Paphos Archaeological Park
Paphos Archaeological Park (also Kato Pafos Archaeological Park) contains the major part of the important ancient Greek and Roman City and is located in Paphos, southwest Cyprus. The park, still under excavation, is within the Nea Pafos ("New Paphos") section of the coastal city.[1]
Its sites and monuments date from prehistoric times through the Middle Ages. Among the most significant remains so far discovered are four large and elaborate Roman villas: the House of Dionysos, the House of Aion, the House of Theseus and the House of Orpheus, all with superb preserved mosaic floors.[2] In addition, excavations have uncovered an Agora, Asklipieion, Basilica, Odeion, Hellenistic-Roman Theatre, and a necropolis known as the "Tombs of the Kings".[3]
In 1980 Nea Pafos was inscribed on the World Heritage List of UNESCO[4] for its outstanding ancient remains.
History
Nea Paphos was probably built by Nicocles, the last king of Paphos, at the end of the 4th c. BC. By the beginning of the 2nd c. BC it became the capital of the island, replacing Salamis during the Hellenistic era under the Ptolemies.
Monuments
House of Dionysos
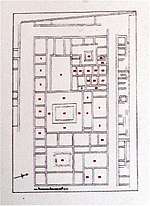
This exceptionally rich villa occupies 2000 sq. m of which 556 are covered with mosaic floors decorated with mythological, vintage and hunting scenes. Its is named after the god Dionysos who features on several of the mosaics.
Its rooms are arranged around a central courtyard, or atrium, which functioned as the core of the house. It was built at the end of the 2nd century AD and was destroyed and abandoned after the earthquakes of the 4th century AD.
A Hellenistic pebble mosaic representing the mythical sea-monster Scylla from an earlier villa of the 3rd c. BC which was found below the Roman villa is on display in situ.
 Apollo und Daphne
Apollo und Daphne Icarus
Icarus Four Seasons
Four Seasons Hunting scene
Hunting scene
House of Aion

Although only three rooms of this large villa have been excavated by the University of Warsaw, the mosaic floor from the House of Aion is considered one of the most exceptional works of ancient Roman art, if not the only work of its kind,[5] and certainly one of the most enigmatic and most fervently discussed by scholars. It dates from around the mid-4th century AD and is named after the god shown in the middle of the mosaic.
The main room was probably a triclinium or reception room. Two smaller rooms had excellent geometric mosaics.
The main mosaic contains 3 horizontal frames with 5 panels all surrounded by a geometric frame.
A villa wall was found collapsed into the adjacent street and has been restored.
Gallery
 Birth of Dionysos
Birth of Dionysos Beauty contest between Cassiopeia and the nereids
Beauty contest between Cassiopeia and the nereids Triumph of Dionysos - Satyr Skirtos offering fruit to Dionysos
Triumph of Dionysos - Satyr Skirtos offering fruit to Dionysos Triumph of Dionysos - Centaur and Maenad
Triumph of Dionysos - Centaur and Maenad
House of Theseus
This exceptionally large villa was the residence of the Roman proconsul or governor, and was divided between rooms for official functions and those for private use. Its name derives from the beautiful mosaic of Theseus and the Minotaur found in the southeast quarter. The villa covered several insulae of the Hellenistic street plan.
It was built in the 2nd half of the 2nd c. AD over ruins of earlier houses and was occupied until the 7th c. AD. So far only the southern half of the villa has been fully excavated.
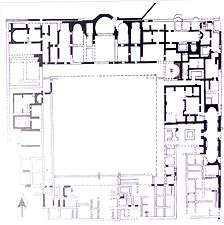 House of Theseus
House of Theseus Theseus Mosaic
Theseus Mosaic Geometric Mosaic
Geometric Mosaic
.jpg)
House of Orpheus
This villa lies to the west of the House of Theseus. The mosaics of the third century AD have three mythological representations: “Orpheus and his Lyre”, “Hercules and the Lion of Nemea” and “the Amazon”, but they are currently not on view to the public.
Theatre

The theatre, located in the northeastern area of the ancient city, is dated to originally the end of the fourth century BC and has been under excavation by the University of Sydney since 1995.[6][7][8]
Odeon

Agora

References
- ↑ Bryant, Sue (13 January 2009). Frommer's Cyprus With Your Family: From the Best Family Beaches to Mountain Villages. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 56–. ISBN 978-0-470-72318-0. Retrieved 11 November 2012.
- ↑ "Department of Antiquities". www.mcw.gov.cy. Retrieved 14 October 2015.
- ↑ "Paphos Archaeological Park". visitpafos.org.cy. Retrieved 11 November 2012.
- ↑ "Paphos-UNESCO". whc.unesco.org/en/list/79. Retrieved 14 October 2015.
- ↑ M.T. OLszewski, The iconographic programme of the Cyprus mosaic from the House of Aion reinterpreted as an anti-Christian polemic, see https://www.academia.edu/5403368
- ↑ J.R. Green, Cyprus Today, vol. XLV, no. 2, 2007. pp. 2-21
- ↑ http://sydney.edu.au/museums/research/paphos-theatre.shtml
- ↑ http://www.paphostheatre.org/archaeological-history.html
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Paphos Archaeological Park. |
Coordinates: 34°45.34′N 32°24.25′E / 34.75567°N 32.40417°E Archeological Park Paphos Life
