Peptidoglycan recognition protein 1
Peptidoglycan recognition protein 1, also known as TAG7, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PGLYRP1 gene.[5][6][7]
Tissue distribution and secretion
The PGLYRP1 gene is highly expressed in bone marrow, circulating Polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMLs), and in the corneal epithelium. The PGLYRP1 protein is primarily found in the granules of PMLs.
Structure
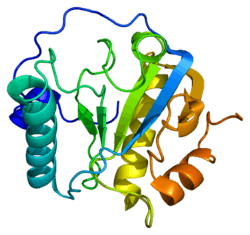
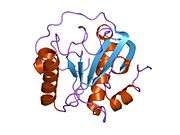
As with most PGRPs, PGLYRP1 has one carboxy-terminal type 2 amidase domain (also known as a PGRP domain) and consists of three alpha helices, five beta strands and coils, and has three pairs of conserved cysteins which form three disulphide bonds.[8] PGLYRP1 can form homodimers for its antimicrobial activity, and can complex with HSP70 for its cytotoxic activity.
Function
The PGLYRP1 protein plays an important role in the innate immune response. It is bactericidal against gram-positive bacteria such as S. aureus, S. epidermidis, and L. monocytogenes and generally has proinflammatory effects, inducing TNF-a and IFN-g in many tissues. PGLYRP-1 is also known to form a cytotoxic complex with HSP-70, suggesting it may also have a role in anti-cancer defense.[9] As a pathogen recognition protein with antimicrobial properties, PGLYRP-1 is suspected to play an important role in maintaining the gut microbial flora.
Mechanism of action
As an antimicrobial, the binding of PGLYRP1 to its target does not permeabilize the bacterial cell wall like defensins and other antimicrobial peptides. Instead, PGLYRP1 binding activates a bacterial stress response that causes the bacterium to shut down transcription and translation, and induces oxidative stress. As a cytotoxic agent, the PGLYRP1-HSP70 complex
Possible pathological role
In humans, single nuclear polymorphisms of the PGLYRP1 gene have been associated with the development of ulcerative colitis.[10]
In mice, the lack of PGLYRP1 is associated with increased susceptibility to infectious disease, but also decreased susceptibility to autoimmune disease. The lack of PGLYRP1 was found to have increased susceptibility to corneal infections, reduced corneal wound healing, and increased scarification of the cornea when infected by P. aeruginosa.[11] But PGLYRP1-deficient mice also had decreased severity of atopic dermatitis and contact dermatitis. and may play a role in the development of asthma.
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000008438 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000030413 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Kang D, Liu G, Lundstrom A, Gelius E, Steiner H (Sep 1998). "A peptidoglycan recognition protein in innate immunity conserved from insects to humans". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 95 (17): 10078–82. PMC 21464
 . PMID 9707603. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.17.10078.
. PMID 9707603. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.17.10078. - ↑ Kibardin AV, Mirkina II, Zakeeva IR, Baranova EV, Georgiev GP, Kiselev SL (Apr 2003). "[Expression analysis of proteins encoded by genes of the tag7/tagL (PGRP-S,L) family in human peripheral blood cells]". Genetika. 39 (2): 244–9. PMID 12669421.
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: PGLYRP1 peptidoglycan recognition protein 1".
- ↑ Guan R, Brown PH, Swaminathan CP, Roychowdhury A, Boons GJ, Mariuzza RA (2006). "Crystal structure of human peptidoglycan recognition protein I alpha bound to a muramyl pentapeptide from Gram-positive bacteria". Protein Sci. 15 (5): 1199–206. PMC 2242522
 . PMID 16641493. doi:10.1110/ps.062077606.
. PMID 16641493. doi:10.1110/ps.062077606. - ↑ Sashchenko LP, Dukhanina EA, Yashin DV, Shatalov YV, Romanova EA, Korobko EV, Demin AV, Lukyanova TI, Kabanova OD, Khaidukov SV, Kiselev SL, Gabibov AG, Gnuchev NV, Georgiev GP (2004). "Peptidoglycan recognition protein tag7 forms a cytotoxic complex with heat shock protein 70 in solution and in lymphocytes". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (3): 2117–24. PMID 14585845. doi:10.1074/jbc.M307513200.
- ↑ Zulfiqar F, Hozo I, Rangarajan S, Mariuzza RA, Dziarski R, Gupta D (2013). "Genetic Association of Peptidoglycan Recognition Protein Variants with Inflammatory Bowel Disease". PLoS ONE. 8 (6): e67393. PMC 3686734
 . PMID 23840689. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0067393.
. PMID 23840689. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0067393. - ↑ Ghosh A, Lee S, Dziarski R, Chakravarti S (2009). "A novel antimicrobial peptidoglycan recognition protein in the cornea". Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 50 (9): 4185–91. PMC 3052780
 . PMID 19387073. doi:10.1167/iovs.08-3040.
. PMID 19387073. doi:10.1167/iovs.08-3040.
Further reading
- Cho JH, Fraser IP, Fukase K, et al. (2005). "Human peptidoglycan recognition protein S is an effector of neutrophil-mediated innate immunity.". Blood. 106 (7): 2551–8. PMC 1895263
 . PMID 15956276. doi:10.1182/blood-2005-02-0530.
. PMID 15956276. doi:10.1182/blood-2005-02-0530. - Guan R, Wang Q, Sundberg EJ, Mariuzza RA (2005). "Crystal structure of human peptidoglycan recognition protein S (PGRP-S) at 1.70 A resolution.". J. Mol. Biol. 347 (4): 683–91. PMID 15769462. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2005.01.070.
- Guan R, Roychowdhury A, Ember B, et al. (2005). "Structural basis for peptidoglycan binding by peptidoglycan recognition proteins.". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101 (49): 17168–73. PMC 535381
 . PMID 15572450. doi:10.1073/pnas.0407856101.
. PMID 15572450. doi:10.1073/pnas.0407856101. - Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC).". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. PMC 528928
 . PMID 15489334. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504.
. PMID 15489334. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. - Guan R, Malchiodi EL, Wang Q, et al. (2004). "Crystal structure of the C-terminal peptidoglycan-binding domain of human peptidoglycan recognition protein Ialpha.". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (30): 31873–82. PMID 15140887. doi:10.1074/jbc.M404920200.
- Grimwood J, Gordon LA, Olsen A, et al. (2004). "The DNA sequence and biology of human chromosome 19.". Nature. 428 (6982): 529–35. PMID 15057824. doi:10.1038/nature02399.
- Sashchenko LP, Dukhanina EA, Yashin DV, et al. (2004). "Peptidoglycan recognition protein tag7 forms a cytotoxic complex with heat shock protein 70 in solution and in lymphocytes.". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (3): 2117–24. PMID 14585845. doi:10.1074/jbc.M307513200.
- Wang ZM, Li X, Cocklin RR, et al. (2004). "Human peptidoglycan recognition protein-L is an N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase.". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (49): 49044–52. PMID 14506276. doi:10.1074/jbc.M307758200.
- Clark HF, Gurney AL, Abaya E, et al. (2003). "The secreted protein discovery initiative (SPDI), a large-scale effort to identify novel human secreted and transmembrane proteins: a bioinformatics assessment.". Genome Res. 13 (10): 2265–70. PMC 403697
 . PMID 12975309. doi:10.1101/gr.1293003.
. PMID 12975309. doi:10.1101/gr.1293003. - Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences.". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. PMC 139241
 . PMID 12477932. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899.
. PMID 12477932. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. - Liu C, Xu Z, Gupta D, Dziarski R (2001). "Peptidoglycan recognition proteins: a novel family of four human innate immunity pattern recognition molecules.". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (37): 34686–94. PMID 11461926. doi:10.1074/jbc.M105566200.