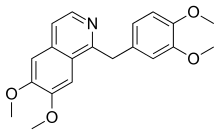
Papaverine
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /pəˈpævəriːn/[1] |
| Trade names | Pavabid, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682707 |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Routes of administration | Oral, intravenous, intramuscular, rectal, intracavernosal |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 80% |
| Protein binding | ~90% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Biological half-life | 1.5–2 hours |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.361 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H21NO4 |
| Molar mass | 339.385 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Papaverine (Latin papaver, "poppy") is an opium alkaloid antispasmodic drug, used primarily in the treatment of visceral spasm, vasospasm (especially those involving the intestines, heart, or brain), and occasionally in the treatment of erectile dysfunction. It is used in the treatment of acute mesenteric ischemia. While it is found in the opium poppy, papaverine differs in both structure and pharmacological action from the analgesic (morphine-related) opium alkaloids (opiates).
History

Papaverine was discovered in 1848 by Georg Merck (1825–1873).[2] Merck was a student of the German chemists Justus von Liebig and August Hofmann, and he was the son of Emanuel Merck (1794–1855), founder of the Merck corporation, a major German chemical and pharmaceutical company.[3]
Uses
Papaverine is approved to treat spasms of the gastrointestinal tract, bile ducts and ureter and for use as a cerebral and coronary vasodilator in subarachnoid hemorrhage (combined with balloon angioplasty)[4] and coronary artery bypass surgery.[5] Papaverine may also be used as a smooth muscle relaxant in microsurgery where it is applied directly to blood vessels.
Papaverine is used as an erectile dysfunction drug, alone or sometimes in combination.[6][7] Papaverine, when injected in penile tissue causes direct smooth muscle relaxation and consequent filling of the corpus cavernosum with blood resulting in erection. A topical gel is also available for ED treatment.[8]
It is also commonly used in cryopreservation of blood vessels along with the other glycosaminoglycans and protein suspensions.[9][10] Functions as a vasodilator during cryopreservation when used in conjunction with verapamil, phentolamine, nifedipine, tolazoline or nitroprusside.[11][12]
Papaverine is also being investigated as a topical growth factor in tissue expansion with some success.[13]
Papaverine is used as an off label prophylaxis (preventative) of migraine headaches.[14][15][16] It is not a first line drug such as a few beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, tricyclic antidepressants, and some anticonvulsants such as divalproex, but rather when these first line drugs and secondary drugs such as SSRIs, angiotensin II receptor antagonists, etc. fail in the prophylaxis of migraines, have intolerable side effects or are contraindicated.
Papaverine is also present in combinations of opium alkaloid salts such as papaveretum (Omnopon, Pantopon) and others, along with morphine, codeine, and in some cases noscapine and others in a percentage similar to that in opium, or modified for a given application.
Mechanism
The in vivo mechanism of action is not entirely clear, but an inhibition of the enzyme phosphodiesterase causing elevation of cyclic AMP levels is significant. It may also alter mitochondrial respiration.
Papaverine has also been demonstrated to be a selective phosphodiesterase inhibitor for the PDE10A subtype found mainly in the striatum of the brain. When administered chronically to mice, it produced motor and cognitive deficits and increased anxiety, but conversely may produce an antipsychotic effect,[17][18] even though not all studies support this view.[19]
Side effects
Frequent side effects of papaverine treatment include polymorphic ventricular tachycardia, constipation, interference with sulphobromophthalein[20] retention test (used to determine hepatic function), increased transaminase levels, increased alkaline phosphatase levels, somnolence, and vertigo.
Rare side effects include flushing of the face, hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating), cutaneous eruption, arterial hypotension, tachycardia, loss of appetite, jaundice, eosinophilia, thrombopenia, mixed hepatitis, headache, allergic reaction, chronic active hepatitis, and paradoxical aggravation of cerebral vasospasm.[21]
Papaverine in the plant Sauropus androgynus is linked to bronchiolitis obliterans.[22]
Formulations and trade names
Papaverine is available as a conjugate of hydrochloride, codecarboxylate, adenylate, and teprosylate. It was also once available as a salt of hydrobromide, camsylate, cromesilate, nicotinate, and amygdalic acid|phenylglycolate. The hydrochloride salt is available for intramuscular, intravenous, rectal and oral administration. The teprosylate is available in intravenous, intramuscular, and orally administered formulations. The codecarboxylate is available in oral form, only, as is the adenylate.
The codecarboxylate is sold under the name Albatran,[23] the adenylate as Dicertan,[24] and the hydrochloride salt is sold variously as Artegodan (Germany), Cardioverina (countries outside Europe and the United States), Dispamil (countries outside Europe and the United States), Opdensit (Germany), Panergon (Germany), Paverina Houde (Italy, Belgium), Pavacap (United States), Pavadyl (United States), Papaverine (Israel), Papaverin-Hamelin (Germany), Paveron (Germany), Spasmo-Nit (Germany), Cardiospan, Papaversan, Cepaverin, Cerespan, Drapavel, Forpaven, Papalease, Pavatest, Paverolan, Therapav (Canada[25]), Vasospan, Cerebid, Delapav, Dilaves, Durapav, Dynovas, Optenyl, Pameion, Papacon, Pavabid, Pavacen, Pavakey, Pavased, Pavnell, Alapav, Myobid, Vasal, Pamelon, Pavadel, Pavagen, Ro-Papav, Vaso-Pav, Papanerin-hcl, Qua bid, Papital T.R., Paptial T.R., Pap-Kaps-150.[26] In Hungary, papaverine and homatropine methylbromide are used in mild drugs that help "flush" the bile.[27]
References
- ↑ Papaverine - EverydayHealth.com
- ↑ Merck Georg (1848). "Vorläufige Notiz über eine neue organische Base im Opium" [Preliminary notice of a new organic base in opium]. Annalen der Chemie und Pharmacie. 66: 125–128. doi:10.1002/jlac.18480660121.
- ↑ William H. Brock, Justus von Liebig: The Chemical Gatekeeper (Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press, 1997). page 120.
- ↑ Liu JK, Couldwell WT (2005). "Intra-arterial papaverine infusions for the treatment of cerebral vasospasm induced by aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage". Neurocrit Care. 2 (2): 124–32. PMID 16159054. doi:10.1385/NCC:2:2:124.
- ↑ Takeuchi K, Sakamoto S, Nagayoshi Y, Nishizawa H, Matsubara J (November 2004). "Reactivity of the human internal thoracic artery to vasodilators in coronary artery bypass grafting". Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 26 (5): 956–9. PMID 15519189. doi:10.1016/j.ejcts.2004.07.047.
- ↑ Desvaux, P (2005). "An overview of the management of erectile disorders". Presse medicale (Paris, France : 1983). 34 (13 Suppl): 5–7. PMID 16158020.
- ↑ Bella, A. J.; Brock, G. B. (2004). "Intracavernous Pharmacotherapy for Erectile Dysfunction". Endocrine. 23 (2–3): 149–155. PMID 15146094. doi:10.1385/ENDO:23:2-3:149.
- ↑ Kim, E.; Elrashidy, R.; McVary, K. (1995). "Papaverine Topical Gel for Treatment of Erectile Dysfunction". The Journal of Urology. 153 (2): 361–5. PMID 7815584. doi:10.1097/00005392-199502000-00019.
- ↑ Müller-Schweinitzer E, Ellis P (May 1992). "Sucrose promotes the functional activity of blood vessels after cryopreservation in DMSO-containing fetal calf serum". Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 345 (5): 594–7. PMID 1528275. doi:10.1007/bf00168954.
- ↑ Müller-Schweinitzer E, Hasse J, Swoboda L (1993). "Cryopreservation of human bronchi". J Asthma. 30 (6): 451–7. PMID 8244915. doi:10.3109/02770909309056754.
- ↑ Brockbank KG (February 1994). "Effects of cryopreservation upon vein function in vivo". Cryobiology. 31 (1): 71–81. PMID 8156802. doi:10.1006/cryo.1994.1009.
- ↑ Giglia JS, Ollerenshaw JD, Dawson PE, Black KS, Abbott WM (November 2002). "Cryopreservation prevents arterial allograft dilation". Ann Vasc Surg. 16 (6): 762–7. PMID 12391500. doi:10.1007/s10016-001-0072-1.
- ↑ Tang Y, Luan J, Zhang X (2004). "Accelerating tissue expansion by application of topical papaverine cream". Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 114 (5): 1166–9. PMID 15457029. doi:10.1097/01.PRS.0000135854.48570.76.
- ↑ Sillanpää, M; Koponen, M (1978). "Papaverine in the prophylaxis of migraine and other vascular headache in children". Acta paediatrica Scandinavica. 67 (2): 209–12. PMID 343489. doi:10.1111/j.1651-2227.1978.tb16304.x.
- ↑ Vijayan, N. (1977). "Brief therapeutic report: papaverine prophylaxis of complicated migraine". Headache. 17 (4): 159–162. PMID 893088. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.1977.hed1704159.x.
- ↑ Poser, C. M. (1974). "Letter: Papaverine in prophylactic treatment of migraine". Lancet. 1 (7869): 1290. PMID 4134173. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(74)90045-2.
- ↑ Siuciak JA, Chapin DS, Harms JF, et al. (August 2006). "Inhibition of the striatum-enriched phosphodiesterase PDE10A: a novel approach to the treatment of psychosis". Neuropharmacology. 51 (2): 386–96. PMID 16780899. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2006.04.013.
- ↑ Hebb AL, Robertson HA, Denovan-Wright EM (May 2008). "Phosphodiesterase 10A inhibition is associated with locomotor and cognitive deficits and increased anxiety in mice". Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 18 (5): 339–63. PMID 17913473. doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2007.08.002.
- ↑ Weber M, Breier M, Ko D, Thangaraj N, Marzan DE, Swerdlow NR (May 2009). "Evaluating the antipsychotic profile of the preferential PDE10A inhibitor, papaverine". Psychopharmacology (Berl.). 203 (4): 723–35. PMC 2748940
 . PMID 19066855. doi:10.1007/s00213-008-1419-x.
. PMID 19066855. doi:10.1007/s00213-008-1419-x. - ↑ "SID 149219 — PubChem Substance Summary".
- ↑ Clyde BL, Firlik AD, Kaufmann AM, Spearman MP, Yonas H (April 1996). "Paradoxical aggravation of vasospasm with papaverine infusion following aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Case report". J. Neurosurg. 84 (4): 690–5. PMID 8613866. doi:10.3171/jns.1996.84.4.0690.
- ↑ Bunawan H, Bunawan SN, Baharum SN, Noor NM (2015). "Sauropus androgynus (L.) Merr. Induced Bronchiolitis Obliterans: From Botanical Studies to Toxicology". Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015: 714158. PMC 4564651
 . PMID 26413127. doi:10.1155/2015/714158.
. PMID 26413127. doi:10.1155/2015/714158. - ↑ "SID 660773 — PubChem Substance Summary".
- ↑ "SID 660767 — PubChem Substance Summary".
- ↑ "THERAPAV (PRODUIT PUR) - Détail". Retrieved 26 September 2005. CSST - Service du répertoire toxicologique. (French)
- ↑ "SID 660767 — PubChem Substance Summary — Depositor-Supplied Synonyms: All".
- ↑ Neo-Bilagit