Piprozolin
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.037.512 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C14H22N2O3S |
| Molar mass | 298.40 g/mol |
| |
| (verify) | |
Piprozolin (or piprozoline) is a medication for bile therapy.[1][2]
Synthesis
Compared to fenclozic acid, piprozolin shows choleretic rather than antiinflammatory activity. That is, the compound is useful in those conditions where the flow of bile is to be increased.
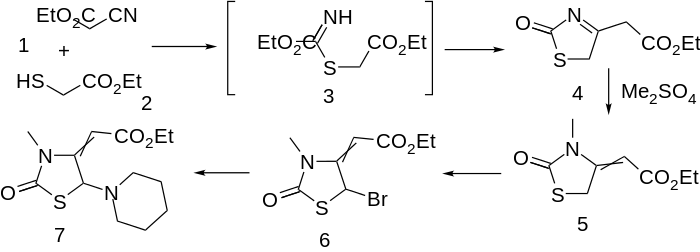
Piprozolin synthesis:[3] G. Satzinger et al., DE 2414345 (1975 to Goedecke), corresp to U.S. Patent 3,971,794 (1976 to Warner-Lambert).
Condensation of ethyl mercaptoacetate with ethyl cyanoacetate leads to thiazolinone (4); an intermediate such as 3, involving addition of the mercaptide to the nitrile function can reasonably be invoked. M/ethylation with di(m)ethyl sulfate proceeds on nitrogen with the comcomitant shift of the enamine to afford olefin (5). Bromination of the active methylene (6) followed by displacement of halogen by piperidine affords the choleretic piprozolin (7).
References
- ↑ Koss, F. W.; Vollmer, K. O.; Herrmann, M. (1972). "Research with experimental animals on the mechanism of action of the new choleretic, 3-ethyl-4-oxo-5-piperidino-delta 2, alpha-thiazolidine-acetic acid ethyl ester (Piprozolin)". Archives Internationales de Pharmacodynamie et de Thérapie. 198 (2): 333–346. PMID 5074733.
- ↑ Drugs-about.com: Piprozolin
- ↑ Satzinger, G. (1963). "Substituierte 2-Methylen-thiazolidone-(4)". Justus Liebigs Annalen der Chemie. 665: 150. doi:10.1002/jlac.19636650118.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.