Fluid power
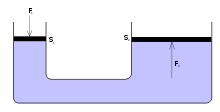
Fluid power is the use of fluids under pressure to generate, control, and transmit power. Fluid power is subdivided into hydraulics using a liquid such as mineral oil or water, and pneumatics using a gas such as air or other gases. Compressed-air and water-pressure systems were once used to transmit power from a central source to industrial users over extended geographic areas; fluid power systems today are usually within a single building or mobile machine.
Elements
A fluid power system has a pump driven by a prime mover (such as an electric motor or internal combustion engine) that converts mechanical energy into fluid energy, Pressurized fluid is controlled and directed by valves into an actuator device such as a hydraulic cylinder or pneumatic cylinder, to provide linear motion, or a hydraulic motor or pneumatic motor, to provide rotary motion or torque. Rotary motion may be continuous or confined to less than one revolution.
Application
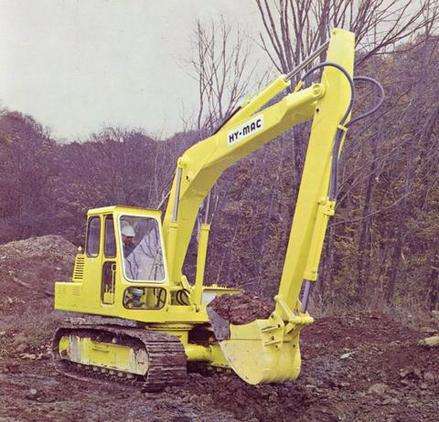
Machinery operated by fluid power covers a wide range of applications in industry. Mobile excavating equipment uses hydraulic systems. Automated production lines may use pneumatic or hydraulic systems to position work pieces or move tools. Variable-flow control valves and position sensors may be included in a servomechanism system for precision machine tools.


Pneumatic and hydraulic systems compared
- Cost: Pneumatics are considerably less expensive to build and operate. For one, air is used as the compressed medium, so there is no need to provide means to drain or recover fluid. With increased working pressures, hydraulics require larger parts than pneumatics.
- Precision: Unlike liquids, gases change volume significantly when pressurized making it difficult to achieve precision.
- Safety: Compressed gases tend to expand at high velocities when decompressed, thus pneumatics are typically limited to a working pressure of up to around 100 psi (7 bar).
See also
- Hydraulic circuit
- Hydraulic power network
- London Hydraulic Power Company
- Pneumatic circuit
- Pneumatic actuator
References
- Esposito, Anthony, Fluid Power with Applications, ISBN 0-13-010225-3
- Hydraulic Power System Analysis, A. Akers, M. Gassman, & R. Smith, Taylor & Francis, New York, 2006, ISBN 0-8247-9956-9