Bordeaux wine
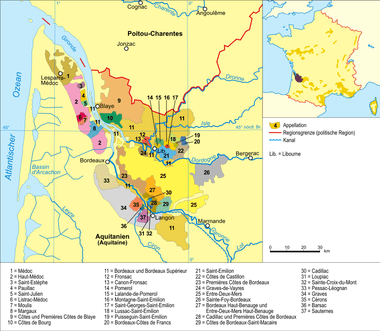
A Bordeaux wine is any wine produced in the Bordeaux region of southwest France, centered on the city of Bordeaux and covering the whole area of the Gironde department, with a total vineyard area of over 120,000 hectares,[1] making it the largest wine growing area in France. Average vintages produce over 700 million bottles of Bordeaux wine, ranging from large quantities of everyday table wine, to some of the most expensive and prestigious wines in the world. The vast majority of wine produced in Bordeaux is red (called "claret" in Britain), with sweet white wines (most notably Sauternes), dry whites, and (in much smaller quantities) rosé and sparkling wines (Crémant de Bordeaux) collectively making up the remainder. Bordeaux wine is made by more than 8,500 producers or châteaux. There are 54 appellations of Bordeaux wine.[1][2]
History
The wine was introduced to the Bordeaux region by the Romans, probably in the mid-1st century, to provide wine for local consumption, and wine production has been continuous in the region since then.[3]
In the 12th century, the popularity of Bordeaux wines in England increased dramatically following the marriage of Henry Plantagenet and Eleanor of Aquitaine.[4] The marriage made the province of Aquitaine part of the Angevin Empire, and thenceforth the wine of Bordeaux was exported to England.[4] At this time, Graves was the principal wine region of Bordeaux, and the principal style was clairet. This accounts for the ubiquity of claret in England. The export of Bordeaux was interrupted by the outbreak of the Hundred Years' War between France and England in 1337.[4] By the end of the conflict in 1453 France had repossessed the province, thus taking control of wine production in the region.[4] As part of the Auld Alliance, Scots merchants were granted by the French a privileged position in the trade of claret, a position which continued largely unchanged with the cession of the military alliance between France and Scotland with the signing of the Treaty of Edinburgh.[5] Even when the by then Protestant kingdoms of England and Scotland, both ruled by the same Stuart king by this point, were trying to militarily aid the Huguenot rebels in their fight against Catholic France in La Rochelle, Scots trading vessels were not only permitted to enter the Gironde, but they were escorted safely to the port of Bordeaux by the French navy for their own protection from Huguenot privateers.
In the seventeenth century, Dutch traders drained the swampy ground of the Médoc in order that it could be planted with vines, and this gradually surpassed Graves as the most prestigious region of Bordeaux. Malbec was the dominant grape here, until the early 19th century, when it was replaced by Cabernet Sauvignon.[6]
In 1855, the châteaux of Bordeaux were classified; this classification remains widely used today. From 1875–1892 almost all Bordeaux vineyards were ruined by Phylloxera infestations.[4] The region's wine industry was rescued by grafting native vines on to pest-resistant American rootstock.[4]
Climate and geography
The major reason for the success of winemaking in the Bordeaux region is an excellent environment for growing vines. The geological foundation of the region is limestone, leading to a soil structure that is heavy in calcium. The Gironde estuary dominates the regions along with its tributaries, the Garonne and the Dordogne rivers, and together irrigate the land and provide an Atlantic Climate, also known as an oceanic climate, for the region.[7]
These rivers define the main geographical subdivisions of the region:
- "The right bank", situated on the right bank of Dordogne, in the northern parts of the region, around the city of Libourne.
- Entre-Deux-Mers, French for "between two seas", the area between the rivers Dordogne and Garonne, both of which are tidal, in the centre of the region.
- "The left bank", situated on the left bank of Garonne, in the west and south of the region, around the city of Bordeaux itself. The left bank is further subdivided into:
In Bordeaux the concept of terroir plays a pivotal role in wine production with the top estates aiming to make terroir driven wines that reflect the place they are from, often from grapes collected from a single vineyard.[8] The soil of Bordeaux is composed of gravel, sandy stone, and clay. The region's best vineyards are located on the well-drained gravel soils that are frequently found near the Gironde river. An old adage in Bordeaux is the best estates can "see the river" from their vineyards. The majority of land facing riverward is occupied by classified estates.[9]
Grapes

Red Bordeaux is generally made from a blend of grapes. Permitted grapes are Cabernet Sauvignon, Cabernet Franc, Merlot, Petit Verdot, Malbec and rarely Carménère.[10] Today Carménère is rarely used, with Château Clerc Milon, a fifth growth Bordeaux, being one of the few to still retain Carménère vines.
As a very broad generalization, Cabernet Sauvignon (Bordeaux's second-most planted grape variety) dominates the blend in red wines produced in the Médoc and the rest of the left bank of the Gironde estuary. Typical top-quality Châteaux blends are 70% Cabernet Sauvignon, 15% Cabernet Franc and 15% Merlot. This is typically referred to as the "Bordeaux Blend." Merlot tends to predominate in Saint-Émilion, Pomerol and the other right bank appellations. These Right Bank blends from top-quality Châteaux are typically 70% Merlot, 15% Cabernet Franc and 15% Cabernet Sauvignon.[11]
White Bordeaux is predominantly, and exclusively in the case of the sweet Sauternes, made from Sémillon, Sauvignon blanc and Muscadelle. Typical blends are usually 80% Sémillon and 20% Sauvignon blanc. As with the reds, white Bordeaux wines are usually blends, most commonly of Sémillon and a smaller proportion of Sauvignon blanc. Other permitted grape varieties are Sauvignon gris, Ugni blanc, Colombard, Merlot blanc, Ondenc and Mauzac.
In the late 1960s Sémillon was the most planted grape in Bordeaux. Since then it has been in constant decline although it still is the most common of Bordeaux's white grapes. Sauvignon blanc's popularity on the other hand has been rising, overtaking Ugni blanc as the second most planted white Bordeaux grape in the late 1980s and now being grown in an area more than half the size of that of the lower yielding Sémillon.
Wineries all over the world aspire to making wines in a Bordeaux style. In 1988, a group of American vintners formed The Meritage Association to identify wines made in this way. Although most Meritage wines come from California, there are members of the Meritage Association in 18 states and five other countries, including Argentina, Australia, Canada, Israel, and Mexico.
Viticulture and winemaking
Viticulture
The red grapes in the Bordeaux vineyard are Merlot (62% by area), Cabernet Sauvignon (25%), Cabernet Franc (12%) and a small amount of Petit Verdot, Malbec and Carménère (1% in total). The white grapes are Sémillon (54% by area), Sauvignon blanc (36%), Muscadelle (7%) and a small amount of Ugni blanc, Colombard and Folle blanche (3% in total).[1] Because of the generally humid Bordeaux climate, a variety of pests can cause a problem for the vigneron. In the past, this was counteracted by the widespread use of pesticides, although the use of natural methods has recently been gaining in popularity. The vines are generally trained in either single or double guyot. Hand-picking is preferred by most of the prestigious châteaux, but machine-harvesting is popular in other places.[12]
Winemaking
Following harvest, the grapes are usually sorted and destemmed before crushing. Crushing was traditionally done by foot, but mechanical crushing is now almost universally used. Chaptalization is permitted, and is fairly common-place. Fermentation then takes place, usually in temperature controlled stainless steel vats. Next the must is pressed and transferred to barriques (in most cases) for a period of ageing (commonly a year). The traditional Bordeaux barrique is an oak barrel with a capacity of 225 litres. At some point between pressing and bottling the wine will be blended. This is an integral part of the Bordeaux winemaking process, as scarcely any Bordeaux wines are varietals; wine from different grape varieties is mixed together, depending on the vintage conditions, so as to produce a wine in the château's preferred style. In addition to mixing wine from different grape varieties, wine from different parts of the vineyard is often aged separately, and then blended into either the main or the second wine (or sold off wholesale) according to the judgment of the winemaker. The wine is then bottled and usually undergoes a further period of ageing before it is released for sale.[13]
Wine styles

The Bordeaux wine region is divided into subregions including Saint-Émilion, Pomerol, Médoc, and Graves. The 60 Bordeaux appellations and the wine styles they represent are usually categorized into six main families, four red based on the subregions and two white based on sweetness:[14]
- Red Bordeaux and Red Bordeaux Supérieur. Bordeaux winemakers may use the two regional appellations throughout the entire wine region, however approximately half of the Bordeaux vineyard is specifically designated under Bordeaux and Bordeaux Supérieur AOCs. With the majority of châteaux located on the Right Bank in the Entre-Deux-Mers area, wines are typically Merlot-dominant, often blended with the other classic Bordeaux varieties. There are many small, family-run châteaux, as well as wines blended and sold by wine merchants under commercial brand names. The Bordeaux AOC wines tend to be fruity, with minimal influence of oak, and are produced in a style meant to be drunk young. Bordeaux Superieur AOC wines are produced in the same area, but must follow stricter controls, such as lower yields, and are often aged in oak. For the past 10 years, there has been strong, ongoing investment by the winemakers in both the vineyards and in the cellar, resulting in ever increasing quality. New reforms for the regional appellations were instituted in 2008 by the Bordeaux and Bordeaux Supérieur Winemakers' Association. In 2010, 55% of all Bordeaux wines sold in the world were from Bordeaux and Bordeaux Supérieur AOCs, with 67% sold in France and 33% exported (+9%), representing 14 bottles consumed per second.[14][15]
- Red Côtes de Bordeaux. Eight appellations are in the hilly outskirts of the region, and produce wines where the blend usually is dominated by Merlot. These wines tend to be intermediate between basic red Bordeaux and the more famous appellations of the left and right bank in both style and quality. However, since none of Bordeaux's stellar names are situated in Côtes de Bordeaux, prices tend to be moderate. There is no official classification in Côtes de Bordeaux.[16] In 2007, 14.7% of the region's vineyard surface was used for wines in this family.[14]
- Red Libourne, or "Right Bank" wines. Around the city of Libourne, 10 appellations produce wines dominated by Merlot with very little Cabernet Sauvignon, the two most famous being Saint-Émilion and Pomerol. These wines often have great fruit concentration, softer tannins and are long-lived. Saint-Émilion has an official classification.[17] In 2007, 10.5% of the region's vineyard surface was used for wines in this family.[14]
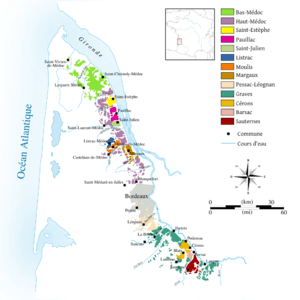
- Red Graves and Médoc or "Left Bank" wines. North and south of the city of Bordeaux, which are the classic areas, produce wines dominated by Cabernet Sauvignon, but often with a significant portion of Merlot. These wines are concentrated, tannic, long-lived and most of them meant to be cellared before drinking. The five First Growths are situated here. There are official classifications for both Médoc and Graves.[18] In 2007, 17.1% of the region's vineyard surface was used for wines in this family.[14]

- Dry white wines. Dry white wines are made throughout the region, using the regional appellation Bordeaux Blanc, often from 100% Sauvignon blanc or a blend dominated by Sauvignon blanc and Sémillon. The Bordeaux Blanc AOC is used for wines made in appellations that only allow red wines. Dry whites from Graves are the most well-known and it is the only subregion with a classification for dry white wines. The better versions tend to have a significant oak influence.[19] In 2007, 7.8% of the region's vineyard surface was used for wines in this family.[14][15]
- Sweet white wines. In several locations and appellations throughout the region, sweet white wine is made from Sémillon, Sauvignon blanc and Muscadelle grapes affected by noble rot. The best-known of these appellations is Sauternes, which also has an official classification, and where some of the world's most famous sweet wines are produced. There are also appellations neighboring Sauternes, on both sides of the Garonne river, where similar wines are made. These include Loupiac, Cadillac, and Sainte Croix du Mont. The regional appellation for sweet white wines is Bordeaux Supérieur Blanc.[20] In 2007, 3.2% of the region's vineyard surface was used for wines in this family.[14][15]
The vast majority of Bordeaux wine is red, with red wine production outnumbering white wine production six to one.[21]
Wine classification

There are four different classifications of Bordeaux, covering different parts of the region:[22][23]
- The Bordeaux Wine Official Classification of 1855, covering (with one exception) red wines of Médoc, and sweet wines of Sauternes-Barsac.
- The 1955 Official Classification of St.-Émilion, which is updated approximately once every ten years, and last in 2006.
- The 1959 Official Classification of Graves, initially classified in 1953 and revised in 1959.
- The Cru Bourgeois Classification, which began as an unofficial classification, but came to enjoy official status and was last updated in 2003. However, after various legal turns, the classification was annulled in 2007.[24] As of 2007, plans exist to revive it as an unofficial classification.[25] 78 producers took legal action against the 2003 classification. In September 2010 a new list of Crus Bourgeois was unveiled as a recognition of quality, with a yearly reappraisal. It is no longer a recognized classification.
- The Cru artisan Classification was recognized by the European Union in June 1994 and published on January 11, 2006. The classification is to be revised every 10 years. The initial list of 44 Cru Artisans was extended to 50 in 2012; see fr:Cru artisan.
The 1855 classification system was made at the request of Emperor Napoleon III for the Exposition Universelle de Paris. This came to be known as the Bordeaux Wine Official Classification of 1855, which ranked the wines into five categories according to price. The first growth red wines (four from Médoc and one, Château Haut-Brion, from Graves), are among the most expensive wines in the world.
The first growths are:
- Château Lafite-Rothschild, in the appellation Pauillac
- Château Margaux, in the appellation Margaux
- Château Latour, in the appellation Pauillac
- Château Haut-Brion, in the appellation Péssac-Leognan
- Château Mouton Rothschild, in the appellation Pauillac, promoted from second to first growth in 1973.
At the same time, the sweet white wines of Sauternes and Barsac were classified into three categories, with only Château d'Yquem being classified as a superior first growth.
In 1955, St. Émilion AOC were classified into three categories, the highest being Premier Grand Cru Classé A with two members:[22]
In the 2012 classification, two more Châteaux became members:
There is no official classification applied to Pomerol. However some Pomerol wines, notably Château Pétrus and Château Le Pin, are often considered as being equivalent to the first growths of the 1855 classification, and often sell for even higher prices.
Wine label

Bordeaux wine labels generally include:[26]
- The name of the estate (Image example: Château L'Angelus)
- The estate's classification (Image example: Grand Cru Classé) This can be in reference to the 1855 Bordeaux classification or one of the Cru Bourgeois.
- The appellation (Image example: Saint-Émilion) Appellation d'origine contrôlée laws dictate that all grapes must be harvested from a particular appellation in order for that appellation to appear on the label. The appellation is a key indicator of the type of wine in the bottle. With the image example, Pauillac wines are always red, and usually Cabernet Sauvignon is the dominant grape variety.
- Whether or not the wine is bottled at the château (Image example: Mis en Bouteille au Château) or assembled by a Négociant.
- The vintage (Image example: 1978)
- Alcohol content (not shown on image)
"Claret" terminology

Claret (/ˈklærᵻt/ KLARR-ət) is a name primarily used in British English for red Bordeaux wine.
Claret derives from the French clairet,[27] a now uncommon dark rosé, which was the most common wine exported from Bordeaux until the 18th century. The name was anglicised to "claret" as a result of its widespread consumption in England during the period in the 12th–15th centuries that Aquitaine was part of the Angevin Empire (please compare the History section). It is a protected name within the European Union, describing a red Bordeaux wine, accepted after the British wine trade demonstrated over 300 years' usage of the term.[27]
Claret is occasionally used in the United States as a semi-generic label for red wine in the style of the Bordeaux, ideally from the same grapes as are permitted in Bordeaux. The French themselves do not use the term, except for export purposes.
The meaning of "claret" has changed over time to refer to a dry, dark red Bordeaux.[27] It has remained a term associated with the English upper class, and consequently appears on bottles of generic red Bordeaux in an effort to raise their status in the market.
In November 2011, the president of the Union des Maisons de Négoce de Bordeaux, announced an intention to use the term Claret de Bordeaux for wines that are "light and fruity, easy to drink, in the same style as the original claret when it was prized by the English in former centuries".[28]
Commercial aspects
Many of the top Bordeaux wines are primarily sold as futures contracts, called selling en primeur. Because of the combination of longevity, fairly large production, and an established reputation, Bordeaux wines tend to be the most common wines at wine auctions. The latest market reports released in February 2009 shows that the market has increased in buying power by 128% while the prices have lowered for the very best Bordeaux wines.[29]
Syndicat des AOC de Bordeaux et Bordeaux Supérieur
Syndicate des Vins de Bordeaux et Bordeaux Supérieur is an organization representing the economic interests of 6,700 wine producers in Bordeaux, France. The wine lake and other economic problems have increased the salience of the winemakers' association, whose members are facing increasing costs and decreasing demand for their product.
As the largest appellation producing fine wines, and the strong foundation of the pyramid of Bordeaux wines, Bordeaux AOC & Bordeaux Supérieur AOC today account for 55% of all Bordeaux wines consumed in the world.
Plan Bordeaux
Plan Bordeaux is an initiative introduced in 2005 by ONIVINS, the French vintners association, designed to reduce France's wine glut and improve sales. Part of the plan is to uproot 17,000 hectares of the 124,000 hectares of vineyards in Bordeaux.[30] The wine industry in Bordeaux has been experiencing economic problems in the face of strong international competition from New World wines and declining wine consumption in France.[31]
In 2004, exports to the U.S. plummeted 59% in value over the previous year. Sales in Britain dropped 33% in value during the same period. The UK, a major market, now imports more wine from Australia than from France. Amongst the possible causes for this economic crisis are that many consumers tend to prefer wine labels that state the variety of grape from which the wine is made, and often find the required French AOC labels difficult to understand.
Christian Delpeuch, president emeritus of Plan Bordeaux hoped to reduce production, improve quality, and sell more wine in the United States. However, two years after the beginning of the program, Mr Delpeuch[32] resigned, "citing the failure of the French government to address properly the wine crisis in Bordeaux." Delpeuch told journalists assembled at the Bordeaux Press Club “I refuse to countenance this continual putting off of decisions which can only end in failure.”[32] "Delpeuch said he was shocked and disappointed by the failure of his efforts—and by the lack of co-operation from winemakers and négociants themselves—to achieve anything concrete in terms of reforms to the Bordeaux wine industry over the last 24 months."[32] The future of Plan Bordeaux is uncertain.
See also
References
- 1 2 3 Bordeaux.com (CIVB): Essential Guide to Bordeaux Wines Archived 2011-07-24 at the Wayback Machine., read on May 28, 2010
- ↑ "Bordeaux in figures". Retrieved 20 July 2012.
- ↑ Johnson, Hugh (1994). World Atlas of Wine (4th ed.). London: Octopus Publishing Group Ltd. p. 13.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "Official Bordeaux website". 2007-04-18. Archived from the original on 2007-09-27.
- ↑ "BBC". 2014-09-09.
- ↑ Johnson, Hugh (1994). World Atlas of Wine (4th ed.). London: Octopus Publishing Group Ltd. p. 88.
- ↑ K. MacNeil The Wine Bible pg 118 Workman Publishing 2001 ISBN 1-56305-434-5
- ↑ K. MacNeil The Wine Bible pg 120 Workman Publishing 2001 ISBN 1-56305-434-5
- ↑ K. MacNeil The Wine Bible pg 122 Workman Publishing 2001 ISBN 1-56305-434-5
- ↑ Stephen Brook, The Complete Bordeaux: The Wines, the Châteaux, the People p. 41. Octopus Publishing Group Ltd. 2007
- ↑ Oz Clarke Encyclopedia of Grapes p. 129 Harcourt Books 2001 ISBN 0-15-100714-4
- ↑ Brook, Stephen (2012). The Complete Bordeaux: The Wines – The Châteaux – The People (revised ed.). London: Octopus Publishing Group. pp. 36–55.
- ↑ Brook, Stephen (2012). The Complete Bordeaux: The Wines – The Châteaux – The People (revised ed.). London: Octopus Publishing Group. pp. 56–74.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Bordeaux.com (CIVB): The 60 Appellations, read on May 28, 2010
- 1 2 3 Bordeaux & Bordeaux Supérieur Press Kit, 2011, CIVB Economie et Etudes Nov 16, 2010.
- ↑ Bordeaux.com (CIVB): The 60 Appellations – Côtes de Bordeaux, read on May 28, 2010
- ↑ Bordeaux.com (CIVB): The 60 Appellations – Saint-Emilion, Pomerol, Fronsac, read on May 28, 2010
- ↑ Bordeaux.com (CIVB): The 60 Appellations – Médoc and Graves, read on May 28, 2010
- ↑ Bordeaux.com (CIVB): The 60 Appellations – Dry white wines, read on May 28, 2010
- ↑ Bordeaux.com (CIVB): The 60 Appellations – Dry white wines, read on May 28, 2010
- ↑ Hugh Johnson, "The World Atlas of Wine"
- 1 2 J. Robinson (ed), "The Oxford Companion to Wine", Third Edition, pp. 175–177, Oxford University Press 2006, ISBN 0-19-860990-6
- ↑ J. Robinson (ed), "The Oxford Companion to Wine", Third Edition, pp. 212–216, Oxford University Press 2006, ISBN 0-19-860990-6
- ↑ Anson, Jane, Decanter (2007-07-10). "Cru Bourgeois classification officially over".
- ↑ Anson, Jane, Decanter (2007-07-27). "Cru Bourgeois to rise again with new name".
- ↑ B. Sanderson "A Master Class in Cabernet" pg 62 Wine Spectator May 15, 2007
- 1 2 3 winepros.com.au. Oxford Companion to Wine. "Claret". Archived from the original on 2012-02-10.
- ↑ Anson, Jane (2011-11-03). "Bordeaux reclaims 'claret' name | Daily wine news – the latest breaking wine news from around the world | News". decanter.com. Retrieved 2012-10-23.
- ↑ Aarash Ghatineh, WineInvestment.org
- ↑ https://web.archive.org/web/20060326064728/http://www.vitisphere.com/dossier--49575-51254.htm. Archived from the original on 2006-03-26. Retrieved 2006-03-26. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑ Archived May 27, 2006, at the Wayback Machine.
- 1 2 3 "Wine Int – International Dreams. Universal Thoughts.". wineint.com. Archived from the original on 2006-06-18.
Further reading
- Echikson, William. Noble Rot: A Bordeaux Wine Revolution. NY: Norton, 2004.
- Teichgraeber. Bordeaux for less dough. San Francisco Chronicle, June 8, 2006
External links
- Official Bordeaux Wine website (CIVB)
- Life Goes Better With Bordeaux (Official CIVB US website)
- Official Bordeaux Classifications
- The wines of Bordeaux – The official website of France (in English)
- Bordeaux Wine Guide
- Wine war: Savy New World marketers are devastating the French wine industry
- Robert Parker's Bordeaux vintage chart
- Enobytes Bordeaux vintage chart