GNOME Disks
 | |
 | |
| Original author(s) | Red Hat |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) | David Zeuthen |
| Stable release | |
| Preview release |
3.25.4 (20 July 2017) [±]
|
| Repository |
git |
| Development status | Active |
| Written in | C |
| Operating system | Linux |
| Platform | GNOME |
| Size | 1.4 MB |
| Available in | Multilingual |
| Type | Disk utility |
| License | LGPL v2+ |
| Website |
git |
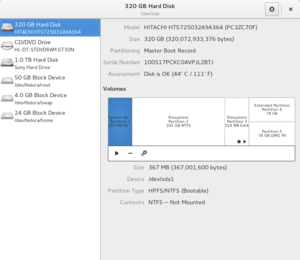
Disks (also known as gnome-disk-utility or GNOME Disks or palimpsest) is a udisks graphical front-end included in the gnome-disk-utility package.[2] Disks can be used for partition management, S.M.A.R.T. monitoring, benchmarking, and software RAID (until v. 3.12).[3] An introduction is included in the GNOME Documentation Project.
Disks used to be known as GNOME Disk Utility or palimpsest. Udisks was named DeviceKit-disks in earlier releases. DeviceKit-disks is part of DeviceKit which was planned to replace certain aspects of HAL. HAL and DeviceKit have been deprecated.
A unique feature of the partition manager is that tasks are executed in the background, even after the application has been closed by the user.
Disks has been included in several operating systems including Debian, Ubuntu, Linux Mint, Trisquel, Fedora, Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6[4] and CentOS.

See also
- List of disk partitioning software
- System monitor
- Comparison of S.M.A.R.T. tools
- GParted – Another free software alternative
- Disk utility
References
- ↑ https://git.gnome.org/browse/epiphany/tag/?h=3.24.3
- ↑ Richard Petersen (December 1, 2010), Fedora 14: Administration and Security, Surfing Turtle Press, pp. 147–, ISBN 978-1-936280-23-0
- ↑ "Disk Utility management for GNOME".
- ↑ "Storage". Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 Documentation. Redhat. Retrieved 21 December 2011.
- ↑ "udisks2 readme".
External links
- Releases at Freedesktop.org
- Palimpsest Disk Utility Manual at gnome.org
- udisks and gnome-disk-utility - past, present and future by David Zeuthen
- Udisks Improvements at fedoraproject.org
- Devicekit at fedoraproject.org
