Pratt & Whitney J57
| J57 / JT3C | |
|---|---|
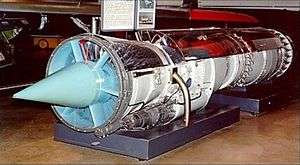 | |
| YJ57-P-3 cut-away demonstrator at USAF Museum | |
| Type | Turbojet |
| National origin | United States |
| Manufacturer | Pratt & Whitney |
| First run | 1950 |
| Major applications | B-52 Stratofortress KC-135 Stratotanker B-57 Canberra Boeing 707 Douglas DC-8 F-8 Crusader F-100 Super Sabre Lockheed U-2 |
| Number built | 21,170 built |
| Developed from | Pratt & Whitney XT45 |
| Variants | JT3D/TF33 |
| Developed into | TF33/JT3D |
The Pratt & Whitney J57 (company designation: JT3C) was an axial-flow turbojet engine developed by Pratt & Whitney in the early 1950s. The J57 (first run January 1950[1]) was the first 10,000 lbf (45 kN) thrust class engine in the United States. The J57/JT3C was developed into the J75/JT4A turbojet, JT3D/TF33 turbofan and the PT5/T57 turboprop.[2]
Design and development
The J57 was a development of the XT45 (PT4) turboprop engine intended for the XB-52. As the B-52 power requirements grew, the design evolved into a turbojet, the JT3. The prestigious Collier Trophy for 1952 was awarded to Leonard S. Hobbs, Chief Engineer of United Aircraft Corporation, for "designing and producing the P&W J57 turbojet engine".[3] On May 25, 1953, a J57-powered YF-100A exceeded Mach 1 on its maiden flight. The engine was produced from 1951 to 1965 with a total of 21,170 built.
One XT57 was installed in the nose of a JC-124C (BuNo 52-1069), and tested in 1956.[4][5]
Variants

- J57-P-1W
- 11,400 lbf (51 kN) s.t with water injection (B-52B)
- J57-P-1WA
- As P-1W
- J57-P-1WB
- As P-1W
- YJ57-P-3
- 8,700 lbf (39 kN) thrust, used in the Convair YB-60
- J57-P-4A
- 16,200 lbf (72.06 kN) thrust
- J57-P-8A
- 10,400 lbf (46.26 kN) thrust
- J57-P-10
- 12,400 lbf (55.16 kN) thrust
- J57-P-11
- 9,700 lbf (43.15 kN) thrust, 14,800 lbf (65.83 kN) thrust
- J57-P-13
- 14,880 lbf (66.19 kN) thrust
- J57-P-16
- 16,900 lbf (75.17 kN) thrust
- J57-P-20
- 18,000 lbf (80.07 kN) thrust[6]
- J57-P-20A
- 18,000 lbf (80.07 kN) thrust
- J57-P-21
- 17,000 lbf (75.62 kN) thrust
- J57-P-25
- 15,000 lbf (66.72 kN) thrust
- J57-P-31
- J57-P-37A
- J57-P-43W
- 13,750 lbf (61.16 kN) thrust
- J57-P-43WB
- 13,750 lbf (61.16 kN) thrust[6]
- J57-P-59W
- 13,750 lbf (61.16 kN) thrust
- T57
- 15,000 hp (11,185.50 kW) turboprop
- JT3C-2
- Civilian derivative of the J57-P-43WB, 13,750 lbf (61.16 kN) thrust[6]
- JT3C-6
- 13,500 lbf (60.05 kN) thrust[6]
- JT3C-7
- 12,000 lbf (53.38 kN) thrust[6]
- JT3C-12
- 13,000 lbf (57.83 kN) thrust[6]
- JT3C-26
- Civilian derivative of the J57-P-20, 18,000 lbf (80.07 kN) thrust[6]
- JT3D/TF33:A turbo-fan derivative of the J57.[6]
- PT5
- Company designation for the T57.
Applications
- J57 (Military)
- Boeing B-52 Stratofortress (dash 1W, 1WA, 1WB)
- Boeing C-135 Stratolifter and KC-135 Stratotanker
- Convair F-102 Delta Dagger (dash 25)
- Convair YB-60 (dash 3)
- Douglas A3D Skywarrior (dash 10)
- Douglas F4D Skyray (dash 8, 8A, 8B)
- Douglas F5D Skylancer
- Lockheed U-2
- Martin B-57 Canberra
- McDonnell F-101 Voodoo (dash 55)
- North American F-100 Super Sabre (dash 21 and 21A)
- Northrop SM-62 Snark
- Vought F-8 Crusader (dash 8)
- JT3C (Civilian)

- T57 turboprop
- Douglas C-124 Globemaster II testbed
- Douglas C-132 (not built)
Engines on display
- There is a J57 cutaway at the New England Air Museum, Bradley International Airport, Windsor Locks, CT.[7]
Specifications (JT3C-7)
Data from Flight [8]
General characteristics
- Type: civil turbojet
- Length: 155in (3937mm)
- Diameter: 39in (990.6mm)
- Dry weight: 4200lb (1905kg)
Components
- Compressor: all-axial, 9-stage LP compressor, 7-stage HP compressor
- Combustors: cannular, 8 flame tubes
- Turbine: all-axial,single stage HP turbine, 2-stage LP turbine
Performance
- Maximum thrust: 12030 lbf (53.5 kN) @ Take-off, SLS, ISA
- Overall pressure ratio: 12.5:1
- Air mass flow: 180 lb/s (81.65 kg/s)
- Specific fuel consumption: 0.785 lb/(h lbf) (22.24 g/(s kN)) @ Take-off, SLS, ISA and 0.909 lb/(h lbf) (25.75g/(s kN)) @Max Cruise 3550 lbf M0.85,35000 ft,ISA
- Thrust-to-weight ratio: 3.44
Specifications (J57-P-23)

Data from
General characteristics
- Type: Afterburning turbojet
- Length: 244 in (6197.6mm)
- Diameter: 39 in (990.6mm)
- Dry weight: 5,175 lb (2,347 kg)
Components
- Compressor: Two-spool 16-stage axial compressor
Performance
- Maximum thrust: 11,700 lbf (52.0 kN) dry, 17,200 lbf (76.5 kN) with afterburner
- Overall pressure ratio: 11.5:1
- Air mass flow: 165 lb/s (75 kg/s) at maximum power
- Turbine inlet temperature: 1,600 °F (870 °C)
- Specific fuel consumption: 2.10 lb/(lbf·h) (59 g/(kN·s)) with afterburner
- Thrust-to-weight ratio: 3.32:1 (32.6 N/kg)
See also
- Related development
- Comparable engines
- Related lists
References
- Notes
- ↑ The Engines of Pratt & Whitney: A Technical History" Jack Connors, AIAA Inc. 2010, ISBN 978-1-60086-711-8, p. 225
- ↑ Gunston, p.167
- ↑ List of Collier Trophy Winners
- ↑ Francillon, René J. McDonnell Douglas aircraft since 1920 (Putnam, 1979), p.470.
- ↑ Connors, p.294
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Taylor, John W.R. FRHistS. ARAeS (1962). Jane's All the World's Aircraft 1962-63. London: Sampson, Low, Marston & Co Ltd.
- ↑ http://neam.org/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&layout=edit&id=1059 "Pratt & Whitney J57 (JTC3) Cutaway"
- ↑ Flightglobal archive - Flight International, 27 November 1953 Retrieved: 04 March 2017
- Bibliography
- Taylor, John W.R. FRHistS. ARAeS (1962). Jane's All the World's Aircraft 1962-63. London: Sampson, Low, Marston & Co Ltd.
- Connors, Jack (2010). The Engines of Pratt & Whitney: A Technical History. Reston. Virginia: American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics. ISBN 978-1-60086-711-8.
- Francillon, René J. McDonnell Douglas Aircraft since 1920. London: Putnam, 1979. ISBN 0-370-00050-1.
- Gunston, Bill (2006). World Encyclopedia of Aero Engines, 5th Edition. Phoenix Mill, Gloucestershire, England, UK: Sutton Publishing Limited. ISBN 0-7509-4479-X.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Pratt & Whitney J57. |
- Pratt & Whitney History page on the J57/JT3
- Pratt & Whitney J57 Turbojet – National Museum of the United States Air Force
- Photo of C-124 with xT57 in Flight magazine
- "Two-Spool Turbo-Wasp" a 1953 Flight article on the J57 by Bill Gunston