Pons
| Pons | |
|---|---|
 Diagram showing the positions of the three principal subarachnoid cisternae (pons visible at center) | |
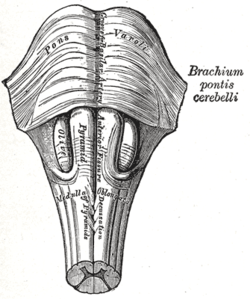 Anteroinferior view of the medulla oblongata and pons | |
| Details | |
| Part of | Brain stem |
| Artery | pontine arteries |
| Vein | transverse and lateral pontine veins |
| Identifiers | |
| MeSH | A08.186.211.132.810.428.600 |
| NeuroNames | hier-538 |
| NeuroLex ID | Pons |
| TA | A14.1.03.010 |
| FMA | 67943 |
The pons is part of the brainstem, and in humans and other bipeds lies inferior to the midbrain, superior to the medulla oblongata and anterior to the cerebellum.
The pons is also called the pons Varolii ("bridge of Varolius"), after the Italian anatomist and surgeon Costanzo Varolio (1543–75).[1] This region of the brainstem includes neural pathways or tracts that conduct signals from the brain down to the cerebellum and medulla, and tracts that carry the sensory signals up into the thalamus.[2]
The pons in humans measures about 2.5 centimetres (0.98 in) in length. Most of it appears as a broad anterior bulge rostral to the medulla. Posteriorly, it consists mainly of two pairs of thick stalks called cerebellar peduncles. They connect the cerebellum to the pons and midbrain.[2]
The pons contains nuclei that relay signals from the forebrain to the cerebellum, along with nuclei that deal primarily with sleep, respiration, swallowing, bladder control, hearing, equilibrium, taste, eye movement, facial expressions, facial sensation, and posture.[2]
Within the pons is the pneumotaxic center consisting of the subparabrachial and the medial parabrachial nuclei. This center regulates the change from inhalation to exhalation.[2]
The pons is implicated in sleep paralysis, and may also play a role in generating dreams.
Structure
The pons can be broadly divided into two parts: the basilar part of the pons, located ventrally, and the pontine tegmentum, located dorsally.
Development
During embryonic development, the metencephalon develops from the rhombencephalon and gives rise to two structures: the pons and the cerebellum.[2] The alar plate produces sensory neuroblasts, which will give rise to the solitary nucleus and its special visceral afferent (SVA) column; the cochlear and vestibular nuclei, which form the special somatic afferent (SSA) fibers of the vestibulocochlear nerve, the spinal and principal trigeminal nerve nuclei, which form the general somatic afferent column (GSA) of the trigeminal nerve, and the pontine nuclei which relays to the cerebellum.
Basal plate neuroblasts give rise to the abducens nucleus, which forms the general somatic efferent fibers (GSE); the facial and motor trigeminal nuclei, which form the special visceral efferent (SVE) column, and the superior salivatory nucleus, which forms the general visceral efferent fibers of the facial nerve.
Nucleus
A number of cranial nerve nuclei are present in the pons:
- mid-pons: the 'chief' or 'pontine' nucleus of the trigeminal nerve sensory nucleus (V)
- mid-pons: the motor nucleus for the trigeminal nerve (V)
- lower down in the pons: abducens nucleus (VI)
- lower down in the pons: facial nerve nucleus (VII)
- lower down in the pons: vestibulocochlear nuclei (vestibular nuclei and cochlear nuclei) (VIII)
Function
The functions of these four cranial nerves (V-VIII) include sensory roles in hearing, equilibrium, and taste, and in facial sensations such as touch and pain, as well as motor roles in eye movement, facial expressions, chewing, swallowing, and the secretion of saliva and tears.[2]
Clinical significance
- Central pontine myelinolysis is a demyelination disease that causes difficulty with sense of balance, walking, sense of touch, swallowing and speaking. In a clinical setting, it is often associated with transplant or rapid correction of blood sodium. Undiagnosed, it can lead to death or locked-in syndrome.
Other animals
Evolution
The pons first evolved as an offshoot of the medullary reticular formation.[3] Since lampreys possess a pons, it has been argued that it must have evolved as a region distinct from the medulla by the time the first agnathans appeared, 505 million years ago.[4]
Additional images
 Location and topography of Pons (animation)
Location and topography of Pons (animation) Axial section of the pons, at its upper part
Axial section of the pons, at its upper part Hind- and mid-brains; posterolateral view
Hind- and mid-brains; posterolateral view Median sagittal section of brain
Median sagittal section of brain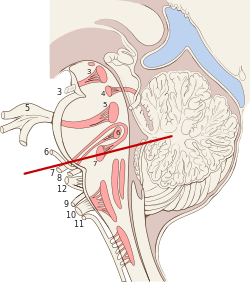 Nuclei of the pons and brainstem
Nuclei of the pons and brainstem- Cerebrum. Deep dissection. Inferior dissection.
References
- ↑ Henry Gray (1862). Anatomy, descriptive and surgical. Blanchard and Lea. pp. 514–. Retrieved 10 November 2010.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Saladin Kenneth S.(2007)
- ↑ Pritchard and Alloway Medical Neuroscience
- ↑ Butler and Hodos Comparative vertebrate neuroanatomy: evolution and adaptation
Saladin Kenneth S.(2007) Anatomy & physiology the unity of form and function. Dubuque, IA: McGraw-Hill
- Pritchard, TE & Alloway, D (1999). Medical neuroscience. Hayes Barton Press. ISBN 978-1-59377-200-0.
- Butler, AB & Hodos, W (2005). Comparative vertebrate neuroanatomy: evolution and adaptation. Wiley-Blackwell. ISBN 978-0-471-21005-4.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Pons. |