Pilgrim: Faith as a Weapon
| Pilgrim: Faith as a Weapon | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Developer(s) | Arxel Tribe |
| Publisher(s) | Infogrames Multimedia |
| Designer(s) | Nicolas Fructus, Moebius |
| Writer(s) | Paulo Coelho |
| Composer(s) | Jacques Nelissen, Kristjan Cocev |
| Series | Q1788490[*] |
| Platform(s) | Microsoft Windows |
| Release | November 1997 |
| Genre(s) | Adventure, educational |
Pilgrim: Faith as a Weapon is a 1997 adventure video game, with a screenplay written by Paulo Coelho, who wrote The Pilgrimage, the novel on which the game is based. Pilgrim has been described as a "commercial cultural heritage game"[1] and "graphic interactive fiction".[2] It is the premiere title of Arxel Tribe[3] and the first in The Paulo Coelho trilogy, alongside The Legend of the Prophet and the Assassin (1999) and The Secrets of Alamut (2001).
Plot
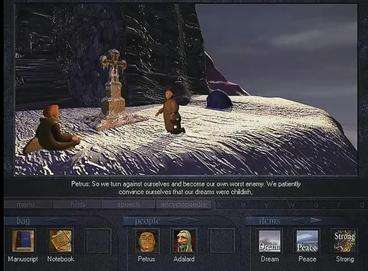
The game is loosely based on Paulo Coelho's autobiographical 1987 novel The Pilgrimage. It is a time of superstition and religious persecution,[4] where Catharism reigns supreme. Set at the beginning of the Albigensian Crusade (1208) in the south of France, the story sees Simon Lancroix aim to complete his dying father's wishes of finding a secret manuscript and delivering it to a friend named Petrus. It is revealed that this actually a Coptic manuscript that a renegade Templar brought back from Crusades; it is believed to be the lost Gospel of Saint Jean. This manuscript gets passed around to various characters and locations. Meanwhile, Pope Innocent III orders the inquisitor Diego de Osma to retrieve the manuscript. Mystical creatures such as angels and demons also become entangled in the battle.[5]
The first half of the game sees the player complete a series of tasks to help other characters, who in return help the player. Halfway through the game, the player meets Petrus, who reveals that the player's father was the leader of a fictional religious sect called "The Tradition", which aims to bring an absolute truth that no other religion can.[6] From this point the game covers symbolic, spiritual, and supernatural philosophies such as dreams, peace, compassion, love, salvation, the four horsemen of the apocalypse, growing up and giving up, and re-learning what we knew as children; the final scene takes place in limbo.[6]
Gameplay
Pilgrim is a first person point-and-click adventure. Players click through a series of static frames—a slideshow of pre-rendered 3D environments—to move around; one is not free of their movements and must often strategically click screen points in a certain order to reach a destination.[6][7] The cursor becomes an arrow to indicate a possible movement, and a click transitions the player to the next location.[7] It is possible to die in the game; causes of death include the player failing to accomplish certain time-dependent challenges.[6] If the player dies they are returned to the beginning of the latest checkpoint, often after a cutscene.[5][6] There are also two unwinnable states; one of them occurs if the player gives all their money to a beggar in Toulouse, despite them needing the money to go past the very next door.[6] The player is encouraged to "save early, save often".[6] The final puzzle of the game has been described as "no less than an exam about what you're supposed to have learned".[6] The game comes with two discs, which are both required for game installation; regardless of where the player is, Disc 1 must be inserted every time the player boots up the game.
The "Inventory" interface contains three elements. "Bag" contains the acquired items[5] (the player is limited in the number of items and the weight they can carry).[7] "People" contains the characters that the player had encountered, knows about, or wants information on.[5] "Items" contains the objects which have been seen or heard about but not acquired.[5] "People" and "Items" of interest can be brought up as conversation topics with others.[5] To use an item in "Bag", the player clicks on it to activate it (it then has a yellow box around it), then clicks "View".[7] To offer a topic of discussion, the player clicks on an item in the "People" or "Items" tabs to activate it, then clicks on a character in the "View" screen to talk about it.[7] The puzzles require both reflection and patience.[5] The "Bag" items and the clues within the "Encyclopedia" can be applied and manipulated to solve puzzles thereby advancing the story.[5] The latter is similar to how the Chronopedia in used in Broderbund adventure game Carmen Sandiego's Great Chase Through Time.[8] The game has a hint system to provide clues for the more obscure puzzles.[5] The entries of the in-game "Encyclopedia" have been described as "spartan" due to consisting exclusively of text.[6] Sometimes when a character mentions a topic that is available in the encyclopedia during a conversation, a keyword will appear on the screen which may then be clicked to bring up the corresponding entry.[6] While not required, this feature allows the player to delve deeper into the interesting historical nuggets that feature throughout the game.[6] The player has an in-game notebook, into which they may copy-paste extracts from the encyclopedia.[6]
Development


Inspiration
Arxel Tribe was founded in 1990 by two Slovenian architects named Matjaž Požlep and Diego Zanco.[6][9] Prior to Pilgrim, the company had been known for designing and producing animated computer graphics for the architecture industry on Silicon Graphics computers from three agencies in Ljubljana, Paris and Milan.[10][11] Frenchmen Stephen Carrière and Guillaume de Fondaumière joined the company three years later in 1993.[6] They helped diversify it into a special effects company for the advertising industry in 1994 by creating an educational film for an Italian design agency, which went on to win awards and be featured at the Berlin Film Festival.[11] That experience gave the team a desire to create graphics as a means of expression, and to pursue more ambitious projects in the entertainment industry; specifically for video games.[11] Arxel Tribe tried to raise funds for over a year to pursue the goal, but were unsuccessful at the time.[11] In 1996, Anne Carriére Multimédia was founded as a subsidiary arm of Anne Carriére, the publishing house in charge of the French publication of work by Brazilian novelist Paulo Coelho[12] and French cartoon artist Jean Giraud (also known as Mœbius).[6] The subsidiary was created to specialise in the production of a genre of video games called "author games"; they chose Arxel Tribe to serve as the development team for the title.[13][14] Stephen Carrière's mother, Anne, was the head of Anne Carriére publishing house; this well-connectedness allowed for the ability for Arxel Tribe to collaborate with a high calibre of creative talent on its debut foray into the video game space[6][15][16]
The premiere project of the new venture was chosen by Anne Carriére Multimédia to be an adventure game based off Coelho's The Pilgrimage (1987) while the artistic direction was handed to French comic artist and frequent video game collaborator Jean Giraud (aka Moebius); The Pilgrimage would be his last gaming project.[13][14][17][18] Moebius had previously contributed art illustrations to the French edition of one of Coelho's books,[6] and had designed covers for gaming projects such as Panzer Dragoon (1995) and Fade to Black (1995).[18] Coelho's books had sold in the millions, and this provided an incentive for the threads of his work to be woven into giant PC games.[19] According to SK Online, Coelho "accepted the proposal with great pleasure" after learning that the general appearance of the game would be decided by Moebius.[20] Moebius and Coelho started the design work in 1996.[21][22] In 1996, one short year since their last diversification, Arxel Tribe had a meeting with Coelho and Moebius, with the result being the company switching gears to become a video game development studio and signing onto the project, which was to be published by Infogrames in 1997.[23][24] Fondaumière recalled "sitting at a bar in Frankfurt with Paulo Coelho [and] discussing the crazy idea of creating a videogame together".[25] Stephen Carrière and Guillaume de Fondaumière helped Arxel Tribe re-position itself as a developer of "author games",[26] and the company bought the rights to publishing a video game adaption of Pilgrim.[11] Arxel Tribe had made a lot of money in the advertising industry and had grown a desire to move into the video gaming industry; they were currently in a financially agreeable state to pursue this vision.[27] Moebius required 20 million francs of investment to become involved.[28] Matja Požlep noted that creating a game based on Coelho's work was useful because potential customers would have already had an acquaintance with his work.[29] Guillaume de Fondaumiere recalled that as professionals, Coelho and Mobius charged a high price for their effort, and had a highly ambitious, challenging, and expensive vision; Arxel Tribe's lack of experience in video game development meant that the collaboration became "fantastic, but also a painful experience" much to their dismay.[11] The game would originally be called Pilgrim during the development stage, and by its release would subtitled with Faith as a Weapon.[13][14]
Adventure gaming was chosen by Arxel Tribe because the genre had recently been experiencing technological advancements that were comparable to those seen in the shooting genre with new releases such as Doom (1993) and Quake (1996), which opened up new graphical and narrative possibilities.[9] Arxel Tribe aimed to create an adventure game with an "epic" and "gripping" narrative to give justice to the source material's "initiatory, romantic and spiritual journey".[13][14] They wanted to make a "humanist journey with a very deep story line", instead of being "just another adventure game".[22] The development company collaborated with Coelho into adapting the story into more of an investigative detective mystery in order to better immerse the player while encouraging them to utilise their logic and imagination.[13][14] The early 13th century was chosen as the game's time period due to its "historical and mythical richness" abundant with heresy, crusades, and errands by knights; the developers felt this was the ideal setting to illustrate the "generous and humanist philosophy" inherent in Coelho's book.[13][14] Stephen Carrière expressed that video game manufacturers were drawn toward comic book writers, screenwriters or cartoonists due to their desire to create a unique graphic universe that sets the game apart from the rest of the market.[30] Matjaz Požlep said the company worked within an adventure gaming niche, and within it an intellectual gaming sub-niche.[9] Around this time 46 people were working on Arxel Tribe games at their Ljubljana company headquarters.[29]
Design


While Guillaume de Fondaumière considered video gaming a mere extension of their 3D studio business, he was neither a programmer or graphic artist, so he assumed the role of producer and sought to find people who cared about the creative side of game development.[27] With a team of "galley slaves", they managed to complete the game in a mere 15 months.[11]
Moebius collaborated with Arxel Tribe artistic director Nicolas Fructus on the game's design elements to draw the concept art for scenes and characters.[12][31] The development company felt that the drawings by Moebius enhanced the magical quality of the story, and provided a sense of cultural and spiritual curiosity, transcending the generic conventions of the adventure game genre.[13][14] The 2D character design work was done in both Ljubljana and Paris, while the adaptation of the designs using 3D graphic software was completed in Ljubljana[15] Computer artists created 3D images from Moebius' drawings using Silicon Graphics computers (such as Onyx and Indigo 2, which they had used in previous non-video game projects[32]); they mixed traditional computer graphics techniques, such as rigging, with motion capture in order to animate the characters.[13][14][33]
Marcin Mierzejewski Zenzire approached Arxel Tribe in 1996 to become a 3D modeller and animator, but was instead hired as a coder for this game. At the time the company had limited coding experience from their previous multimedia projects, so they needed a professional coder.[34] Zenzire "set up the initial architecture for the game engine, coded some UI routines and the game's interactive encyclopedia", using expertise from his work using hypertext. He also "supervised the code and offered assistance with other programming tasks".[34]
Early in development, a complete literature research was carried out in order to provide the team with a comprehensive and faithful design guide containing each historical element the project required, such as clothes, architecture, and landscapes.[13][14] To give the player a colourful window into the complexities of the time period, a multimedia encyclopedia containing biographical information such as maps, articles, and paintings was included in-game; the over 150 page data bank is divided into three parts: "History & Geography", "Life in the Middle Ages" and "Religion".[5][13][14] This 13th century information was added to provide additional historical knowledge and context.[15] The game was created with the participation of Le Centre National de la Cinématographie and the Ministèr Délégué à la Poste aux Télécommunications et à l'Espace.[35]
Most of the game's background music was not written for the game; it was instead chosen from preexisting music, largely from the Medieval and Romantic periods.[16] This includes: Symphony No. 1 in D major by Gustav Mahler, a piece by Fernando Sor, a guitar-transcribed version of Isaac Albéniz's piano pieces Suite Española No. 1, Op. 47 and Cantos de España, and Greensleeves.[5][7] The pieces are relatively short and loop indefinitely in their respective locations.[6] The game is in the SVGA 640x480 aspect ratio,[7] and was made available into English, French, German and Brazilian Portuguese.[22]
Release
In June 1997, Arxel reported on their website that the game was likely to be completed that December, with a world release planned for the Spring of 1998.[13][14][15] At the time, Parisian company Anne Carierre Multimedia was confirmed as co-producer of the game, while the major worldwide distribution companies were still being negotiated.[13][14][15] Later that year, Infogrames Entertainment signed a first publishing and distribution contract with Arxel Tribe.[21] The project was officially announced to the press during a candlelit dinner held in a castle in Ljubljana in September 1997, with an intended release date of November of that year.[12] The small multimedia studio treated the journalists to a sample of local handicrafts at the beginning of the evening, and then invited them to a memorable conference in the castle hall.[36]
The game would be released in the USA and Europe in November 1997 in English, French (Pilgrim: Par le Livre et par l'Epée), and German (Pilgrim: Das Geheimnis der Schrift), with a Brazilian Portuguese release entitled O Diário de um Mago being released in January 1998.[12] The game ended up being published first in the UK in February 1998 by Infogrames Multimedia; the French publication was handled by Wanadoo Edition (formed by index+'s acquisition of France Télécom Multimédia), and the French trailer was created by Eurospace, advertised by Infogrames, and directed by Lioux Philippe.[21][37] The game was also available for purchase via the Arxel Tribe webstore.[38] As a promotion, Arxel Tribe announced they would give a free copy of the game to the first 200 people to send the company their full details.[32] In total, $2 million was invested into the venture; of this, $1 million went toward the production of the title by Arxel Tribe and Anne Carrière Multimedia, while another $1 million was spent to promote the title which was distributed worldwide by French company Infogrames.[12] 250,000 copies of the video game were published.[39]
Just Adventure described Pilgrim as a "little-known title", noting that by the time of its sequel's release in 1999, Pilgrim had still never released in North America.[40] It noted that there were three potential culprits to the gaming "gem" suffering in terms of recognition: little to no marketing by Arxel Tribe, the publisher not understanding how to sell the product, and the gaming industry simply being apathetic toward adventure games at the time.[40] Game coder Marcin Mierzejewski Zenzire would later argue that while the title was a decent success among adventure fans and created a reasonable amount of media buzz, Arxel Tribe used the boom in popularity to promote themselves rather than the game, which meant a "comparatively small number of copies was printed and therefore sold out almost immediately".[34] SK Online wrote that the game was only a half-hearted success, partly because of the lack of advertising, but also because it had some technical deficiencies when compared to its contemporaries.[20] Clovis of Gameboomers noted that during its rollout, there were "significant delays in delivery".[38] Just Adventure reported that Pilgrim was originally supposed to be included as a bonus feature in the release of The Legend of the Prophet and the Assassin, but that this idea was later abandoned, describing it as "yet another marketing mistake".[41] The article, published between the Pilgrim's original and re-releases, further explained that while the game was very rare, it could occasionally be located on eBay and the Game Trading Zone.[41] In its review of The Secrets of Alamut in July 2001, Just Adventure wrote that Pilgrim had experienced a "rejuvenation in sales" in the time since it had been listed it in The Ten Best Games That (Almost) No One Has Ever Played article.[42] Despite that, in 2002 Tap Repeatedly would still lament that the game had sunk into relative obscurity between its 1998 and 2001 releases.[43] On the contrary, VGDb said the game was a "great success",[44] while Arxel Tribe asserted that their game had been recognised by both players and critics for its originality and being faithful to Coelho's work.[45] Guillaume de Fondaumiere told Game.EXE that the game sold "surprisingly well", and that due to the efforts of Infogrames, 40,000 copies were sold in France alone.[11] Relations Presse asserted that the game received an impressive number of articles in the public press as a result of their public relations stunt at the Ljubljana castle.[36]
The game would not be reprinted until three years after its original release; it was re-released in France in March 2001 and the USA in November 2001 (by Selectsoft Publishing) as a Deluxe Edition, in some cases without its subtitle as just Pilgrim.[34][46][47] The re-release contained 3 CD-ROMs: the game discs and a bonus "Making Of" disc featuring an interview of Coelho, 14 storyboards by Moebius, an encyclopaedia of the Middle Ages, and a walkthrough solution of the game.[47] On February 28, 2001, French adventure company Nival Interactive announced that it had signed a contract with Wanadoo Edition for the release of a Russian version of Pilgrim in the second quarter of that year, but this project was never realised (however 1C would publish the Russian versions of the sequels).[16] In March 2001, Guillaume de Fondaumiere expressed a desire to find a publisher to facilitate the localization and distribution of the title in Russia, suggesting that players should play the game in their own languages to fully appreciate it.[11] In 2002, CD Projekt would issue a Polish version of the game in response to the wave of popularity around Paolo Coelho and The Pilgrimage at the time.[48] While created for Windows 3.1 or Windows 95, to be played using a Pentium 75 MHz chip and at least 16 Mbytes of RAM, the game is able to run under XP and Vista on 32-bit.[7][12]
Reception
| Reception | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
In June 1997 before the game's release, Stop magazine published an article in which they described the game's genre as most akin to the video game Myst (1993), in terms of technical design.[15] Upon the game's announcement in September 1997, Marijô Zilveti of Folha De S.Paulo expressed joy that the game would bear a resemblance to Coelho's novel as he was directly involved in the creation of the script.[12] In October 1997, PC Jeux wrote that its beauty and intensity made up for its "technical poverty".[49] In November 1997, La Croix selected the game for its article French creators innovate with poetry, describing the game as a "historical-New Age quest".[50] That month, PC Joker wrote that the game's bugs were enough to sour the experience, despite the title's beautiful aesthetic design.[51] In December 1997, PC Player said it was imitially turned off by the cumbersome, bland, and strange game, but after a while became enamoured by the "mystery and profundity" of the game's images and sounds.[52] Power Play negatively compared the game to Broken Sword: The Shadow of the Templars,[53] PC Action described the interface as "unusual but very intuitive",[54] GameStar negatively compared the game to Riven and Zork: Grand Inquisitor while accusing it of being both too complicated and obsolete,[55] and PC Games said the game lacked tension, variety and mental challenge.[56] In January 1998, PC Power praised the animations and the elaborate background information, though lamented that it missed award status by having handling and gameplay issues.[57][58] That year, Joe Nettleback of PowerPlay wrote that he was pleased with the German dub.[59] In 1998, Nataliya Dubrovskaya of Game.EXE expressed that the game was a beautiful entry in the "euroadventure" genre, along with such contemporaries as Dark Earth, Nightmare Creatures, and Cryo Interactive titles like Atlantis: The Lost Tales, Dreams to Reality, and Versailles, despite finding it an "ugly term"; the site praised the game's beauty and solid story.[60] Meanwhile, Privat Computer PC loathed the game, describing it as a "French failure"[61] In 2000, Annemarie of Adventure-Archiv noted that while she had not played the predecessor to The Legend of the Prophet and the Assassin so did not know what to expect going in, she still found enjoyment from Pilgrim's sequel.[62][63]
In 2001, Ray Ivey of Just Adventure, a self-professed fan of the developer due to Ring (1999) and Faust (1999), picked up Pilgrim "mostly out of academic interest" to examine Axel Tribe's debut work; he described the title as "lovely", "mysterious", "educational", "compelling", and a great entry in the adventure game genre.[2] That same year the publication's Randy Sluganski ranked the game 7th in his list of The 10 Best Adventure Games That (Almost) No One Has Ever Played, complimenting it for tackling foreign video game territory such as theology and superstition, and describing it as an "artistic tour-de-force" that addresses its themes with a sense of adventurousness, power, and scope.[41] Gordon Aplin of Metzomagic and Quandary didn't buy the game on its original release as the box cover mislead him into thinking the game was action/adventure ala Knight's Chase; upon playing the game in 2001 he deemed it a valiant first effort by Arxel but incomparable to the later titles like Ring and Faust,[64][65] and in a 1999 Faust review Metzomagic's Steve Metzler would say the company had "improved tremendously" when compared to Pilgrim's "incomprehensible" puzzle design.[66] Upon the release of The Legend of the Prophet & the Assassin, SK Online gave Arxel Tribe the distinction of being the first company from the former Yugoslavia to have "seriously sailed the choppy waters of the market of computer entertainment", citing the company's decision to adapt Coelho's novel into a computer game as a sign of them pursuing original ideas from the very start.[20] In a 2002 review Tap Repeatedly's Enigma described the game as "mind-blowing", "stunning", "outrageous", and "constantly interesting".[43]
In 2003, Polish adventure game review site Przygodoskop wrote that the title had outdated graphics, a dull narrative, and ordinary puzzles, and considered its Polish release a cash-grab due to the popularity around the author at the time.[48] In a 2004 review of the game, JPP of Jeux Video said he preferred the beginning of the game due to its logical puzzles, as opposed to the latter half's "spiritual initiatory quest" narrative which has vague puzzles to match.[67] In their first issue of 2004, Polish video gaming magazine Play DVD noted that Coelho, was known for creating "neat", "fast", "dramatic", and "instructional" work, and compared this checklist against the video game.[68][69][70] In 2006, Avsn-nikki of Adventurespiele admitted that the graphics appeared outdated, and noted that in order to succeed you need to ask every individual character every tiny conversation thread.[71] Old-Games.ru listed the game in its International Festival of Adventure as a rare and interesting entry in the genre.[72] The site noted that the game was released just after historical-themed adventure games came into fashion in the late 1990s, while praising the novice developer for its Moebius' beautiful work and favourably comparing Coelho's confident script to the work of Cryo Interactive and index+; the site criticised the interface for taking up nearly half the screen and the transformation of Moebius' "cute and stylish" 2D drawings into low-polygon 3D dummies, but deemed it a historical, cultural, and entertainment achievement, and praised the developer's use of authentic melodies expressing a desire for them to continue this in their future work.[16] AVEC thought there was deservedly no interest in the game.[73]
Puntaeclicca's Aspide Gioconda liked the game from both a historical and puzzle design perspective, though thought the game's bugs slightly conditioned its quality level.[4] Quedzas Video Games thought the game's music was beautiful and atmospheric, citing the tune playing at Saint-Sernin as evoking a sense of mystery.[5] Mr. Bill & Lela from Mr. Bill's Adventureland Review praised the game for mixing educational historical elements seamlessly into the intriguing story.[74] Abandonware France thought the graphics were plasticy, yet detailed and impressive for the time; the site also thought the French voice acting was generally good.[7] The book Le livre de sagesse: supports, médiations, usages noted that games like Pilgrim demonstrate how the player's actions allow them to write or rewrite history; the fate of the narrative is in their hands.[75] Studies in Medievalism explained that Pilgrim is one of only a handful of adventure video games set in the medieval period, alongside entries like Cryo Interactive's Arthur's Knights; the book suggested that Pilgrim "tries so hard to be authentic".[76] Camille Saint-Jacques of Arts contemporains, 1950–2000 thought Moebius' contribution toward the game was an example of the interest graphic artists of the time (particularly young ones) were having toward the multimedia and video games industry, which offered a more magnetic pull than traditional neuvième art (comic books); it noted that the Slovenian designers did not "disdain to be interested" in collaborating with a comic book artist.[77] On his review site Feibel, German journalist Thomas Feibel accused the 3D characters of moving around like "living helium balloons", due to their movements lacking in detail and precision.[78] Gameboomers reviewer Clovis noted that pixel hunting is required early on, and that puzzles toward the end were so obscure he was forced to use a walkthough.[38]
Damien Poussier of Hardcore Gaming 101 asserted that Pilgrim is the resulting blend of the "relative seriousness" and "classic feel" of Arxel Tribe (which he compared with Cryo Interactive), the "great artwork" of Moebius, and the "ridiculous new age philosophy" and "low-grade proselytizing" of Coelho.[6] Poussier also compared the gameplay to Myst and liked that the game didn't follow the book too closely, noting that a "stain" of the "author's influence" wasn't noticeable until the game's midpoint; he thought the scene with Petrus was "completely out of the blue" and "filled with absolute nonsense that even the stonest of all hippies would find laughable".[6] The Hardcore Gaming 101 reviewer also criticised the plasticy characters which did not resemble Moebius' work, having to wait for characters to complete an animation before answering each question, and the "excruciatingly awful" voice acting of many characters, particularly the incorrect French and Spanish accents.[6] Poussier praised the atmospheric music, as well as the "well-handed" education despite lamenting that the encyclopedia would have been more paletable had its walls of text been sprinkled with some images.[6]
Legacy
The game received the Golden CD-ROM award in France, and various other international awards.[21][79] According to Arxel Tribe, the game's release saw the developer become recognized for its "author games", which had beautiful graphics and scenario depth.[80] The game turned out to be Arxel Tribe's prelude; it was followed by the company's "international breakthrough" hit Ring (1998), based on an opera by Richard Wagner, which would sell 600,000 copies.[3][81] Ring's game engine was based on the one created for Pilgrim; therefore the titles had a similar architecture and design.[34]
After the release of Pilgrim, Paulo Coelho decided to use this collaboration and newfound interest in interactive entertainment as the inspiration behind a recurring plot point in his 1998 novel Veronika Decides to Die, which was released the same year as Pilgrim sequel The Legend of the Prophet and the Assassin. In Veronika Decides to Die, the suicidal Ljubljana-born heroine reads an article in the French magazine Homme about a computer game developed in Slovenia and written by Coelho.[20][45][82] There are many references to Pilgrim and Coelho's thoughts on the experience throughout the book; the following passage illustrates this:
"Having nothing more interesting to do, [Veronika] decided to read the whole article, and she learned that the said computer game had been made in Slovenia -that strange country that no one seemed quite able to place, except the people who lived there – because it was a cheap source of labor. A few months before, when the product was launched, the French manufacturer had given a party for journalists from all over the world in a castle in Vled. Veronika remembered reading something about the party; which had been quite an event in the city, not just because the castle had been redecorated in order to match as closely as possible the medieval atmosphere of the CD-ROM, but because of the controversy in the local press: Journalists from Germany, France, Britain, Italy and Spain had been invited, but not a single Slovene..."— Paulo Coelho, excerpt from his 1998 novel Veronika Decides to Die[83]
After Pilgrim, it was decided that the " fruitful collaboration" between Arxel Tribe and Coelho would continue; this resulted in the creation of two more games set in the Medieval Middle East, creating an adventure trilogy.[20][45] The Legend of the Prophet and the Assassin, also known as The Prophet's Trail, (and called The Legend of As-Sayf: The Prophet and the Assasin during the development stage[11]), is sometimes referred to as Pilgrim II; it is however less a direct sequel and more an "entirely new story about the same era as seen from another perspective", which carries over into the third game The Secrets of Alamut.[84] Described by Guillaume de Fondaumiere as a "kind of continuation",[11] the game takes place 50 years after the events witnessed in Pilgrim, although the game explores many of the same themes.[20] Just Adventure noted that when the sequel was released in North America, Pilgrim still had not been, so there was no point in marketing the game as Pilgrim II.[40] In some releases the two games are considered Part 1 and Part 2 of the Legend series, with the bundled release also known as The Legend of the Prophet and the Assassin.[40] Throughout The Paul Coelho trilogy, Pilgrim protagonist Simon de Lancroix evolves from a "young, sense-seeking" person to someone who has "matured to a prophet, although not loved by everyone", according to Adventure-Archiv.[85] However, Damien Poussier of Hardcore Gaming 101 argues that while Simon de Lancroix is mentioned in the sequel, the name is not referring to the same character from Pilgrim.[6] The Lancroix of the sequels is a European prophet who wanted to construct an oasis of peace called Jébus.[20] The three titles which would form a collection; (alongside The Legend of the Prophet and the Assassin (2000) and The Secrets of Alamut (2001), which continued the story, the three games would be collectively be known as The Paulo Coelho trilogy).[13][14][86]
Guillaume de Fondaumiere later said that while he was proud of the game, it was not particularly impressive by the standards of the time.[11] Many of the crew for this game would work together on other projects. 20 and 14 members of the creative team collaborated on Faust: Seven Games of the Soul (1999) and The Legend of the Prophet and the Assassin (2000 – also written by Coelho), respectively.[35] Arxel Tribe would develop fifteen games, which would mostly share a series of common aspects: educational adventure games, set in specific historic times, and inspired by real or mythological events.[6] Arxel Tribe would eventually be renamed Art Rebel, and create the graphic production and modeling for French video game developer White Birds Productions.[87]
References
- ↑ de Leede, Judith. "Main trends in the serious gaming industry". Alliance Experts. Retrieved 2017-01-28.
- 1 2 Ivey, Ray (July 20, 2001). "Review: Pilgrim". Just Adventure. Archived from the original on July 20, 2001. Retrieved 2017-01-28.
- 1 2 "Guillaume DE FONDAUMIERE". DigiWorld Summit. November 20, 2014.
- 1 2 Gioconda, Aspide. "Pilgrim (Italian)". Puntaeclicca. Retrieved 2017-01-28.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 "Pilgrim (French)". Quedzas Video Games. Retrieved 2017-01-28.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 Poussier, Damien (July 12, 2012). "Pigrim: Faith as a Weapon". Hardcore Gaming 101. Retrieved 2017-01-29.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 "Pilgrim: Par le Livre et par l'Epée (French)". Abandonware France. Retrieved 2017-01-29.
- ↑ "Carmen Sandiego's Great Chase Through Time". Learning Village. Retrieved October 27, 2012.
- 1 2 3 Ivanc, Staš (November 8, 2011). "Z računalniškimi igrami na svetovni trg (Slovenian)". Delo. Retrieved 2017-01-31.
- ↑ "Article about Arxel Tribe (Slovenian)". Media and Marketing Magazine. June 1997. Retrieved 2017-01-28.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 "The Legend of the Prophet and the Assasin (Russian)". Game.EXE. March 22, 2001. Archived from the original on August 21, 2014. Retrieved 2017-02-01.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Zilveti, Marijô (September 17, 1997). ""Diário de Um Mago" vira game (Brazilian Portuguese)". Folha De S.Paulo.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 "Work In Progress". Arxel Tribe. 1997. Archived from the original on 1997-06-26. Retrieved 2017-01-28.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 "Pilgrim". Arxel Tribe. Archived from the original on 1997-06-26. Retrieved 2017-01-28.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "Article about Arxel Tribe: NA ROMARSKI POTI (Slovenian)". Stop magazine. June 1997. Retrieved 2017-01-28.
- 1 2 3 4 Uka. "Pilgrim: Faith as a Weapon (Russian)". Old-Games.ru. Retrieved 2017-01-31.
- ↑ Plunkett, Luke (March 12, 2012). "Remembering Moebius, A Man Who Helped Video Games More Than You Might Think". Kotaku. Retrieved 2017-01-28.
- 1 2 BOUNTHAVY (May 5, 2014). "Moebius et le jeu vidéo : game over (French)". Difficile d'écrire sur des futilités. Retrieved 2017-01-31.
- ↑ "Render-Adventure im Stil von Myst (German)". PC Games. September 27, 2001. Retrieved 2017-01-30.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 MACEDONIĆ, Slobodan (March 2001). "The Legend of the Prophet & the Assassin (Serbian)". SK Online. Retrieved 2017-01-30.
- 1 2 3 4 "About The Tribe". Arxel Tribe. August 2, 2002. Archived from the original on August 2, 2002. Retrieved 2017-01-29.
- 1 2 3 "Pilgrim information". Arxel Tribe. August 2, 2002. Archived from the original on August 2, 2002. Retrieved 2017-01-29.
- ↑ "4th INTERNATIONAL VIDEO GAME FORUM: Guillaume DE FONDAUMIERE (French)". Content Industries & Broadband Economies. November 22, 2005. Retrieved 2017-01-29.
- ↑ "MILIA GAMES '99: Getting Ahead of the Game". Business Wire. December 2, 1998. Retrieved 2017-01-29.
- ↑ Martin, Matt (September 29, 2010). "Celebrating 15 Years of PlayStation". GamesIndustry.biz. Retrieved 2017-02-01.
- ↑ "Guillaume de Fondaumière". Game Connection. Retrieved 2017-01-29.
- 1 2 Schneeweiss, Hans (February 23, 2010). "Interview Guillaume de Fondaumière, Co-CEO von Quantic Dream und Produzent von Heavy Rain (German)". Gameswelt. Retrieved 2017-01-29.
- ↑ Paris Match (French). 1998-12-01.
- 1 2 Fridi, Malda (June 10, 1999). "Osnovna vrednota so mediloveški odnosi (Slovenian)". Tednik (23). p. 5.
- ↑ Riviore, Annick (May 7, 1999). "Les éditeurs de jeux sollicitent de plus en plus les auteurs de bande dessinée dont ils prisent la créativité et les qualités de scénariste (French)". Liberation. Retrieved 2017-01-29.
- ↑ Fructus, Nicolas. "Nicolas Fructus dessinateur, scénariste (French)". Humano. Retrieved 2017-01-28.
- 1 2 "Arxel Tribe – History". Arxel Tribe. 1997. Archived from the original on 1997-06-26. Retrieved 2017-01-28.
- ↑ "Samo Homsak" (PDF).
- 1 2 3 4 5 Zenzire, Marcin Mierzejewski (November 18, 2011). "Arxel Tribe (1996–2003)". Sinister Systems. Retrieved 2017-01-29.
- 1 2 "Pilgrim: Faith as a Weapon credits". MobyGames. Retrieved 2017-01-28.
- 1 2 Ichbiah, Daniel. Relations Presse (French). Daniel Ichbiah. ISBN 9781291317022.
- ↑ "Pilgrim (French)". Institut National de l'Audiovisuel. Retrieved 2017-02-01.
- 1 2 3 Clovis (December 8, 2003). "Pilgrim". Gameboomers. Archived from the original on December 8, 2003. Retrieved 2017-01-31.
- ↑ "Guillaume de Fondaumière (French)". LinkedIn. January 10, 2013. Archived from the original on January 10, 2013. Retrieved 2017-01-29.
- 1 2 3 4 Sluganski, Randy (July 20, 2001). "Review: The Legend of the Prophet and the Assassin". Just Adventure. Archived from the original on July 20, 2001. Retrieved 2017-01-30.
- 1 2 3 Sluganski, Randy (July 20, 2001). "The 10 Best Adventure Games That (Almost) No One Has Ever Played". Just Adventure. Archived from the original on July 20, 2001. Retrieved 2017-01-30.
- ↑ Sluganski, Randy (July 16, 2001). "The Secrets of Alamut". Just Adventure. Archived from the original on July 16, 2001. Retrieved 2017-01-30.
- 1 2 Enigma (February 2002). "Pilgrim: Faith as a Weapon". Tap Repeatedly. Retrieved 2017-01-28.
- ↑ "GUILLAUME DE FONDAUMIERE (Polish)". VGDb. Retrieved 2017-01-29.
- 1 2 3 "Paulo Coelho & Arxel Tribe (French')". Arxel Tribe. 1999. Retrieved 2017-01-31.
- ↑ "Pilgrim: Faith as a Weapon". AdventureGamers. Retrieved 2017-01-28.
- 1 2 "Les Secrets D'alamut – Présentation (French)". Arxel Tribe. May 8, 2001. Archived from the original on May 8, 2001. Retrieved 2017-01-29.
- 1 2 Wilczek, Tomasz (October 28, 2003). "Pielgrzym (Polish)". Przygodoskop. Retrieved 2017-01-31.
- ↑ "Pilgrim: Faith as a Weapon (French)". PC Jeux. October 1997. Retrieved 2017-02-01.
- ↑ Ferre, Jean-Luc (November 24, 1997). "Les créateurs français innovent avec poésie (French)". La Croix. Retrieved 2017-02-01.
- ↑ "Pilgrim: Faith as a Weapon (German)". PC Joker. November 1997. Retrieved 2017-02-01.
- ↑ "Pilgrim: Faith as a Weapon (German)". PC Player. December 1997. Retrieved 2017-02-01.
- ↑ "Pilgrim: Faith as a Weapon for Windows". PowerPlay. December 1997. Retrieved 2017-02-01.
- ↑ "Pilgrim: Faith as a Weapon (German)". PC Action. December 17, 1997. Retrieved 2017-02-01.
- ↑ "Pilgrim: Faith as a Weapon (German)". GameStar. December 1997. Retrieved 2017-02-01.
- ↑ "Pilgrim: Faith as a Weapon (German)". PC Games. December 3, 1997. Retrieved 2017-02-01.
- ↑ "Pilgrim". PC Power. January 1998. Retrieved 2017-01-28.
- ↑ "Pilgrim (German)". PC Power. January 1998. Retrieved 2017-01-28.
- ↑ Nettelbeck, Joe (January 1998). "Pilgrim (German)". PowerPlay. Retrieved 2017-01-28.
- ↑ Dubrovskaya, Nataliya (1998). "Pilgrim: Faith as a Weapon (Russian)". Game.EXE. 32 (3): 72.
- ↑ "Pilgrim: Faith as a Weapon (Danish)". Privat Computer PC. 1998. Retrieved 2017-02-01.
- ↑ Annemarie (November 20, 2000). "The Legend of the Prophet and the Assassin – Part 1". Adventure-Archiv. Retrieved 2017-01-28.
- ↑ Annemarie (November 20, 2000). "Die Legende des Propheten und des Mörders Teil 1 (German)". Adventure-Archiv. Retrieved 2017-02-01.
- ↑ Aplin, Gordon (July 2001). "Pilgrim: Faith as a Weapon". Metzomagic.com. Retrieved 2017-01-28.
- ↑ Aplin, Gordon (July 2001). "Pilgrim: Faith as a Weapon". Quandary. Archived from the original on 2004-01-09. Retrieved 2017-01-28.
- ↑ Metzler, Steve (November 1999). "Seven Games of the Soul / Faust (Second Opinion)". Metzomagic. Retrieved 2017-01-31.
- ↑ JPP (November 24, 2004). "Test de Pilgrim: Faith as a Weapon (French)". Jeux Video. Retrieved 2017-01-28.
- ↑ "Baza gier (Polish)". Markolf. Retrieved 2017-01-31.
- ↑ "Opis gry: Pilgrim (Polish)". Markolf. August 18, 2004. Retrieved 2017-01-31.
- ↑ Banan & Elektryczny (August 18, 2004). "PLAY DVD już w kioskach (Polish)". Gry. Retrieved 2017-01-31.
- ↑ Avsn-nikki (September 11, 2006). "Pilgrim: Das Geheimnis der Schrift (German)". Adventurespiele. Retrieved 2017-01-28.
- ↑ "Новости (Russian)". Questzone. Retrieved 2017-01-31.
- ↑ Maroni, Andrea "Maro". "Ring (Italian)". AVEC. Retrieved 2017-02-01.
- ↑ Mr. Bill & Lela. "Pilgrim: Faith as a Weapon". Mr. Bill's Adventureland Review. Retrieved 2017-01-28.
- ↑ Brucker, Nicolas. "Le livre de sagesse (French)". Retrieved 2017-01-28.
- ↑ Studies in Medievalism. D.S. Brewer. 2008-01-01.
- ↑ Saint-Jacques, Camille (2002-01-01). Arts contemporains, 1950–2000 (French). Autrement. ISBN 9782746702820.
- ↑ Feibel, Thomas. "Pilgrim (German)". Feibel. Retrieved 2017-01-31.
- ↑ Steingrad, Elena. "Pilgrim". History Adventures. Retrieved 2017-01-28.
- ↑ "Arxel Tribe: About The Tribe". Arxel Tribe. April 12, 2004. Archived from the original on April 12, 2004. Retrieved 2017-01-28.
- ↑ "GameHorizon Conference 2009". GamesIndustry.biz. Retrieved 2017-01-28.
- ↑ "Excerpt from Veronika Decides to Die". wiztrit.com. Retrieved 2017-01-31.
- ↑ http://wiztrit.com/excerpt/?e=20t
- ↑ "The Legend of the Prophet and the Assassin Review – Mr. Bill's Adventureland". www.mrbillsadventureland.com. Retrieved 2017-01-29.
- ↑ slydos. "The Secret of Alamut – The Legend of the Prophet and the Assassin Part 2 – Review english". www.adventurearchiv.de. Retrieved 2017-01-29.
- ↑ "Secrets of Alamut (Polish)". Gry. Retrieved 2017-01-29.
- ↑ "Visit to the studios of White Birds Productions From Lochness". Atlantis Amerzone Et Cie. Retrieved 2017-01-28.
External links
- Official Pilgrim website
- Mobygames
- Design elements: [2], [3], [4] [5]
- Featured in Electre multimédia