Oxidative stress
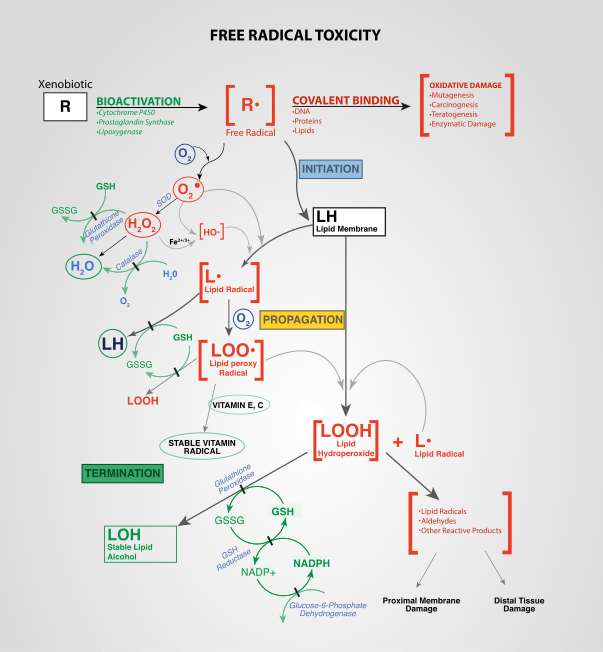
Oxidative stress reflects an imbalance between the systemic manifestation of reactive oxygen species and a biological system's ability to readily detoxify the reactive intermediates or to repair the resulting damage. Disturbances in the normal redox state of cells can cause toxic effects through the production of peroxides and free radicals that damage all components of the cell, including proteins, lipids, and DNA. Oxidative stress from oxidative metabolism causes base damage, as well as strand breaks in DNA. Base damage is mostly indirect and caused by reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated, e.g. O2− (superoxide radical), OH (hydroxyl radical) and H2O2 (hydrogen peroxide).[1] Further, some reactive oxidative species act as cellular messengers in redox signaling. Thus, oxidative stress can cause disruptions in normal mechanisms of cellular signaling.
In humans, oxidative stress is thought to be involved in the development of Asperger syndrome,[2] ADHD,[3] cancer,[4] Parkinson's disease,[5] Lafora disease,[6] Alzheimer's disease,[7] atherosclerosis,[8] heart failure,[9] myocardial infarction,[10][11] fragile X syndrome,[12] Sickle Cell Disease,[13] lichen planus,[14] vitiligo,[15] autism,[16] infection, Chronic fatigue syndrome,[17] and Depression.[18] However, reactive oxygen species can be beneficial, as they are used by the immune system as a way to attack and kill pathogens.[19] Short-term oxidative stress may also be important in prevention of aging by induction of a process named mitohormesis.[20]
Chemical and biological effects
Chemically, oxidative stress is associated with increased production of oxidizing species or a significant decrease in the effectiveness of antioxidant defenses, such as glutathione.[21] The effects of oxidative stress depend upon the size of these changes, with a cell being able to overcome small perturbations and regain its original state. However, more severe oxidative stress can cause cell death, and even moderate oxidation can trigger apoptosis, while more intense stresses may cause necrosis.[22]
Production of reactive oxygen species is a particularly destructive aspect of oxidative stress. Such species include free radicals and peroxides. Some of the less reactive of these species (such as superoxide) can be converted by oxidoreduction reactions with transition metals or other redox cycling compounds (including quinones) into more aggressive radical species that can cause extensive cellular damage.[23] Most long-term effects are caused by damage to DNA.[24] DNA damage induced by ionizing radiation is similar to oxidative stress, and these lesions have been implicated in aging and cancer. Biological effects of single-base damage by radiation or oxidation, such as 8-oxoguanine and thymine glycol, have been extensively studied. Recently the focus has shifted to some of the more complex lesions. Tandem DNA lesions are formed at substantial frequency by ionizing radiation and metal-catalyzed H2O2 reactions. Under anoxic conditions, the predominant double-base lesion is a species in which C8 of guanine is linked to the 5-methyl group of an adjacent 3'-thymine (G[8,5- Me]T).[25] Most of these oxygen-derived species are produced at a low level by normal aerobic metabolism. Normal cellular defense mechanisms destroy most of these. Likewise, any damage to cells is constantly repaired. However, under the severe levels of oxidative stress that cause necrosis, the damage causes ATP depletion, preventing controlled apoptotic death and causing the cell to simply fall apart.[26][27]
Polyunsaturated fatty acids, particularly arachidonic acid and linoleic acid, are primary targets for free radical and singlet oxygen oxidations. For example, in tissues and cells, the free radical oxidation of linoleic acid produces racemic mixtures of 13-hydroxy-9Z,11E-octadecadienoic acid, 13-hydroxy-9E,11E-octadecadienoic acid, 9-hydroxy-10E,12-E-octadecadienoic acid (9-EE-HODE), and 11-hydroxy-9Z,12-Z-octadecadienoic acid as well as 4-Hydroxynonenal while singlet oxygen attacks linoleic acid to produce (presumed but not yet proven to be racemic mixtures of) 13-hydroxy-9Z,11E-octadecadienoic acid, 9-hydroxy-10E,12-Z-octadecadienoic acid, 10-hydroxy-8E,12Z-octadecadienoic acid, and 12-hydroxy-9Z-13-E-octadecadienoic (see 13-Hydroxyoctadecadienoic acid and 9-Hydroxyoctadecadienoic acid).[28][29][30] Similar attacks on arachidonic acid produce a far larger set of products including various isoprostanes, hydroperoxy- and hydroxy- eicosatetraenoates, and 4-hydroxyalkenals.[29][31] While many of these products are used as markers of oxidative stress, the products derived from linoleic acid appear far more predominant than arachidonic acid products and therefore easier to identify and quantify in, for example, atheromatous plaques.[32] Certain linoleic acid products have also been proposed to be markers for specific types of oxidative stress. For example, the presence of racemic 9-HODE and 9-EE-HODE mixtures reflects free radical oxidation of linoleic acid whereas the presence of racemic 10-hydroxy-8E,12Z-octadecadienoic acid and 12-hydroxy-9Z-13-E-octadecadienoic acid reflects singlet oxygen attack on linoleic acid.[30][33] In addition to serving as markers, the linoleic and arachidonic acid products can contribute to tissue and/or DNA damage but also act as signals to stimulate pathways which function to combat oxidative stress.[29][34][35][36][37]
| Oxidant | Description |
|---|---|
| •O− 2, superoxide anion |
One-electron reduction state of O 2, formed in many autoxidation reactions and by the electron transport chain. Rather unreactive but can release Fe2+ from iron-sulfur proteins and ferritin. Undergoes dismutation to form H 2O 2 spontaneously or by enzymatic catalysis and is a precursor for metal-catalyzed •OH formation. |
| H 2O 2, hydrogen peroxide |
Two-electron reduction state, formed by dismutation of •O− 2 or by direct reduction of O 2. Lipid-soluble and thus able to diffuse across membranes. |
| •OH, hydroxyl radical | Three-electron reduction state, formed by Fenton reaction and decomposition of peroxynitrite. Extremely reactive, will attack most cellular components |
| ROOH, organic hydroperoxide | Formed by radical reactions with cellular components such as lipids and nucleobases. |
| RO•, alkoxy and ROO•, peroxy radicals | Oxygen centred organic radicals. Lipid forms participate in lipid peroxidation reactions. Produced in the presence of oxygen by radical addition to double bonds or hydrogen abstraction. |
| HOCl, hypochlorous acid | Formed from H 2O 2 by myeloperoxidase. Lipid-soluble and highly reactive. Will readily oxidize protein constituents, including thiol groups, amino groups and methionine. |
| ONOO-, peroxynitrite | Formed in a rapid reaction between •O− 2 and NO•. Lipid-soluble and similar in reactivity to hypochlorous acid. Protonation forms peroxynitrous acid, which can undergo homolytic cleavage to form hydroxyl radical and nitrogen dioxide. |
Table adapted from.[38][39][40]
Production and consumption of oxidants
One source of reactive oxygen under normal conditions in humans is the leakage of activated oxygen from mitochondria during oxidative phosphorylation. However, E. coli mutants that lack an active electron transport chain produced as much hydrogen peroxide as wild-type cells, indicating that other enzymes contribute the bulk of oxidants in these organisms.[41] One possibility is that multiple redox-active flavoproteins all contribute a small portion to the overall production of oxidants under normal conditions.[42][43]
Other enzymes capable of producing superoxide are xanthine oxidase, NADPH oxidases and cytochromes P450. Hydrogen peroxide is produced by a wide variety of enzymes including several oxidases. Reactive oxygen species play important roles in cell signalling, a process termed redox signaling. Thus, to maintain proper cellular homeostasis, a balance must be struck between reactive oxygen production and consumption.
The best studied cellular antioxidants are the enzymes superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase, and glutathione peroxidase. Less well studied (but probably just as important) enzymatic antioxidants are the peroxiredoxins and the recently discovered sulfiredoxin. Other enzymes that have antioxidant properties (though this is not their primary role) include paraoxonase, glutathione-S transferases, and aldehyde dehydrogenases.
The amino acid methionine is prone to oxidation, but oxidized methionine can be reversible. Oxidation of methionine is shown to inhibit the phosphorylation of adjacent Ser/Thr/Tyr sites in proteins.[44] This gives a plausible mechanism for cells to couple oxidative stress signals with cellular mainstream signaling such as phosphorylation.
Diseases
Oxidative stress is suspected to be important in neurodegenerative diseases including Lou Gehrig's disease (aka MND or ALS), Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, Huntington's disease, Depression, and Multiple sclerosis.[45][46] Indirect evidence via monitoring biomarkers such as reactive oxygen species, and reactive nitrogen species production, antioxidant defense indicates oxidative damage may be involved in the pathogenesis of these diseases,[47][48] while cumulative oxidative stress with disrupted mitochondrial respiration and mitochondrial damage are related with Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and other neurodegenerative diseases.[49]
Oxidative stress is thought to be linked to certain cardiovascular disease, since oxidation of LDL in the vascular endothelium is a precursor to plaque formation. Oxidative stress also plays a role in the ischemic cascade due to oxygen reperfusion injury following hypoxia. This cascade includes both strokes and heart attacks. Oxidative stress has also been implicated in chronic fatigue syndrome.[50] Oxidative stress also contributes to tissue injury following irradiation and hyperoxia, as well as in diabetes.
Oxidative stress is likely to be involved in age-related development of cancer. The reactive species produced in oxidative stress can cause direct damage to the DNA and are therefore mutagenic, and it may also suppress apoptosis and promote proliferation, invasiveness and metastasis.[4] Infection by Helicobacter pylori which increases the production of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species in human stomach is also thought to be important in the development of gastric cancer.[51]
Antioxidants as supplements
The use of antioxidants to prevent some diseases is controversial.[52] In a high-risk group like smokers, high doses of beta carotene increased the rate of lung cancer since high doses of beta-carotene in conjunction of high oxygen tension due to smoking results in a pro-oxidant effect and an antioxidant effect when oxygen tension isn't high.[53][54] In less high-risk groups, the use of vitamin E appears to reduce the risk of heart disease.[55] However, while consumption of food rich in vitamin E may reduce the risk of coronary heart disease in middle-aged to older men and women, using vitamin E supplement also appears to result in an increase in total mortality, heart failure, and hemorrhagic stroke. The American Heart Association therefore recommends the consumption of food rich in antioxidant vitamins and other nutrients, but does not recommend the use of vitamin E supplements to prevent cardiovascular disease.[56] In other diseases, such as Alzheimer's, the evidence on vitamin E supplementation is also mixed.[57][58] Since dietary sources contain a wider range of carotenoids and vitamin E tocopherols and tocotrienols from whole foods, ex post facto epidemiological studies can have differing conclusions than artificial experiments using isolated compounds. However, AstraZeneca's radical scavenging nitrone drug NXY-059 shows some efficacy in the treatment of stroke.[59]
Oxidative stress (as formulated in Harman's free radical theory of aging) is also thought to contribute to the aging process. While there is good evidence to support this idea in model organisms such as Drosophila melanogaster and Caenorhabditis elegans,[60][61] recent evidence from Michael Ristow's laboratory suggests that oxidative stress may also promote life expectancy of Caenorhabditis elegans by inducing a secondary response to initially increased levels of reactive oxygen species.[62] This process was previously named mitohormesis or mitochondrial hormesis on a purely hypothetical basis.[63] The situation in mammals is even less clear.[64][65][66] Recent epidemiological findings support the process of mitohormesis, however a 2007 meta-analysis indicating studies with a low risk of bias (randomization, blinding, follow-up) find that some popular antioxidant supplements (Vitamin A, Beta Carotene, and Vitamin E) may increase mortality risk (although studies more prone to bias reported the reverse).[67]
The USDA removed the table showing the Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity (ORAC) of Selected Foods Release 2 (2010) table due to the lack of evidence that the antioxidant level present in a food translated into a related antioxidant effect in the body.[68]
Metal catalysts
Metals such as iron, copper, chromium, vanadium, and cobalt are capable of redox cycling in which a single electron may be accepted or donated by the metal. This action catalyzes production of reactive radicals and reactive oxygen species.[69] The presence of such metals in biological systems in an uncomplexed form (not in a protein or other protective metal complex) can significantly increase the level of oxidative stress. These metals are thought to induce Fenton reactions and the Haber-Weiss reaction, in which hydroxyl radical is generated from hydrogen peroxide. The hydroxyl radical then can modify amino acids. For example, meta-tyrosine and ortho-tyrosine form by hydroxylation of phenylalanine. Other reactions include lipid peroxidation and oxidation of nucleobases. Metal catalyzed oxidations also lead to irreversible modification of R (Arg), K (Lys), P (Pro) and T (Thr) Excessive oxidative-damage leads to protein degradation or aggregation.[70]
The reaction of transition metals with proteins oxidated by Reactive Oxygen Species or Reactive Nitrogen Species can yield reactive products that accumulate and contribute to aging and disease. For example, in Alzheimer's patients, peroxidized lipids and proteins accumulate in lysosomes of the brain cells.[71]
Non-metal redox catalysts
Certain organic compounds in addition to metal redox catalysts can also produce reactive oxygen species. One of the most important classes of these are the quinones. Quinones can redox cycle with their conjugate semiquinones and hydroquinones, in some cases catalyzing the production of superoxide from dioxygen or hydrogen peroxide from superoxide.
Immune defense
The immune system uses the lethal effects of oxidants by making production of oxidizing species a central part of its mechanism of killing pathogens; with activated phagocytes producing both ROS and reactive nitrogen species. These include superoxide (•O−
2), nitric oxide (•NO) and their particularly reactive product, peroxynitrite (ONOO-).[72] Although the use of these highly reactive compounds in the cytotoxic response of phagocytes causes damage to host tissues, the non-specificity of these oxidants is an advantage since they will damage almost every part of their target cell.[40] This prevents a pathogen from escaping this part of immune response by mutation of a single molecular target.
See also
- reductive stress
- Acatalasia
- Antioxidant
- Bruce Ames
- Denham Harman
- Malondialdehyde, an oxidative stress marker
- Mitochondrial free radical theory of aging
- Mitohormesis
- Nitric oxide
- Pro-oxidant
- Antioxidative stress
References
- ↑ Chandra Kala; Syed Salman Ali; Abid Mohd; Sweety Rajpoot; Najam Ali Khan (2015). "Protection Against FCA Induced Oxidative Stress Induced DNA Damage as a Model of Arthritis and In vitro Anti-arthritic Potential of Costus speciosus Rhizome Extract". International Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemical Research. 7 (2): 383–389.
- ↑ Parellada M, Moreno C, Mac-Dowell K, Leza JC, Giraldez M, Bailón C, Castro C, Miranda-Azpiazu P, Fraguas D, Arango C (2012). "Plasma antioxidant capacity is reduced in Asperger syndrome.". J Psychiatr Res. 46: 394–401. PMID 22225920. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychires.2011.10.004.
- ↑ Joseph N, Zhang-James Y, Perl A, Faraone SV (2015). "Oxidative Stress and ADHD: A Meta-Analysis.". J Atten Disord. 19: 915–24. PMID 24232168. doi:10.1177/1087054713510354.
- 1 2 Halliwell, Barry (2007). "Oxidative stress and cancer: have we moved forward?" (PDF). Biochem. J. 401 (1): 1–11. PMID 17150040. doi:10.1042/BJ20061131.
- ↑ Hwang O (2013). "Role of Oxidative Stress in Parkinson's Disease". Exp Neurobiol. 22: 11–7. PMC 3620453
 . PMID 23585717. doi:10.5607/en.2013.22.1.11.
. PMID 23585717. doi:10.5607/en.2013.22.1.11. - ↑ Romá-Mateo C, Aguado C, García-Giménez JL, Ibáñez-Cabellos JS, Seco-Cervera M, Pallardó FV, Knecht E, Sanz P (2015). "Increased oxidative stress and impaired antioxidant response in lafora disease.". Mol. Neurobiol. 51: 932–46. PMID 24838580. doi:10.1007/s12035-014-8747-0.
- ↑ Valko, M., Leibfritz, D., Moncol, J., Cronin, MTD., Mazur, M., Telser, J. (August 2007). "Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease". International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology. 39 (1): 44–84. PMID 16978905. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2006.07.001.
- ↑ Bonomini F, Tengattini S, Fabiano A, Bianchi R, Rezzani R (2008). "Atherosclerosis and oxidative stress.". Histol. Histopathol. 23: 381–90. PMID 18072094.
- ↑ Singh, N., Dhalla, A.K., Seneviratne, C., Singal, P.K. (June 1995). "Oxidative stress and heart failure". Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry. 147 (1): 77–81. doi:10.1007/BF00944786.
- ↑ Ramond A, Godin-Ribuot D, Ribuot C, Totoson P, Koritchneva I, Cachot S, Levy P, Joyeux-Faure M (December 2011). "Oxidative stress mediates cardiac infarction aggravation induced by intermittent hypoxia.". Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 27 (3): 252–261. PMID 22145601. doi:10.1111/j.1472-8206.2011.01015.x.
- ↑ Dean OM, van den Buuse M, Berk M, Copolov DL, Mavros C, Bush AI (July 2011). "N-acetyl cysteine restores brain glutathione loss in combined 2-cyclohexene-1-one and D-amphetamine-treated rats: relevance to schizophrenia and bipolar disorder". Neurosci Lett. 499 (3): 149–53. PMID 21621586. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2011.05.027.
- ↑ de Diego-Otero Y, Romero-Zerbo Y, el Bekay R, Decara J, Sanchez L, Rodriguez-de Fonseca F, del Arco-Herrera I (March 2009). "Alpha-tocopherol protects against oxidative stress in the fragile X knockout mouse: an experimental therapeutic approach for the Fmr1 deficiency.". Neuropsychopharmacology. 34 (4): 1011–26. PMID 18843266. doi:10.1038/npp.2008.152.
- ↑ Amer, J., Ghoti, H., Rachmilewitz, E., Koren, A., Levin, C. and Fibach, E. (January 2006). "Red blood cells, platelets and polymorphonuclear neutrophils of patients with sickle cell disease exhibit oxidative stress that can be ameliorated by antioxidants". British Journal of Haematology. 132 (1): 108–113. PMID 16371026. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2141.2005.05834.x.
- ↑ Aly, D. G.; Shahin, R. S. (2010). "Oxidative stress in lichen planus". Acta Dermatovenerologica Alpina, Pannonica et Adriatica. 19 (1): 3–11. PMID 20372767.
- ↑ Arican, O.; Kurutas, EB. (Mar 2008). "Oxidative stress in the blood of patients with active localized vitiligo.". Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Panonica Adriat. 17 (1): 12–6. PMID 18454264.
- ↑ James, SJ.; Cutler, P.; Melnyk, S.; Jernigan, S.; Janak, L.; Gaylor, DW.; Neubrander, JA. (Dec 2004). "Metabolic biomarkers of increased oxidative stress and impaired methylation capacity in children with autism.". Am J Clin Nutr. 80 (6): 1611–7. PMID 15585776.
- ↑ Gwen Kennedy; Vance A. Spence; Margaret McLaren; Alexander Hill; Christine Underwood; Jill J. F. Belch (September 2005). "Oxidative stress levels are raised in chronic fatigue syndrome and are associated with clinical symptoms". Free radical biology & medicine. 39 (5): 584–9. PMID 16085177. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2005.04.020.
- ↑ "J Clin Psychiatry/Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Parameters in Patients With Major Depressive Disorder Compared to Healthy Controls Before and After Antidepressant Treatment: Results From a Meta-Analysis". www.psychiatrist.com. Retrieved 2016-03-02.
- ↑ Segal, AW (2005). "How neutrophils kill microbes". Annu Rev Immunol. 23 (5): 197–223. PMC 2092448
 . PMID 15771570. doi:10.1146/annurev.immunol.23.021704.115653.
. PMID 15771570. doi:10.1146/annurev.immunol.23.021704.115653. - ↑ Gems D, Partridge L (March 2008). "Stress-response hormesis and aging: "that which does not kill us makes us stronger"" (PDF). Cell Metab. 7 (3): 200–3. PMID 18316025. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2008.01.001.
- ↑ Schafer FQ, Buettner GR (2001). "Redox environment of the cell as viewed through the redox state of the glutathione disulfide/glutathione couple". Free Radic. Biol. Med. 30 (11): 1191–212. PMID 11368918. doi:10.1016/S0891-5849(01)00480-4.
- ↑ Lennon SV, Martin SJ, Cotter TG (1991). "Dose-dependent induction of apoptosis in human tumour cell lines by widely diverging stimuli". Cell Prolif. 24 (2): 203–14. PMID 2009322. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2184.1991.tb01150.x.
- ↑ Valko M, Morris H, Cronin MT (May 2005). "Metals, toxicity and oxidative stress". Curr. Med. Chem. 12 (10): 1161–208. PMID 15892631. doi:10.2174/0929867053764635.
- ↑ Evans MD, Cooke MS (May 2004). "Factors contributing to the outcome of oxidative damage to nucleic acids". BioEssays. 26 (5): 533–42. PMID 15112233. doi:10.1002/bies.20027.
- ↑ LC Colis; P Raychaudhury; AK Basu (2008). "Mutational specificity of gamma-radiation-induced guanine-thymine and thymine-guanine intrastrand cross-links in mammalian cells and translesion synthesis past the guanine-thymine lesion by human DNA polymerase eta". Biochemistry. 47 (6): 8070–9. PMC 2646719
 . PMID 18616294. doi:10.1021/bi800529f.
. PMID 18616294. doi:10.1021/bi800529f. - ↑ Lelli JL, Becks LL, Dabrowska MI, Hinshaw DB (1998). "ATP converts necrosis to apoptosis in oxidant-injured endothelial cells". Free Radic. Biol. Med. 25 (6): 694–702. PMID 9801070. doi:10.1016/S0891-5849(98)00107-5.
- ↑ Lee YJ, Shacter E (1999). "Oxidative stress inhibits apoptosis in human lymphoma cells". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (28): 19792–8. PMID 10391922. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.28.19792.
- ↑ Akazawa-Ogawa Y, Shichiri M, Nishio K, Yoshida Y, Niki E, Hagihara Y (2015). "Singlet-oxygen-derived products from linoleate activate Nrf2 signaling in skin cells". Free Radic Biol Med. 79: 164–75. PMID 25499849. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.12.004.
- 1 2 3 Riahi Y, Cohen G, Shamni O, Sasson S (2010). "Signaling and cytotoxic functions of 4-hydroxyalkenals". Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 299 (6): E879–86. PMID 20858748. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00508.2010.
- 1 2 J Oleo Sci. 2015;64(4):347-56. doi:10.5650/jos.ess14281
- ↑ Vigor C, Bertrand-Michel J, Pinot E, Oger C, Vercauteren J, Le Faouder P, Galano JM, Lee JC, Durand T (2014). "Non-enzymatic lipid oxidation products in biological systems: assessment of the metabolites from polyunsaturated fatty acids". J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 964: 65–78. PMID 24856297. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2014.04.042.
- ↑ Atherosclerosis. 2003 Mar;167(1):111-20
- ↑ Free Radic Biol Med. 2015 Feb;79:164-75. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.12.004
- ↑ Kyung-Jin Cho, Ji-Min Seo, Jae-Hong Kim (2011). "Bioactive lipoxygenase metabolites stimulation of NADPH oxidases and reactive oxygen species". Molecules and Cells. 32 (1): 1–5. PMC 3887656
 . PMID 21424583. doi:10.1007/s10059-011-1021-7.
. PMID 21424583. doi:10.1007/s10059-011-1021-7. - ↑ Galano JM, Mas E, Barden A, Mori TA, Signorini C, De Felice C, Barrett A, Opere C, Pinot E, Schwedhelm E, Benndorf R, Roy J, Le Guennec JY, Oger C, Durand T (2013). "Isoprostanes and neuroprostanes: Total synthesis, biological activity and biomarkers of oxidative stress in humans". Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 107: 95–102. doi:10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2013.04.003.
- ↑ Cohen G, Riahi Y, Sunda V, Deplano S, Chatgilialoglu C, Ferreri C, Kaiser N, Sasson S (2013). "Signaling properties of 4-hydroxyalkenals formed by lipid peroxidation in diabetes". Free Radic Biol Med. 65: 978–87. PMID 23973638. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.08.163.
- ↑ N Speed & I A Blair (2011). "Cyclooxygenase- and lipoxygenase-mediated DNA damage". Cancer Metastasis Rev. 30 (3–4): 437–47. PMC 3237763
 . PMID 22009064. doi:10.1007/s10555-011-9298-8.
. PMID 22009064. doi:10.1007/s10555-011-9298-8. - ↑ Sies, H. (1985). "Oxidative stress: introductory remarks". In H. Sies. Oxidative Stress. London: Academic Press. pp. 1–7.
- ↑ Docampo, R. (1995). "Antioxidant mechanisms". In J. Marr; M. Müller. Biochemistry and Molecular Biology of Parasites. London: Academic Press. pp. 147–160.
- 1 2 Rice-Evans CA, Gopinathan V (1995). "Oxygen toxicity, free radicals and antioxidants in human disease: biochemical implications in atherosclerosis and the problems of premature neonates". Essays Biochem. 29: 39–63. PMID 9189713.
- ↑ Seaver LC, Imlay JA (November 2004). "Are respiratory enzymes the primary sources of intracellular hydrogen peroxide?". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (47): 48742–50. PMID 15361522. doi:10.1074/jbc.M408754200.
- ↑ Messner KR, Imlay JA (November 2002). "Mechanism of superoxide and hydrogen peroxide formation by fumarate reductase, succinate dehydrogenase, and aspartate oxidase". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (45): 42563–71. PMID 12200425. doi:10.1074/jbc.M204958200.
- ↑ Imlay JA (2003). "Pathways of oxidative damage". Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 57 (1): 395–418. PMID 14527285. doi:10.1146/annurev.micro.57.030502.090938.
- ↑ Hardin, SC; Larue, CT; Oh, MH; Jain, V; Huber, SC (2009). "Coupling oxidative signals to protein phosphorylation via methionine oxidation in Arabidopsis". Biochem J. 422 (2): 305–312. PMC 2782308
 . PMID 19527223. doi:10.1042/BJ20090764.
. PMID 19527223. doi:10.1042/BJ20090764. - ↑ http://brain.oxfordjournals.org/content/134/7/1914.short
- ↑ Patel VP, Chu CT (2011). "Nuclear transport, oxidative stress, and neurodegeneration.". Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 4 (3): 215–29. PMC 3071655
 . PMID 21487518.
. PMID 21487518. - ↑ Nunomura A, Castellani RJ, Zhu X, Moreira PI, Perry G, Smith MA (2005). "Involvement of oxidative stress in Alzheimer disease.". J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 65 (7): 631–41. PMID 16825950. doi:10.1097/01.jnen.0000228136.58062.bf.
- ↑ Bošković M, Vovk T, Kores Plesničar B, Grabnar I (2011). "Oxidative stress in schizophrenia". Curr Neuropharmacol. 9 (2): 301–12. PMC 3131721
 . PMID 22131939. doi:10.2174/157015911795596595.
. PMID 22131939. doi:10.2174/157015911795596595. - ↑ Ramalingam M, Kim SJ (2012). "Reactive oxygen/nitrogen species and their functional correlations in neurodegenerative diseases". Journal of Neural Transmission. 119 (8): 891–910. PMID 22212484. doi:10.1007/s00702-011-0758-7.
- ↑ Nijs J, Meeus M, De Meirleir K (2006). "Chronic musculoskeletal pain in chronic fatigue syndrome: recent developments and therapeutic implications.". Man Ther. 11 (3): 187–91. PMID 16781183. doi:10.1016/j.math.2006.03.008.
- ↑ Handa O, Naito Y, Yoshikawa T (2011). "Redox biology and gastric carcinogenesis: the role of Helicobacter pylori". Redox Rep. 16 (1): 1–7. PMID 21605492. doi:10.1179/174329211X12968219310756.
- ↑ Meyers DG, Maloley PA, Weeks D (1996). "Safety of antioxidant vitamins". Arch. Intern. Med. 156 (9): 925–35. PMID 8624173. doi:10.1001/archinte.156.9.925.
- ↑ Ruano-Ravina A, Figueiras A, Freire-Garabal M, Barros-Dios JM (2006). "Antioxidant vitamins and risk of lung cancer". Curr. Pharm. Des. 12 (5): 599–613. PMID 16472151. doi:10.2174/138161206775474396.
- ↑ P Zhang, S.T Omaye (2001). "Antioxidant and prooxidant roles for β-carotene, α-tocopherol and ascorbic acid in human lung cells". Toxicol In Vitro. 15 (1): 13–24. PMID 11259865. doi:10.1016/S0887-2333(00)00054-0.
- ↑ Pryor WA (2000). "Vitamin E and heart disease: basic science to clinical intervention trials". Free Radic. Biol. Med. 28 (1): 141–64. PMID 10656300. doi:10.1016/S0891-5849(99)00224-5.
- ↑ Saremi A1, Arora R. (May–Jun 2010). "Vitamin E and cardiovascular disease". Am J Ther. 17 (3): e56–65. PMID 19451807. doi:10.1097/MJT.0b013e31819cdc9a.
- ↑ Boothby LA, Doering PL (2005). "Vitamin C and vitamin E for Alzheimer's disease". Ann Pharmacother. 39 (12): 2073–80. PMID 16227450. doi:10.1345/aph.1E495.
- ↑ Kontush K, Schekatolina S (2004). "Vitamin E in neurodegenerative disorders: Alzheimer's disease". Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1031 (1): 249–62. PMID 15753151. doi:10.1196/annals.1331.025.
- ↑ Fong JJ, Rhoney DH (2006). "NXY-059: review of neuroprotective potential for acute stroke". Ann Pharmacother. 40 (3): 461–71. PMID 16507608. doi:10.1345/aph.1E636.
- ↑ Larsen PL (1993). "Aging and resistance to oxidative damage in Caenorhabditis elegans". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 90 (19): 8905–9. PMC 47469
 . PMID 8415630. doi:10.1073/pnas.90.19.8905.
. PMID 8415630. doi:10.1073/pnas.90.19.8905. - ↑ Helfand SL, Rogina B (2003). "Genetics of aging in the fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster". Annu. Rev. Genet. 37 (1): 329–48. PMID 14616064. doi:10.1146/annurev.genet.37.040103.095211.
- ↑ Schulz, TJ; Zarse, K; Voigt, A; Urban, N; Birringer, M; Ristow, M (Oct 2007). "Glucose restriction extends Caenorhabditis elegans life span by inducing mitochondrial respiration and increasing oxidative stress.". Cell Metabolism. 6 (4): 280–93. PMID 17908557. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2007.08.011.
- ↑ Tapia PC (2006). "Sublethal mitochondrial stress with an attendant stoichiometric augmentation of reactive oxygen species may precipitate many of the beneficial alterations in cellular physiology produced by caloric restriction, intermittent fasting, exercise and dietary phytonutrients: "Mitohormesis" for health and vitality". Med. Hypotheses. 66 (4): 832–43. PMID 16242247. doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2005.09.009.
- ↑ Sohal RS, Mockett RJ, Orr WC (2002). "Mechanisms of aging: an appraisal of the oxidative stress hypothesis". Free Radic. Biol. Med. 33 (5): 575–86. PMID 12208343. doi:10.1016/S0891-5849(02)00886-9.
- ↑ Sohal RS (2002). "Role of oxidative stress and protein oxidation in the aging process". Free Radic. Biol. Med. 33 (1): 37–44. PMID 12086680. doi:10.1016/S0891-5849(02)00856-0.
- ↑ Rattan SI (2006). "Theories of biological aging: genes, proteins, and free radicals". Free Radic. Res. 40 (12): 1230–8. PMID 17090411. doi:10.1080/10715760600911303.
- ↑ Bjelakovic G, Nikolova D, Gluud LL, Simonetti RG, Gluud C (2007). "Mortality in randomized trials of antioxidant supplements for primary and secondary prevention: systematic review and meta-analysis". JAMA. 297 (8): 842–57. PMID 17327526. doi:10.1001/jama.297.8.842.. See also the letter to JAMA by Philip Taylor and Sanford Dawsey and the reply by the authors of the original paper.
- ↑ USDA. "Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity (ORAC) of Selected Foods, Release 2 (2010)". http://www.ars.usda.gov/Services/docs.htm?docid=15866
- ↑
- Pratviel, Genevieve (2012). "Chapter 7. Oxidative DNA Damage Mediated by Transition Metal Ions and Their Complexes". In Astrid Sigel, Helmut Sigel and Roland K. O. Sigel. Interplay between Metal Ions and Nucleic Acids. Metal Ions in Life Sciences. 10. Springer. pp. 201–216. doi:10.1007/978-94-007-2172-2_7.
- ↑ Dalle-Donne, Isabella; Aldini, Giancarlo; Carini, Marina; Colombo, Roberto; Rossi, Ranieri; Milzani, Aldo "Protein carbonylation, cellular dysfunction, and disease progression" Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine 2006, volume 10, pp. 389-406. doi:10.1111/j.1582-4934.2006.tb00407.x. Grimsrud, Paul A.; Xie, Hongwei; Griffin, Timothy J.; Bernlohr, David A. "Oxidative stress and covalent modification of protein with bioactive aldehydes" Journal of Biological Chemistry (2008), volume 283, 21837-21841. doi:10.1074/jbc.R700019200
- ↑ Devasagayam, TPA; Tilac JC; Boloor KK; Sane Ketaki S; Ghaskadbi Saroj S; Lele RD (October 2004). "Free Radicals and Antioxidants in Human Health: Current Status and Future Prospects". Journal of Association of Physicians of India. 52: 796.
- ↑ Nathan C, Shiloh MU (2000). "Reactive oxygen and nitrogen intermediates in the relationship between mammalian hosts and microbial pathogens". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 97 (16): 8841–8. PMC 34021
 . PMID 10922044. doi:10.1073/pnas.97.16.8841.
. PMID 10922044. doi:10.1073/pnas.97.16.8841.