Pygmy sperm whale
| Pygmy sperm whale[1] | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Illustration from the 19th century | |
 | |
| Size compared to an average human | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Synapsida |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Artiodactyla |
| Infraorder: | Cetacea |
| Family: | Kogiidae |
| Genus: | Kogia |
| Species: | K. breviceps |
| Binomial name | |
| Kogia breviceps Blainville, 1838 | |
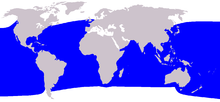 | |
| Pygmy sperm whale range | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Euphysetes breviceps | |
The pygmy sperm whale (Kogia breviceps) is one of three species of toothed whale in the sperm whale family. They are not often sighted at sea, and most of what is known about them comes from the examination of stranded specimens.
Taxonomy
Debate exists as to the correct classification of the pygmy and dwarf sperm whales (see sperm whale family for details). The two were widely considered to be the same species, until 1966, when a scientist at the Smithsonian Institution definitively identified them as separate species.[3] The pygmy sperm whale was first named by Henri Marie Ducrotay de Blainville in 1838.[4]
Description
The pygmy sperm whale is not much larger than many dolphins. They are about 1.2 m (3 ft 11 in) at birth, growing to about 3.5 m (11 ft) at maturity. Adults weigh about 400 kg (880 lb). The underside is a creamy, occasionally pinkish colour and the back and sides are a bluish grey; however, considerable intermixing occurs between the two colours. The shark-like head is large in comparison to body size, given an almost swollen appearance when viewed from the side. A whitish marking, often described as a "false gill", is seen behind each eye.[5][6]

The lower jaw is very small and slung low. The blowhole is displaced slightly to the left when viewed from above facing forward. The dorsal fin is very small and hooked; its size is considerably smaller than that of the dwarf sperm whale and may be used for diagnostic purposes.
Anatomy
Like its giant relative, the sperm whale, the pygmy sperm whale has a spermaceti organ in its forehead (see sperm whale for a discussion of its purpose). It also has a sac in its intestines that contains a dark red fluid. The whale may expel this fluid when frightened, perhaps to confuse and disorient predators.[7]
Pygmy sperm whales have from 50 to 55 vertebrae, and from 12 to 14 ribs on either side, although the latter are not necessarily symmetrical, and the hindmost ribs do not connect with the vertebral column. Each of the flippers has seven carpals, and a variable number of phalanges in the digits, reportedly ranging from two in the first digit to as many as 10 in the second digit. No true innominate bone exists; it is replaced by a sheet of dense connective tissue. The hyoid bone is unusually large, and presumably has a role in the whale's suction feeding.[6]
Teeth
The pygmy sperm has between 20 and 32 teeth, all of which are set into the rostral part of the lower jaw.[8] Unusually, adults lack enamel due to a mutation in the enamelysin gene,[9] although enamel is present in very young individuals.[6]

Melon

Like other toothed whales, the pygmy sperm whale has a "melon", a body of fat and wax in the head that it uses to focus and modulate the sounds it makes.[10] The inner core of the melon has a higher wax content than the outer cortex. The inner core transmits sound more slowly than the outer layer, allowing it to refract sound into a highly directional beam.[11] Behind the melon, separated by a thin membrane, is the spermaceti organ. Both the melon and the spermaceti organ are encased in a thick fibrous coat, resembling a bursa.[12] The whale produces sound by moving air through the right nasal cavity, which includes a valvular structure, or museau de singe, with a thickened vocal reed, functioning like the vocal cords of humans.
Note that the view pictured on the right is an axial view, not coronal as noted
Stomach
The stomach has three chambers. The first chamber, or forestomach, is not glandular, and opens directly into the second, fundic chamber, which is lined by digestive glands. A narrow tube runs from the second to the third, or pyloric, stomach, which is also glandular, and connects, via a sphincter, to the duodenum. Although fermentation of food material apparently occurs in the small intestine, no caecum is present.[13]
Brain
The rostroventral dura of the brain contains a significant concentration of magnetite crystals, which suggests that K. breviceps can navigate by magnetoreception.[6]
Echolocation
Like all toothed whales, the pygmy sperm whale hunts prey by echolocation. The frequencies it uses are mostly ultrasonic,[11] peaking around 125 kHz.[14]
Reproduction
Although firm details concerning pygmy sperm whale reproduction are limited, they are believed to mate from April to September in the southern hemisphere.[6] Gestation lasts eleven months and, unusually for cetaceans, the female gives birth to the calf head-first.[15] Newborn calves are about 1.2 metres (3 ft 11 in) in length, and are weaned at around one year of age.[6]
Behaviour
The whale makes very inconspicuous movements. It rises to the surface slowly, with little splash or blow, and remains there motionless for some time. In Japan, the whale was historically known as the "floating whale" because of this. Its dive is equally lacking in grand flourish - it simply drops out of view. The species has a tendency to back away from rather than approach boats. Breaching has been observed, but is not common.
Pygmy sperm whales are normally either solitary, or found in pairs,[16] but have been seen in groups up to six. Dives have been estimated to last an average of 11 minutes, although longer dives up to 45 minutes have been reported.[6] The ultrasonic clicks of pygmy sperm whales range from 60 to 200 kHz, peaking at 125 kHz,[14] and the animals also make much lower-frequency "cries" at 1 to 2 kHz.[17]
Analysis of stomach contents suggests that pygmy sperm whales feed primarily on cephalopods, most commonly including bioluminescent species found in midwater environments. The most common prey are reported to include glass squid, and lycoteuthid and ommastrephid squid, although the whales also consume other squid, and octopuses. They have also been reported to eat some deep-sea shrimps, but, compared with dwarf sperm whales, relatively few fish.[6]
Predators may include great white sharks[18] and killer whales.[19]
Pygmy sperm whales and dwarf sperm whales are unique among cetaceans in using a form of "ink" to evade predation in a manner similar to squid. Both species have a sac in the lower portion of their intestinal tract that contains up to 12 l of dark reddish-brown fluid, which can be ejected to confuse or discourage potential predators.[20]
Population and distribution
Pygmy sperm whales are found throughout the tropical and temperate waters of the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian Oceans.[6] However, they are rarely sighted at sea, so most data come from stranded animals - making a precise range and migration map difficult. They are believed to prefer off-shore waters, and are most frequently sighted in waters ranging from 400 to 1,000 m (1,300 to 3,300 ft) in depth, especially where upwelling water produces local concentrations of zooplankton and animal prey.[21] Their status is usually described as rare, but occasional patches of higher density of strandings suggest it may be rather more common than previously supposed. The total population is unknown.
Fossils identified as belonging to K. breviceps have been recovered from Miocene deposits in Italy, as well as from Japan and southern Africa.[6]
Human interaction
Pygmy sperm whales have never been hunted on a wide scale. Land-based whalers have hunted them from Indonesia, Japan, and the Lesser Antilles. Individuals have also been recorded killed in drift nets. Some stranded animals have been found with plastic bags in their stomachs - which may be a cause for concern. It is not known whether these activities are causing long-term damage to the survival of the species.
Pygmy sperm whales do not do well in captivity.[22][23] The longest recorded survival in captivity is 21 months, and most captive individuals die within one month, mostly due to dehydration or dietary problems.[24]
Conservation
The pygmy sperm whale is covered by the Agreement on the Conservation of Small Cetaceans of the Baltic, North East Atlantic, Irish and North Seas (ASCOBANS)[25] and the Agreement on the Conservation of Cetaceans in the Black Sea, Mediterranean Sea and Contiguous Atlantic Area (ACCOBAMS).[26] The species is further included in the Memorandum of Understanding Concerning the Conservation of the Manatee and Small Cetaceans of Western Africa and Macaronesia (Western African Aquatic Mammals MoU)[27] and the Memorandum of Understanding for the Conservation of Cetaceans and Their Habitats in the Pacific Islands Region (Pacific Cetaceans MoU).[28]
Specimens
- MNZ MM002651, collected Hawke's Bay, New Zealand, no date data.
See also
Footnotes
References
- ↑ Mead, J.G.; Brownell, R. L. Jr. (2005). "Order Cetacea". In Wilson, D.E.; Reeder, D.M. Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 737. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.
- ↑ Taylor, B.L.; Baird, R.; Barlow, J.; Dawson, S.M.; Ford, J.K.B.; Mead, J.G.; Notarbartolo di Sciara, G.; Wade, P.; Pitman, R.L. (2012). "Kogia breviceps". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2014.3. International Union for Conservation of Nature. Retrieved 2015-01-11.
- ↑ Handley, C. O. Jr. 1966. A synopsis of the genus Kogia (pygmy sperm whales). pp. 62-69 In: K. S. Norris (ed.), Whales, dolphins and porpoises. University of California Press, Berkeley
- ↑ "Kogia breviceps (de Blainville, 1838)". Collections Online. Museum of New Zealand Te Papa Tongarewa. Retrieved 17 July 2010.
- ↑ Roest, A.I. (1970). "Kogia simus and other cetaceans from San Luis Obispo County, California". Journal of Mammalogy. 51 (2): 410–417. JSTOR 1378507. doi:10.2307/1378507.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Bloodworth, B.E. & Odell, D.K. (2008). "Kogia breviceps (Cetacea: Kogiidae)". Mammalian Species. 819: Number 819: pp. 1–12. doi:10.1644/819.1.
- ↑ Scott, M.D. & Cordaro, J.G. (1987). "Behavioral observations of the dwarf sperm whale, Kogia simus". Marine Mammal Science. 3 (4): 353–354. doi:10.1111/j.1748-7692.1987.tb00322.x.
- ↑ Bloodworth Brian E., Odell Daniel K. (2008). "Kogia breviceps". Mammalian Species. 819: 1–12.
- ↑ http://rspb.royalsocietypublishing.org/content/278/1708/993.short?rss=1
- ↑ Clarke, M.R. (2003). "Production and control of sound by the small sperm whale, Kogia breviceps and K. sima and their implications for other Cetacea". Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom. 83 (2): 241–263. doi:10.1017/S0025315403007045h.
- 1 2 R., Karol; C., Litchfield; D., Caldwell; M., Caldwell (1978). Compositional topography of melon and spermaceti organ lipids in the pygmy sperm whale Kogia breviceps: Implications for echolocation. Marine Biology , Volume 47 (2)
- ↑ Cranford, T.W.; et al. (1996). "Functional morphology and homology in the odontocete nasal complex: implications for sound generation". Journal of Morphology. 228 (2): 223–285. PMID 8622183. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4687(199606)228:3<223::AID-JMOR1>3.0.CO;2-3.
- ↑ Hagey, L.R.; et al. (1993). "Biliary bile acid composition of the Physeteridae (sperm whales)". Marine Mammal Science. 9 (1): 23–33. doi:10.1111/j.1748-7692.1993.tb00423.x.
- 1 2 Marten, K. (2000). "Ultrasonic analysis of pygmy sperm whale (Kogia breviceps) and Hubbs' beaked whale (Mesoplodon carlhubbsi) clicks" (PDF). Aquatic Mammals. 26 (1): 45–48.
- ↑ Huckstadt, L.A. & Antezana, T. (2001). "An observation of parturition in a stranded Kogia breviceps". Marine Mammal Science. 17 (2): 362–365. doi:10.1111/j.1748-7692.2001.tb01277.x.
- ↑ Willis, P.M. & Baird, R.W. (1998). "Status of the dwarf sperm whale, Kogia simus, with special reference to Canada". Canadian Field Naturalist. 112 (1): 114–125.
- ↑ Thomas, J.A.; et al. (1990). "A new sound from a stranded pygmy sperm whale" (PDF). Aquatic Mammals. 16 (1): 28–30.
- ↑ Long, D.J. (1991). "Apparent predation by a white shark Carcharadon charcharias on a pygmy sperm whale Kogia breviceps" (PDF). Fishery Bulletin. 89 (3): 538–540.
- ↑ Dunphy-Daly, M.M.; et al. (2008). "Temporal variation in dwarf sperm whale (Kogia sima) habitat use and group size off Great Abaco Island, Bahamas". Marine Mammal Science. 24 (1): 171–182. doi:10.1111/j.1748-7692.2007.00183.x.
- ↑ "Pygmy sperm whale (Kogia breviceps)". NOAA Fisheries Office of Protected Resources web site. NOAA. 2014-10-20. Archived from the original on 2013-10-03. Retrieved 2015-01-11.
- ↑ Davis, R.W.; et al. (1998). "Physical habitat of cetaceans along the continental slope in the north-central and western Gulf of Mexico". Marine Mammal Science. 14 (3): 490–607. doi:10.1111/j.1748-7692.1998.tb00738.x.
- ↑ Loranger, Linda. "Pygmy Sperm Whale Dies In Mystic After Record Time In Captivity". Hartford Courant. Retrieved 3 December 1991. Check date values in:
|access-date=(help) - ↑ Klingener, Nancy. "Pygmy Whale Snags Fence, Dies After Four Months In Captivity". Sun Sentinel. Retrieved 2 September 2000. Check date values in:
|access-date=(help) - ↑ Manire, C.A.; et al. (2004). "An approach to the rehabilitation of Kogia spp.". Aquatic Mammals. 30 (2): 257–270. doi:10.1578/AM.30.2.2004.257.
- ↑ Official website of the Agreement on the Conservation of Small Cetaceans of the Baltic, North East Atlantic, Irish and North Seas
- ↑ Official website of the Agreement on the Conservation of Cetaceans in the Black Sea, Mediterranean Sea and Contiguous Atlantic Area
- ↑ Memorandum of Understanding Concerning the Conservation of the Manatee and Small Cetaceans of Western Africa and Macaronesia
- ↑ Official webpage of the Memorandum of Understanding for the Conservation of Cetaceans and Their Habitats in the Pacific Islands Region
Further reading
- Pygmy and Dwarf Sperm Whales by Donald F. McAlpine in Encyclopedia of Marine Mammals pp. 1007–1009 ISBN 978-0-12-551340-1
- Whales Dolphins and Porpoises, Mark Carwardine, Dorling Kindersley Handbooks, ISBN 0-7513-2781-6
- National Audubon Society Guide to Marine Mammals of the World, Reeves, Stewart, Clapham and Powell, ISBN 0-375-41141-0
External links
| Wikispecies has information related to: Kogia breviceps |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Kogia breviceps. |
- UMMZ Skull photos
- Photo of skull
- Max Newman's Pygmy Sperm Whale Research Paper
- dolphin rescues Pygmy Sperm whales
- Arkive
- Voices in the Sea - Sounds of the Pygmy sperm Whale
