Scientific racism

| Race |
|---|
| Genetics and differences |
| Society |
| Race and... |
| Related topics |
|
| This article is part of a series on |
| Alternative and pseudo‑medicine |
|---|
 |
|
Fringe medicine and science |
|
Scientific racism (sometimes race biology or racial biology)[1] is the pseudoscientific belief that empirical evidence exists to support or justify racism (racial discrimination), racial inferiority, or racial superiority;[2][3][4] alternatively, it is the practice of classifying[5] individuals of different phenotypes or genotype into discrete races. Historically it received credence in the scientific community, but is no longer considered scientific.[3][4]
Scientific racism employs anthropology (notably physical anthropology), anthropometry, craniometry, and other disciplines or pseudo-disciplines, in proposing anthropological typologies supporting the classification of human populations into physically discrete human races, that might be asserted to be superior or inferior. Scientific racism was common during the period from 1600s to the end of World War I. Since the second half of 20th century, scientific racism has been criticized as obsolete and discredited, yet historically has persistently been used to support or validate racist world-views, based upon belief in the existence and significance of racial categories and a hierarchy of superior and inferior races.[6]
After the end of World War II, scientific racism in theory and action was formally denounced, especially in UNESCO's early antiracist statement "The Race Question" (1950): "The biological fact of race and the myth of 'race' should be distinguished. For all practical social purposes 'race' is not so much a biological phenomenon as a social myth. The myth of 'race' has created an enormous amount of human and social damage. In recent years, it has taken a heavy toll in human lives, and caused untold suffering".[7] Such "biological fact" is no longer considered to exist as developments in human evolutionary genetics showed that human genetic differences are nearly totally gradual.[5]
The term "scientific racism" is generally used pejoratively as applied to more modern theories, as in The Bell Curve (1994). Critics argue that such works postulate racist conclusions unsupported by available evidence. Publications such as the Mankind Quarterly, founded explicitly as a "race-conscious" journal, are generally regarded as platforms of scientific racism for publishing articles on fringe interpretations of human evolution, intelligence, ethnography, language, mythology, archaeology, and race subjects.
The label "scientific racism" is used to criticize studies claiming to establish a connection between, for example, race and intelligence, and is used to argue that this promotes the idea of "superior" and "inferior" human races.[8]
Antecedents
Classical thinkers
Benjamin Isaac, in The Invention of Racism in Classical Antiquity (2006), reports that scientific racism is rooted in Græco–Roman antiquity.[9] A prime example is the 5th century BC treatise Airs, Waters, Places by Hippocrates, about which Pseudo-Aristotle notes:
The idea that dark people are cowards, and light people courageous fighters, is found already in Airs, Waters, Places.[10]
On the other hand the ancient Indians considered all foreigners as barbarians. The 11th century Muslim scholar Al-Biruni wrote that the Indians call the foreigners impure.[11] A few centuries later Dubois observes that Hindus look upon Europeans as barbarians totally ignorant of all principles of honour and good breeding... In the eyes of a Hindu, a Pariah (outcast) and a European are on the same level.[11]
The Chinese also viewed the Europeans as repulsive, ghost-like creatures and even devils. The Chinese writers also referred to the Europeans as barbarians.[12]
A further example is the Roman writer, architect, and engineer Vitruvius (70–25 BC), who, relying upon the racial theories of the Greek Stoic polymath Posidonius (c. 135 – 51 BC), said:
... those races nearest to the southern half of the axis are of lower stature, with swarthy complexions, curly hair, black eyes, and little blood, on account of the sun. This poverty of blood makes them over-timid to stand up against the sword ... On the other hand, men born in cold countries are, indeed, ready to meet the shock of arms with great courage and without timidity.[13]
Enlightenment thinkers
During the Age of Enlightenment (an era from the 1650s to the 1780s), concepts of monogenism and polygenism became popular, though they would only be systematized epistemologically during the 19th century. Monogenism contends that all races have a single origin, while polygenism is the idea that each race has a separate origin. Until the 18th century, the words "race" and "species" were interchangeable.[14]
Robert Boyle vs. Henri de Boulainvilliers
An early scientist who studied race was Robert Boyle (1627–1691), an Anglo-Irish natural philosopher, chemist, physicist, and inventor. Boyle believed in what today is called 'monogenism', that is, that all races, no matter how diverse, came from the same source, Adam and Eve. He studied reported stories of parents' giving birth to different coloured albinos, so he concluded that Adam and Eve were originally white and that whites could give birth to different coloured races. Theories of Robert Hooke and Isaac Newton about color and light via optical dispersion in physics were also extended by Robert Boyle into discourses of polygenesis,[14] speculating that maybe these differences were due to "seminal impressions". However, Boyle's writings mention that at his time, for "European Eyes", beauty was not measured so much in colour, but in "stature, comely symmetry of the parts of the body, and good features in the face".[15] Various members of the scientific community rejected his views and described them as "disturbing" or "amusing".[16]
On the other hand, historian Henri de Boulainvilliers (1658–1722) divided the French as two races: (i) the aristocratic "French race" descended from the invader Germanic Franks, and (ii) the indigenous Gallo-Roman race (the political Third Estate populace). The Frankish aristocracy dominated the Gauls by innate right of conquest, the contrary of modern nationalism.
In his time, Henri de Boulainvilliers, a believer in the "right of conquest", did not understand "race" as biologically immutable, but as a contemporary (racist) cultural construct. His racialist account of French history was not entirely mythical: despite "supporting" hagiographies and epic poetry, such as The Song of Roland (La Chanson de Roland, c. 12th century), he sought scientific legitimation by basing his racialist distinction on the historical existence of genetically and linguistically distinguished Germanic and Latin-speaking peoples in France. His theoretic racialism was distinct from the biologic facts manipulated in 19th-century scientific racism. (cf. Cultural relativism)
Voltaire
_-002.jpg)
Voltaire (1694-1778) was a French Enlightenment writer, historian and philosopher. He was a polygenist: one who believed that each race had separate origins. Voltaire found biblical monogenism laughable, as he expressed:
It is a serious question among them whether the Africans are descended from monkeys or whether the monkeys come from them. Our wise men have said that man was created in the image of God. Now here is a lovely image of the Divine Maker: a flat and black nose with little or hardly any intelligence. A time will doubtless come when these animals will know how to cultivate the land well, beautify their houses and gardens, and know the paths of the stars: one needs time for everything.[17]
When comparing Europeans to Negroes, Voltaire compared them to different breeds of dog:
The Negro race is a species of men different from ours as the breed of spaniels is from that of greyhounds. The mucous membrane, or network, which Nature has spread between the muscles and the skin, is white in us and black or copper-colored in them.[18]
Lord Kames
The Scottish lawyer Henry Home, Lord Kames (1696-1782) was a polygenist: he believed God had created different races on Earth in separate regions. In his 1734 book Sketches on the History of Man, Home claimed that the environment, climate, or state of society could not account for racial differences, so the races must have come from distinct, separate stocks.[19]
Carl Linnaeus

Meanwhile, Carl Linnaeus (1707–1778), the Swedish physician, botanist, and zoologist, modified the established taxonomic bases of binomial nomenclature for fauna and flora, and was a pioneer researcher in biologically defining human race. In Systema Naturae (1767), he labeled five[20] "varieties"[21][22] of human species. Each one was described as possessing the following physiognomic characteristics "varying by culture and place":[23]
- The Americanus: red, choleraic, righteous; black, straight, thick hair; stubborn, zealous, free; painting himself with red lines, and regulated by customs.[24]
- The Europeanus: white, sanguine, browny; with abundant, long hair; blue eyes; gentle, acute, inventive; covered with close vestments; and governed by laws.[25]
- The Asiaticus: yellow, melancholic, stiff; black hair, dark eyes; severe, haughty, greedy; covered with loose clothing; and ruled by opinions.[26]
- The Afer or Africanus: black, phlegmatic, relaxed; black, frizzled hair; silky skin, flat nose, tumid lips; females without shame; mammary glands give milk abundantly; crafty, sly, lazy, cunning, lustful, careless; anoints himself with grease; and governed by caprice.[27]
- The Monstrosus were mythologic humans which didn't appear in the first editions of Systema Naturae. The sub-species included the "four-footed, mute, hairy" Homo feralis (Feral man); the animal-reared Juvenis lupinus hessensis (Hessian wolf boy), the Juvenis hannoveranus (Hannoverian boy), the Puella campanica (Wild-girl of Champagne), and the agile, but faint-hearted Homo monstrosus (Monstrous man): the Patagonian giant, the Dwarf of the Alps, and the monorchid Khoikhoi (Hottentot). In Amoenitates academicae (1763), Linnaeus presented the mythologic Homo anthropomorpha (Anthropomorphic man), humanoid creatures, such as the troglodyte, the satyr, the hydra, and the phoenix, incorrectly identified as simian creatures.
There are disagreements about what was the basis for Linnaeus' human taxa. On the one hand, the harshest critics say that the classification not only was ethnocentric but seemed to be based upon skin-color. On the other hand, Quintyn (2010) points out that some authors believe the classification was based upon geographical distribution, being cartographically based, and not hierarchical.[28] Paleontologist Stephen Jay Gould (1994) argues that the taxa was "not in the ranked order favored by most Europeans in the racist tradition," and that Linnaeus' division was influenced by the medical theory of humors which said that a person's temperament may be related to biological fluids.[29][30] In the opinion of Kenneth A. R. Kennedy (1976), Linneus certainly considered his own culture better, but his motives for classification of human varieties were not race-centered.[31] The Linnean Society of London has stated that in Linnaeus' view, "Europeans' superiority resides in "culture," and that the decisive factor in Linnaeus' taxa was "culture," not race. Thus, regarding this topic, they consider Linnaeus view as merely "eurocentric," arguing that Linnaeus never called for racist action, and did not use the word "race", which was only introduced later "by his French opponent Buffon".[32] Scholar Stanley A. Rice agrees that Linnaeus' classification was not meant to "imply a hierarchy of humanness or superiority;"[33] although modern critics see that his classification was obviously stereotyped, and erroneous for having included anthropological, non-biological features such as customs or traditions.
John Mitchell
The colonial American doctor John Mitchell (1711–1768) took up a study of climate and race and wrote a book in 1744 called An Essay upon the Causes of the Different Colours of People in Different Climates. In the book he claimed that the first race on Earth had been a brown and reddish colour. He said "that an intermediate tawny colour found amongst Asiatics and Native Amerindians" had been the "original complexion of mankind" and that other races came about by the original race spending generations in different climates.[34]
Immanuel Kant
.jpg)
Immanuel Kant (1724–1804) was a German philosopher who encouraged the examination of man's inner self rather than making inferences about the inner self based upon the exterior physical self.[35] In 1775, Kant published On the Different Races of Man (Über die verschiedenen Rassen der Menschen), which proposed natural or purposive causes of variation, as opposed to mechanical law or a product of chance. He distinguished four fundamental races: whites, blacks, Kalmuck, and Hindustanic, and attributed the variation to differences in environment and climate, such as the air and sun, but clarified by saying that the variation served a purpose and was not purely superficial. Kant argued that human beings were equipped with the same seeds (Keime) and the natural predispositions or characteristics (Anlagen) that when expressed were dependent upon climate and served a purpose due to the circumstance. After this process had occurred, it was also irreversible. Therefore, race could not be undone by changes in climate. "Whichever germ was actualized by the conditions, the other germs would retire into inactivity." Kant stated:
The yellow Indians do have a meagre talent. The Negroes are far below them, and at the lowest point are a part of the American people.[36]

John Hunter
John Hunter (1728–1793), a Scottish surgeon, said that originally the Negroid race was white at birth. He thought that over time because of the sun, the people turned dark skinned, or "black". Hunter also said that blisters and burns would likely turn white on a Negro, which he believed was evidence that their ancestors were originally white.[37]
Charles White
Charles White (1728–1813), an English physician and surgeon, believed that races occupied different stations in the "Great Chain of Being", and he tried to scientifically prove that human races have distinct origins from each other. He believed that whites and Negroes were two different species. White was a believer in polygeny, the idea that different races had been created separately. His Account of the Regular Gradation in Man (1799) provided an empirical basis for this idea. White defended the theory of polygeny by refuting French naturalist Georges-Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon's interfertility argument, which said that only the same species can interbreed. White pointed to species hybrids such as foxes, wolves, and jackals, which were separate groups that were still able to interbreed. For White, each race was a separate species, divinely created for its own geographical region.[19]

Buffon and Blumenbach
The French naturalist Georges-Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon (1707–1788) and the German anatomist Johann Blumenbach (1752–1840) were believers in monogenism, the concept that all races have a single origin. They also believed in the "degeneration theory" of racial origins. They both said that Adam and Eve were Caucasian and that other races came about by degeneration from environmental factors, such as the sun and poor dieting. They believed that the degeneration could be reversed if proper environmental control was taken, and that all contemporary forms of man could revert to the original Caucasian race.[38]
They thought Negroid pigmentation arose because of the heat of the tropical sun. They suggested cold wind caused the tawny colour of the Eskimos. They thought the Chinese relatively fair skinned compared to the other Asian stocks because they kept mostly in towns and were protected from environmental factors. Buffon said that food and the mode of living could make races degenerate and differentiate them from the original Caucasian race.[38] According to Blumenbach, there are five races, all belonging to a single species: Caucasian, Mongolian, Ethiopian, American, and Malay. Blumenbach said:
"I have allotted the first place to the Caucasian for the reasons given below which make me esteem it the primeval one."[39]
Georges-Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon believed humanity was only 6000 years old (the time since Adam). Many scientific racialists pointed out at the time that it would have been difficult for races to change so markedly in genotype and phenotype in such a short period of time. Believing in monogenism, Buffon thought that skin colour could change in a single lifetime, depending on the conditions of climate and diet.[40]
Benjamin Rush
Benjamin Rush (1745–1813), a Founding Father of the United States and a physician, proposed that being black was a hereditary skin disease, which he called "negroidism", and that it could be cured. Rush believed non-whites were really white underneath but they were stricken with a non-contagious form of leprosy which darkened their skin color. Rush drew the conclusion that "whites should not tyrannize over [blacks], for their disease should entitle them to a double portion of humanity. However, by the same token, whites should not intermarry with them, for this would tend to infect posterity with the 'disorder'... attempts must be made to cure the disease".[41]
Christoph Meiners

Christoph Meiners (1747–1810) was a German polygenist and believed that each race had a separate origin. Meiner studied the physical, mental and moral characteristics of each race, and built a race hierarchy based on his findings. Meiners split mankind into two divisions, which he labelled the "beautiful white race" and the "ugly black race". In Meiners's book The Outline of History of Mankind, he said that a main characteristic of race is either beauty or ugliness. He thought only the white race to be beautiful. He considered ugly races to be inferior, immoral and animal-like. He said that the dark, ugly peoples were distinct from the white, beautiful peoples by their "sad" lack of virtue and their "terrible vices".[42] According to Meiners,
The more intelligent and noble people are by nature, the more adaptable, sensitive, delicate, and soft is their body; on the other hand, the less they possess the capacity and disposition towards virtue, the more they lack adaptability; and not only that, but the less sensitive are their bodies, the more can they tolerate extreme pain or the rapid alteration of heat and cold; when they are exposed to illnesses, the more rapid their recovery from wounds that would be fatal for more sensitive peoples, and the more they can partake of the worst and most indigestible foods ... without noticeable ill effects.
Meiners said the Negro felt less pain than any other race and lacked in emotions. Meiners wrote that the Negro had thick nerves and thus was not sensitive like the other races. He went as far as to say that the Negro has "no human, barely any animal, feeling". He described a story where a Negro was condemned to death by being burned alive. Halfway through the burning, the Negro asked to smoke a pipe and smoked it like nothing was happening while he continued to be burned alive. Meiners studied the anatomy of the Negro and came to the conclusion that the Negro have bigger teeth and jaws than any other race, as Negroes are all carnivores. Meiners claimed the skull of the Negro was larger but the brain of the Negro was smaller than any other race. Meiners claimed the Negro was the most unhealthy race on Earth because of its poor diet, mode of living and lack of morals.[43]
Meiners also claimed the "Americans" were an inferior stock of people. He said they could not adapt to different climates, types of food, or modes of life, and that when exposed to such new conditions, they lapse into a "deadly melancholy". Meiners studied the diet of the Americans and said they fed off any kind of "foul offal". He thought they consumed very much alcohol. He believed their skulls were so thick that the blades of Spanish swords shattered on them. Meiners also claimed the skin of an American is thicker than that of an ox.[43]
Meiners wrote that the noblest race was the Celts. They were able to conquer various parts of the world, they were more sensitive to heat and cold, and their delicacy is shown by the way they are selective about what they eat. Meiners claimed that Slavs are an inferior race, "less sensitive and content with eating rough food". He described stories of Slavs allegedly eating poisonous fungi without coming to any harm. He claimed that their medical techniques were also backward: he used as an example their heating sick people in ovens, then making them roll in the snow.[43]
In Meiners's large work entitled Researches on the Variations in Human Nature (1815), he studied also the sexology of each race. He claimed that the African Negroids have unduly strong and perverted sex drives, whilst only the white Europeans have it just right.
Later thinkers
Samuel Stanhope Smith
Samuel Stanhope Smith (1751–1819) was an American Presbyterian Minister and author of Essay on the Causes of Variety of Complexion and Figure in the Human Species in 1787. Smith claimed that Negro pigmentation was nothing more than a huge freckle that covered the whole body as a result of an oversupply of bile, which was caused by tropical climates.[44]
Georges Cuvier

Racial studies by Georges Cuvier (1769–1832), the French naturalist and zoologist, influenced scientific polygenism and scientific racism. Cuvier believed there were three distinct races: the Caucasian (white), Mongolian (yellow) and the Ethiopian (black). He rated each for the beauty or ugliness of the skull and quality of their civilizations. Cuvier wrote about Caucasians: "The white race, with oval face, straight hair and nose, to which the civilised people of Europe belong and which appear to us the most beautiful of all, is also superior to others by its genius, courage and activity".[45]
Regarding Negros, Cuvier wrote:
The Negro race ... is marked by black complexion, crisped or woolly hair, compressed cranium and a flat nose. The projection of the lower parts of the face, and the thick lips, evidently approximate it to the monkey tribe: the hordes of which it consists have always remained in the most complete state of barbarism.[46]
He thought Adam and Eve were Caucasian and hence the original race of mankind. The other two races arose by survivors' escaping in different directions after a major catastrophe hit the earth 5,000 years ago. He theorized that the survivors lived in complete isolation from each other and developed separately.[47][48]
One of Cuvier's pupils, Friedrich Tiedemann, was one of the first to make a scientific contestation of racism. He argued based on craniometric and brain measurements taken by him from Europeans and black people from different parts of the world that the then-common European belief that Negroes have smaller brains, and are thus intellectually inferior, is scientifically unfounded and based merely on the prejudice of travellers and explorers.[49]
Arthur Schopenhauer
The German philosopher Arthur Schopenhauer (1788–1860) attributed civilizational primacy to the white races, who gained sensitivity and intelligence via the refinement caused by living in the rigorous Northern climate:
The highest civilization and culture, apart from the ancient Hindus and Egyptians, are found exclusively among the white races; and even with many dark peoples, the ruling caste, or race, is fairer in colour than the rest, and has, therefore, evidently immigrated, for example, the Brahmins, the Inca, and the rulers of the South Sea Islands. All this is due to the fact that necessity is the mother of invention, because those tribes that emigrated early to the north, and there gradually became white, had to develop all their intellectual powers, and invent and perfect all the arts in their struggle with need, want, and misery, which, in their many forms, were brought about by the climate. This they had to do in order to make up for the parsimony of nature, and out of it all came their high civilization.[50]
Franz Ignaz Pruner
Franz Ignaz Pruner (1808–1882) was a medical doctor who studied the racial structure of Negroes in Egypt. In a book which he wrote in 1846 he claimed that Negro blood had a negative influence on the Egyptian moral character. He published a monograph on Negroes in 1861. He claimed that the main feature of the Negro's skeleton is prognathism, which he claimed was the Negro's relation to the ape. He also claimed that Negroes had very similar brains to apes and that Negros have a shortened big toe, which is a characteristic connecting Negroes closely to apes.[51]
Racial theories in physical anthropology, 1850–1918

The scientific classification established by Carl Linnaeus is requisite to any human racial classification scheme. In the 19th century, unilineal evolution (a.k.a. classical social evolution) was a conflation of competing sociologic and anthropologic theories proposing that Western European culture was the acme of human socio-cultural evolution. The proposal that social status is unilineal—from primitive to civilized, from agricultural to industrial—became popular among philosophers, including Friedrich Hegel, Immanuel Kant, and Auguste Comte. The Christian Bible was interpreted to sanction slavery and from the 1820s to the 1850s was often used in the antebellum Southern United States, by writers such as the Rev. Richard Furman and Thomas R. Cobb, to enforce the idea that Negroes had been created inferior, and thus suited to slavery.[52]
Charles Darwin

Charles Darwin's influential 1859 book On the Origin of Species did not discuss human origins. The extended wording on the title page, which adds by Means of Natural Selection, or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life, uses the general term "races" as an alternative for "varieties" and does not carry the modern connotation of human races. The first use in the book refers to "the several races, for instance, of the cabbage" and proceeds to a discussion of "the hereditary varieties or races of our domestic animals and plants".[53] In The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex (1871), Darwin examined the question of "Arguments in favour of, and opposed to, ranking the so-called races of man as distinct species" and reported no racial distinctions that would indicate that human races are discrete species:
It may be doubted whether any character can be named, which is distinctive of a race and is constant ... they graduate into each other, and ... it is hardly possible to discover clear, distinctive characters between them ... As it is improbable that the numerous, and unimportant, points of resemblance, between the several races of man, in bodily structure and mental faculties (I do not here refer to similar customs) should all have been independently acquired, they must have been inherited from progenitors who had these same characters.[52][54]
In Richard Weikart's 2004 book From Darwin to Hitler: Evolutionary Ethics, Eugenics and Racism in Germany he claims:
Darwin clearly believed that the struggle for existence among humans would result in racial extermination. In Descent of Man he asserted, "At some future period, not very distant as measured by centuries, the civilised races of man will almost certainly exterminate and replace throughout the world the savage races".[55][56][57][58][59]
According to talk.origins, this is a common creationist quote mine.[60] They argue that when Darwin referred to "race" he meant "varieties", not human races,[61] as per the cabbage example cited above. Apart from the plain meaning of the words, they assert "there is nothing in Darwin's words to support (and much in his life to contradict) any claim that Darwin wanted the 'lower' or 'savage races' to be exterminated. He was merely noting what appeared to him to be factual, based in no small part on the evidence of a European binge of imperialism and colonial conquest during his lifetime".[62] The quoted passage, in full context, reads:
The great break in the organic chain between man and his nearest allies, which cannot be bridged over by any extinct or living species, has often been advanced as a grave objection to the belief that man is descended from some lower form; but this objection will not appear of much weight to those who, from general reasons, believe in the general principle of evolution. Breaks often occur in all parts of the series, some being wide, sharp and defined, others less so in various degrees; as between the orang and its nearest allies—between the Tarsius and the other Lemuridae between the elephant, and in a more striking manner between the Ornithorhynchus or Echidna, and all other mammals. But these breaks depend merely on the number of related forms which have become extinct. At some future period, not very distant as measured by centuries, the civilised races of man will almost certainly exterminate, and replace, the savage races throughout the world. At the same time the anthropomorphous apes, as Professor Schaaffhausen has remarked, will no doubt be exterminated. The break between man and his nearest allies will then be wider, for it will intervene between man in a more civilised state, as we may hope, even than the Caucasian, and some ape as low as a baboon, instead of as now between the negro or Australian and the gorilla.— The Descent of Man (1871), Volume I, Chapter VI: "On the Affinities and Genealogy of Man", pages 200–201
In the Chapter "On the Development of the Intellectual and Moral Faculties during Primeval and Civilised Times" Darwin claimed that "the western nations of Europe, who now so immeasurably surpass their former savage progenitors, and stand at the summit of civilisation, owe little or none of their superiority to direct inheritance from the old Greeks".[63]
While proposing a sole human species, Darwin contrasted the "civilized races" with the "savage races". Like most of his contemporaries, except the naturalist Alfred Russel Wallace, he did not distinguish "biological race" from "cultural race". Moreover, he noted that savage races risked extinction more from white European colonialism, than from evolutionary inadequacy.[52][64]
On the question of differences between races, Darwin wrote:
There is, however, no doubt that the various races, when carefully compared and measured, differ much from each other,—as in the texture of the hair, the relative proportions of all parts of the body, the capacity of the lungs, the form and capacity of the skull, and even in the convolutions of the brain. But it would be an endless task to specify the numerous points of structural difference. The races differ also in constitution, in acclimatisation, and in liability to certain diseases. Their mental characteristics are likewise very distinct; chiefly as it would appear in their emotional, but partly in their intellectual, faculties. Every one who has had the opportunity of comparison, must have been struck with the contrast between the taciturn, even morose, aborigines of S. America and the light-hearted, talkative negroes. There is a nearly similar contrast between the Malays and the Papuans, who live under the same physical conditions, and are separated from each other only by a narrow space of sea.[65]
Arthur de Gobineau

The French aristocrat and writer Arthur de Gobineau (1816–1882), is best known for his book An Essay on the Inequality of the Human Races (1853–55) which proposed three human races (black, white and yellow) were natural barriers and claimed that race mixing would lead to the collapse of culture and civilization. claimed that "The white race originally possessed the monopoly of beauty, intelligence and strength" and that any positive accomplishments or thinking of blacks and Asians were due to an admixture with whites. His works were praised by many white supremacist American pro-slavery thinkers such as Josiah C. Nott and Henry Hotze.
Gobineau believed that the different races originated in different areas, the white race had originated somewhere in Siberia, the Asians in the Americas and the blacks in Africa. He believed that the white race was superior, he wrote:
I will not wait for the friends of equality to show me such and such passages in books written by missionaries or sea captains, who declare some Wolof is a fine carpenter, some Hottentot a good servant, that a Kaffir dances and plays the violin, that some Bambara knows arithmetic… Let us leave aside these puerilities and compare together not men, but groups.[66]
Gobineau later used the term "Aryans" to describe the Germanic peoples ("'la race germanique'").[67]
Gobineau's works were also influential to the Nazi party who published his works in German and played a key role in the master race theory of Nazism.
Karl Vogt
Another polygenist evolutionist was Karl Vogt (1817–1895) who believed that the Negro race was related to the ape. He wrote the white race was a separate species to Negroes. In Chapter VII of his lectures of man (1864) he compared the Negro to the white race whom he described as "two extreme human types". The difference between them, he claimed are greater than those between two species of ape; and this proves that Negroes are a separate species from the whites.[68]
Herbert Hope Risley

As an exponent of race science, Colonial administrator Herbert Hope Risley (1851 – 1911) used the ratio of the width of a nose to its height to divide Indian people into Aryan and Dravidian races, as well as seven castes.[69][70]
Ernst Haeckel

Like most of Darwin's supporters, Ernst Haeckel (1834-1919) put forward a doctrine of evolutionary polygenism based on the ideas of the linguist and polygenist August Schleicher, in which several different language groups had arisen separately from speechless prehuman Urmenschen (German for "original humans"), which themselves had evolved from simian ancestors. These separate languages had completed the transition from animals to man, and, under the influence of each main branch of languages, humans had evolved as separate species, which could be subdivided into races. Haeckel divided human beings into ten races, of which the Caucasian was the highest and the primitives were doomed to extinction.[71] Haeckel was also an advocate of the out of Asia theory by writing that the origin of humanity was to be found in Asia; he believed that Hindustan (South Asia) was the actual location where the first humans had evolved. Haeckel argued that humans were closely related to the primates of Southeast Asia and rejected Darwin's hypothesis of Africa.[72][73]
Haeckel also wrote that Negroes have stronger and more freely movable toes than any other race which is evidence that Negroes are related to apes because when apes stop climbing in trees they hold on to the trees with their toes, Haeckel compared Negroes to "four-handed" apes. Haeckel also believed Negroes were savages and that whites were the most civilised.[68]
Nationalism: de Lapouge and Herder
At the 19th century's end, scientific racism conflated Græco–Roman eugenicism with Francis Galton's concept of voluntary eugenics to produce a form of coercive, anti-immigrant government programs influenced by other socio-political discourses and events. Such institutional racism was effected via Phrenology, telling character from physiognomy; craniometric skull and skeleton studies; thus skulls and skeletons of black people and other colored volk, were displayed between apes and white men.
In 1906, Ota Benga, a Pygmy, was displayed as the "Missing Link", in the Bronx Zoo, New York City, alongside apes and animals. The most influential theorists included the anthropologist Georges Vacher de Lapouge (1854–1936) who proposed "anthroposociology"; and Johann Gottfried Herder (1744–1803), who applied "race" to nationalist theory, thereby developing the first conception of ethnic nationalism. In 1882, Ernest Renan contradicted Herder with a nationalism based upon the "will to live together", not founded upon ethnic or racial prerequisites. Scientific racist discourse posited the historical existence of "national races" such as the Deutsche Volk in Germany, and the "French race" being a branch of the basal "Aryan race" extant for millennia, to advocate for geopolitical borders parallel to the racial ones.
Craniometry and physical anthropology
.jpg)
The Dutch scholar Pieter Camper (1722–89), an early craniometric theoretician, used "craniometry" (interior skull-volume measurement) to scientifically justify racial differences. In 1770, he conceived of the facial angle to measure intelligence among species of men. The facial angle was formed by drawing two lines: a horizontal line from nostril to ear; and a vertical line from the upper-jawbone prominence to the forehead prominence. Camper's craniometry reported that antique statues (the Græco–Roman ideal) had a 90-degree facial angle, whites an 80-degree angle, blacks a 70-degree angle, and the orangutan a 58-degree facial angle—thus he established a racist biological hierarchy for mankind, per the Decadent conception of history. Such scientific racist researches were continued by the naturalist Étienne Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire (1772–1844) and the anthropologist Paul Broca (1824–80).
Samuel George Morton

In the 19th century, an early American physical anthropologist, physician and polygenist Samuel George Morton (1799–1851), collected human skulls from worldwide, and attempted a logical classification scheme. Influenced by contemporary racialist theory, Dr Morton said he could judge racial intellectual capacity by measuring the interior cranial capacity, hence a large skull denoted a large brain, thus high intellectual capacity. Conversely, a small skull denoted a small brain, thus low intellectual capacity; superior and inferior established. After inspecting three mummies from ancient Egyptian catacombs, Morton concluded that Caucasians and Negroes were already distinct three thousand years ago. Since the bible indicated that Noah's Ark had washed up on Mount Ararat, only a thousand years ago before this, Morton claimed that Noah's sons could not possibly account for every race on earth. According to Mortons theory of polygenesis, races have been separate since the start.[74]
In Morton's Crania Americana, his claims were based on Craniometry data, that the Caucasians had the biggest brains, averaging 87 cubic inches, Native Americans were in the middle with an average of 82 cubic inches and Negroes had the smallest brains with an average of 78 cubic inches.[74]
In The Mismeasure of Man (1981), the historian of science Stephen Jay Gould argued that Samuel Morton had falsified the craniometric data, perhaps inadvertently over-packing some skulls, to so produce results that would legitimize the racist presumptions he was attempting to prove. A subsequent study by the anthropologist John Michael found Morton's original data to be more accurate than Gould describes, concluding that "[c]ontrary to Gould's interpretation... Morton's research was conducted with integrity".[75] Jason Lewis and colleagues reached similar conclusions as Michael in their reanalysis of Morton's skull collection; however, they depart from Morton's racist conclusions by adding that "studies have demonstrated that modern human variation is generally continuous, rather than discrete or “racial,” and that most variation in modern humans is within, rather than between, populations".[76]
In 1873, Paul Broca, founder of the Anthropological Society of Paris (1859), found the same pattern of measures—that Crania Americana reported—by weighing specimen brains at autopsy. Other historical studies, proposing a black race–white race, intelligence–brain size difference, include those by Bean (1906), Mall (1909), Pearl (1934), and Vint (1934).

Nicolás Palacios
After the War of the Pacific (1879–83) there was a rise of racial and national superiority ideas among the Chilean ruling class.[77] In his 1918 book physician Nicolás Palacios argued for the existence of Chilean race and its superiority when compared to neighboring peoples. He though Chileans were a mix of two martial races: the indigenous Mapuches and the Visigoths of Spain, who where ultimately from Götaland in Sweden. Palacios argued on medical grounds against immigration to Chile from southern Europe claiming that Mestizos who are of south European stock lack "cerebral control" and are a social burden.[78]
Monogenism and polygenism
Samuel Morton's followers, especially Dr Josiah C. Nott (1804–1873) and George Gliddon (1809–57), extended Dr Morton's ideas in Types of Mankind (1854), claiming that Morton's findings supported the notion of polygenism—mankind has discrete genetic ancestries; the races are evolutionarily unrelated, and is predecessor of the modern human multiregional origin hypothesis. Moreover, Morton himself had been reluctant to espouse polygenism, because it theologically challenged the Christian creation myth espoused in the Bible.
Later, in The Descent of Man (1871), Charles Darwin proposed the single-origin hypothesis, i.e., monogenism—mankind has a common genetic ancestry, the races are related, opposing everything that the polygenism of Nott and Gliddon proposed.
Typologies
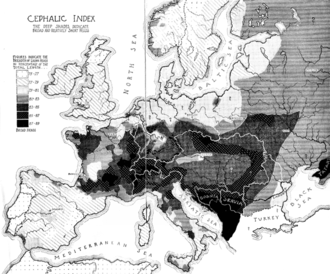
One of the first typologies used to classify various human races was invented by Georges Vacher de Lapouge (1854–1936), a theoretician of eugenics, who published in 1899 L'Aryen et son rôle social (1899—"The Aryan and his social role"). In this book, he classified humanity into various, hierarchized races, spanning from the "Aryan white race, dolichocephalic", to the "brachycephalic", "mediocre and inert" race, best represented by the "Jew". Between these, Vacher de Lapouge identified the "Homo europaeus (Teutonic, Protestant, etc.), the "Homo alpinus" (Auvergnat, Turkish, etc.), and finally the "Homo mediterraneus" (Neapolitan, Andalus, etc.) Vacher de Lapouge became one of the leading inspiration of Nazi antisemitism and Nazi racist ideology.[79]
Vacher de Lapouge's classification was mirrored in William Z. Ripley in The Races of Europe (1899), a book which had a large influence on American white supremacism. Ripley even made a map of Europe according to the alleged cephalic index of its inhabitants. He was an important influence of the American eugenist Madison Grant.

Furthermore, according to John Efron of Indiana University, the late 19th century also witnessed "the scientizing of anti-Jewish prejudice," stigmatizing Jews with male menstruation, pathological hysteria, and nymphomania.[80][81] At the same time, several Jews, such as Joseph Jacobs or Samuel Weissenberg, also endorsed the same pseudoscientific theories, convinced that the Jews formed a distinct race.[80][81] Chaim Zhitlovsky also attempted to define Yiddishkayt (Ashkenazi Jewishness) by turning to contemporary racial theory.[82]
Joseph Deniker (1852–1918) was one of William Z. Ripley's principal opponents; whereas Ripley maintained, as did Vacher de Lapouge, that the European populace comprised three races, Joseph Deniker proposed that the European populace comprised ten races (six primary and four sub-races). Furthermore, he proposed that the concept of "race" was ambiguous, and in its stead proposed the compound word "ethnic group", which later prominently featured in the works of Julian Huxley and Alfred C. Haddon. Moreover, Ripley argued that Deniker's "race" idea should be denoted a "type", because it was less biologically rigid than most racial classifications.
Ideological applications

Nordicism
Joseph Deniker's contribution to racist theory was La Race nordique (the Nordic race), a generic, racial-stock descriptor, which the American eugenicist Madison Grant (1865–1937) presented as the white racial engine of world civilization. Having adopted Ripley's three-race European populace model, but disliking the "Teuton" race name, he transliterated la race nordique into "The Nordic race", the acme of the concocted racial hierarchy, based upon his racial classification theory, popular in the 1910s and 1920s.
Statens institut för rasbiologi and its director Herman Lundborg in Sweden were active in racist research. Furthermore, much of early research on Ural-Altaic languages was coloured by attempts at justifying the view that European peoples east of Sweden were Asian and thus of inferior race, justifying colonialism, eugenics and racial hygiene.
United States: slavery justified

In the United States, scientific racism justified Black African slavery to assuage moral opposition to the Atlantic slave trade. Alexander Thomas and Samuell Sillen described black men as uniquely fitted for bondage, because of their "primitive psychological organization".[83] In 1851, in antebellum Louisiana, the physician Samuel A. Cartwright (1793–1863), considered slave escape attempts as "drapetomania", a treatable mental illness, that "with proper medical advice, strictly followed, this troublesome practice that many Negroes have of running away can be almost entirely prevented". The term drapetomania (mania of the runaway slave) derives from the Greek δραπέτης (drapetes, "a runaway [slave]") and μανία (mania, "madness, frenzy")[84] Cartwright also described dysaesthesia aethiopica, called "rascality" by overseers. The 1840 United States Census claimed that Northern, free blacks suffered mental illness at higher rates than did their Southern, enslaved counterparts. Though the census was later found to have been severely flawed by the American Statistical Association, John Quincy Adams, and others, it became a political weapon against abolitionists. Southern slavers concluded that escaping Negroes were suffering from "mental disorders".[85][86]
At the time of the American Civil War (1861–65), the matter of miscegenation prompted studies of ostensible physiological differences between Caucasians and Negroes. Early anthropologists, such as Josiah Clark Nott, George Robins Gliddon, Robert Knox, and Samuel George Morton, aimed to scientifically prove that Negroes were a human species different from the white people species; that the rulers of Ancient Egypt were not African; and that mixed-race offspring (the product of miscegenation) tended to physical weakness and infertility. After the Civil War, Southern (Confederacy) physicians wrote textbooks of scientific racism based upon studies claiming that black freemen (ex-slaves) were becoming extinct, because they were inadequate to the demands of being a free man—implying that black people benefited from enslavement.
South African apartheid
Scientific racism played a role in establishing apartheid in South Africa. In South Africa, white scientists, like Dudly Kidd, who published The essential Kafir in 1904, sought to "understand the African mind". They believed that the cultural differences between whites and blacks in South Africa might be caused by physiological differences in the brain. Rather than suggesting that Africans were "overgrown children", as early white explorers had, Kidd believed that Africans were "misgrown with a vengeance". He described Africans as at once "hopelessly deficient", yet "very shrewd".[87]
The Carnegie Commission on the Poor White Problem in South Africa played a key role in establishing apartheid in South Africa. According to one memorandum sent to Frederick Keppel, then president of the Carnegie Corporation, there was "little doubt that if the natives were given full economic opportunity, the more competent among them would soon outstrip the less competent whites".[88] Keppel's support for the project of creating the report was motivated by his concern with the maintenance of existing racial boundaries.[88] The preoccupation of the Carnegie Corporation with the so-called poor white problem in South Africa was at least in part the outcome of similar misgivings about the state of poor whites in the southern United States.[88]
The report was five volumes in length.[89] Around the start of the 20th century, white Americans, and whites elsewhere in the world, felt uneasy because poverty and economic depression seemed to strike people regardless of race.[89]
Though the ground work for apartheid began earlier, the report provided support for this central idea of black inferiority. This was used to justify racial segregation and discrimination[90] in the following decades.[91] The report expressed fear about the loss of white racial pride, and in particular pointed to the danger that the poor white would not be able to resist the process of "Africanisation".[88]
Although scientific racism played a role in justifying and supporting institutional racism in South Africa, it was not as important in South Africa as it has been in Europe and the United States. This was due in part to the "poor white problem", which raised serious questions for supremacists about white racial superiority.[87] Since poor whites were found to be in the same situation as natives in the African environment, the idea that intrinsic white superiority could overcome any environment did not seem to hold. As such, scientific justifications for racism were not as useful in South Africa.[87]
Eugenics

Stephen Jay Gould described Madison Grant's The Passing of the Great Race (1916) as "the most influential tract of American scientific racism." In the 1920s–30s, the German racial hygiene movement embraced Grant's Nordic theory. Alfred Ploetz (1860–1940) coined the term Rassenhygiene in Racial Hygiene Basics (1895), and founded the German Society for Racial Hygiene in 1905. The movement advocated selective breeding, compulsory sterilization, and a close alignment of public health with eugenics.
Racial hygiene was historically tied to traditional notions of public health, but with emphasis on heredity—what philosopher and historian Michel Foucault has called state racism. In 1869, Francis Galton (1822–1911) proposed the first social measures meant to preserve or enhance biological characteristics, and later coined the term "eugenics". Galton, a statistician, introduced correlation and regression analysis and discovered regression toward the mean. He was also the first to study human differences and inheritance of intelligence with statistical methods. He introduced the use of questionnaires and surveys to collect data on population sets, which he needed for genealogical and biographical works and for anthropometric studies. Galton also founded psychometrics, the science of measuring mental faculties, and differential psychology, a branch of psychology concerned with psychological differences between people rather than common traits.
Like scientific racism, eugenics grew popular in the early 20th century, and both ideas influenced Nazi racial policies and Nazi eugenics. In 1901, Galton, Karl Pearson (1857–1936) and Walter F. R. Weldon (1860–1906) founded the Biometrika scientific journal, which promoted biometrics and statistical analysis of heredity. Charles Davenport (1866–1944) was briefly involved in the review. In Race Crossing in Jamaica (1929), he made statistical arguments that biological and cultural degradation followed white and black interbreeding. Davenport was connected to Nazi Germany before and during World War II. In 1939 he wrote a contribution to the festschrift for Otto Reche (1879–1966), who became an important figure within the plan to remove populations considered "inferior" from eastern Germany.[92]
Interbellum to World War II
Scientific racism continued through the early 20th century, and soon intelligence testing became a new source for racial comparisons. Before World War II (1939–45), scientific racism remained common to anthropology, and was used as justification for eugenics programs, compulsory sterilization, anti-miscegenation laws, and immigration restrictions in Europe and the United States. The war crimes and crimes against humanity of Nazi Germany (1933–45), discredited scientific racism in academia, but racist legislation based upon it remained in some countries until the late 1960s.
Early intelligence testing and the Immigration Act of 1924
Before the 1920s, social scientists agreed that whites were superior to blacks, but they needed a way to prove this in order to back social policy in favor of whites. They felt the best way to gauge this was through testing intelligence. By interpreting the tests to show favor to whites these test makers’ research results portrayed all minority groups very negatively.[8][93] In 1908, Henry Goddard translated the Binet intelligence test from French and in 1912 began to apply the test to incoming immigrants on Ellis Island.[94] Some claim that in a study of immigrants Goddard reached the conclusion that 87% of Russians, 83% of Jews, 80% of Hungarians, and 79% of Italians were feeble-minded and had a mental age less than 12.[95] Some have also claimed that this information was taken as "evidence" by lawmakers and thus it affected social policy for years.[96] Bernard Davis has pointed out that, in the first sentence of his paper, Goddard wrote that the subjects of the study were not typical members of their groups but were selected because of their suspected sub-normal intelligence. Davis has further noted that Goddard argued that the low IQs of the test subjects were more likely due to environmental rather than genetic factors, and that Goddard concluded that "we may be confident that their children will be of average intelligence and if rightly brought up will be good citizens".[97] In 1996 the American Psychological Association's Board of Scientific Affairs stated that IQ tests were not discriminative towards any ethnic/racial groups.[98]
In his book The Mismeasure of Man, Stephen Jay Gould argued that intelligence testing results played a major role in the passage of the Immigration Act of 1924 that restricted immigration to the United States.[99] However, Mark Snyderman and Richard J. Herrnstein, after studying the Congressional Record and committee hearings related to the Immigration Act, concluded "the [intelligence] testing community did not generally view its findings as favoring restrictive immigration policies like those in the 1924 Act, and Congress took virtually no notice of intelligence testing".[100]
Juan N. Franco contested the findings of Snyderman and Herrnstein. Franco stated that even though Snyderman and Herrnstein reported that the data collected from the results of the intelligence tests were in no way used to pass The Immigration Act of 1924; the IQ test results were still taken into consideration by legislators. As suggestive evidence, Franco pointed to the following fact: Following the passage of the immigration act, information from the 1890 census was used to set quotas based on percentages of immigrants coming from different countries. Based on these data, the legislature restricted the entrance of immigrants from southern and eastern Europe into the United States and allowed more immigrants from northern and Western Europe into the country. The use of the 1900, 1910 or 1920 census data sets would have resulted in larger numbers of immigrants from southern and eastern Europe being allowed into the U.S. However, Franco pointed out that using the 1890 census data allowed congress to exclude southern and eastern Europeans (who performed worse on IQ tests of the time than did western and northern Europeans) from the U.S. Franco argued that the work Snyderman and Herrnstein conducted on this matter neither proved or disproved that intelligence testing influenced immigration laws.[101]
Sweden
Following the creation of the first society for the promotion of racial hygiene, the German Society for Racial Hygiene in 1905—a Swedish society was founded in 1909 as "Svenska sällskapet för rashygien" as third in the world.[102][103] By lobbying Swedish parliamentarians and medical institutes the society managed to pass a decree creating a government run institute in the form of the Swedish State institute of racial biology in 1921.[102] By 1922 the institute was built and opened at Uppsala University.[102] It was the first such government-funded institute in the world performing research into "racial biology" and remains highly controversial to this day.[102][104] The goal was to cure criminality, alcoholism and psychiatric problems through research in eugenics and racial hygiene.[102] As a result of the institutes work a law permitting compulsory sterilization of certain groups was enacted in Sweden in 1934.[105] The second president of the institute Gunnar Dahlberg was highly critical of the validity of the science performed at the institute and reshaped the institute toward a focus on genetics.[106] In 1958 it closed down and all remaining research was moved to the institute of genetics at Uppsala University.[106]
Nazi Germany


The Nazi Party and its sympathizers published many books on scientific racism, seizing on the eugenicist and antisemitic ideas with which they were widely associated, although these ideas had been in circulation since the 19th century. Books such as Rassenkunde des deutschen Volkes ("Ethnology of the German People") by Hans F. K. Günther and Rasse und Seele ("Race and Soul") by Ludwig Ferdinand Clauss attempted to scientifically identify differences between the German, Nordic, or Aryan people and other, supposedly inferior, groups. German schools used these books as texts during the Nazi era.[107] In the early 1930s, the Nazis used racialized scientific rhetoric based on social Darwinism to push its restrictive and discriminatory social policies.
During World War II, Nazi racialist beliefs became anathema in the United States, and Boasians such as Ruth Benedict consolidated their institutional power. After the war, discovery of the Holocaust and Nazi abuses of scientific research (such as Josef Mengele's ethical violations and other war crimes revealed at the Nuremberg Trials) led most of the scientific community to repudiate scientific support for racism.
Propaganda for the Nazi eugenics program began with propaganda for eugenic sterilization. Articles in Neues Volk described the appearance of the mentally ill and the importance of preventing such births.[108] Photographs of mentally incapacitated children were juxtaposed with those of healthy children.[109] The film Das Erbe showed conflict in nature in order to legitimate the Law for the Prevention of Hereditarily Diseased Offspring by sterilization.
Although the child was "the most important treasure of the people", this did not apply to all children, even German ones, only those with no hereditary weaknesses.[110] Nazi Germany's racially based social policies placed the improvement of the Aryan race through eugenics at the center of Nazis ideology. Those humans were targeted who were identified as "life unworthy of life" (German: Lebensunwertes Leben), including but not limited to Jewish people, criminals, degenerate, dissident, feeble-minded, homosexual, idle, insane, and the weak, for elimination from the chain of heredity. Despite their still being regarded as "Aryan", Nazi ideology deemed Slavs (i.e., Poles, Russians, Ukrainians, etc.) to be inferior to the Germanic master race, suitable for expulsion, enslavement, or even extermination.[111]
Adolf Hitler banned intelligence quotient (IQ) testing for being "Jewish" as did Joseph Stalin for being "bourgeois".[112]
United States
In the 20th century, concepts of scientific racism, which sought to prove the physical and mental inadequacy of groups deemed "inferior," was relied upon to justify involuntary sterilization programs.[113][114] Such programs, promoted by eugenicists such as Harry H. Laughlin, were upheld as constitutional by the U.S. Supreme Court in Buck v. Bell (1927). In all, between 60,000 and 90,000 Americans were subjected to involuntary sterilization.[113]
Scientific racism was also used as a justification for the Emergency Quota Act of 1921 and the Immigration Act of 1924 (Johnson-Reed Act), which imposed racial quotas limiting Italian American immigration to the United States and immigration other southern European and eastern European nations. Proponents of these quotas, who sought to block "undesirable" immigrants, justifying restrictions by invoking scientific racism.[115]
Lothrop Stoddard published many racialist books on what he saw as the peril of immigration, his most famous being The Rising Tide of Color Against White World-Supremacy in 1920. In this book he presented a view of the world situation pertaining to race focusing concern on the coming population explosion among the "colored" peoples of the world and the way in which "white world-supremacy" was being lessened in the wake of World War I and the collapse of colonialism.
Stoddard's analysis divided world politics and situations into "white", "yellow", "black", "Amerindian", and "brown" peoples and their interactions. Stoddard argued race and heredity were the guiding factors of history and civilization, and that the elimination or absorption of the "white" race by "colored" races would result in the destruction of Western civilization. Like Madison Grant (see The Passing of the Great Race), Stoddard divided the white race into three main divisions: Nordic, Alpine, and Mediterranean. He considered all three to be of good stock, and far above the quality of the colored races, but argued that the Nordic was the greatest of the three and needed to be preserved by way of eugenics. Unlike Grant, Stoddard was less concerned with which varieties of European people were superior to others (Nordic theory), but was more concerned with what he called "bi-racialism," seeing the world as being composed of simply "colored" and "white" races. In the years after the Great Migration and World War I, Grant's racial theory would fall out of favor in the U.S. in favor of a model closer to Stoddard's.
An influential publication was The Races of Europe (1939) by Carleton S. Coon, president of the American Association of Physical Anthropologists from 1930 to 1961. Coon was a proponent of Multiregional origin of modern humans. He divided Homo sapiens into five main races:
Coon's school of thought was the object of increasing opposition in mainstream anthropology after World War II. Ashley Montagu was particularly vocal in denouncing Coon, especially in his Man's Most Dangerous Myth: The Fallacy of Race. By the 1960s, Coon's approach had been rendered obsolete in mainstream anthropology, but his system continued to appear in publications by his student John Lawrence Angel as late as in the 1970s.
In the late 19th century, the Plessy v. Ferguson (1896) United States Supreme Court decision—which upheld the constitutional legality of racial segregation under the doctrine of "separate but equal"—was intellectually rooted in the racism of the era, as was the popular support for the decision.[116] Later, in the mid 20th century, the Supreme Court's Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka (1954) decision rejected racialist arguments about the "need" for racial segregation—especially in public schools.
After 1945
By 1954, 58 years after the Plessy v. Ferguson upholding of racial segregation in the United States, American popular and scholarly opinions of scientific racism and its sociologic practice had evolved.[116] In 1960 the journal Mankind Quarterly started, which some see as a venue for scientific racism. It is criticized for a claimed extremist right-wing politics, antisemitic bent, and espousing academic hereditarianism.[117] The magazine was founded in 1960, partly in response to the Supreme Court decision Brown v. Board of Education which desegregated the American public schooling.[118][119]
In April 1966, Alex Haley interviewed American Nazi Party founder George Lincoln Rockwell for Playboy. Rockwell justified his belief that blacks were inferior to whites by citing a long 1916 study by G.O. Ferguson which claimed to show that the intellectual performance of black students was correlated with their percentage of white ancestry, stating "pure negroes, negroes three-fourths pure, mulattoes and quadroons have, roughly, 60, 70, 80 and 90 percent, respectively, of white intellectual efficiency."[120] Playboy later published the interview with an editorial note claiming the study was a "discredited [...] pseudoscientific rationale for racism."[121]

International bodies such as UNESCO attempted to draft resolutions that would summarize the state of scientific knowledge about race and issued calls for the resolution of racial conflicts. In its 1950 The Race Question, UNESCO did not reject the idea of a biological basis to racial categories,[122] but instead defined a race as: "A race, from the biological standpoint, may therefore be defined as one of the group of populations constituting the species Homo sapiens", which were broadly defined as the Caucasian, Mongoloid, Negroid races but stated that "It is now generally recognized that intelligence tests do not in themselves enable us to differentiate safely between what is due to innate capacity and what is the result of environmental influences, training and education."[123]
Today, the term "scientific racism" is used to refer to research seeming to scientifically justify racist ideology. The accusation of scientific racism often is cast upon researchers claiming the existence races and or of quantifiable differences in intelligence among these races, especially if said differences are partly genetic in origin. Contemporary researchers include the late Arthur Jensen (The g Factor: The Science of Mental Ability); the late J. Philippe Rushton, president of the Pioneer Fund (Race, Evolution, and Behavior); Chris Brand (The g Factor: General Intelligence and Its Implications); Richard Lynn (IQ and the Wealth of Nations); and Charles Murray and the late Richard Herrnstein (The Bell Curve), among others.[124] These authors themselves, while seeing their work as scientific, may dispute the term "racism" and may prefer terms such as "race realism" or "racialism".[125]
See also
References
- ↑ Weitz, Eric D. (2015-04-27). A Century of Genocide: Utopias of Race and Nation. Princeton University Press. ISBN 9781400866229.
- ↑ "Ostensibly scientific": cf. Theodore M. Porter, Dorothy Ross (eds.) 2003.The Cambridge History of Science: Volume 7, The Modern Social Sciences Cambridge University Press, p. 293 "Race has long played a powerful popular role in explaining social and cultural traits, often in ostensibly scientific terms"; Adam Kuper, Jessica Kuper (eds.), The Social Science Encyclopedia (1996), "Racism", p. 716: "This [sc. scientific] racism entailed the use of 'scientific techniques', to sanction the belief in European and American racial Superiority"; Routledge Encyclopedia of Philosophy: Questions to Sociobiology (1998), "Race, theories of", p. 18: "Its exponents [sc. of scientific racism] tended to equate race with species and claimed that it constituted a scientific explanation of human history"; Terry Jay Ellingson, The myth of the noble savage (2001), 147ff. "In scientific racism, the racism was never very scientific; nor, it could at least be argued, was whatever met the qualifications of actual science ever very racist" (p. 151); Paul A. Erickson,Liam D. Murphy, A History of Anthropological Theory (2008), p. 152: "Scientific racism: Improper or incorrect science that actively or passively supports racism".
- 1 2 Gould, Stephen Jay (1981). The Mismeasure of Man. New York, NY: W W Norton and Co. pp. 28–29. ISBN 0-393-01489-4.
Few tragedies can be more extensive than the stunting of life, few injustices deeper than the denial of an opportunity to strive or even to hope, by a limit imposed from without, but falsely identified as lying within.
- 1 2 Kurtz, Paul (Sep 2004). "Can the Sciences Help Us to Make Wise Ethical Judgments?". Skeptical Inquirer Magazine. Committee for Skeptical Inquiry. Archived from the original on 23 November 2007. Retrieved 1 December 2007.
There have been abundant illustrations of pseudoscientific theories-monocausal theories of human behavior that were hailed as "scientific"-that have been applied with disastrous results. Examples: ... Many racists today point to IQ to justify a menial role for blacks in society and their opposition to affirmative action.
- 1 2 Cavalli-Sforza, L.L. (2001). Genes, Peoples and Languages, p. 30. Penguin Books, London. ISBN 9780865475298.
- ↑ Cf. Patricia Hill Collins, Black feminist thought: knowledge, consciousness, and the politics of empowerment (2nd ed., 2000), Glossary, p. 300: "Scientific racism was designed to prove the inferiority of people of color"; Simon During, Cultural studies: a critical introduction (2005), p. 163: "It [sc. scientific racism] became such a powerful idea because ... it helped legitimate the domination of the globe by whites"; David Brown and Clive Webb, Race in the American South: From Slavery to Civil Rights (2007), p. 75: "...the idea of a hierarchy of races was driven by an influential, secular, scientific discourse in the second half of the eighteenth century and was rapidly disseminated during the nineteenth century".
- ↑ UNESCO, The Race Question, p. 8
- 1 2 Tucker 2007
- ↑ Isaac 2006
- ↑ Isaac 2006, p. 356
- 1 2 The First Spring: The Golden Age of India by Abraham Eraly p.313
- ↑ The Haunting Past: Politics, Economics and Race in Caribbean Life by Alvin O. Thompson p.210
- ↑ Isaac 2006, p. 83
- 1 2 Jen E. Boyle (2010), "Anamorphosis in Early Modern Literature: Mediation and Affect", Ashgate, page 74
- ↑ Robert Boyle (1664), "Experiments and Considerations Touching Colours", Henry Herringman, London, pages 160–161
- ↑ Palmeri, Frank (2006). Humans And Other Animals in Eighteenth-Century British Culture: Representation, Hybridity, Ethics. pp. 49–67.
- ↑ Voltaire Les Lettres d'Amabed (1769), Septième Lettre d'Amabed
- ↑ Voltaire The Works of Voltaire, Vol. XIX (Philosophical Letters) (1733)
- 1 2 Jackson, John P.; Weidman, Nadine M. (2005). Race, Racism, and Science: Social Impact and Interaction. Rutgers University Press. pp. 39–41.
- ↑ Initially, Linnaeus had only described four categories: Europseus albus, Americanus rubescens, Asiaticus fuscus, & Africanus niger. Only later editions included the "Monstrosus".
- ↑ Linnaeus did not use the term "race." He used the term "Homo variat", as can be seen in Systema naturae, p. 34.
- ↑ Gloria Ramon (2002), "Race: Social Concept, Biological Idea"
- ↑ Linnaeus used the Latin term: diurnus, varians cultura, loco: Systema Naturae, 13th edition, p. 29
- ↑ In latin: rufus, cholericus, rectus. Pilis: nigris, rectis, crassis. Naribus: Patulis. Facie: ephelitica. Mento: subimberbi. Pertinax, contentus, liber. Pingit: Se lineis daedaleis rubris. Regitur Consuetudine.
- ↑ In latin: albus, sanguineus, torosus. Pilis flavescentibus, prolixis. Oculis caeruleis. Levis, argutus, inventor. Tegitur Vestimentis arctis. Regitur Ritibus.
- ↑ In latin: luridus, melancholicus, rigidus. Pilis nigricantibus. Oculis fuscis. Severus, fastuosus, avarus. Tegitur Indumentis laxis. Regitur Opinionibus.
- ↑ In latin: niger, phlegmaticus, laxus. Pilis atris, contortuplicatis. Cute holosericea. Naso simo. Labiis tumidis. Feminis sinus pudoris. Mammae lactantes prolixae. Vafer, segnis, negligens. Ungit se pingui. Regitur Arbitrio.
- ↑ Conrad B. Quintyn (2010), "The Existence Or Non-existence of Race?, Teneo Press p.17
- ↑ Gould, S. J. (1981), The mismeasure of man. New York: W. W. Norton & Company, p. 67.
- ↑ Rachel N. Hastings (2008), "Black Eyez: Memoirs of a Revolutionary", p. 17
- ↑ Kenneth A. R. Kennedy (1976), "Human Variation in Space and Time". Wm. C. Brown Company, p. 25. Kennedy writes that while "Linnaes was the first to use biological traits as a basis for further subdivisions of the species into varieties. It would be unfair to ascribe racist motives to this effort."
- ↑ Mary J. Morris & Leonie Berwick (2008), The Linnaean Legacy: Three Centuries after his brith, A forum for natural history. The Linnean Special Issue No. 8. Linnean Society of London, Burlington House, Piccadilly, London. Was Linnaeus a racist?, p. 25
- ↑ Stanley A. Rice (2009), "Encyclopedia of Evolution", Infobase Publishing, p. 195. Stanley states: "Even though the prejudice and racism of the attributes are obvious to modern scientists, Linnaeus did not apparently mean to imply a hierarchy of humanness or superiority."
- ↑ Colin Kidd, The Forging of Races: Race and Scripture in the Protestant Atlantic World, 1600–2000, 2006, p. 30
- ↑ Hannaford, Ivan. Race: the History of an Idea in the West. Baltimore: The Johns Hopkins University Press, 1996.
- ↑ Race and Racism (O. R. P.) (Oxford Readings in Philosophy) (Paperback) by Bernard Boxill
- ↑ Harris 2001, p. 85
- 1 2 Harris, Marvin (2001). The Rise of Anthropological Theory: A History of Theories of Culture. p. 84.
- ↑ Emmanuel Chukwudi Eze, Race and the Enlightenment: A Reader, 1997, p. 84
- ↑ Harris 2001, p. 86
- ↑ Rush, Benjamin (1799). "Observations Intended to Favour a Supposition That the Black Color (As It Is Called) of the Negroes Is Derived from the Leprosy". Transactions of the American Philosophical Society 4.
- ↑ Isaac 2006, p. 150
- 1 2 3 Das Gupta, Tania (2007). Race and Racialization: Essential Readings. pp. 25–26.
- ↑ Harris 2001, p. 87
- ↑ Georges Cuvier, Tableau elementaire de l'histoire naturelle des animaux (Paris, 1798) p. 71
- ↑ Georges Cuvier, The Animal Kingdom: Arranged in Conformity with its Organization, Translated from the French by H. M. Murtrie, p. 50.
- ↑ Jackson & Weidman 2005, pp. 41–42
- ↑ Colin Kidd, The Forging of Races: Race and Scripture in the Protestant Atlantic World, 1600–2000, 2006, p. 28
- ↑ Tiedemann, Friedrich (1836). "On the Brain of the Negro, Compared with that of the European and the Orang-outang" (PDF). Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. 126: 497–527. Bibcode:1836RSPT..126..497T. doi:10.1098/rstl.1836.0025.
- ↑ Schopenhauer, Parerga and Paralipomena: Short Philosophical Essays, Volume II, Section 92
- ↑ Gustav Jahoda, Images of Savages: Ancients [sic] Roots of Modern Prejudice in Western Culture, 1999, p. 82
- 1 2 3 Price, R.G. (June 24, 2006). "The Mis-portrayal of Darwin as a Racist". rationalrevolution.net. Retrieved 2008-01-06.
- ↑ Darwin 1859, p. 15
- ↑ "It may be doubted whether any character can be named which is distinctive of a race and is constant... they graduate into each other, and.. it is hardly possible to discover clear distinctive characters between them... As it is improbable that the numerous and unimportant points of resemblance between the several races of man in bodily structure and mental faculties (I do not here refer to similar customs) should all have been independently acquired, they must have been inherited from progenitors who had these same characters.", Charles Darwin, The Descent of Man p. 225 onwards,
- ↑ Richard Weikart, From Darwin to Hitler, Page 186
- ↑ Also cited by Richard Weikart in Re-examining the Darwin-Hitler Link Discovery Institute, February 28, 2008
- ↑ Also cited by Richard Weikart in Was It Immoral for "Expelled" to Connect Darwinism and Nazi Racism? Discovery Institute, May 2, 2008
- ↑ Also cited by Richard Weikart in "Darwin and the Nazis," The American Spectator, April 16, 2008
- ↑ Also cited by Richard Weikart in The Impact of Darwinism The Stanford Review April 22, 2008
- ↑ Quote Mine Project: Darwin Quotes -Quote #2.10 talk.origins
- ↑ Creationist Claim CA005.2 talk.origins
- ↑ Quote #4.6 talk.origins
- ↑ The Descent of Man, (Second edition, 1874) page 141
- ↑ "Quote Mine Project: Assorted Quotes". TalkOrigins Archive. Retrieved 2007-12-29.
- ↑ The Descent of Man, (First edition, 1871) pages 216–217
- ↑ D'Souza, Dinesh "Is Racism a Western Idea?" pages 517–539 from The American Scholar, Vol. 64, No. 4 Autumn 1995, p.538
- ↑ A. J. Woodman, 2009, The Cambridge Companion to Tacitus, p. 294. (The Germanic race was also regarded by Gobineau as beautiful, honourable and destined to rule: 'cette illustre famille humaine, la plus noble'. While arya was originally an endonym used only by Indo-Iranians, "Aryan" became, partly because of the Essai a racial designation of a race, which Gobineau specified as 'la race germanique'.
- 1 2 Gustav Jahoda, Images of Savages: Ancients [sic] Roots of Modern Prejudice in Western Culture, 1999, p. 83
- ↑ Trautmann (1997)
- ↑ Walsh (2011)
- ↑ Jackson & Weidman 2005, p. 87
- ↑ Palmer, Douglas (2006). Prehistoric Past Revealed: The Four Billion Year History of Life on Earth. Berkeley: University of California Press. p. 43. ISBN 0-520-24827-9.
- ↑ Regal, Brian (2004). Human Evolution: A Guide to the Debates. Santa Barbara, Calif: ABC-CLIO. pp. 73–75. ISBN 1-85109-418-0.
- 1 2 David Hurst Thomas, Skull Wars: Kennewick Man, Archaeology, And The Battle For Native American Identity, 2001, pp. 38–41
- ↑ Michael, J.S. (1988). "A New Look at Morton's Craniological Research". Current Anthropology. 29 (2): 349–354. doi:10.1086/203646.
- ↑ Lewis, Jason E.; Degusta, David; Meyer, Marc R.; Monge, Janet M.; Mann, Alan E.; Holloway, Ralph L. (2011). "The Mismeasure of Science: Stephen Jay Gould versus Samuel George Morton on Skulls and Bias". PLoS Biology. 9 (6): e1001071+. PMC 3110184
 . PMID 21666803. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1001071. Retrieved 2011-06-08.
. PMID 21666803. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1001071. Retrieved 2011-06-08. - ↑ Ericka Beckman Imperial Impersonations: Chilean Racism and the War of the Pacific University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
- ↑ Palacios, Nicolás (1918), Raza Chilena (in Spanish), Editorial Chilena
- ↑ See Pierre-André Taguieff, La couleur et le sang — Doctrines racistes à la française ("Colour and Blood — Racist doctrines à la française"), Paris, Mille et une nuits, 2002, 203 pages, and La Force du préjugé — Essai sur le racisme et ses doubles, Tel Gallimard, La Découverte, 1987, 644 pages
- 1 2 Efron 1994
- 1 2 Richard Bodek. "Review of John M. Efron, Defenders of the Race: Jewish Doctors & Race Science in Fin-de-Siècle Europe", H-SAE, H-Net Reviews, May, 1996 (in English)
- ↑ Hoffman, Matthew (January 2005). "From Pintele Yid to Racenjude: Chaim Zhitlovsky and Racial Conceptions of Jewishness". Jewish History. 19 (1): 65–78. doi:10.1007/s10835-005-4358-7.
- ↑ Alexander Thomas and Samuell Sillen (1972). Racism and Psychiatry. New York: Carol Publishing Group.
- ↑ Samual A. Cartwright, "Diseases and Peculiarities of the Negro Race", DeBow's Review—Southern and Western States, Volume XI, New Orleans, 1851
- ↑ Higgins, 1994
- ↑ See also the article + references for John Wingate Thornton
- 1 2 3 Dubow, Saul (1995). Scientific Racism in Modern South Africa. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-47907-X.
- 1 2 3 4 Füredi, Frank (1998). The Silent War: Imperialism and the Changing Perception of Race. New Brunswick, N.J: Rutgers University Press. pp. 66–67. ISBN 0-8135-2612-4.
- 1 2 Slater, David; Taylor, Peter J. (1999). The American Century: Consensus and Coercion in the Projection of American Power. Oxford: Blackwell. p. 290. ISBN 0-631-21222-1.
- ↑ Verbeek, Jennifer (1986). "Racially Segregated School Libraries in KwaZulu/Natal, South Africa". Journal of Librarianship and Information Science. 18 (1): 23–46. doi:10.1177/096100068601800102.
- ↑ Stoler, Ann Laura (2006). Haunted by Empire: Geographies of Intimacy in North American History. Durham, N.C: Duke University Press. p. 66. ISBN 0-8223-3724-X.
- ↑ Kühl 1994
- ↑ Richards 1997
- ↑ Shultz & Shultz 2008, pp. 233,236
- ↑ Gould 1981
- ↑ Shultz & Shultz 2008, p. 237
- ↑ Davis, Bernard (1983). "Neo-Lysenkoism, IQ and the Press". The Public Interest. 74 (2): 45.
- ↑ American Psychologist 1996
- ↑ Gould, S. J. The Mismeasure of Man. W. W. Norton & Company. ISBN 978-0-393-31425-0.
- ↑ Snyderman, M.; Herrnstein, R.J. (1983). "Intelligence Tests and the Immigration Act of 1924". American Psychologist. 38 (9): 986–95. doi:10.1037/0003-066x.38.9.986.
- ↑ Franco, J.N. (1985). "Intelligence tests and social policy". Journal of Counseling and Development. 64 (4): 278–9. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6676.1985.tb01101.x.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "En meningslös sortering av människor". Forskning & Framsteg. Retrieved 2016-11-07.
- ↑ Björkman, Maria; Widmalm, Sven (2010-12-20). "Selling eugenics: the case of Sweden". Notes and Records of the Royal Society. 64 (4): 379–400. ISSN 0035-9149. PMID 21553636. doi:10.1098/rsnr.2010.0009.
- ↑ Ambrosiani, Aron (2009). Rektor Lennmalms förslag — Om 1918–1921 års diskussioner kring ett Nobelinstitut i rasbiologi vid Karolinska institutet. (PDF). NOBEL MUSEUM OCCASIONAL PAPERS. p. 4.
- ↑ "Kapitel 3: Rasbiologin i Sverige". Forum för levande historia. Retrieved 2016-11-07.
- 1 2 "Rasbiologiska institutet - Uppsala universitetsbibliotek - Uppsala universitet". ub.uu.se. Retrieved 2016-11-07.
- ↑ Smith, Justin E. H., (2015). Nature, Human Nature, and Human Difference. Princeton University Press. pp. 10–15. ISBN 9781400866311.
- ↑ "Women Who May Not Be Allowed to become Mothers"
- ↑ Koonz, Claudia (2003). The Nazi Conscience. Harvard University Press. p. 119. ISBN 978-0-674-01172-4.
- ↑ Lynn H. Nicholas (2006). Cruel World: The Children of Europe in the Nazi Web. Vintage. p. 6. ISBN 978-0-679-77663-5.
- ↑ Operation Barbarossa: Ideology and Ethics against Human Dignity, by André Mineau, (Rodopi, 2004) page 180
- ↑ The Structure & Measurement of Intelligence, Hans Jürgen Eysenck and David W. Fulker, Transaction Publishers, 1979, page 16.
- 1 2 John P. Jackson & Nadine M. Weidman, Race, Racism, and Science: Social Impact and Interaction (Rutgers University Press, 2006), p. 119.
- ↑ Juliet Hooker, Theorizing Race in the Americas: Douglass, Sarmiento, Du Bois, and Vasconcelos (Oxford University Press, 2017), pp. 9-10.
- ↑ Christa Wirth, Memories of Belonging: Descendants of Italian Migrants to the United States, 1884-Present (Brill Publishers, 2015), pp. 190 & 198.
- 1 2 Sarat, Austin (1997). Race, Law, and Culture: Reflections on Brown v. Board of Education. Oxford [Oxfordshire]: Oxford University Press. pp. 55, 59. ISBN 0-19-510622-9.
- ↑ E.g., Arvidsson, Stefan (2006), Aryan Idols: Indo-European Mythology as Ideology and Science, translated by Sonia Wichmann, Chicago and London: The University of Chicago Press.
- ↑ Schaffer 2007, pp. 253–278
- ↑ Jackson, John; McCarthy, John P. Jr (2005). Science for Segregation: Race, Law, and the Case against Brown v. Board of Education. New York: New York University Press. p. 148. ISBN 0-8147-4271-8.
- ↑ Ferguson, G. O. (April 1916). "The Psychology of the Negro". Archives of Psychology. 36: 125.
- ↑ Haley, Alex (April 1966). "Interview: George Lincoln Rockwell". Playboy.
- ↑ Banton. Michael (2008). "Race, Unesco statements on". In Schaefer, Richard T. Encyclopedia of Race, Ethnicity and Society. Sage. p. 1096; 1098. ISBN 978-1-4129-2694-2.
- ↑
- ↑ Purpel, David E.; Shapiro, H. A. (2005). Critical Social Issues in American Education: Democracy and Meaning in a Globalizing World. Hillsdale, N.J: L. Erlbaum Associates. p. 228. ISBN 0-8058-4452-X.
- ↑ Rushton, J. Philippe; Jensen, Arthur R. (2005). "Wanted: More race realism, less moralistic fallacy.". Psychology, Public Policy, and Law. 11 (2): 328–336. doi:10.1037/1076-8971.11.2.328.
Bibliography
- Asséo, Henriette; Fings, Karola; Sparing, Frank; Kenrick, Donald; Heuss, Herbert (1997). From "race science" to the camps. The Gypsies During the Second World War. 1. Hatfield: University of Hertfordshire Press. ISBN 0-900458-78-X.
- Barkan, Elazar (1992). The Retreat of Scientific Racism: Changing Concepts of Race in Britain and the United States between the World Wars. New York: Cambridge University Press.
- Biddiss, Michael D. (1970). Father of Racist Ideology: The Social and Political Thought of Count Gobineau. New York: Weybright and Talley.
- Dennis, Rutledge M. (1995). "Social Darwinism, scientific racism, and the metaphysics of race". Journal of Negro Education. 64 (3): 243–52. JSTOR 2967206. doi:10.2307/2967206.
- Detterman, Douglas K. 2006. "Intelligence." Microsoft Student 2007 DVD. Redmond, WA: Microsoft Corporation.
- Efron, John M. (1994). Defenders of the race: Jewish doctors and race science in fin-de-siècle Europe. New Haven CT: Yale University Press. ISBN 0-300-05440-8.
- Ehrenreich, Eric (2007). The Nazi ancestral proof: genealogy, racial science, and the final solution. Bloomington: Indiana University Press. ISBN 0-253-34945-1.
- Ewen, Stuart; Ewen, Elizabeth (2007). Typecasting: On the Arts and Sciences of Human Inequality. New York: Seven Stories Press. ISBN 1-58322-776-8.
- Gould, Stephen Jay (1981). The Mismeasure of Man. New York: Norton.
- Levitt, N.; Gross, Paul F. (1994). Higher Superstition: The Academic Left and Its Quarrels With Science. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 0-8018-4766-4.
- Higgins, A.C. n.d. "Scientific Racism: A Review of The Science and Politics of Racial Research by William H. Tucker". Chicago: University of Illinois Press, 1994. Accessed 21 October 2007.
- Isaac, Benjamin H. (2004). The Invention of Racism in Classical Antiquity. Princeton NJ: Princeton University Press.
- Mintz, Frank P (1985). The Liberty Lobby and the American Right: Race, Conspiracy, and Culture. Westport CT: Greenwood.
- Kühl, Stefan (1994). The Nazi Connection: Eugenics, American Racism, and German National Socialism. New York NY: Oxford University Press.
- Lombardo, Paul A. (2002). "'The American Breed': Nazi Eugenics and the Origins of the Pioneer Fund". Albany Law Review. 65 (3): 743–830. PMID 11998853.
- Murray, Charles (September 2005). "The Inequality Taboo". Commentary Magazine.
- Poliakov, Leon (1974). Aryan Myth: A History of Racist and Nationalist Ideas in Europe. New York NY: Basic Books.
- Proctor, Robert N. (1988). Racial Hygiene: Medicine under the Nazis. Cambridge MA: Harvard University Press.
- Sapp, Jan (1987). Beyond the gene: cytoplasmic inheritance and the struggle for authority in genetics. Oxford [Oxfordshire]: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-504206-9.
- Schaffer, Gavin (2007). ""'Scientific' Racism Again?": Reginald Gates, the Mankind Quarterly and the Question of "Race" in Science after the Second World War". Journal of American Studies. 41 (2): 253–278. doi:10.1017/S0021875807003477.
- Taguieff, Pierre-André (1987). La Force du préjugé. Essai sur le racisme et ses doubles (in French). Paris: Gallimard, La Découverte. ISBN 2-07-071977-4.
- Tucker, William H. (2007). The funding of Scientific Racism: Wickliffe Draper and the Pioneer Fund. University of Illinois Press. ISBN 978-0-252-07463-9. Lay summary (4 September 2010).
- UNESCO. 1950. The Race Question.
- Jackson, J. (2004). "Racially stuffed shirts and other enemies of mankind: Horace Mann Bond's parody of segregationist psychology in the 1950s". In Winston, A. Defining difference: Race and Racism in the History of Psychology. Washington DC: American Psychological Association. pp. 261–283.
- Neisser, U.; Boodoo, G.; Bouchard, T.J. Jr.; Boykin, A.W.; Brody, N.; Ceci, S.J.; et al. (1996). "Intelligence: Knowns and unknowns" (PDF). American Psychologist. 51 (2): 77–101. doi:10.1037/0003-066X.51.2.77.
- Richards, G. (1997). Race, Racism, and Psychology: Towards a Reflexive History. New York: Routledge.
- Shultz, D.P.; Shultz, S.E. (2008). A History of Modern Psychology (9th ed.). Belmont CA: Thomson Higher Education.
- Trautmann, Thomas R. (1997), Aryans and British India, Vistaar
- Tucker, W.H. (1994). The Science and Politics of Racial Research. Urbana: University of Illinois Press.
- Walsh, Judith E. (2011), A Brief History of India, Facts On File, ISBN 978-0-8160-8143-1
Further reading
- Redman, Samuel J. (2016). Bone Rooms: From Scientific Racism to Human Prehistory in Museums. Harvard University Press. ISBN 9780674660410.
- Spiro, Jonathan P. (2009). Defending the Master Race: Conservation, Eugenics, and the Legacy of Madison Grant. University of Vermont Press. ISBN 978-1-58465-715-6. Lay summary (29 September 2010).
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Scientific racism. |
- Links to scholarly websites about "race science" by Nizkor Project
- The Problem of Human Diversity in the European Cultural Experience of the Eighteenth Century (Trieste, 14–15 February 2002)
- The Mis-portrayal of Darwin as a Racist — Refutes claims that Darwin was a racist or that his views inspired the Nazis
- Purves D; Augustine GJ; Fitzpatrick D; et al., eds. (2001). "Box D. Brain Size and Intelligence". Neuroscience (2nd ed.). Sunderland MA: Sinauer Associates.
- Reviews of Race: The Reality of Human Differences
- RaceSci.org: History of Race in Science
- Gardner, Dan. Race Science: When Racial Categories Make No Sense. The Globe and Mail, October 27, 1995.
- Institute for the study of academic racism (ISAR)
- Race, Science, and Social Policy. From Race: The Power of an Illusion. PBS.
- Arthur Hu's Index of Diversity
- Kenan Malik discusses race and intelligence
