Terphenyl
| | |
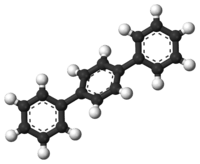 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1,4-Diphenylbenzene | |
| Other names
p-Terphenyl; 1,4-Diphenylbenzene; para-Diphenylbenzene; p-Diphenylbenzene; para-Triphenyl; p-Triphenyl | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H14 | |
| Molar mass | 230.31 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White powder[1] |
| Density | 1.24 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 212 to 214 °C (414 to 417 °F; 485 to 487 K)[1] 212-213 °C[2] |
| Boiling point | 389 °C (732 °F; 662 K)[2] |
| Insoluble[1] | |
| Refractive index (nD) |
1.65[3] |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Iritant (Xi) |
| R-phrases (outdated) | R36/37/38 R50/53 |
| S-phrases (outdated) | S26 S60 S61 |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Flash point | 207 °C (405 °F; 480 K)[2] |
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |
| PEL (Permissible) |
C 9 mg/m3 (1 ppm)[4][5][6] |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Terphenyls are a group of closely related aromatic hydrocarbons. Also known as diphenylbenzenes or triphenyls, they consist of a central benzene ring substituted with two phenyl groups. The three isomers are ortho-terphenyl, meta-terphenyl, and para-terphenyl. Commercial grade terphenyl is generally a mixture of the three isomers. This mixture is used in the production of polychlorinated terphenyls, which were formerly used as heat storage and transfer agents.[1]
p-Terphenyl is the most common isomer. It is used as a laser dye and a sunscreen ingredient.[1]
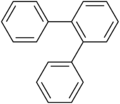 ortho-Terphenyl
ortho-Terphenyl meta-Terphenyl
meta-Terphenyl para-Terphenyl
para-Terphenyl
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 p-Terphenyl at chemicalland21.com
- 1 2 3 p-Terphenyl at Sigma-Aldrich
- ↑
- ↑ "NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards #0591". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ↑ "NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards #0592". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ↑ "NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards #0593". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
External links
- p-Terphenyl at the Oregon Laser Medical Center
- o-Terphenyl, m-Terphenyl, p-Terphenyl at Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.
