty Years of Radiation Protection, physics.isu.edu
- ↑ Hrabak, M.; Padovan, R. S.; Kralik, M.; Ozretic, D.; Potocki, K. (July 2008). "Nikola Tesla and the Discovery of X-rays". RadioGraphics. 28 (4): 1189–92. PMID 18635636. doi:10.1148/rg.284075206.
- ↑ Geoff Meggitt (2008), Taming the Rays - A history of Radiation and Protection., Lulu.com, ISBN 978-1-4092-4667-1
References
- Harvard University Radiation Protection Office Providing radiation guidance to Harvard University and affiliated institutions.
- Journal of Solid State Phenomena Tara Ahmadi, Use of Semi-Dipole Magnetic Field for Spacecraft Radiation Protection.
External links
- - "The confusing world of radiation dosimetry" - M.A. Boyd, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. An account of chronological differences between USA and ICRP dosimetry systems.
- "Halving-thickness for various materials". "The Compass DeRose Guide to Emergency Preparedness - Hardened Shelters".
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Radiation protection. |