Peveril Castle
| Peveril Castle | |
|---|---|
| Castleton, Derbyshire | |
|
Peveril Castle from Cavedale with Lose Hill in the background | |
 Peveril Castle | |
| Coordinates |
53°20′25″N 1°46′38″W / 53.3402°N 1.7772°WCoordinates: 53°20′25″N 1°46′38″W / 53.3402°N 1.7772°W grid reference SK14948260 |
| Site information | |
| Owner | Duchy of Lancaster |
| Open to the public |
yes |
Listed Building – Grade I | |
| Official name | Peveril Castle, Curtain Walls and fragmentary foundations |
| Designated | 17 April 1985 |
| Reference no. | 1250966 |
| Condition | Ruins |
Peveril Castle (also Castleton Castle or Peak Castle)[1] is a ruined 11th-century castle overlooking the village of Castleton in the English county of Derbyshire. It was the main settlement (or caput) of the feudal barony of William Peverel, known as the Honour of Peverel,[2] and was founded some time between the Norman Conquest of 1066 and its first recorded mention in the Domesday Survey of 1086, by Peverel, who held lands in Nottinghamshire and Derbyshire as a tenant-in-chief of the king. The town became the economic centre of the barony. The castle has views across the Hope Valley and Cave Dale.
William Peveril the Younger inherited his father's estates, but in 1155 they were confiscated by King Henry II. While in royal possession, Henry visited the castle in 1157, 1158, and 1164, the first time hosting King Malcolm IV of Scotland. During the Revolt of 1173–1174, the castle's garrison was increased from a porter and two watchmen to a force led by 20 knights shared with the castles of Bolsover and Nottingham. The Earls of Derby had a claim to the Peveril family's estates through marriage, and in 1199 William de Ferrers, the fourth earl, paid 2,000 marks for the Peak lordship, although the castle remained under royal control. The closest Peveril Castle came to seeing battle was in 1216, when King John gave the castle to William de Ferrers, but the castellan refused to relinquish control. Although they were both John's supporters, the king authorised the earl to use force to evict the castellan, who eventually capitulated, although there is no evidence that the castle was assaulted.
In 1223 the castle returned to the Crown. In the 13th century there were periods of building work at the castle, and by 1300 its final form had been established. Toward the end of the 14th century, the barony was granted to John of Gaunt, Duke of Lancaster. Having little use for the castle, he ordered some of its material to be stripped out for re-use, marking the beginning of its decline. From the time of John of Gaunt to the present day, the castle has been owned and administered by the Duchy of Lancaster. Peveril Castle became less important administratively, and by 1609 it was "very ruinous and serveth for no use".[3] In the 19th century, Sir Walter Scott featured the castle in his novel Peveril of the Peak. The site is situated in a national park, and cared for by English Heritage. Peveril Castle is protected as a scheduled monument and a Grade I listed building.
History
Peveril Castle stands on a limestone outcrop overlooking the west end of Hope Valley, in the midst of an ancient landscape. Overlooking the head of the valley, 2 km to the west, is Mam Tor, a Bronze Age hill fort, and 2 miles (3 km) to the east at Brough-on-Noe is the Roman fort of Navio. The valley formed a natural line of communication and had extra importance due to valuable mineral resources in the area, particularly lead.[4]
From the Norman Conquest
The small Hope Castle lay halfway along the valley.[5] The castle's founder, William Peveril, was a follower of William the Conqueror and was rewarded for supporting him during the Norman Conquest. The first mention of him in England records that in 1068 he was granted the new castle at Nottingham by William the Conqueror, who was in the process of subduing the Midlands and northern England. An unsubstantiated legend states that Peveril was William's illegitimate son.[6] By the Domesday Book of 1086, Peveril had become a powerful landowner, with holdings in Nottinghamshire and Derbyshire.[6] The exact year he founded the castle is uncertain, although it must have been started by 1086 as it is recorded in the Domesday Book,[6] one of 48 castles mentioned in the survey and the only one in Derbyshire.[7] The castle was recorded as standing at Pechesers which has been translated as both "Peak's Tail" and "Peak's Arse".[6][8] Although the earliest Norman castles were usually built in timber, Peveril Castle seems to have been designed from outset to be built in stone.[6]

William Peveril had custody of royal lands such as the district of Hope, and although he had his own estates, he relied on continued royal favour to maintain power in this way. In 1100 the new king, Henry I, granted William "his demesne in the Peak". Thus the Peak became an independent lordship under William Peveril's control, and the castle became an important centre of administration for the area, allowing the collection of taxes. Castleton benefited from the castle's new status and began to grow as the lordship's economic heart.[9] William Peveril died in 1114 and was succeeded by his son, William Peveril the Younger. In the civil war known as The Anarchy between King Stephen and the Empress Matilda, Peveril backed the losing side and his fortunes suffered after his capture at the Battle of Lincoln in 1141. In 1153 Peveril was suspected of attempting to poison Ranulf de Gernon, 4th Earl of Chester. In 1153 the future King Henry II accused Peveril of "plundering and treachery" and threatened to confiscate his estates and hand them over to the Earl of Chester.[10] Two years later Henry, now king, followed through his threat. The Earl of Chester was dead by this time, and the king kept the property for himself.[10] Once under royal control, Peveril became the administrative centre of the Forest of High Peak.[11]
William Peveril the Younger died in 1155, and as his only male heir had predeceased him, the family's claim on the confiscated estates was taken up by the husband of William's daughter, Margaret Peveril. Margaret had married Robert de Ferrers, 2nd Earl of Derby.[10] King Henry II visited Peveril Castle three times during his reign. During the first visit, in 1157, he hosted King Malcolm IV of Scotland[12] who paid homage to Henry after ceding Cumberland and Westmorland to the English king.[13] Henry II visited again in 1158 and 1164. When a group of barons led by Henry's sons Henry the Young King, Geoffrey, Duke of Brittany, and Prince Richard, later Richard the Lionheart, took part in the Revolt of 1173–1174 against the king's rule, the king spent £116 on building work at Peveril and Bolsover Castles in Derbyshire. The garrison was also increased. Previously Peveril was guarded by two watchmen and a porter, but this was expanded to a force led by 20 knights shared with Bolsover and Nottingham castles during the revolt. After the revolt ended in 1174, further steps were taken to improve Peveril Castle, and the Pipe Rolls (records of royal expenditure) show that between 1175 and 1177 £184 was spent on building the keep.[12] Building in stone was expensive, and though Peveril's keep was small, moderately-sized stone castles such as the contemporary Orford could cost thousands of pounds.[14] Henry II's average income during his reign has been estimated to be around £10,000 per year.[15] As few documents have survived, it is uncertain when parts of the castle were built, and archaeological investigations have been unsuccessful in dating the stonework.[9] Henry II died in 1189 and was succeeded by his son, Richard the Lionheart. Soon after his coronation, Richard granted the lordship of the Peak, including the castle, to his brother John. While Richard was on crusade, John rebelled and on his return Richard confiscated the lordship.[16]
John became king in 1199 after Richard's death. William de Ferrers, 4th Earl of Derby maintained the claim of the Earls of Derby to the Peveril estates. He paid King John 2000 marks (£1333) for the lordship of the Peak, but the Crown retained possession of Peveril and Bolsover Castles. John finally gave Ferrers these castles in 1216 to secure his support in the face of country-wide rebellion. However, the castellan Brian de Lisle refused to hand them over. Although de Lisle and Ferrers were both King John's supporters, the king gave Ferrers permission to use force to retake the castles.
Henry III
The situation was still chaotic when King Henry III became king after his father's death in 1216. Although Bolsover fell to Ferrers' forces in 1217 after a siege, there is no indication that Peveril was assaulted, and it is likely that Brian de Lisle negotiated his surrender. Ferrers only had possession of the lordship until King Henry III came of age. When the time came he was reluctant to hand over the property, and after an initial deadlock the Crown took control in 1223. Although contemporary Pipe Roll records of expenditure at Peveril survive, they do not specify how the money was spent. As a result, it is unclear what constitutes maintenance and what marks substantial construction work; however, Richard Eales, who wrote the 2006 English Heritage guidebook, suggests that there were two periods of building, when sums spent were larger than usual: £54 in 1204–1207 and £67 in 1210–1212.[16] The medieval historian Sidney Painter estimated that in about 1200 there were only seven magnates in England whose annual income exceeded £400 and a knight could easily live on £10 to £20 per year.[17]
The rest of the 13th century was relatively peaceful, and records show that Peveril Castle was maintained by the Crown. In 1235, in preparation for the king's visit, the north wall and bridge were repaired. After significant work in 1250–52 (£60 spent), 1272–1275 (£40) and 1288–1290 (£151), it is likely that the castle buildings were complete by 1300.[18] King Henry gave Prince Edward (later King Edward I) Peveril Castle along with the County Palatine of Chester with the royal holdings in Wales and Ireland. Some of the lands, including Peveril, were made part of Eleanor of Castile's dower, to come into her possession should her husband, Prince Edward, die. At this time, the Peak lordship was worth around £300 a year. At the outbreak of the Second Barons' War in 1264, Peveril Castle was occupied by Robert de Ferrers, 6th Earl of Derby. Simon de Montfort pressured King Henry III into giving him Peveril, although it was recovered by the Crown after De Montfort's death in 1265. The castle was returned to Eleanor's dower, and as she predeceased her husband the lordship returned into royal hands.[19] Its income was used to provide for members of the royal family such as King Edward II's queen, Isabella of France, and their children, and royal favourites such as Piers Gaveston. In 1331 Edward III gave the lordship to his wife, Philippa of Hainault. It was given to John de Warenne, 7th Earl of Surrey, in 1345. After its return to the Crown, the estate was given to John of Gaunt, Edward III's third surviving son, partially in exchange for the Earldom of Richmond.[20]
The Lancastrians
John of Gaunt's ownership marked the start of Peveril Castle's decline. He was the richest nobleman in England and held several castles. As Peveril Castle was relatively unimportant, John decided not to maintain it and in 1374 gave orders to strip the lead from the buildings for re-use at Pontefract Castle. It was inherited by his son Henry Bolingbroke, later King Henry IV, and remained under royal control, administered by the Duchy of Lancaster.[21] During the 15th century, Peveril became less important as administrative functions were moved elsewhere. Although other castles administered by the Duchy of Lancaster were repaired in 1480, there is no indication that this happened at Peveril.[22] A survey conducted for the Duchy in 1561 revealed that Peveril was in a state of decay, and as a result, along with Donnington, was one of two castles that were subsequently abandoned.[23] The castle however hosted local courts until 1600. A survey in 1609 found that Peveril was "very ruinous and serveth for no use".[22] At some point in the post-medieval period the keep's facing stone was removed from three sides. The steep slope prevented the removal of the stone from the fourth side.[24] At one point, the castle was used to house animals.
Modern era
With the advent of the railways in the 19th century, the area became a tourist attraction. The Duchy of Lancaster undertook maintenance in the 19th century to ensure the castle's condition did not deteriorate further, mostly by clearing rubble and adding mortar.[25] Sir Walter Scott's 1823 novel Peveril of the Peak, set in the mid 17th century, described the castle ruins.[26][27]
In 1932 the Duchy gave custody of the castle to the Office of Works, while retaining ownership. The site is today cared for by English Heritage, the successor to the Office of Works. The surrounding landscape has been protected as a national park since 1951.[25] The castle is a scheduled monument,[26] which means it is a "nationally important" historic building and archaeological site which has been given protection against unauthorised change.[28] It is also a Grade I listed building (first listed in 1985),[29] and recognised as an internationally important structure.[30] It has been described as "perhaps the finest medieval landmark of the Peak District",[31] and architectural historian Nikolaus Pevsner remarked that it is "By far the most important castle in the county – in fact the only one of importance".[32] Before Duffield Castle in the south of the county was destroyed in 1266 it had one of the largest keeps in England, though only the foundations survive.[33]
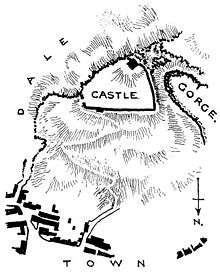
Layout


Peveril Castle in Castleton is roughly triangular in shape, about 90 by 65 m (295 by 213 ft),[34] on top of a hill overlooking the Hope Valley. The land slopes steeply away from the castle's perimeter, forming an almost sheer face to the south east, and the winding approach from the north is the most practical way to the castle. Not only was the site naturally defensible, but its prominence would have allowed the castle to be a highly visible symbol of the builder's power. The town of Castleton provided supplies to the castle.[35] It commands views of Hope Valley below and Treak Cliff, Mam Tor, Black Tor, and Lose Hill.[36] The castle was entered through the gatehouse to the east. Its design was simple, 7 m (23 ft) wide with a gatepassage 2.5 m (8 ft 2 in) across. Little survives, although earlier drawings contain details of mouldings that suggest the structure was built in the 12th century, perhaps by Henry II or King John.[37]
The curtain walls enclosing the castle show the multiple phases of construction at Peveril, with stonework from the Norman period – differentiated by the use of opus spicatum – to modern repairs.[37] The walls were surmounted by walkways, which next to the gatehouse would have stood about 5 m (16 ft) above the ground level immediately outside the castle. In the 12th century, a tower projecting less than 2 m (6 ft 7 in) was added to the north wall. In Eales' opinion, it "would have been of limited military value, compared with the boldly projecting towers of later castles"[36] which allowed defenders to deploy flanking fire along the base of the walls.[38] The land within the castle slopes downwards from west to east.[39] Water storage would have been a concern for the garrison of the castle, but how they procured water is uncertain.[40]


The southern curtain wall is a modern replacement along the line of the medieval wall. There are the remains of two round or semi-circular towers projecting from the wall. Enough of one tower survives that one can see the use of Roman tiles in the construction, probably from the fort of Navio 2 mi (3 km) away. It is uncertain when these towers were built, although it is thought they may date from the 13th century.[40] Foundations mark the position of buildings abutting the south wall, probably the old hall and a chapel. A document from 1246 recorded a chapel at the castle; the remains of the easternmost building against the south wall are assumed to mark the site of the chapel, as they are oriented roughly east–west.[41] Foundations at the west end of the north wall mark a large building: probably a hall where the lord of the castle would have eaten and entertained high-status guests. It is unclear when the new hall was built, probably replacing the old hall in the south of the castle, although an "old hall" was mentioned in a document of 1251, implying there was also a new hall by that time. The kitchen and food stores would have stood at the east end of the hall, although little remains of those structures.[42] Buildings were also constructed against the west curtain wall, probably high-status apartments. Although the main approach to Peveril Castle was from the north, there was also a gate in the west. A bridge spanned the gorge, linking the castle with an enclosure on the other side. As it has not been excavated, the exact form the enclosure took is uncertain. Its purpose is also a matter of speculation, whether it was an elaborate outer bailey for defence or used for storage and stabling.[43]
The keep occupies the southern corner of Peveril Castle.[44] Construction probably began in around 1176, instigated by Henry II.[32] Its plan is square, measuring less than 12 by 12 m (39 by 39 ft), and the parapet is 15 m (49 ft) above the keep's base; as the ground is uneven, on the other side it rises 10.5 m (34 ft) above ground level. It is smaller than contemporary royal keeps such as those at Dover and Scarborough Castles. Today the exterior is coarse, but originally the facing would have been smooth; the south-east side, where the steep natural slope prevented removal of the facing stone, gives an idea of how it may once have appeared. A projection in the south-east face of the keep housed a garderobe. As was usual with Norman keeps, Peveril's was entered through the first floor and was accessed by a staircase. This entrance level would have been a large public room and the basement used for storage. A narrow staircase in the east corner allowed access to the basement and the wall walk around the top of the keep.[44]
See also
References
- Notes
- ↑ Cathcart King 1983, p. 110
- ↑ Sanders, I.J., English Baronies, Oxford, 1960, p.136
- ↑ Eales 2006, p. 30
- ↑ Eales 2006, pp. 19, 21
- ↑ Creighton 2002, p. 101
- 1 2 3 4 5 Eales 2006, p. 20
- ↑ Harfield 1991, p. 384
- ↑ Harfield 1991, p. 376
- 1 2 Eales 2006, pp. 20–22
- 1 2 3 Eales 2006, p. 22
- ↑ Creighton 2002, pp. 91–92
- 1 2 Eales 2006, p. 23
- ↑ Hull 2008, p. 109
- ↑ McNeill 1992, pp. 41–42
- ↑ Brown 2004, p. 109
- 1 2 Eales 2006, p. 24
- ↑ Brown 2004, pp. 109–110
- ↑ Eales 2006, pp. 26–27
- ↑ Eales 2006, pp. 27–28
- ↑ Eales 2006, p. 28
- ↑ Eales 2006, p. 29
- 1 2 Eales 2006, p. 30
- ↑ Goodall 2011, pp. 450–451
- ↑ Rakoczy 2007, p. 120
- 1 2 Eales 2006, pp. 30–32
- 1 2 Historic England, "Peveril Castle (309632)", PastScape, retrieved 2008-03-17
- ↑ Brown 1979, p. 187
- ↑ "Scheduled Monuments", Pastscape, Historic England, retrieved 2011-07-27
- ↑ Historic England, "Peveril Castle, Curtain Walls and fragmentary foundations (Grade I) (1250966)", National Heritage List for England, retrieved 2014-05-10
- ↑ "Frequently asked questions", Images of England, Historic England, retrieved 2010-01-03
- ↑ Milward & Robinson 1975, p. 233
- 1 2 Pevsner & Williamson 1978, p. 298
- ↑ Jessop & Beauchamp 2015, p. 29
- ↑ Eales 2006, p. 8
- ↑ Eales 2006, p. 5
- 1 2 Eales 2006, p. 9
- 1 2 Eales 2006, p. 7
- ↑ Friar 2003, p. 86
- ↑ Eales 2006, pp. 7–9
- 1 2 Eales 2006, p. 16
- ↑ Eales 2006, pp. 16–17
- ↑ Eales 2006, p. 10
- ↑ Eales 2006, pp. 11–12
- 1 2 Eales 2006, pp. 12–15
- Bibliography
- Brown, David (1979), Walter Scott and the Historical Imagination, Routledge, ISBN 978-0-7100-0301-0
- Brown, Reginald Allen (2004) [1954], Allen Brown's English Castles, Woodbridge: The Boydell Press, ISBN 1-84383-069-8
- Cathcart King, D. J. (1983), Castellarium Anglicanum: An Index and Bibliography of the Castles in England, Wales and the Islands. Volume I, New York: Kraus International Publications, ISBN 0-527-50110-7
- Creighton, Oliver (2002), Castles and Landscapes, London: Continuum, ISBN 0-8264-5896-3
- Eales, Richard (2006), Peveril Castle, London: English Heritage, ISBN 978-1-85074-982-0
- Friar, Stephen (2003), The Sutton Companion to Castles, Stroud: Sutton Publishing, ISBN 978-0-7509-3994-2
- Goodall, John (2011), The English Castle 1066–1650, London: Yale University Press, ISBN 978-0-300-11058-6
- Harfield, C. G. (1991), "A Hand-list of Castles Recorded in the Domesday Book", English Historical Review, 106: 371–392, JSTOR 573107, doi:10.1093/ehr/CVI.CCCCXIX.371
- Hull, Lisa (2008), Understanding the Castle Ruins of England and Wales: How to Interpret the History and Meaning of Masonry and Earthworks, McFarland & Co, ISBN 978-0-7864-3457-2
- Jessop, Oliver; Beauchamp, Victoria (2015), Duffield Castle, Duffield, Derbyshire: a reappraisal, The JESSOP Consultancy, doi:10.5284/1031936
- McNeill, Tom (1992), English Heritage Book of Castles, London: English Heritage and B. T. Batsford, ISBN 0-7134-7025-9
- Milward, Roy; Robinson, Adrian (1975), The Peak District, Taylor & Francis, ISBN 978-0-413-31550-2
- Pevsner, Nikolaus; Williamson, Elizabeth (1978) [1953], Derbyshire: Volume 8 of Buildings of England Pevsner architectural guides (2nd ed.), Penguin Books, ISBN 978-0-14-071008-3
- Rakoczy, Lila (2007), Archaeology of destruction: a reinterpretation of castle slightings in the English Civil War, University of York (PhD thesis)

Further reading
- Great Britain. Department of the Environment (1979). Peveril Castle. HMSO. ISBN 0-11-671466-2.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Peveril Castle. |
- Peveril Castle on English Heritage website
- Bibliography of sources relating to Peveril Castle
- 1909 plan of Peveril Castle's keep



