Quinazolinone
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Quinazolin-4(3H)-one | |
| Other names
4(3H)-Quinazolinone; 4(1H)-Quinazolinone; 3,4-Dihydroquinazolin-4-one; 4(3H)-Quinazolone; 4-Hydroxyquinazoline; 4-Oxo-3,4-dihydroquinazoline; 4-Oxoquinazoline; 4-Quinazolinol; 4-Quinazolinone; 4-Quinazolone | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H6N2O | |
| Molar mass | 146.15 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Quinazolinone is a heterocyclic chemical compound. There are two structural isomers, 2-quinazolinone and 4-quinazolinone, with the 4-isomer being the more common.
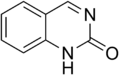 2-Quinazolinone
2-Quinazolinone 4-Quinazolinone
4-Quinazolinone
Derivatives
Jafari et al.[1] state that "One of the most important [groups of] heterocycles in medicinal chemistry are quinazolines[,] possessing [a] wide spectrum of biological properties like antibacterial, antifungal, anticonvulsant, anti-inflammatory, anti-HIV, anticancerous and analgesic activities. This skeleton is an important pharmacophore considered as a privileged structure."[1] Their review discusses quinazolines and quinazolinone derivatives with antimicrobial and cytotoxic activities.[1]
Quinazolinone drugs that function as hypnotic/sedatives usually contain a 4-quinazolinone core. The 4-Q isomer type, has also been proposed in the treatment of cancer.[2]
See also
- Idelalisib (Zydelig)
- Methaqualone (Quaalude)
References
- 1 2 3 Jafari, E; et al. (2016), "Quinazolinone and quinazoline derivatives: recent structures with potent antimicrobial and cytotoxic activities", Res Pharm Sci, 11 (1): 1–14, PMC 4794932
 , PMID 27051427.
, PMID 27051427. - ↑ Chen K, Wang K, Kirichian AM, et al. (December 2006). "In silico design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of radioiodinated quinazolinone derivatives for alkaline phosphatase-mediated cancer diagnosis and therapy". Mol. Cancer Ther. 5 (12): 3001–13. PMID 17172404. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0465.