Provinces of China
| Provincial division 省份 Shěngfèn | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Category | Unitary State |
| Location | People's Republic of China (PRC) |
| Number | 34 (33 controlled by PRC & 1 controlled by ROC) |
| Populations | 552,300 (Macau) – 104,303,132 (Guangdong) |
| Areas | 31 km2 (12 sq mi) (Macau) – 730,000 km2 (280,000 sq mi) (Qinghai) |
| Government |
Dual-Party Government SARs: 1 country, 2 systems |
| Subdivisions | Sub-provincial city, Prefecture |
| Province-level administrative divisions | |||||||||
| Chinese name | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simplified Chinese | 省级行政区 | ||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 省級行政區 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Alternative Chinese name | |||||||||
| Chinese | 省 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Tibetan name | |||||||||
| Tibetan | ཞིང་ཆེན། | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Zhuang name | |||||||||
| Zhuang | Swngj | ||||||||
| Mongolian name | |||||||||
| Mongolian script | ᠮᠤᠵᠢ | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Uyghur name | |||||||||
| Uyghur |
ئۆلكە | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| This article is part of a series on |
| Administrative divisions of China |
|---|
|
Analogous county level units Management areas Management committee |
|
Townships
Subdistricts County-controlled districts (pilot) |
|
Analogous township level units Management areas Management committee Areas Farms area, Prison area, University towns etc. |
|
|
|
History: before 1912, 1912–49, 1949–present Administrative division codes |
Provinces (Chinese: 省; pinyin: Shěng), formally provincial-level administrative divisions (Chinese: 省级行政区; pinyin: Shěng Jí Xíngzhèngqū) or first-level administrative divisions (Chinese: 一级行政区; pinyin: Yī Jí Xíngzhèngqū), are the highest-level Chinese administrative divisions. There are 33 such divisions, classified as 22 provinces (not including Taiwan, which is claimed but not actually controlled by the People's Republic of China[1]), four municipalities, five autonomous regions, and two Special Administrative Regions.
The People's Republic of China (PRC) claims sovereignty over the territory administered by the Republic of China (ROC), claiming most of it as its Taiwan Province. The ROC also administers some offshore islands which form Fujian Province, ROC. These were part of an originally unified Fujian province, which since the stalemate of the Chinese Civil War in 1949 has been divided between the PRC and ROC.
Note that every province (except Hong Kong and Macau, the two special administrative regions) has a Communist Party of China provincial committee (Chinese: 省委; pinyin: shěng wěi), headed by a secretary (Chinese: 书记; pinyin: shūjì). The committee secretary is in effective charge of the province, rather than the nominal governor of the provincial government.
Province
The government of each standard province (Chinese: 省; pinyin: shěng) is nominally led by a provincial committee, headed by a secretary. The committee secretary is first-in-charge of the province; second-in-command is the governor of the provincial government.
The People's Republic of China claims the island of Taiwan and its surrounding islets, including Penghu, as "Taiwan Province". (Kinmen and the Matsu Islands are claimed by the PRC as part of its Fujian Province. Pratas and Itu Aba are claimed by the PRC as part of Guangdong and Hainan provinces respectively.) The territory is controlled by the Republic of China (ROC, commonly called "Taiwan").
Other types of province-level divisions
Municipality
A municipality (Chinese: 直辖市; pinyin: zhíxiáshì) or direct-controlled municipality is a higher level of city which is directly under the Chinese government, with status equal to that of the provinces. In practice, their political status is higher than that of common provinces.
Autonomous region
An autonomous region (simplified Chinese: 自治区; traditional Chinese: 自治區; pinyin: zìzhìqū) is a minority subject which has a higher population of a particular minority ethnic group along with its own local government, but an autonomous region theoretically has more legislative rights than in actual practice. The governor of each autonomous region is usually appointed from the respective minority ethnic group.
Special administrative region (SAR)
A special administrative region (SAR) (simplified Chinese: 特别行政区; traditional Chinese: 特別行政區; pinyin: tèbié xíngzhèngqū) is a highly autonomous and self-governing sub national subject of the People's Republic of China that is directly under the Central People's Government. Each SAR has a chief executive as head of the region and head of government. The region's government is not fully independent, as foreign policy and military defence are the responsibility of the central government, according to the basic laws.
List of province-level divisions
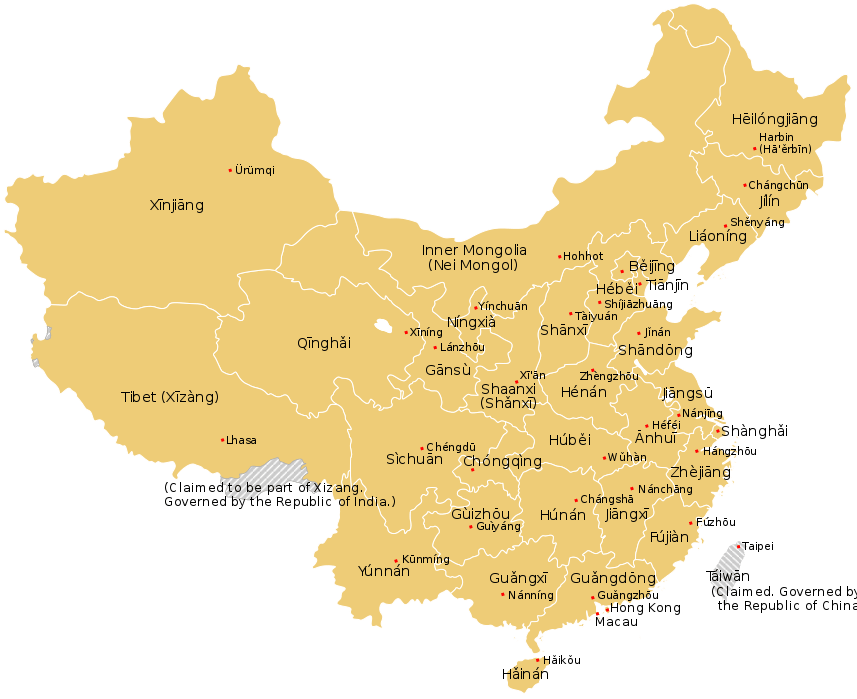
 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB/T 2260-2002[2] | ISO[3] | Province | Chinese Hanyu Pinyin |
Capital | Population[lower-alpha 1] | Density[lower-alpha 2] | Area[lower-alpha 3] | Abbreviation[lower-alpha 4] |
| BJ | CN-11 | Beijing Municipality | 北京市 Běijīng Shì |
Beijing | 19,612,368 | 1,167.40 | 16,800 | 京 Jīng |
| TJ | CN-12 | Tianjin Municipality | 天津市 Tiānjīn Shì |
Tianjin | 12,938,224 | 1,144.46 | 11,305 | 津 Jīn |
| HE | CN-13 | Hebei Province | 河北省 Héběi Shěng |
Shijiazhuang | 71,854,202 | 382.81 | 187,700 | 冀 Jì |
| SX | CN-14 | Shanxi Province | 山西省 Shānxī Shěng |
Taiyuan | 35,712,111 | 228.48 | 156,300 | 晋 Jìn |
| NM | CN-15 | Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region | 內蒙古自治区 Nèi Měnggǔ Zìzhìqū |
Hohhot | 24,706,321 | 20.88 | 1,183,000 | 內蒙古(蒙) Nèi Měnggǔ (Měng) |
| LN | CN-21 | Liaoning Province | 辽宁省 Liáoníng Shěng |
Shenyang | 43,746,323 | 299.83 | 145,900 | 辽 Liáo |
| JL | CN-22 | Jilin Province | 吉林省 Jílín Shěng |
Changchun | 27,462,297 | 146.54 | 187,400 | 吉 Jí |
| HL | CN-23 | Heilongjiang Province | 黑龙江省 Hēilóngjiāng Shěng |
Harbin | 38,312,224 | 84.38 | 454,000 | 黑 Hēi |
| SH | CN-31 | Shanghai Municipality | 上海市 Shànghǎi Shì |
Shanghai | 23,019,148 | 3,630.20 | 6,341 | 沪 Hù |
| JS | CN-32 | Jiangsu Province | 江苏省 Jiāngsū Shěng |
Nanjing | 78,659,903 | 766.66 | 102,600 | 苏 Sū |
| ZJ | CN-33 | Zhejiang Province | 浙江省 Zhèjiāng Shěng |
Hangzhou | 54,426,891 | 533.59 | 102,000 | 浙 Zhè |
| AH | CN-34 | Anhui Province | 安徽省 Ānhuī Shěng |
Hefei | 59,500,510 | 425.91 | 139,700 | 皖 Wǎn |
| FJ | CN-35 | Fujian Province | 福建省 Fújiàn Shěng |
Fuzhou | 36,894,216 | 304.15 | 121,300 | 闽 Mǐn |
| JX | CN-36 | Jiangxi Province | 江西省 Jiāngxī Shěng |
Nanchang | 44,567,475 | 266.87 | 167,000 | 赣 Gàn |
| SD | CN-37 | Shandong Province | 山东省 Shāndōng Shěng |
Jinan | 95,793,065 | 622.84 | 153,800 | 鲁 Lǔ |
| HA | CN-41 | Henan Province | 河南省 Hénán Shěng |
Zhengzhou | 94,023,567 | 563.01 | 167,000 | 豫 Yù |
| HB | CN-42 | Hubei Province | 湖北省 Húběi Shěng |
Wuhan | 57,237,740 | 307.89 | 185,900 | 鄂 È |
| HN | CN-43 | Hunan Province | 湖南省 Húnán Shěng |
Changsha | 65,683,722 | 312.77 | 210,000 | 湘 Xiāng |
| GD | CN-44 | Guangdong Province | 广东省 Guǎngdōng Shěng |
Guangzhou | 104,303,132 | 579.46 | 180,000 | 粤 Yuè |
| GX | CN-45 | Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region | 广西壮族自治区 Guǎngxī Zhuàngzú Zìzhìqū |
Nanning | 46,026,629 | 195.02 | 236,000 | 桂 Guì |
| HI | CN-46 | Hainan Province | 海南省 Hǎinán Shěng |
Haikou | 9,171,300[4] | 255.04 | 34,000 | 琼 Qióng |
| CQ | CN-50 | Chongqing Municipality | 重庆市 Chóngqìng Shì |
Chongqing | 28,846,170 | 350.50 | 82,300 | 渝 Yú |
| SC | CN-51 | Sichuan Province | 四川省 Sìchuān Shěng |
Chengdu | 80,418,200 | 165.81 | 485,000 | 川(蜀) Chuān (Shǔ) |
| GZ | CN-52 | Guizhou Province | 贵州省 Guìzhōu Shěng |
Guiyang | 34,746,468 | 197.42 | 176,000 | 贵(黔) Guì (Qián) |
| YN | CN-53 | Yunnan Province | 云南省 Yúnnán Shěng |
Kunming | 45,966,239 | 116.66 | 394,000 | 云(滇) Yún (Diān) |
| XZ | CN-54 | Tibet Autonomous Region | 西藏自治区 Xīzàng Zìzhìqū |
Lhasa | 3,002,166 | 2.44 | 1,228,400 | 藏 Zàng |
| SN | CN-61 | Shaanxi Province | 陕西省 Shǎnxī Shěng |
Xi'an | 37,327,378 | 181.55 | 205,600 | 陕(秦) Shǎn (Qín) |
| GS | CN-62 | Gansu Province | 甘肃省 Gānsù Shěng |
Lanzhou | 25,575,254 | 56.29 | 454,300 | 甘(陇) Gān (Lǒng) |
| QH | CN-63 | Qinghai Province | 青海省 Qīnghǎi Shěng |
Xining | 5,626,722 | 7.80 | 721,200 | 青 Qīng |
| NX | CN-64 | Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region | 宁夏回族自治区 Níngxià Huízú Zìzhìqū |
Yinchuan | 6,301,350 | 94.89 | 66,400 | 宁 Níng |
| XJ | CN-65 | Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region | 新疆维吾尔自治区 Xīnjiāng Wéiwú'ěr Zìzhìqū |
Ürümqi | 21,813,334 | 13.13 | 1,660,400 | 新 Xīn |
| TW | CN-71[lower-alpha 5] | Taiwan Province[lower-alpha 6] | 台湾省 Táiwān Shěng |
Taipei | — | — | — | 台 Tái |
| HK | CN-91[lower-alpha 7] | Hong Kong Special Administrative Region | 香港特别行政区 Xiānggǎng Tèbié Xíngzhèngqū |
Hong Kong | 7,061,200 | 6,396.01 | 1,104 | 港 Gǎng |
| MO | CN-92[lower-alpha 8] | Macau Special Administrative Region | 澳门特别行政区 Àomén Tèbié Xíngzhèngqū |
Macau | 552,300 | 19,044.82 | 29 | 澳 Ào |
- ↑ as of 2010
- ↑ per km2
- ↑ km2
- ↑ Abbreviation in the parentheses is informal
- ↑ Has separate ISO 3166-2 code:
TW - ↑ Since founding in 1949, the People's Republic of China (PRC) has considered Taiwan to be its 23rd province. However, the PRC has never controlled Taiwan. Taiwan (officially the Republic of China) currently administers Taiwan, Penghu, Kinmen and Matsu. The subject of whether or not Taiwan is part of "China" is often debated, with no clear conclusion.
- ↑ Has separate ISO 3166-2 code:
HK - ↑ Has separate ISO 3166-2 code:
MO
History



Yuan provinces
The rulers of China first set up provinces—initially 10 in number—during the Yuan Dynasty (1271–1368) with the addition of the Central Region ruled by the Zhongshu Sheng (中書省) and the Tibetan Plateau ruled by the Bureau of Buddhist and Tibetan Affairs (宣政院).
- Gansu (甘肅行省)
- Huguang (湖廣行省)
- Henanjiangbei (河南江北行省)
- Jiangxi (江西行省)
- Jiangzhe (江浙行省)
- Jiaozhi/Annan (交趾行省/安南行省) special province
- Jinghuzhancheng (荊湖占城行省) special province
- Liaoyang (遼陽行省)
- Lingbei (嶺北行省)
- Shaanxi (陝西行省)
- Sichuan (四川行省)
- Yunnan (雲南行省)
- Zhengdong (征東行省) special province
- Zhengmian (徵緬行省) special province
Ming provinces
The Ming Dynasty (1368–1644) kept the province system set up by the Yuan Dynasty, however, it divided the original 10 provinces into 16 provinces.
Qing provinces
By the time of the establishment of the Qing Dynasty (1644–1912) in 1644 there were 18 provinces, all of them in China proper.
New provinces
- Xinjiang (新疆省) 1884–1912
- Fengtian (奉天省) 1907–1912
- Jilin (吉林省) 1907–1912
- Heilongjiang (黑龍江省) 1907–1912
- Taiwan (台灣省) 1885–1895
Each province had a xunfu (巡撫; xúnfǔ; translated as "governor"), a political overseer on behalf of the emperor, and a tidu (提督; tídū; translated as "captain general"), a military governor. In addition, there was a zongdu (總督; zǒngdū), a general military inspector or governor general, for every two to three provinces.
Outer regions of China (those beyond China proper) were not divided into provinces. Military leaders or generals (將軍; jiāngjūn) oversaw Manchuria (consisting of Fengtian (now Liaoning), Jilin, Heilongjiang), Xinjiang, and Mongolia, while vice-dutong (副都統; fù dūtǒng) and civilian leaders headed the leagues (盟長; méng zhǎng), a subdivision of Mongolia. The ambans (駐藏大臣; zhù cáng dàchén) supervised the administration of Tibet.
In 1884 Xinjiang became a province; in 1907 Fengtian, Jilin, and Heilongjiang were made provinces as well. Taiwan became a province in 1885, but China ceded Taiwan to Japan in 1895. As a result, there were 22 provinces in China (Outer China and China proper) near the end of the Qing Dynasty.
ROC provinces (1912–1949)
The Republic of China, established in 1912, set up four more provinces in Inner Mongolia and two provinces in historic Tibet, bringing the total to 28. In 1931, Ma Zhongying established Hexi in the northern parts of Gansu but the ROC never acknowledged the province. But China lost four provinces with the establishment of the Japanese puppet state of Manchukuo in Manchuria. After the defeat of Japan in World War II in 1945, China re-incorporated Manchuria as 10 provinces, and assumed control of Taiwan as a province. As a result, the Republic of China in 1946 had 35 provinces. Although the Republic of China now only controls one province (Taiwan), and some islands of a second province (Fujian), it continues to formally claim all 35 provinces (including those that no longer form part of the area of the People's Republic of China).
- Andong (安東省) 1947–1949
- Anhui (安徽省)
- Fujian (福建省)
- Gansu (甘肅省)
- Guangdong (廣東省)
- Guangxi (廣西省)
- Guizhou (貴州省)
- Heilongjiang (黑龍江省)
- Zhili (直隸省) renamed Hebei (河北省)
- Hejiang (合江省) 1947–1949
- Henan (河南省)
- Hexi (河西省) 1931, not acknowledged by ROC
- Hubei (湖北省)
- Hunan (湖南省)
- Jiangsu (江蘇省)
- Jiangxi (江西省)
- Jilin (吉林省)
- Liaobei (遼北省) 1947–1949
- Fengtian (奉天省) renamed Liaoning (遼寧省)
- Nenjiang (嫩江省) 1947–1949
- Ningxia (寧夏省) 1928–1949
- Qahar (察哈爾省) 1928–1949
- Qinghai (青海省) 1928–1949
- Rehe (熱河省) 1928–1949
- Shaanxi (陝西省)
- Shandong (山東省)
- Shanxi (山西省)
- Sichuan (四川省)
- Songjiang (松江省) 1947–1949
- Suiyuan (綏遠省) 1928–1949
- Taiwan (台灣省) 1945–1949
- Xing'an (興安省) 1947–1949
- Xikang (西康省) 1928–1949
- Xinjiang (新疆省)
- Yunnan (雲南省)
- Zhejiang (浙江省)
Other province-level divisions
- Chuanbian Special Administrative Region (川邊特別行政區) 1914–1935
- Dongsheng Special Region (東省特別行政區) 1923–1932
- Hainan Special Administrative Region (海南特別行政區) 1944–1949
- Qahar Special Administrative Region (察哈爾特別行政區) 1914–1928
- Rehe Special Administrative Region (熱河特別行政區) 1914–1928
- Suiyuan Special Administrative Region (綏遠特別行政區) 1914–1928
- Weihai Special Administrative Region (威海衛特別行政區) 1930–1945
- Mongolia Area (蒙古地方) 1928–1946
- Tibet Area (西藏地方) 1928–1949
- Beiping Yuan-controlled Municipality (北平市) 1928–1949
- Chongqing Yuan-controlled Municipality (重慶市) 1939–1949
- Dalian Yuan-controlled Municipality (大連市) 1945–1949
- Guangzhou Yuan-controlled Municipality (廣州市) 1930, 1947–1949
- Hankou Yuan-controlled Municipality (漢口市) 1927–1949
- Harbin Yuan-controlled Municipality (哈爾濱市) 1946–1949
- Nanjing Yuan-controlled Municipality (南京市) 1927–1949
- Qingdao Yuan-controlled Municipality (青島市) 1929–1949
- Shanghai Yuan-controlled Municipality (上海市) 1927–1949
- Shenyang Yuan-controlled Municipality (瀋陽市) 1947–1949
- Tianjin Yuan-controlled Municipality (天津市) 1928–1949
- Xi'an Yuan-controlled Municipality (西安市) 1948–1949
List of PRC province-level divisions
abolished claimed
Greater administrative areas
| Name | Hanzi | Pinyin | Translation | Capital | Hanzi | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Huabei | 华北 | Huáběi | "North China" | Beijing | 北京 | 1949–1954 | |
| Dongbei | 东北 | Dōngběi | "Northeast" | Shenyang | 沈阳 | 1949–1954 | |
| Huadong | 华东 | Huádōng | "East China" | Shanghai | 上海 | 1949–1954 | |
| Zhongnan | 中南 | Zhōngnán | "South Central" | Wuhan | 武汉 | 1949–1954 | |
| Xibei | 西北 | Xīběi | "Northwest" | Xi'an | 西安 | 1949–1954 | |
| Xinan | 西南 | Xīnán | "Southwest" | Chongqing | 重庆 | 1949–1954 | |
Provinces
| Name | Hanzi | Pinyin | Abbreviation | Capital | Hanzi | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Andong | 安东 | Āndōng | 安 ān | Tonghua | 通化 | 1949 abolished → Liaodong, Jilin |
| Anhui | 安徽 | Ānhuī | 皖 wǎn | Hefei | 合肥 | 1949 abolished → Wanbei, Wannan; 1952 reverted |
| Chahar | 察哈尔 | Cháhā'ěr | 察 chá | Zhangjiakou | 张家口 | 1952 abolished → Inner Mongolia, Hebei |
| Fujian | 福建 | Fújiàn | 闽 mǐn | Fuzhou | 福州 | |
| Gansu | 甘肃 | Gānsù | 甘 gān | Lanzhou | 兰州 | 1958 Ningxia split into its own autonomous region |
| Guangdong | 广东 | Guǎngdōng | 粤 yuè | Guangzhou | 广州 | 1952 & 1965 Fangchenggang, Qinzhou, Beihai → Guangxi; 1955 reverted 1988 Hainan split into its own province |
| Guangxi | 广西 | Guǎngxī | 桂 guì | Nanning | 南宁 | 1958 province → autonomous region |
| Guizhou | 贵州 | Guìzhōu | 黔 qián | Guiyang | 贵阳 | |
| Hainan | 海南 | Hǎinán | 琼 qióng' | Haikou | 海口 | |
| Hebei | 河北 | Héběi | 冀 jì | Baoding (1949–54; 1967–68) Tianjin (1954–67) Shijiazhuang (present) | 保定 天津 石家庄 | 1967 Tianjin split into its own municipality |
| Hejiang | 合江 | Héjiāng | 合 hé | Jiamusi | 佳木斯 | 1949 abolished → Heilongjiang |
| Heilongjiang | 黑龙江 | Hēilóngjiāng | 黑 hēi | Qiqihar (1949–54) Harbin (present) | 齐齐哈尔 哈尔滨 | 1952 part of Xing'an split into Inner Mongolia |
| Henan | 河南 | Hénán | 豫 yù | Kaifeng (1949–54) Zhengzhou (present) | 开封 郑州 | |
| Hubei | 湖北 | Húběi | 鄂 è | Wuhan | 武汉 | |
| Hunan | 湖南 | Húnán | 湘 xiāng | Changsha | 长沙 | |
| Jiangsu | 江苏 | Jiāngsū | 苏 sū | Nanjing | 南京 | 1949 abolished → Subei, Subnan; 1952 reverted |
| Jiangxi | 江西 | Jiāngxī | 赣 gàn | Nanchang | 南昌 | |
| Jilin | 吉林 | Jílín | 吉 jí | Jilin (1949–54) Changchun (present) | 吉林 长春 | 1952 north part split into Inner Mongolia |
| Liaobei | 辽北 | Liáoběi | 洮 táo | Liaoyuan | 辽源 | 1949 abolished → Jilin, Liaoning |
| Liaodong | 辽东 | Liáodōng | 关 guān | Dandong | 丹东 | 1954 abolished → Liaoning |
| Liaoning | 辽宁 | Liáoníng | 辽 liáo | Shenyang | 沈阳 | 1949 abolished → Liaodong, Liaoxi; 1954 reverted 1952 north part split into Inner Mongolia |
| Liaoxi | 辽西 | Liáoxī | 辽 liáo | Jinzhou | 锦州 | 1954 abolished → Liaoning |
| Nenjiang | 嫩江 | Nènjiāng | 嫩 nèn | Qiqihar | 齐齐哈尔 | 1949 abolished → Heilongjiang |
| Ningxia | 宁夏 | Níngxià | 宁 níng | Yinchuan | 银川 | 1954 province → Gansu |
| Mudanjiang | 牡丹江 | Mǔdānjiāng | 丹 dān | Mudanjiang | 牡丹江 | 1949 abolished → Heilongjiang |
| Pingyuan | 平原 | Píngyuán | 平 píng | Xinxiang | 新乡 | 1952 abolished → Henan, Shandong |
| Qinghai | 青海 | Qīnghǎi | 青 qīng | Xining | 西宁 | |
| Rehe | 热河 | Rèhé | 热 rè | Chengde | 承德 | 1955 abolished → Inner Mongolia, & Liaoning |
| Sichuan | 四川 | Sìchuān | 川 chuān | Chengdu | 成都 | 1949 abolished → Chuanbei, Chuandong, Chuannan, Chuanxi; 1952 reverted 1997 Chongqing split into its own municipality |
| Shaanxi | 陕西 | Shǎnxī | 陕 shǎn | Xi'an | 西安 | |
| Shandong | 山东 | Shāndōng | 鲁 lǔ | Jinan | 济南 | |
| Shanxi | 山西 | Shānxī | 晋 jìn | Taiyuan | 太原 | |
| Songjiang | 松江 | Sōngjiāng | 松 sōng | Harbin | 哈尔滨 | 1954 abolished → Heilongjiang |
| Suiyuan | 绥远 | Suíyuǎn | 绥 suí | Hohhot | 呼和浩特 | 1954 abolished → Inner Mongolia |
| Taiwan | 台湾 | Táiwān | 台 tái | Taipei | 台北 | claimed since 1949 the founding of the PRC |
| Xikang | 西康 | Xīkāng | 康 kāng | Kangding (1949–50) Ya'an (1950–55) | 康定 雅安 | 1955 abolished → Sichuan & Qamdo |
| Xing'an | 兴安 | Xīng'ān | 兴 xīng | Hulunbuir | 呼伦贝尔 | 1949 abolished → Heilongjiang |
| Xinjiang | 新疆 | Xīnjiāng | 疆 jiāng | Ürümqi | 乌鲁木齐 | 1955 province → autonomous region |
| Yunnan | 云南 | Yúnnán | 滇 diān | Kunming | 昆明 | |
| Zhejiang | 浙江 | Zhèjiāng | 浙 zhè | Hangzhou | 杭州 |
Autonomous regions
| Name | Hanzi | Pinyin | Abbreviation | Capital | Hanzi | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangxi | 广西 | Guǎngxī | 桂 guì | Nanning | 南宁 | 1958 province → autonomous region |
| Inner Mongolia | 內蒙古 | Nèi Měnggǔ | 蒙 měng | Ulaanhot (1947–50) Hohhot (present) | 乌兰浩特 呼和浩特 | 1947 created; 1969 truncated → Liaoning, Heilongjiang, Jilin, Gansu, Ningxia; 1979 reverted |
| Ningxia | 宁夏 | Níngxià | 宁 níng | Yinchuan | 银川 | 1958 special region → autonomous region |
| Tibet | 西藏 | Xīzàng | 藏 zàng | Lhasa | 拉萨 | 1965 area → autonomous region |
| Xinjiang | 新疆 | Xīnjiāng | 疆 jiāng | Ürümqi | 乌鲁木齐 | 1955 province → autonomous region |
Municipalities
| Name | Hanzi | Pinyin | Abbreviation | Capital | Hanzi | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anshan | 鞍山 | Ānshān | 鞍 ān | Tiedong District | 铁东区 | 1954 abolished → Liaoning |
| Beijing | 北京 | Běijīng | 京 jīng | Dongcheng District Tongzhou District | 东城区 通州区 | |
| Benxi | 本溪 | Běnxī | 本 běn | Pingshan District | 平山区 | 1954 abolished → Liaoning |
| Changchun | 长春 | Chángchūn | 春 chūn | Nanguan District | 南关区 | 1953 created; 1954 abolished → Jilin |
| Chongqing | 重庆 | Chóngqìng | 渝 yú | Yuzhong District | 渝中区 | 1954 abolished → Sichuan; 1997 reverted |
| Dalian → Lüda | 大连→旅大 | Dàlián | 连 lián | Xigang District | 西岗区 | 1949 abolished → Luda, 1950 reverted, 1954 abolished → Liaoning |
| Fushun | 抚顺 | Fǔshùn | 抚 fǔ | Shuncheng District | 顺城区 | 1954 abolished → Liaoning |
| Guangzhou | 广州 | Guǎngzhōu | 穗 suì | Yuexiu District | 越秀区 | 1954 abolished → Guangdong |
| Harbin | 哈尔滨 | Hā'ěrbīn | 哈 hā | Nangang District | 南岗区 | 1953 created, 1954 abolished → Heilongjiang |
| Nanjing | 南京 | Nánjīng | 宁 níng | Xuanwu District | 玄武区 | 1952 abolished → Jiangsu |
| Shanghai | 上海 | Shànghǎi | 沪 hù | Huangpu District | 黄浦区 | |
| Shenyang | 沈阳 | Shěnyáng | 沈 shěn | Shenhe District | 沈河区 | 1954 abolished → Liaoning |
| Tianjin | 天津 | Tiānjīn | 津 jīn | Heping District | 和平区 | 1954 abolished → Hebei, 1967 reverted |
| Hankou → Wuhan | 汉口→武汉 | Wǔhàn | 汉 hàn | Jiang'an District | 江岸区 | 1949 abolished → Hubei |
| Xi'an | 西安 | Xī'ān | 镐 hào | Weiyang District | 未央区 | 1954 abolished → Shaanxi |
Special administrative regions
| Name | Hanzi | Pinyin | Abbreviation | Capital | Hanzi | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hong Kong | 香港 | Xiānggǎng | 港 gǎng | Hong Kong | 香港 | created 1997 (Transfer of sovereignty over Hong Kong) |
| Macau | 澳门 | Àomén | 澳 ào | Macau | 澳门 | created 1999 (Transfer of sovereignty over Macau) |
Administrative territories
| Name | Hanzi | Pinyin | Abbreviation | Capital | Hanzi | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chuanbei | 川北 | Chuānběi | 充 chōng | Nanchong | 南充 | 1950 created; 1952 abolished → Sichuan |
| Chuandong | 川东 | Chuāndōng | 渝 yú | Chongqing | 重庆 | 1950 created; 1952 abolished → Sichuan |
| Chuannan | 川南 | Chuānnán | 泸 lú | Luzhou | 泸州 | 1950 created; 1952 abolished → Sichuan |
| Chuanxi | 川西 | Chuānxī | 蓉 róng | Chengdu | 成都 | 1950 created; 1952 abolished → Sichuan |
| Hainan | 海南 | Hǎinán | 琼 qióng | Haikou | 海口 | 1949 abolished → Guangdong |
| Lüda | 旅大 | Lǚdà | 旅 lǚ | Dalian | 大连 | 1949 created; 1950 abolished → Dalian |
| Subei | 苏北 | Sūběi | 扬 yáng | Yangzhou | 扬州 | 1949 created; 1952 abolished → Jiangsu |
| Sunan | 苏南 | Sūnán | 锡 xī | Wuxi | 无锡 | 1949 created; 1952 abolished → Jiangsu |
| Wanbei | 皖北 | Wǎnběi | 合 hé | Hefei | 合肥 | 1949 created; 1952 abolished → Anhui |
| Wannan | 皖南 | Wǎnnán | 芜 wú | Wuhu | 芜湖 | 1949 created; 1952 abolished → Anhui |
Regions
| Name | Hanzi | Pinyin | Abbreviation | Capital | Hanzi | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tibet | 西藏 | Xīzàng | 藏 zàng | Lhasa | 拉萨 | 1965 region → autonomous region |
Territories
| Name | Hanzi | Pinyin | Abbreviation | Capital | Hanzi | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qamdo | 昌都 | Chāngdū | 昌 chāng | Qamdo | 昌都 | 1965 merged into Tibet |
The People's Republic of China abolished many of the provinces in the 1950s and converted a number of them into autonomous regions. Hainan became a separate province in 1988, bringing the total number of provinces under PRC control to 22.
Economies
The provinces in south coastal area of China—such as Zhejiang, Jiangsu, Fujian and (mainly) Guangdong—tend to be more industrialized, with regions in the hinterland less developed.
See also
- Chinese federalism
- List of China administrative divisions by population
- List of Chinese administrative divisions by GDP
- List of provincial leaders of the People's Republic of China
- Regional discrimination in China
- Taiwan Province, People's Republic of China
- Tiao-kuai
- Yangtze River Delta
- Zhou (country subdivision)
References
- ↑ Administrative divisions of China
- ↑ GB/T 2260 codes for the provinces of China
- ↑ ISO 3166-2:CN (ISO 3166-2 codes for the provinces of China)
- ↑ "Doing Business in China - Survey". Ministry Of Commerce - People's Republic Of China. Retrieved 5 August 2013.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Provinces of China. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for List of Chinese provinces and regions. |
- Interactive Dbresearch.com: WebMap — with economic indicators for all Chinese Provinces.
