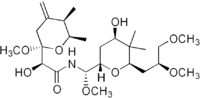
Pederin
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2S)-N-[(S)-[(2S,4R,6R)-6-[(2S)-2,3-dimethoxypropyl]-4-hydroxy-5,5-dimethyl-2-tetrahydropyranyl]-methoxymethyl]-2-hydroxy-2-[(2R,5R,6R)-2-methoxy-5,6-dimethyl-4-methylene-2-tetrahydropyranyl]acetamide | |
| Other names
Pederine | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C25H45NO9 | |
| Molar mass | 503.6261 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Pederin is a vesicant toxic amide with two tetrahydropyran rings, found in the haemolymph of the Paederus genus of beetles, including the Nairobi fly, belonging to the Staphylinidae family. It was first characterized by processing 25 million field-collected P. fuscipes.[1] It makes up approximately 0.025% of an insects weight (for P. fuscipes).[1]
It has been demonstrated that the production of pederin relies on the activities of an endosymbiont (Pseudomonas ssp.) within Paederus.[2]
The manufacture of pederin is largely confined to adult female beetles—larvae and males only store pederin acquired maternally (i.e., through eggs) or by ingestion.[1]
Physical Effects
Skin contact with pederin from the coelomic fluid exuded from a female Paederus beetle causes Paederus dermatitis. This is a rash that varies from a slight erythema to severe blistering, depending on the concentration and duration of exposure.[3] Treatment involves washing the irritated area with cool soapy water. Application of a topical steroid is also recommended for more intense exposures.[4] These measures can significantly reduce the physical effects the toxin has on the affected area.

Synthesis
An efficient total synthesis of pederin is known. Beginning with (+)-benzoylselenopederic acid, Zn(BH4)2 reduction is applied, introducing stereoselective reduction of the acyclic ketone. Michael addition of nitromethane is performed. After several steps of Moffatt oxidation, phenylselenation, hydrolysis, and reduction, pederic acid is reached.[5]
The final steps of the synthesis of pederin are shown to the right. Here, pederic acid is added to the protected compound in LiHMDS and THF, producing a 75% yield. The protecting groups are then removed using TBAF and a hydrolytic quench. This step gives an 88% yield.[6]

Mode of action
Pederin blocks mitosis at levels as low as 1 ng/ml, by inhibiting protein and DNA synthesis without affecting RNA synthesis,[7] prevents cell division, and has been shown to extend the life of mice bearing a variety of tumors. For these reasons, it has garnered interest as a potential anti-cancer treatment.
Uses
Pederin and its derivatives are being researched as anticancer drugs. This family of compounds is able to inhibit protein and DNA biosynthesis,[8] making it useful to slow the division of cancer cells. One derivative of pederin, psymberin, has been found to be highly selective in targeting solid tumor cells.[9]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 Bugs Don’t Have to Bite to Do Damage:The Tale of the Paederus Beetle
- ↑ Piel J (2002). "A polyketide synthase-peptide synthetase gene cluster from an uncultured bacterial symbiont of Paederus beetles". PNAS. 99 (22): 14002–14007. PMC 137826
 . PMID 12381784. doi:10.1073/pnas.222481399.
. PMID 12381784. doi:10.1073/pnas.222481399. - ↑ Singh G, Yousuf Ali S (2007). "Paederus dermatitis". Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 73 (1): 13–15. doi:10.4103/0378-6323.30644.
- ↑ Paederus Dermatitis
- ↑ Nakata T, Nagao S, Oishi T (1985). "Total synthesis of (+)-pederin. 2. Stereocontrolled synthesis of (+)-benzoylselenopederic acid and total synthesis of (+)-pederin". Tetrahedron Letters. 26 (52): 6465–6468.
- ↑ Jewett JC, Rawal VH (2007). "Total Synthesis of Pederin". Angewandte Chemie. 46 (34): 6502–6504.
- ↑ Frank JH, Kanamitsu K (1987). "Paederus, Sensu Lato (Coleoptera: Staphylinidae): Natural History and Medical Importance". J. Med. Entomol. 24 (2): 155–191. PMID 3295241.
- ↑ Narquizian R, Kocienski PJ (2000). "In The Role of Natural Products in Drug Discovery". 32 (1).
- ↑ Piel, Jörn, et al. (2005). "Exploring the Chemistry of Uncultivated Bacterial Symbionts: Antitumor Polyketides of the Pederin Family". Journal of Natural Products. 68 (3): 472–479.