Pike's Peak Gold Rush

The Pike's Peak Gold Rush (later known as the Colorado Gold Rush) was the boom in gold prospecting and mining in the Pike's Peak Country of western Kansas Territory and southwestern Nebraska Territory of the United States that began in July 1858 and lasted until roughly the creation of the Colorado Territory on February 28, 1861. An estimated 100,000 gold seekers took part in one of the greatest gold rushes in North American history.[1]
The participants in the gold rush were known as "Fifty-Niners" after 1859, the peak year of the rush and often used the motto Pike's Peak or Bust! But in fact the location of the Pike's Peak Gold Rush was 85 miles (137 km) north of Pike's Peak. It was only named Pike's Peak Gold Rush because of how well known and important Pike's Peak was.[2]
Overview

The Pike's Peak Gold Rush, which followed the California Gold Rush by approximately one decade, produced a dramatic but temporary influx of immigrants into the Pike's Peak Country of the Southern Rocky Mountains. The rush was exemplified by the slogan "Pike's Peak or Bust!", a reference to the prominent mountain at the eastern edge of the Rocky Mountains that guided many early prospectors to the region westward over the Great Plains. The prospectors provided the first major European-American population in the region.
The rush created a few mining camps such as Denver City and Boulder City that would develop into cities. Many smaller camps such as Auraria and Saint Charles City were absorbed by larger camps and towns. Scores of other mining camps have faded into ghost towns, but quite a few camps such as Central City, Black Hawk, Georgetown, and Idaho Springs survive.
Discovery

For many years people had suspected the mountains had numerous rich gold deposits. In 1835, a French trapper by the name of Eustace Carriere had ended up losing his party and wandered through the mountains for many weeks. During these weeks he found many gold specimens which he later took back to New Mexico for examination. Upon examination, they turned out to be "pure gold". But when he tried to lead an expedition back to the location of where he found the gold, they came up short because he could not quite remember the location.[3]
In 1849 and 1850, several parties of gold seekers bound for the California Gold Rush panned small amounts of gold from various streams in the South Platte River valley at the foot of the Rocky Mountains. The Rocky Mountain gold failed to impress or delay men with visions of unlimited wealth in California, and the discoveries were not reported for several years.[4]
As the hysteria of the California Gold Rush faded, many discouraged gold seekers returned home. Rumors of gold in the Rocky Mountains persisted and several small parties explored the region. In the summer of 1857, a party of Spanish-speaking gold seekers from New Mexico worked a placer deposit along the South Platte River about 5 miles (8 kilometers) above Cherry Creek in what is today Denver.[1]

William Greeneberry "Green" Russell was a Georgian who worked in the California gold fields in the 1850s. Russell was married to a Cherokee woman, and through his connections to the tribe, he heard about an 1849 discovery of gold along the South Platte River. Green Russell organized a party to prospect along the South Platte River, setting off with his two brothers and six companions in February 1858. They rendezvoused with Cherokee tribe members along the Arkansas River in present-day Oklahoma and continued westward along the Santa Fe Trail. Others joined the party along the way until their number reached 107.[4]
Upon reaching Bent's Fort, they turned to the northwest, reaching the confluence of Cherry Creek and the South Platte on May 23. The site of their initial explorations is in present-day Confluence Park in Denver. They began prospecting in the river beds, exploring Cherry Creek and nearby Ralston Creek but without success. In the first week of July 1858, Green Russell and Sam Bates found a small placer deposit near the mouth of Little Dry Creek that yielded about 20 troy ounces (622 grams) of gold, the first significant gold discovery in the Rocky Mountain region. The site of the discovery is in the present-day Denver suburb of Englewood, just north of the junction of U.S. Highway 285 and U.S. Highway 85.[4]
The initial boom
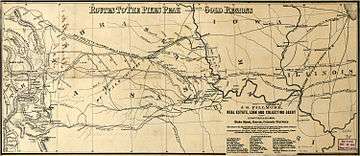
The first decade of the boom was largely concentrated along the South Platte River at the base of the mountains, the canyon of Clear Creek in the mountains west of Golden City, at Breckenridge and in South Park at Como, Fairplay, and Alma. By 1860, Denver City, Golden City, and Boulder City were substantial towns serving the mines. Rapid population growth led to the creation of the Colorado Territory in 1861.
The Pike's Peak Gold Rush sent many into a frenzy, prompting them to pack up their belongings and head to Colorado. They gathered their supplies, wagons, mules, mining equipment, anything they could think of to sustain them when they arrived at their destination. As early as the spring of 1859, people raced to the Pike's Peak country. Some even dared to go out in the winter of 1858 to try to get a head start, only to realize that they would have to wait until the snow melted to even begin their mining for gold.[5]
Free gold
Hardrock mining boomed for a few years, but then declined in the mid-1860s as the miners exhausted the shallow parts of the veins that contained free gold, and found that their amalgamation mills could not recover gold from the deeper sulfide ores.[6] This problem was eventually solved and gold and silver mining in Colorado became a major industry.
Colorado produced 150,000 ounces of gold in 1861 and 225,000 troy ounces in 1862. This led Congress to establish the Denver Mint. Cumulative Colorado production by 1865 was 1.25 million ounces, of which sixty percent was placer gold.[7]:28–30
See also
- Silver mining in Colorado
- Colorado Silver Boom
- Horace Greeley, namesake of Greeley, Colorado, who mined for gold in the rush
References
- 1 2 Thomas J. Noel (December 19, 2006). "Denver History – The Arapaho Camp" (ASP/HTML). Mile High City. City and County of Denver. Retrieved December 19, 2006.
- ↑ Brown, Robert (1985). The Great Pikes Peak Gold Rush. Caldwell, Idaho: Caxton Press. ISBN 0-87004-412-5.
- ↑ Hafen, Le Roy Reuben (1859). The Illustrated Miners' Hand-book and Guide to Pike's Peak: With a New and Reliable Map, Showing All the Routes and the Gold Regions of Western Kansas and Nebraska. Saint Louis: Parker and Huyett.
- 1 2 3 Gehling, Richard (2006). "The Pike's Peak Gold Rush". The Pike's Peak Gold Rush. Richard Gehling. Archived from the original on 2006-02-15. Retrieved December 19, 2006.
- ↑ "Pike's Peak Gold Rush". Explore Old West Colorado. Retrieved July 29, 2014.
- ↑ A. H. Koschman and M. H. Bergendahl (1968) Principal Gold-Producing Districts of the United States, US Geological Survey, Professional Paper 610, p.86.
- ↑ Voynick, S.M., 1992, Colorado Gold, Missoula: Mountain Press Publishing Company, ISBN 0878424555
