Black pepper
| Black pepper | |
|---|---|
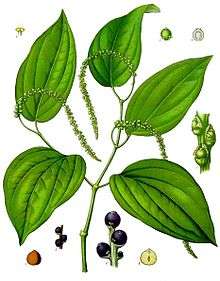 | |
| Pepper plant with immature peppercorns | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Magnoliids |
| Order: | Piperales |
| Family: | Piperaceae |
| Genus: | Piper |
| Species: | P. nigrum |
| Binomial name | |
| Piper nigrum L.[1] | |
Black pepper (Piper nigrum) is a flowering vine in the family Piperaceae, cultivated for its fruit, which is usually dried and used as a spice and seasoning. When dried, the fruit is known as a peppercorn. When fresh and fully mature, it is approximately 5 millimetres (0.20 in) in diameter, dark red, and, like all drupes, contains a single seed. Peppercorns, and the ground pepper derived from them, may be described simply as pepper, or more precisely as black pepper (cooked and dried unripe fruit), green pepper (dried unripe fruit) and white pepper (ripe fruit seeds).
Black pepper is native to south India and is extensively cultivated there and elsewhere in tropical regions. Currently, Vietnam is the world's largest producer and exporter of pepper, producing 34% of the world's Piper nigrum crop as of 2013.
Dried ground pepper has been used since antiquity for both its flavour and as a traditional medicine. Black pepper is the world's most traded spice. It is one of the most common spices added to cuisines around the world. The spiciness of black pepper is due to the chemical piperine, not to be confused with the capsaicin characteristic of chili peppers. Black pepper is ubiquitous in the modern world as a seasoning and is often paired with salt.
Etymology
The word "pepper" has its roots in the Sanskrit word for long pepper, pippali.[2][3][4] Ancient Greek and Latin turned pippali into the Greek πέπερι peperi and then into the Latin piper, which was used by the Romans to refer both to black pepper and long pepper, as the Romans erroneously believed that both of these spices were derived from the same plant.
Today's "pepper" derives from the Old English pipor.[5] and from Latin which was the source of Romanian piper, Italian pepe, Dutch peper, German Pfeffer, French poivre, and other similar forms.[5]
In the 16th century, pepper started referring to the unrelated New World chili pepper as well. "Pepper" was used in a figurative sense to mean "spirit" or "energy" at least as far back as the 1840s; in the early 20th century, this was shortened to pep.[5]
Varieties

Black pepper
Black pepper is produced from the still-green, unripe drupes of the pepper plant. The drupes are cooked briefly in hot water, both to clean them and to prepare them for drying; the heat ruptures cell walls in the pepper, speeding the work of browning enzymes during drying. The drupes are dried in the sun or by machine for several days, during which the pepper around the seed shrinks and darkens into a thin, wrinkled black layer. Once dried, the spice is called black peppercorn. On some estates, the berries are separated from the stem by hand and then sun-dried without the boiling process.
Once the peppercorns are dried, pepper spirit and oil can be extracted from the berries by crushing them. Pepper spirit is used in many medicinal and beauty products. Pepper oil is also used as an ayurvedic massage oil and used in certain beauty and herbal treatments.
 Black pepper (Piper nigrum) essential oil in a clear glass vial
Black pepper (Piper nigrum) essential oil in a clear glass vial Ground black pepper and a plastic pepper shaker
Ground black pepper and a plastic pepper shaker Roughly cracked black peppercorns, also known as mignonette or poivre mignonette
Roughly cracked black peppercorns, also known as mignonette or poivre mignonette

White pepper

White pepper consists solely of the seed of the pepper plant, with the darker-coloured skin of the pepper fruit removed. This is usually accomplished by a process known as retting, where fully ripe red pepper berries are soaked in water for about a week, during which the flesh of the pepper softens and decomposes. Rubbing then removes what remains of the fruit, and the naked seed is dried. Sometimes alternative processes are used for removing the outer pepper from the seed, including removing the outer layer through mechanical, chemical or biological methods.[6]
Ground white pepper is used in Chinese and Thai cuisine, but also in salads, cream sauces, light-coloured sauces, and mashed potatoes (where black pepper would visibly stand out). White pepper has a different flavour from black pepper; it lacks certain compounds present in the outer layer of the drupe.

Green pepper
Green pepper, like black, is made from the unripe drupes. Dried green peppercorns are treated in a way that retains the green colour, such as treatment with sulphur dioxide, canning or freeze-drying. Pickled peppercorns, also green, are unripe drupes preserved in brine or vinegar. Fresh, unpreserved green pepper drupes, largely unknown in the West, are used in some Asian cuisines, particularly Thai cuisine. Their flavour has been described as spicy and fresh, with a bright aroma.[7] They decay quickly if not dried or preserved.
Wild pepper
Wild pepper grows in the Western Ghats region of India. Into the 19th century, the forests contained expansive wild pepper vines, as recorded by the Scottish physician Francis Buchanan (also a botanist and geographer) in his book A journey from Madras through the countries of Mysore, Canara and Malabar (Volume III).[8] However, deforestation resulted in wild pepper growing in more limited forest patches from Goa to Kerala, with the wild source gradually decreasing as the quality and yield of the cultivated variety improved. No successful grafting of commercial pepper on wild pepper has been achieved to date.[8]
Orange pepper and red pepper
Orange pepper or red pepper usually consists of ripe red pepper drupes preserved in brine and vinegar. Ripe red peppercorns can also be dried using the same colour-preserving techniques used to produce green pepper.[9]
Pink pepper and other plants used as pepper
"Pink peppercorns" are the fruits of a plant from a different family, the Peruvian pepper tree, Schinus molle, or its relative the Brazilian pepper tree, Schinus terebinthifolius. A pink peppercorn (French: baie rose, "pink berry") is a dried berry of the shrub Schinus molle, commonly known as the Peruvian peppertree. As they are members of the cashew family, they may cause allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis, for persons with a tree nut allergy.
The bark of Drimys winteri ("Canelo" or "Winter's Bark") is used as a substitute for pepper in cold and temperate regions of Chile and Argentina where it is easily available.
In New Zealand the seeds of Kawakawa (Macropiper excelsum), a relative of black pepper, are sometimes used as pepper, and the leaves of Pseudowintera colorata (mountain horopito) are another replacement for pepper.
Several plants in the United States are used also as pepper substitutes, such as Lepidium campestre, Lepidium virginicum, shepherd's purse, horseradish, and field pennycress.
Plant

_fruits.jpg)
The pepper plant is a perennial woody vine growing up to 4 metres (13 ft) in height on supporting trees, poles, or trellises. It is a spreading vine, rooting readily where trailing stems touch the ground. The leaves are alternate, entire, 5 to 10 centimetres (2.0 to 3.9 in) long and 3 to 6 centimetres (1.2 to 2.4 in) across. The flowers are small, produced on pendulous spikes 4 to 8 centimetres (1.6 to 3.1 in) long at the leaf nodes, the spikes lengthening up to 7 to 15 centimetres (2.8 to 5.9 in) as the fruit matures.[10] The fruit of the black pepper is called a drupe and when dried is known as a peppercorn.
Pepper can be grown in soil that is neither too dry nor susceptible to flooding, moist, well-drained and rich in organic matter (the vines do not do too well over an altitude of 900 m (3,000 ft) above sea level). The plants are propagated by cuttings about 40 to 50 centimetres (16 to 20 in) long, tied up to neighbouring trees or climbing frames at distances of about 2 metres (6 ft 7 in) apart; trees with rough bark are favoured over those with smooth bark, as the pepper plants climb rough bark more readily. Competing plants are cleared away, leaving only sufficient trees to provide shade and permit free ventilation. The roots are covered in leaf mulch and manure, and the shoots are trimmed twice a year. On dry soils the young plants require watering every other day during the dry season for the first three years. The plants bear fruit from the fourth or fifth year, and typically continue to bear fruit for seven years. The cuttings are usually cultivars, selected both for yield and quality of fruit.
A single stem will bear 20 to 30 fruiting spikes. The harvest begins as soon as one or two fruits at the base of the spikes begin to turn red, and before the fruit is fully mature, and still hard; if allowed to ripen completely, the fruit lose pungency, and ultimately fall off and are lost. The spikes are collected and spread out to dry in the sun, then the peppercorns are stripped off the spikes.[10]
Black pepper is native either to Southeast Asia[11] or South Asia.[12] Within the genus Piper, it is most closely related to other Asian species such as Piper caninum.[12]

- Pepper vine, Tiruvannamalai, Tamil Nadu, India
Production and trade
| Top black pepper producers in 2013[13]
(thousands of tonnes) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Country | Production | |
| | 163 | |
| | 89 | |
| | 53 | |
| | 42 | |
| | 31 | |
| 473 | ||
As of 2013, Vietnam was the world's largest producer and exporter of black peppercorns, producing 163,000 tonnes or 34% of the world total of 473,000 tonnes (table).[13] Other major producers include Indonesia (19%), India (11%) and Brazil (9%) (table). Global pepper production may vary annually[14] according to crop management, disease and weather. Vietnam dominates the export market, using almost none of its production domestically.[14]
Peppercorns are among the most widely traded spice in the world, accounting for 20 percent of all spice imports.
History


Pepper is native to South Asia and Southeast Asia and has been known to Indian cooking since at least 2000 BCE.[15] J. Innes Miller notes that while pepper was grown in southern Thailand and in Malaysia, its most important source was India, particularly the Malabar Coast, in what is now the state of Kerala[16] Peppercorns were a much-prized trade good, often referred to as "black gold" and used as a form of commodity money. The legacy of this trade remains in some Western legal systems which recognize the term "peppercorn rent" as a form of a token payment made for something that is in fact being given.
The ancient history of black pepper is often interlinked with (and confused with) that of long pepper, the dried fruit of closely related Piper longum. The Romans knew of both and often referred to either as just "piper". In fact, it was not until the discovery of the New World and of chili peppers that the popularity of long pepper entirely declined. Chili peppers, some of which when dried are similar in shape and taste to long pepper, were easier to grow in a variety of locations more convenient to Europe.
Before the 16th century, pepper was being grown in Java, Sunda, Sumatra, Madagascar, Malaysia, and everywhere in Southeast Asia. These areas traded mainly with China, or used the pepper locally.[17] Ports in the Malabar area also served as a stop-off point for much of the trade in other spices from farther east in the Indian Ocean. Following the British hegemony in India, virtually all of the black pepper found in Europe, the Middle East, and North Africa was traded from Malabar region.
Ancient times
Black peppercorns were found stuffed in the nostrils of Ramesses II, placed there as part of the mummification rituals shortly after his death in 1213 BCE.[18] Little else is known about the use of pepper in ancient Egypt and how it reached the Nile from South Asia.
Pepper (both long and black) was known in Greece at least as early as the 4th century BCE, though it was probably an uncommon and expensive item that only the very rich could afford.

By the time of the early Roman Empire, especially after Rome's conquest of Egypt in 30 BCE, open-ocean crossing of the Arabian Sea direct to southern India's Malabar Coast was near routine. Details of this trading across the Indian Ocean have been passed down in the Periplus of the Erythraean Sea. According to the Roman geographer Strabo, the early Empire sent a fleet of around 120 ships on an annual one-year trip to China, Southeast Asia, India and back. The fleet timed its travel across the Arabian Sea to take advantage of the predictable monsoon winds. Returning from India, the ships travelled up the Red Sea, from where the cargo was carried overland or via the Nile-Red Sea canal to the Nile River, barged to Alexandria, and shipped from there to Italy and Rome. The rough geographical outlines of this same trade route would dominate the pepper trade into Europe for a millennium and a half to come.
With ships sailing directly to the Malabar coast, black pepper was now travelling a shorter trade route than long pepper, and the prices reflected it. Pliny the Elder's Natural History tells us the prices in Rome around 77 CE: "Long pepper ... is fifteen denarii per pound, while that of white pepper is seven, and of black, four." Pliny also complains "there is no year in which India does not drain the Roman Empire of fifty million sesterces," and further moralizes on pepper:
It is quite surprising that the use of pepper has come so much into fashion, seeing that in other substances which we use, it is sometimes their sweetness, and sometimes their appearance that has attracted our notice; whereas, pepper has nothing in it that can plead as a recommendation to either fruit or berry, its only desirable quality being a certain pungency; and yet it is for this that we import it all the way from India! Who was the first to make trial of it as an article of food? and who, I wonder, was the man that was not content to prepare himself by hunger only for the satisfying of a greedy appetite? (N.H. 12.14)[19]
Black pepper was a well-known and widespread, if expensive, seasoning in the Roman Empire. Apicius' De re coquinaria, a 3rd-century cookbook probably based at least partly on one from the 1st century CE, includes pepper in a majority of its recipes. Edward Gibbon wrote, in The History of the Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire, that pepper was "a favorite ingredient of the most expensive Roman cookery".
Postclassical Europe
Pepper was so valuable that it was often used as collateral or even currency. In the Dutch language, "pepper expensive" (peperduur) is an expression for something very expensive. The taste for pepper (or the appreciation of its monetary value) was passed on to those who would see Rome fall. Alaric the Visigoth included 3,000 pounds of pepper as part of the ransom he demanded from Rome when he besieged the city in 5th century.[20] After the fall of Rome, others took over the middle legs of the spice trade, first the Persians and then the Arabs; Innes Miller cites the account of Cosmas Indicopleustes, who travelled east to India, as proof that "pepper was still being exported from India in the sixth century".[21] By the end of the Early Middle Ages, the central portions of the spice trade were firmly under Islamic control. Once into the Mediterranean, the trade was largely monopolized by Italian powers, especially Venice and Genoa. The rise of these city-states was funded in large part by the spice trade.
A riddle authored by Saint Aldhelm, a 7th-century Bishop of Sherborne, sheds some light on black pepper's role in England at that time:
I am black on the outside, clad in a wrinkled cover,
Yet within I bear a burning marrow.
I season delicacies, the banquets of kings, and the luxuries of the table,
Both the sauces and the tenderized meats of the kitchen.
But you will find in me no quality of any worth,
Unless your bowels have been rattled by my gleaming marrow.[1]
- ^ Translation from Turner, p 94. The riddle's answer is of course pepper.
It is commonly believed that during the Middle Ages, pepper was used to conceal the taste of partially rotten meat. There is no evidence to support this claim, and historians view it as highly unlikely: in the Middle Ages, pepper was a luxury item, affordable only to the wealthy, who certainly had unspoiled meat available as well.[22] In addition, people of the time certainly knew that eating spoiled food would make them sick. Similarly, the belief that pepper was widely used as a preservative is questionable: it is true that piperine, the compound that gives pepper its spiciness, has some antimicrobial properties, but at the concentrations present when pepper is used as a spice, the effect is small.[23] Salt is a much more effective preservative, and salt-cured meats were common fare, especially in winter. However, pepper and other spices certainly played a role in improving the taste of long-preserved meats.

Its exorbitant price during the Middle Ages—and the monopoly on the trade held by Italy—was one of the inducements which led the Portuguese to seek a sea route to India. In 1498, Vasco da Gama became the first person to reach India by sailing around Africa (see Age of Discovery); asked by Arabs in Calicut (who spoke Spanish and Italian) why they had come, his representative replied, "we seek Christians and spices". Though this first trip to India by way of the southern tip of Africa was only a modest success, the Portuguese quickly returned in greater numbers and eventually gained much greater control of trade on the Arabian sea. The 1494 Treaty of Tordesillas with the Spanish granted Portugal exclusive rights to the half of the world where black pepper originated.
Unsurprisingly, the Portuguese proved unable to monopolize the spice trade. Older Arab and Venetian trade networks successfully imported enormous quantities of spices, and pepper once again flowed through Alexandria and Italy, as well as around Africa. In the 17th century, the Portuguese lost almost all of their valuable Indian Ocean trade to the Dutch and the English who, taking advantage from the Spanish ruling over Portugal (1580–1640), occupied by force almost all Portuguese dominations in the area. The pepper ports of Malabar began to trade increasingly with the Dutch in the period 1661–1663.

As pepper supplies into Europe increased, the price of pepper declined (though the total value of the import trade generally did not). Pepper, which in the early Middle Ages had been an item exclusively for the rich, started to become more of an everyday seasoning among those of more average means. Today, pepper accounts for one-fifth of the world's spice trade.[24]
China
It is possible that black pepper was known in China in the 2nd century BCE, if poetic reports regarding an explorer named Tang Meng (唐蒙) are correct. Sent by Emperor Wu to what is now south-west China, Tang Meng is said to have come across something called jujiang or "sauce-betel". He was told it came from the markets of Shu, an area in what is now the Sichuan province. The traditional view among historians is that "sauce-betel" is a sauce made from betel leaves, but arguments have been made that it actually refers to pepper, either long or black.[25]
In the 3rd century CE, black pepper made its first definite appearance in Chinese texts, as hujiao or "foreign pepper". It does not appear to have been widely known at the time, failing to appear in a 4th-century work describing a wide variety of spices from beyond China's southern border, including long pepper.[26] By the 12th century, however, black pepper had become a popular ingredient in the cuisine of the wealthy and powerful, sometimes taking the place of China's native Sichuan pepper (the tongue-numbing dried fruit of an unrelated plant).
Marco Polo testifies to pepper's popularity in 13th-century China when he relates what he is told of its consumption in the city of Kinsay (Hangzhou): "... Messer Marco heard it stated by one of the Great Kaan's officers of customs that the quantity of pepper introduced daily for consumption into the city of Kinsay amounted to 43 loads, each load being equal to 223 lbs."[27] Marco Polo is not considered a very reliable source regarding China, and this second-hand data may be even more suspect, but if this estimated 10,000 pounds (4,500 kg) a day for one city is anywhere near the truth, China's pepper imports may have dwarfed Europe's.
During the course of the treasure voyages in the early 15th century, Admiral Zheng He and his expeditionary fleets returned with such a large amount of black pepper that the once-costly luxury became a common commodity.[28]
Phytochemicals, folk medicine and research

Like many eastern spices, pepper was historically both a seasoning and a folk medicine. Long pepper, being stronger, was often the preferred medication, but both were used. Black pepper (or perhaps long pepper) was believed to cure several illnesses, such as constipation, insomnia, oral abscesses, sunburn and toothaches, among others.[29] Various sources from the 5th century onward recommended pepper to treat eye problems, often by applying salves or poultices made with pepper directly to the eye. There is no current medical evidence that any of these treatments has any benefit.[30]
Pepper is known to cause sneezing. Some sources say that piperine, a substance present in black pepper, irritates the nostrils, causing the sneezing.[31] Few, if any, controlled studies have been carried out to answer the question.
Piperine is under study for its potential to increase absorption of selenium, vitamin B12, beta-carotene and curcumin, as well as other compounds.[32] As a folk medicine, pepper appears in the Buddhist Samaññaphala Sutta, chapter five, as one of the few medicines allowed to be carried by a monk.[33] Pepper contains phytochemicals,[34] including amides, piperidines, pyrrolidines and trace amounts of safrole which may be carcinogenic in laboratory rodents.[35]
Piperine is under study for a variety of possible physiological effects,[36] although this work is preliminary and mechanisms of activity for piperine in the human body remain unknown.
Nutrition
One tablespoon (6 grams) of ground black pepper contains moderate amounts of vitamin K (13% of the daily value or DV), iron (10% DV) and manganese (18% DV), with trace amounts of other essential nutrients, protein and dietary fibre.[37]
Flavor


Pepper gets its spicy heat mostly from piperine derived both from the outer fruit and the seed. Black pepper contains between 4.6% and 9.7% piperine by mass, and white pepper slightly more than that.[38] Refined piperine, by weight, is about one percent as hot as the capsaicin found in chili peppers.[39] The outer fruit layer, left on black pepper, also contains aroma-contributing terpenes, including germacrene (11%), limonene (10%), pinene (10%), alpha-phellandrene (9%), and beta-caryophyllene (7%),[40] which give citrusy, woody, and floral notes. These scents are mostly missing in white pepper, which is stripped of the fruit layer. White pepper can gain some different odours (including musty notes) from its longer fermentation stage.[41] The aroma of pepper is attributed to rotundone (3,4,5,6,7,8-Hexahydro-3α,8α-dimethyl-5α-(1-methylethenyl)azulene-1(2H)-one), a sesquiterpene originally discovered in the tubers of cyperus rotundus, which can be detected in concentrations of 0.4 nanograms/L in water and in wine: rotundone is also present in marjoram, oregano, rosemary, basil, thyme, and geranium, as well as in some Shiraz wines.[42]
Pepper loses flavour and aroma through evaporation, so airtight storage helps preserve its spiciness longer. Pepper can also lose flavour when exposed to light, which can transform piperine into nearly tasteless isochavicine.[41] Once ground, pepper's aromatics can evaporate quickly; most culinary sources recommend grinding whole peppercorns immediately before use for this reason. Handheld pepper mills or grinders, which mechanically grind or crush whole peppercorns, are used for this, sometimes instead of pepper shakers that dispense pre-ground pepper. Spice mills such as pepper mills were found in European kitchens as early as the 14th century, but the mortar and pestle used earlier for crushing pepper have remained a popular method for centuries as well.[43]
See also
Notes and references
- ↑ "Piper nigrum information from NPGS/GRIN". www.ars-grin.gov. Retrieved 2 March 2008.
- ↑ Dravidian India - T.R. Sesha Iyengar - Google Books. Books.google.com. Retrieved on 31 October 2012.
- ↑ Intercourse Between India and the Western World - H. G. Rawlinson - Google Books. Books.google.com. Retrieved on 31 October 2012.
- ↑ Antiquities of India: An Account of the History and Culture of Ancient Hindustan - Lionel D. Barnett - Google Books. Books.google.com. Retrieved on 31 October 2012.
- 1 2 3 "Pepper (noun)". Online Etymology Dictionary, Douglas Harper. 2016. Retrieved 24 September 2016.
- ↑ "Cleaner technology for white pepper production". The Hindu Business line. 27 March 2008. Retrieved 29 January 2009.
- ↑ Ochef, Using fresh green peppercorns. Retrieved 6 November 2005.
- 1 2 Manjunath Hegde, Bomnalli (19 October 2013). "Meet the pepper queen" (Bangalore). Deccan Herald. Retrieved 22 January 2015.
- ↑ Katzer, Gernot (2006). Pepper. Gernot Katzer's Spice Pages. Retrieved 2 December 2012.
- 1 2 "Black Pepper Cultivation and Harvest". Thompson Martinez. Retrieved 14 May 2014.
- ↑ "Piper nigrum Linnaeus". Flora of China.
- 1 2 Jaramillo, M. Alejandra; Manos (2001). "Phylogeny and Patterns of Floral Diversity in the Genus Piper (Piperaceae)". American Journal of Botany. 88 (4): 706–16. PMID 11302858. doi:10.2307/2657072.
- 1 2 "Pepper (piper spp.), Production/Crops". Food And Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Statistical Division (FAOSTAT). 2013. Retrieved 7 November 2015.
- 1 2 "Karvy's special Reports — Seasonal Outlook Report Pepper" (PDF). Karvy Comtrade Limited. 15 May 2008. Retrieved 29 January 2008.
- ↑ Davidson & Saberi 178
- ↑ J. Innes Miller, The Spice Trade of the Roman Empire (Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1969), p. 80
- ↑ Dalby p. 93.
- ↑ Stephanie Fitzgerald (8 September 2008). Ramses II, Egyptian Pharaoh, Warrior, and Builder. Compass Point Books. p. 88. ISBN 0-7565-3836-X. Retrieved 29 January 2008.
- ↑ From Bostock and Riley's 1855 translation. Text online.
- ↑ J. Norwich, Byzantium: The Early Centuries, 134
- ↑ Innes Miller, The Spice Trade, p. 83
- ↑ Dalby p. 156; also Turner pp. 108–109, though Turner does go on to discuss spices (not pepper specifically) being used to disguise the taste of partially spoiled wine or ale.
- ↑ H. J. D. Dorman; S. G. Deans (2000). "Antimicrobial agents from plants: antibacterial activity of plant volatile oils". Journal of Applied Microbiology. 88 (2): 308–16. PMID 10736000. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2672.2000.00969.x.. Full text at Blackwell website; purchase required. "Spices, which are used as integral ingredients in cuisine or added as flavouring agents to foods, are present in insufficient quantities for their antimicrobial properties to be significant."
- ↑ Jaffee, p. 10.
- ↑ Dalby pp. 74–75. The argument that jujiang was long pepper goes back to the 4th century CE botanical writings of Ji Han; Hui-lin Li's 1979 translation of and commentary on Ji Han's work makes the case that it was piper nigrum.
- ↑ Dalby p. 77.
- ↑ Yule, Henry; Cordier, Henri, Translation from The Travels of Marco Polo: The Complete Yule-Cordier Edition, Vol. 2, Dover. ISBN 0-486-27587-6. p. 204.
- ↑ Finlay, Robert (2008). "The Voyages of Zheng He: Ideology, State Power, and Maritime Trade in Ming China". Journal of the Historical Society. 8 (3): 337. doi:10.1111/j.1540-5923.2008.00250.x.
- ↑ Turner p. 160.
- ↑ Turner p. 171.
- ↑ U.S. Library of Congress Science Reference Services "Everyday Mysteries", Why does pepper make you sneeze?. Retrieved 12 November 2005.
- ↑ Dudhatra, GB; Mody, SK; Awale, MM; Patel, HB; Modi, CM; Kumar, A; Kamani, DR; Chauhan, BN (2012). "A comprehensive review on pharmacotherapeutics of herbal bioenhancers". The Scientific World Journal. 2012 (637953): 637953. PMC 3458266
 . PMID 23028251. doi:10.1100/2012/637953.
. PMID 23028251. doi:10.1100/2012/637953. - ↑ Thanissaro Bhikkhu (30 November 1990). Buddhist Monastic Code II. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-36708-5. Retrieved 29 January 2008.
- ↑ Dawid, Corinna; Henze, Andrea; Frank, Oliver; Glabasnia, Anneke; Rupp, Mathias; Büning, Kirsten; Orlikowski, Diana; Bader, Matthias; Hofmann, Thomas (2012). "Structural and Sensory Characterization of Key Pungent and Tingling Compounds from Black Pepper (Piper nigrum L.)". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 60 (11): 2884–2895. PMID 22352449. doi:10.1021/jf300036a.
- ↑ James A. Duke (16 August 1993). CRC Handbook of Alternative Cash Crops. CRC Press. p. 395. ISBN 0-8493-3620-1. Retrieved 29 January 2009.
- ↑ Srinivasan K (2007). "Black pepper and its pungent principle-piperine: a review of diverse physiological effects". Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 47 (8): 735–48. PMID 17987447. doi:10.1080/10408390601062054.
- ↑ "Nutrition facts for black pepper, one tablespoon (6 g); USDA Nutrient Database, version SR-21". Conde Nast. 2014. Retrieved 25 October 2014.
- ↑ Pepper. Tis-gdv.de. Retrieved on 31 October 2012.
- ↑ Lawless, Harry T.; Heymann, Hildegarde (2010). Sensory Evaluation of Food: Principles and Practices. Springer. pp. 62–3. ISBN 1441964886.
- ↑ Jirovetz, L; Buchbauer, G; Ngassoum, M. B.; Geissler, M (2002). "Aroma compound analysis of Piper nigrum and Piper guineense essential oils from Cameroon using solid-phase microextraction-gas chromatography, solid-phase microextraction-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and olfactometry". Journal of Chromatography A. 976 (1–2): 265–75. PMID 12462618.
- 1 2 McGee p. 428.
- ↑ Siebert, Tracey E.; Wood, Claudia; Elsey, Gordon M.; Alan (2008). "Determination of Rotundone, the Pepper Aroma Impact Compound, in Grapes and Wine". J. Agric. Food Chem. 56 (10): 3745–3748. PMID 18461962. doi:10.1021/jf800184t.
- ↑ Montagne, Prosper (2001). Larousse Gastronomique. Hamlyn. p. 726. ISBN 0-600-60235-4. OCLC 47231315. "Mill".
Bibliography
- Dalby, Andrew (2002). Dangerous Tastes. Berkeley: University of California Press. ISBN 0-520-23674-2.
- Davidson, Alan (2002). Wilder Shores of Gastronomy: Twenty Years of the Best Food Writing from the Journal Petits Propos Culinaires. Berkeley: Ten Speed Press. ISBN 978-1-58008-417-8.
- Jaffee, Steven (2004). "Delivering and Taking the Heat: Indian Spices and Evolving Process Standards" (PDF). An Agriculture and Rural Development Discussion Paper. Washington: World Bank.
- McGee, Harold (2004). "Black Pepper and Relatives". On Food and Cooking (Revised Edition). Scribner. pp. 427–429. ISBN 0-684-80001-2. OCLC 56590708.
- Turner, Jack (2004). Spice: The History of a Temptation. London: Vintage Books. ISBN 0-375-70705-0. OCLC 61213802.
External links
-
 Media related to Piper nigrum at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Piper nigrum at Wikimedia Commons -
 Data related to Piper nigrum at Wikispecies
Data related to Piper nigrum at Wikispecies -
 Pepper at Wikibook Cookbooks
Pepper at Wikibook Cookbooks