RPO-A Shmel
| RPO-A Shmel | |
|---|---|
|
RPO-Shmel and Launcher | |
| Type | Rocket launcher |
| Place of origin | Soviet Union |
| Service history | |
| In service | Late 1980s |
| Used by | See Operators |
| Wars | See Service history |
| Production history | |
| Designer | KBP |
| Designed | 1980s |
| Manufacturer | KBP |
| Produced | Late 1980s |
| Variants | RPO-A, RPO-Z, RPO-D, Shmel-M, MRO, MGK Bur |
| Specifications | |
| Weight | 11 kg (24 lb) |
| Length |
Launcher: 920 mm Rocket: 700mm |
|
| |
| Caliber | 93 mm |
| Muzzle velocity | 125 ±5 m/s |
| Effective firing range |
20 m – 1000 m (sighting range is 600 m) RPO-M is 1700 m (sighting range is 800 m) |
| Sights | iron |
The RPO-A Shmel (Russian: реактивный пехотный огнемёт-А Шмель (РПО-А Шмель), Rocket-propelled Infantry Flamethrower-A Bumblebee) is a man-portable rocket launcher, although it is classified as a flamethrower by its manufacturer KBP.
The Shmel is designed, produced and exported by the Russian Federation and previously by the Soviet Union. It entered service with the Soviet Armed Forces at the end of the 1980s as the successor for the RPO Rys.
Description
The RPO-A is a single-shot, self-contained tube shaped launcher that operates much like some RPG and LAW rocket launchers. The launcher is a sealed tube, carried in a man-pack in pairs. The same person can remove the tube, place it in firing position, and launch the weapon without assistance. After launch, the tube is discarded. All models are externally similar.
Ammunition
Each weapon contains a single rocket, of which there are three varieties. The basic rocket is the RPO-A, which has a thermobaric warhead and is designed for attacking soft targets under moderate cover. The RPO-Z is the incendiary warhead (Rus. зажигательный / Zazhigatel'nyy, Incendiary) designed to spread fire and ignite targets. There is a smoke-producing warhead (Rus. дымовой / Dymovoy, Smoke) offered, the RPO-D.
Specifications

Specifications provided by Jane's:[1]
- Calibre: 93 mm
- Length:
- Launcher: 920 mm
- Rocket: 700 mm
- Weight:
- Single weapon: 11 kg
- Transit pack of two: 22 kg
- Range:
- Minimum: 20 m
- Effective: 200 m
- Sighting: 600 m
- Maximum: 1,000 m
- Initial velocity: 125 ±5 m/s
- Warhead:
- RPO-A: 2.1 kg thermobaric
- RPO-Z: 2.1 kg incendiary
- RPO-D: 2.3 kg smoke
- Operational temperature range: −50 to +50 °C
- Shelf life: 10 years
Variants

An updated development is the improved RPO-M "Shmel-M" that was shown for the first time at Eurosatory 2006. This version is similar to the original weapon, but has a calibre of 90 mm, a weight of 8.8 kg (19 lb), and an overall length of 940 mm. The system has better ergonomics, an improved rocket, and better ballistics and terminal effects. It consists of a disposable launching tube attached to a reusable fire control unit that includes the pistol grip, electronic trigger and safety, and a folding base with an optical sight and additional rail for an infrared/night vision sight. Effective range is 300 m, maximum sighting range is 800 m, and maximum range is 1,700 m. The thermobaric warhead's blast effect is equivalent to 5.5 kg (12 lb) of TNT, comparable to a 155 mm artillery shell. The "Shmel-M" is also known as RPO PDM-A (Rus. Повышенной Дальности и Мощности / Povyshennoy Dal'nosti i Moshchnosti — "enhanced range and lethality") and is produced for the local and export markets. Version with a mechanical sight adopted on 24 December 2003.[2][3][4][5][6]
The MRO-A is a smaller development of the RPO-series with caliber reduced to 72.5 mm, similar to the RShG-2. It is self-contained, disposable, single-shot recoilless launcher with an overall length of 900 mm, weight of 4.7 kg (10 lb), and has a folding forward grip. The sights are RPO-based, with a fixed front and folding ladder-type diopter rear, giving an effective range of 90 m and maximum range of 450 m. The MRO-series includes different versions, again based on RPO versions: MRO-A thermobaric; MRO-D white phosphorus smoke; and MRO-Z incendiary. It was adopted by the Russian Army around 2002 and issued to chemical troops to supplement the larger RPO-A.[7][8][9][10]
MGK Bur (Rus. Малогабаритный Гранатомётный Комплекс "Бур" / Malogabaritnyy Granatomotnyy Kompleks "Bur" — Compact Grenade-launching System "Auger") is a 62 mm version of the RPO-M consisting of two major components: the disposable launch tube and reusable fire control unit. Described as "the most compact grenade launcher in the world," the weapon has an overall length of 742 mm and weighs 5 kg (11 lb). Loaded tubes weigh 3.5 kg (7.7 lb) and can fire thermobaric (blast yield similar to 6 kg (13 lb) of TNT, or a 122 mm artillery rocket) or fragmentation warheads. The fire control unit is the same one used on the RPO-M, weighing 1.5 kg (3.3 lb) and enabling ranges of 25–650 m with the baseline day sight; night and thermal systems are also available. Maximum range is 950 meters, with a firing mechanism service life of at least 500 rounds. It can be fired in confined spaces with a volume of at least 30 cubic meters. As of October 2014, it has been accepted into service and serial production has been started.[11][12][13][14][15][16]
Service history
RPO weapons have seen use by the Soviet Army in Afghanistan and by both the Russian and the separatist forces in the First and Second Chechen Wars. According to state Duma member Yuri Savelyev the first explosion prior to the exchange of gun-fire during the Beslan school siege on 1 September 2004 was most likely a thermobaric RPO-A Shmel. On 9 August 2014, during the Donbass War, the Ukrainian border checkpoint of Milove was attacked using RPO flamethrowers. The main building was hit by five incendiary rockets.[17] It was used by Indian Army para-commandos in September 2016 for surgical strike against terrorists in Pakistan Occupied Kashmir successfully. Also used on 8 February 2017 in Ukraine, killing DPR commander Mikhail "Givi" Tolstykh.[18]
Operators
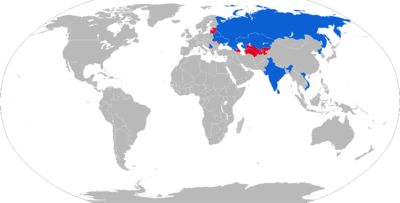
Current operators
Former operators
See also
- FHJ 84 — an over/under two-shot variant from China
- M202A1 FLASH — a similar weapon developed by the US Army
- List of Russian weaponry
References
- ↑ Gander, Terry (2001-01-05). "RPO-A Shmel rocket infantry flame-thrower". Land Forces. Jane's. Archived from the original on July 9, 2006.
- ↑ http://kbptula.ru/eng/atgw/shmelm.htm Archived March 27, 2010, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "Modern Firearms". Retrieved 26 November 2014.
- ↑ David Crane (19 July 2006). "New RPO Shmel-M Infantry Rocket Flamethrower Man-Packable Thermobaric Weapon". DefenseReview.com (DR): An online tactical technology and military defense technology magazine with particular focus on the latest and greatest tactical firearms news (tactical gun news), tactical gear news and tactical shooting news. Retrieved 26 November 2014.
- ↑ "Rocket Flamethrower Shmel-M (Огнемет Шмель-М)". YouTube. Retrieved 26 November 2014.
- ↑ "ОАО "Конструкторское бюро приборостроения" - РПО ПДМ-А Шмель-М". Retrieved 26 November 2014.
- ↑ MRO-A small disposable thermbaric grenade launcher /rocket propelled flame-thrower (Russia) - Modernfirearms.net
- ↑ Russian MRO-A Rocket Launchers in Ukraine - Armamentresearch.com, 1 June 2014
- ↑ Russian MRO-A thermobaric rocket launchers in Syria - Armamentresearch.com, 30 October 2015
- ↑ Russian MRO-A Rocket Launchers in the Ukraine - SAdefensejournal.com, 1 January 2016
- ↑ (in English) http://kbptula.ru/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=309&Itemid=653&lang=en#spoiler_0
- ↑ "Впервые на IDEX-2013 КБП рекламирует многоцелевой ракетный комплекс дальнего действия «Корнет-ЭМ»". ЦАМТО (in Russian). Moscow: Centre for Analysis of World Arms Trade. 18 February 2013. Retrieved 25 March 2013.
- ↑ "ТАСС: Армия и ОПК - В Туле налажен серийный выпуск гранатометов "Бур"". ТАСС. Retrieved 26 November 2014.
- ↑ BUR grenade launcher - Modernfirearms.net
- ↑ Small-size grenade launcher in production - Janes.com, 6 November 2014
- ↑ Bur small-sized grenade launcher entered in service with Russian anti-terrorist units - Armyrecognition.com, 29 June 2016
- ↑ "Погранзаставу в Меловом обстреляли из огнеметов с территории РФ". Liga News. 9 August 2014.
- ↑ "Separatist commander Mikhail Tolstykh, 'Givi', killed in eastern Ukraine". CBCNews. Retrieved 3 April 2017.
- ↑ ":: Rosyjska broń dla Fidżi" (in Polish). altair.pl. Retrieved 2016-02-21.
- ↑ "Armament of the Georgian Army". Georgian Army. Retrieved 2007-06-25.
- ↑ https://twitter.com/green_lemonnn/status/677294880771719168
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AayuHEMfz1A?t=157
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Shmel. |
