African pitta
| African pitta | |
|---|---|
 | |
| P. a. longipennis | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Pittidae |
| Genus: | Pitta |
| Species: | P. angolensis |
| Binomial name | |
| Pitta angolensis Vieillot, 1816 | |
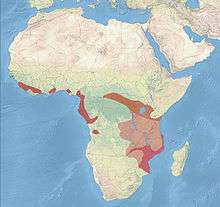 | |
Range
| |
The African pitta (Pitta angolensis) is an Afrotropical bird of the family Pittidae. It is a locally common[2] to uncommon species, resident and migratory in the west, and an intra-African migrant between equatorial and southeastern Africa.[3] They are elusive and hard to observe despite their brightly coloured plumage,[4] and their loud, explosive calls are infrequently heard. The plump, somewhat thrush-like birds[5] forage on leaf litter under the canopy of riparian or coastal forest and thickets,[6] or in climax miombo forest. They spend much time during mornings and at dusk scratching in leaf litter or around termitaria,[7] or may stand motionless for long periods.[8] Following rains[9] breeding birds call and display from the mid-canopy.[8]
Relationships
The closely related green-breasted pitta replaces it in the interior of Africa's tropical rainforests. Together they form part of a wide-ranging Old World superspecies, which in relatively recent times colonised Africa from the east.[9]
Description
Sexes are alike.[8] The crown, face and ear coverts are solid black, and the throat is pale salmon pink. The broad eyebrow is buff to brownish buff. The flanks, breast and side of neck are a mustard yellow, washed olive on the upper breast. Some western birds have the breast very greenish.[10] The wing coverts are deep green and tipped turquoise blue, or black and tipped turquoise and royal blue. The mantle and back are green, and the rump and upper tail coverts pale turquoise blue. The wings are rounded, and the primaries are black with pale and white tips. The bases of the central primaries form a white square, conspicuous in flight[5] or display. The belly and undertail coverts are crimson red, and the legs are pink. Immature birds have a duller plumage with a buffy-pink vent[8] and fawn-coloured throat.[7]
Habitat
It is a migratory species to southeastern Africa and the Congo basin. Its breeding habitat in southeastern Africa is deciduous,[11] lowland riparian forest or thicket[3] with intermittent dense understorey and small sub-canopy glades.[4] On migration however, they may sojourn at any areas of bush or woodland. Fallen dead trees and open branches are favoured perches when performing their peculiar bouncing display.[4] They are more numerous in undisturbed vegetation, and the opening up of the riparian woodland by elephants may reduce their habitat.[4]
Habits and foraging
Move about by quick hops.[7] It forages singly on leaf litter, where it scratches to uncover insects and mollusks. It may flit the tail as it walks, and run or jump to a low branch when alarmed,[5] or fly to a high branch where it hides by crouching.[7] It has a fast and direct flight.[5]
It has various call notes, including a querulous scolding "skeeow", noted by Moreau, a short, deep trill followed by a wing-clap,[5] and a sproo note, accompanied by a small jump.[7] A croaking call may be heard during migration,[8] and a guttural alarm note has been recorded.[7]
Breeding


They are probably monogamous, and display for a few weeks after arrival.[11] Displaying birds utter a far-carrying and explosive "quoip" as they leap from a lateral branch in mid-canopy.[8] At the same time the wings are opened to reveal the white bases to the primary feathers. Pairs may be spaced 150 meters from one another.[11]
The bulky, untidy nest[11] is a dome-shape structure composed of small sticks, grass and dry leaves.[4][7] The inside is lined with finer twigs, tendrils and some dry leaves.[7] It is placed 2 to 4 metres above ground in the fork of a sapling, or in the thorny and leafy branches of Acacia, Ziziphus, Ximenia or Dichrostachys. A projecting lip beside the side entrance is used as a landing platform.[11] Egg-laying takes place from November to December[4][9] in southeastern Africa, and the birds fall silent once incubation starts.[11] Three to four eggs are laid, that are white or cream in colour,[7] and flecked with grey and blackish-brown near the thicker end.[11] The nestlings are altricial and nidicolous.[11]
Migration
Race P. a. longipennis spends the austral winter in the western Ugandan forests as far north as Budongo, and coastal Kenya as far north as Gedi ruins.[3] A bird found at Minziro Forest in northwestern Tanzania was in heavy moult, suggestive that the area is on the southeastern fringe of the non-breeding range.[6]
They arrive in southern Africa from late October, though mainly in November and early December.[3] They seldom breed north of the Rukwa Valley[3] and Rufiji River in Tanzania,[6] and no further south than central Mozambique. They depart again in February, though occasionally as late as April.[4][9] Ringing studies in the Pugu hills and Mufindi have confirmed the timing of northwestward migration.[6] Exhausted and perished birds are regularly found during migration, especially November to December and April to June.[3] Southward migrating birds sometimes overshoot when they follow moist tropical fronts (at night), which may account for their vagrancy in the north-eastern Transvaal and Zimbabwean plateau.[4]
Races and ranges
- P. a. pulih Fraser, 1843 – coastal West Africa
- P. a. angolensis Vieillot, 1816 – southern Cameroon to northern Angola
- The western races are recorded from Angola, Cameroon, Republic of the Congo, DRC, Ivory Coast, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Ghana, Liberia, Nigeria, Sierra Leone and Togo.
- P. a. longipennis Reichenow, 1901 – central to east Africa[12]
Status
A decline has been noted in the coastal forests of Kenya after 1983.[5] Concern has been expressed about lighted buildings in coastal Tanzania, which might pose a collision risk, as the birds are nocturnal migrants.[6] Breeding habitat in the Zambezi valley has been impacted by elephants[4] and agricultural expansion. Habitat loss and fragmentation is ongoing.[13]
References
- ↑ BirdLife International (2012). "Pitta angolensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2013.2. International Union for Conservation of Nature. Retrieved 26 November 2013.
- ↑ Lambert, F.; Woodcock, M. (1996). Pittas, broadbills and asities. Robertsbridge, U.K.: Pica Press. ISBN 1873403240.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Britton, P. L., ed. (1980). Birds of East Africa: their habitat, status and distribution. Nairobi: East Africa Natural History Society. p. 112.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Tree, A. J. Angola Pitta (PDF). South African Bird Atlas Project (SABAP).
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Zimmerman, Dale A.; et al. (1999). Birds of Kenya and Northern Tanzania. Princeton University Press. p. 495. ISBN 0691010226.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "African Pitta". Preliminary Map. Tanzania Bird Atlas. Retrieved 4 December 2013.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 McLachlan, G. R.; Liversidge, R. (1965). Roberts birds of South Africa (5th impression, revised ed.). Cape Town: John Voelcker Bird Book Fund. p. 246. ISBN 0620005750.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Terry Stevenson; John Fanshawe (2004). Birds of East Africa: Kenya, Tanzania, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi. Helm Field Guides. p. 278. ISBN 0713673478.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Irwin, M. P. S. (1981). The Birds of Zimbabwe. Salisbury: Quest Publishing. pp. 221–222. ISBN 086-9251-554.
- ↑ Borrow, Nik. "The Internet Bird Collection". Photos: African Pitta (Pitta angolensis). Retrieved 3 December 2013.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Tarboton, Warwick (2001). A Guide to the Nests and Eggs of Southern African Birds. Cape Town: Struik. p. 141. ISBN 1-86872-616-9.
- ↑ "African Pitta (Pitta angolensis) - HBW 8, p. 149". Pittas (Pittidae). The Internet Bird Collection. Retrieved 3 December 2013.
- ↑ del Hoyo, J.; Elliott, A.; Christie, D. (2003). Handbook of the Birds of the World, vol. 8: Broadbills to Tapaculos. Barcelona: Lynx Edicions.
- Encyclopedia of Animals: Mammals, Birds, Reptiles and Amphibians. Harold G. Cogger, Edwin Gould, Joseph Forshaw
External links
- African pitta - Species text in The Atlas of Southern African Birds.
