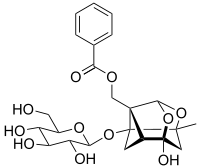
Paeoniflorin
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Paeonia moutan Paeony root Peoniflorin | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.041.327 |
| PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C23H28O11 | |
| Molar mass | 480.47 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Paeoniflorin is a chemical compound which is one of the major constituents of an herbal medicine derived from Paeonia lactiflora.[1] It can also be isolated from the fresh water fern Salvinia molesta.[2]
In Paeonia, it can form new compounds with addition of phenolic substituents.[3] In a study in female rats, paeoniflorin was found to inhibit the production of testosterone within the ovaries by promoting the activity of aromatase.[4][5]
References
- ↑ Yan, D.; Saito, K.; Ohmi, Y.; Fujie, N.; Ohtsuka, K. (2004). "Paeoniflorin, a novel heat shock protein–inducing compound". Cell Stress & Chaperones. 9 (4): 378–89. PMC 1065277
 . PMID 15633296. doi:10.1379/CSC-51R.1.
. PMID 15633296. doi:10.1379/CSC-51R.1. - ↑ Choudhary, M. I.; Naheed, N.; Abbaskhan, A.; Musharraf, S. G.; Siddiqui, H.; Atta-Ur-Rahman (2008). "Phenolic and other constituents of fresh water fern Salvinia molesta". Phytochemistry. 69 (4): 1018–1023. PMID 18177906. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2007.10.028.
- ↑ Tanaka, T.; Kataoka, M.; Tsuboi, N.; Kouno, I. (2000). "New monoterpene glycoside esters and phenolic constituents of Paeoniae radix, and increase of water solubility of proanthocyanidins in the presence of paeoniflorin". Chemical & pharmaceutical bulletin. 48 (2): 201–207. PMID 10705504. doi:10.1248/cpb.48.201.
- ↑ Grant; Ramasamy (April 2012). "An Update on Plant Derived Anti-Androgens". International Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism. 10 (2): 497–502. PMC 3693613
 . PMID 23843810. doi:10.5812/ijem.3644.
. PMID 23843810. doi:10.5812/ijem.3644. - ↑ Takeuchi, Toru; Nishii, Osamu; Okamura, Takashi; Yaginuma, Tsutomu (1991). "Effect of Paeoniflorin, Glycyrrhizin and Glycyrrhetic acid on Ovarian Androgen Production". The American Journal of Chinese Medicine. 19 (1): 73–8. PMID 1897494. doi:10.1142/S0192415X91000119.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.