Odisha
| Odisha | ||
|---|---|---|
| State | ||
| ||
 | ||
| Coordinates (Bhubneswar): 20°09′N 85°30′E / 20.15°N 85.50°ECoordinates: 20°09′N 85°30′E / 20.15°N 85.50°E | ||
| Country |
| |
| Statehood |
01 April 1936 (Utkal Dibasa) | |
| Capital | Bhubaneswar | |
| Largest city | Bhubaneswar[1] | |
| Boroughs | 30 | |
| Government | ||
| • Body | Government of Odisha | |
| • Governor | S.C. Jamir | |
| • Chief Minister | Naveen Patnaik (BJD) | |
| • Legislature | Unicameral (147 seats) | |
| • Parliamentary constituency |
21 Lok Sabha; 10 Rajya Sabha[2] | |
| • High Court | Odisha High Court, Cuttack | |
| Area | ||
| • Total | 155,820 km2 (60,160 sq mi) | |
| Area rank | 9th | |
| Population (2011) | ||
| • Total | 41,947,358 | |
| • Rank | 11th | |
| • Density | 270/km2 (700/sq mi) | |
| Demonym(s) | Odia | |
| Time zone | IST (UTC+05:30) | |
| ISO 3166 code | IN-OR | |
| HDI |
| |
| Literacy | 73.45%[3] | |
| Official language | Odia[4] | |
| Website |
www | |
| Language | Odia |
|---|
Odisha ( /əˈdɪsə/[5]) (formerly Orissa)[6][7] (/ɒˈrɪsə, ɔː-, oʊ-/;[8] is one of the 29 states of India, located in the eastern coast. It is surrounded by the states of West Bengal to the north-east, Jharkhand to the north, Chhattisgarh to the west and north-west, and Andhra Pradesh to the south. Odisha has 485 kilometres (301 mi) of coastline along the Bay of Bengal on its east, from Balasore to Malkangiri.[9] It is the 9th largest state by area, and the 11th largest by population. It is also the 3rd most populous state of India in terms of tribal population.[10] Odia (formerly known as Oriya)[11] is the official and most widely spoken language, spoken by 33.2 million according to the 2001 Census.[12]
The ancient kingdom of Kalinga, which was invaded by the Mauryan emperor Ashoka in 261 BCE resulting in the Kalinga War, coincides with the borders of modern-day Odisha.[13] The modern state of Orissa was established on 1 April 1936, as a province in British India, and consisted predominantly of Odia-speaking regions.[13] April 1 is celebrated as Odisha Day.[14] The region is also known as Utkala and is mentioned in India's national anthem, "Jana Gana Mana".[15] Cuttack was made the capital of the region by Anantavarman Chodaganga in c. 1135,[16] after which the city was used as the capital by many rulers, through the British era until 1948. Thereafter, Bhubaneswar became the capital of Odisha.[17]
Etymology
The term "Odisha" is derived from the ancient Prakrit word "Odda Visaya" (also "Udra Bibhasha" or "Odra Bibhasha") as in the Tirumalai inscription of Rajendra Chola I, which is dated to 1025.[18] Sarala Das, who translated the Mahabharata into the Odia language in the 15th century, calls the region Odra Rashtra and Odisha. The inscriptions of Kapilendra Deva of the Gajapati Kingdom (1435–67) on the walls of temples in Puri call the region Odisha or Odisha Rajya.[19]
The name of the state was changed from Orissa to Odisha, and the name of its language from Oriya to Odia, in 2011, by the passage of the Orissa (Alteration of Name) Bill, 2010 and the Constitution (113th Amendment) Bill, 2010 in the Parliament. After a brief debate, the lower house, Lok Sabha, passed the bill and amendment on 9 November 2010.[20] On 24 March 2011, Rajya Sabha, the upper house of Parliament, also passed the bill and the amendment.[21]
History

Prehistoric Acheulian tools dating to Lower Paleolithic era have been discovered in various places in the region, implying an early settlement by humans.[22] Kalinga has been mentioned in ancient texts like Mahabharata, Vayu Purana and Mahagovinda Suttanta.[23][24] The Sabar people of Odisha have also been mentioned in the Mahabharata.[25][26] Baudhayana mentions Kalinga as not yet being influenced by Vedic traditions, implying it followed mostly tribal traditions.[27]
Ashoka of the Mauryan dynasty conquered Kalinga in the bloody Kalinga War in 261 BCE,[28] which was the eighth year of his reign.[29] According to his own edicts, in that war about 100,000 people were killed, 150,000 were captured and several more were affected.[28] The resulting bloodshed and suffering of the war is said to have deeply affected Ashoka. He turned into a pacifist and converted to Buddhism.[29][30]
By c. 150 CE, emperor Kharavela, who was possibly a contemporary of Demetrius I of Bactria,[31] conquered a major part of the Indian sub-continent. Kharavela was a Jain ruler. He also built the monastery atop the Udayagiri hill.[32] Subsequently, the region was ruled by monarchs, such as Samudragupta[33] and Shashanka.[34] It was also a part of Harsha's empire.[35]
Later, the kings of the Somavamsi dynasty began to unite the region. By the reign of Yayati II, c. 1025 CE, they had integrated the region into a single kingdom. Yayati II is supposed to have built the Lingaraj temple at Bhubaneswar.[13] They were replaced by the Eastern Ganga dynasty. Notable rulers of the dynasty were Anantavarman Chodaganga, who began construction on the present-day Jagannath Temple in Puri (c. 1135), and Narasimhadeva I, who constructed the Konark temple (c. 1250).[36][37]
The Eastern Ganga Dynasty was followed by the Gajapati Kingdom. The region resisted integration into the Mughal empire until 1568, when it was conquered by Sultanate of Bengal.[38] Mukunda Deva, who is considered the last independent king of Kalinga, was defeated and was killed in battle by a rebel Ramachandra Bhanja. Ramachandra Bhanja himself was killed by Bayazid Khan Karrani.[39] In 1591, Man Singh I, then governor of Bihar, led an army to take Odisha from the Karranis of Bengal. They agreed to treaty because their leader Qutlu Khan Lohani had recently died. But, they then broke the treaty by attacking the temple town of Puri. Man Singh returned in 1592 and pacified the region.[40]

Orissa was the first subah (imperial top-level province) added to Akbar's fifteen by Shah Jahan. It had Cuttack as seat and bordered Bihar, Bengal and Golconda subahs as well as the remaining independent and tributary chiefs. From 1717, the Orissa and Bijar governos were reduced to deputies of the Nawab (later Nizam) of the pseudo-autonomous Bengal Subah.
In 1751, the Nawab of Bengal Alivardi Khan ceded the region to the Maratha Empire.[13]
The British had occupied the Northern Circars, comprising the southern coast of Odisha, as a result of the 2nd Carnatic War by 1760, and incorporated them into the Madras Presidency gradually.[41] In 1803, the British ousted the Marathas from the Puri-Cuttack region of Odisha during the Second Anglo-Maratha War. The northern and western districts of Odisha were incorporated into the Bengal Presidency.[42]
The Orissa famine of 1866 caused an estimated 1 million deaths.[43] Following this, large-scale irrigation projects were undertaken.[44] In 1903, the Utkal Sammilani organisation was founded to demand the unification of Odia-speaking regions into one state.[45] On 1 April 1912, the Bihar and Orissa Province was formed.[46] On 1 April 1936, Bihar and Orissa were split into separate provinces.[47] The new province of Orissa came into existence on a linguistic basis during the British rule in India, with Sir John Austen Hubback as the first governor.[47][48] Following India's independence, on 15 August 1947, 27 princely states signed the document to join Orissa.[49]
Geography

Odisha lies between the latitudes 17.780N and 22.730N, and between longitudes 81.37E and 87.53E. The state has an area of 155,707 km2, which is 4.87% of total area of India, and a coastline of 450 km.[50] In the eastern part of the state lies the coastal plain. It extends from the Subarnarekha River in the north to the Rushikulya river in the south. The lake Chilika is part of the coastal plains. The plains are rich in fertile silt deposited by the six major rivers flowing into the Bay of Bengal: Subarnarekha, Budhabalanga, Baitarani, Brahmani, Mahanadi and Rushikulya.[50] The Central Rice Research Institute (CRRI), a Food and Agriculture Organization-recognised rice gene bank and research institute, is situated on the banks of Mahanadi in Cuttack.[51]
Three-quarters of the state is covered in mountain ranges. Deep and broad valleys have been made in them by rivers. These valleys have fertile soil and are densely populated. Odisha also has plateaus and rolling uplands, which have lower elevation than the plateaus.[50] The highest point in the state is Deomali at 1672 metres. The other high peaks are: Sinkaram (1620 m), Golikoda (1617 m), and Yendrika (1582 metres).[52]
Climate
The state experiences four meteorological seasons: winter (January to February), pre-monsoon season (March to May), south-west monsoon season (June to September) and north east monsoon season (October–December). However, locally the year is divided into six traditional seasons (or rutus): Basanta (spring), Grishma (summer), Barsha (rainy season), Sharad (autumn), Hemant (winter), and Shishir (cool season).[50]
| Mean Temperature and Precipitation of Selected Weather Stations[53] | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bhubaneswar (1952–2000) |
Balasore (1901–2000) |
Gopalpur (1901–2000) |
Sambalpur (1901–2000) | |||||||||
| Max (C) | Min (C) | Rainfall (mm) | Max (C) | Min (C) | Rainfall (mm) | Max (C) | Min (C) | Rainfall (mm) | Max (C) | Min (C) | Rainfall (mm) | |
| January | 28.5 | 15.5 | 13.1 | 27.0 | 13.9 | 17.0 | 27.2 | 16.9 | 11.0 | 27.6 | 12.6 | 14.2 |
| February | 31.6 | 18.6 | 25.5 | 29.5 | 16.7 | 36.3 | 28.9 | 19.5 | 23.6 | 30.1 | 15.1 | 28.0 |
| March | 35.1 | 22.3 | 25.2 | 33.7 | 21.0 | 39.4 | 30.7 | 22.6 | 18.1 | 35.0 | 19.0 | 20.9 |
| April | 37.2 | 25.1 | 30.8 | 36.0 | 24.4 | 54.8 | 31.2 | 25.0 | 20.3 | 39.3 | 23.5 | 14.2 |
| May | 37.5 | 26.5 | 68.2 | 36.1 | 26.0 | 108.6 | 32.4 | 26.7 | 53.8 | 41.4 | 27.0 | 22.7 |
| June | 35.2 | 26.1 | 204.9 | 34.2 | 26.2 | 233.4 | 32.3 | 26.8 | 138.1 | 36.9 | 26.7 | 218.9 |
| July | 32.0 | 25.2 | 326.2 | 31.8 | 25.8 | 297.9 | 31.0 | 26.1 | 174.6 | 31.1 | 24.9 | 459.0 |
| August | 31.6 | 25.1 | 366.8 | 31.4 | 25.8 | 318.3 | 31.2 | 25.9 | 195.9 | 30.7 | 24.8 | 487.5 |
| September | 31.9 | 24.8 | 256.3 | 31.7 | 25.5 | 275.8 | 31.7 | 25.7 | 192.0 | 31.7 | 24.6 | 243.5 |
| October | 31.7 | 23.0 | 190.7 | 31.3 | 23.0 | 184.0 | 31.4 | 23.8 | 237.8 | 31.7 | 21.8 | 56.6 |
| November | 30.2 | 18.8 | 41.7 | 29.2 | 17.8 | 41.6 | 29.5 | 19.7 | 95.3 | 29.4 | 16.2 | 17.6 |
| December | 28.3 | 15.2 | 4.9 | 26.9 | 13.7 | 6.5 | 27.4 | 16.4 | 11.4 | 27.2 | 12.1 | 4.8 |
Biodiversity




According to a Forest Survey of India report released in 2012, Odisha has 48,903 km2 of forests which cover 31.41% of the state's total area. The forests are classified into: dense forest (7,060 km2), medium dense forest (21,366 km2), open forest (forest without closed canopy; 20,477 km2) and scrub forest (4,734 km2). The state also has bamboo forests (10,518 km2) and mangroves (221 km2). The state is losing its forests to timber smuggling, mining, industrialisation and grazing. There have been attempts at conservation and reforestation.[55]
Due to the climate and good rainfall, Odisha's evergreen and moist forests are suitable habitats for wild orchids. Around 130 species have been reported from the state.[56] 97 of them are found in Mayurbhanj district alone. The Orchid House of Nandakanan Biological Park hosts some of these species.[57]
Simlipal National Park is a protected wildlife area and tiger reserve spread over 2750 km2 of the northern part of Mayurbhanj district. It has 1078 species of plants, including 94 orchids. The sal tree is the primary tree species there. The park has 55 mammals, including barking deer, Bengal tiger, common langur, four-horned antelope, Indian bison, Indian elephant, Indian giant squirrel, Indian leopard, jungle cat, sambar deer, and wild boar. There are 304 species of birds in the park, such as the common hill myna, grey hornbill, Indian pied hornbill and Malabar pied hornbill. It also has 60 species of reptiles, notable among which are the king cobra and tricarinate hill turtle. There is also a mugger crocodile breeding program in nearby Ramtirtha.[58] The Chandaka Elephant Sanctuary is a 190 km2 protected area near the capital city, Bhubaneswar. However, urban expansion and over-grazing have reduced the forests and are driving herds of elephants to migration. In 2002, there were about 80 elephants. But by 2012, their numbers had been reduced to 20. Many of the animals have migrated toward the Barbara reserve forest, Chilika, Nayagarh district, and Athagad. Some elephants have died in conflicts with villagers, while some have died during migration from being electrocuted by power lines or hit by trains. Outside the protected area, they are killed by poachers.[59][60] Besides elephants, the sanctuary also has Indian leopards, jungle cats and chitals.[61]
The Bhitarkanika National Park in Kendrapara District covers 650 km2, of which 150 km2 are mangroves. The Gahiramatha beach in Bhitarkanika is the world's largest nesting site for olive ridley sea turtles.[62] Other major nesting grounds for the turtle in the state are Rushikulya, in Ganjam district,[63] and the mouth of the Devi river.[64] The Bhitarkanika sanctuary is also noted for its large population of salt-water crocodiles.[65] In winter, the sanctuary is also visited by migratory birds. Among the species of birds spotted in the sanctuary are the black-crowned night heron, darter, grey heron, Indian cormorant, Oriental white ibis, purple heron, and sarus crane.[66] The possibly endangered horseshoe crab is also found in this region.[67]
Chilika Lake is a brackish water lagoon on the east coast of Odisha with an area of 1105 km2. It is connected to the Bay of Bengal by a 35-km-long narrow channel and is a part of the Mahanadi delta. In the dry season, the tides bring in salt water. In the rainy season, the rivers falling into the lagoon decrease its salinity.[68] Birds from places like the Caspian Sea, Lake Baikal, other parts of Russia, Central Asia, South-East Asia, Ladakh and the Himalayas migrate to the lagoon in winter.[69] Among the birds spotted there are Eurasian wigeon, pintail, bar-headed goose, greylag goose, flamingo, mallard and Goliath heron.[70][71] The lagoon also has a small population of the endangered Irrawaddy dolphins.[72] The state's coastal region has also had sightings of finless porpoise, bottlenose dolphin, humpback dolphin and spinner dolphin in its waters.[73]
Government and politics

All states in India are governed by a parliamentary system of government based on universal adult franchise.[74] India's parliament is bicameral.[75] The lower house is called the Lok Sabha. Odisha contributes 21 members to Lok Sabha. They are directly elected by the electorates. The upper house is called the Rajya Sabha. Odisha contributes 10 members to Rajya Sabha. They are elected by the state's legislature.[2][76]
The main parties active in the politics of Odisha are the Biju Janata Dal, the Indian National Congress and Bhartiya Janata Party, CPI(M). Following the Odisha State Assembly Election in 2014, the Naveen Patnaik-led Biju Janata Dal stayed in power for the fourth consecutive term.[77]
Legislative assembly
The Odisha state has a unicameral legislature.[75] The Odisha Legislative Assembly consists of 147 elected members,[77] and special office bearers such as the Speaker and Deputy Speaker, who are elected by the members. Assembly meetings are presided over by the Speaker, or by the Deputy Speaker in the Speaker's absence.[78] Executive authority is vested in the Council of Ministers headed by the Chief Minister, although the titular head of government is the Governor of Odisha. The Governor is appointed by the President of India. The leader of the party or coalition with a majority in the Legislative Assembly is appointed as the Chief Minister by the Governor, and the Council of Ministers are appointed by the Governor on the advice of the Chief Minister. The Council of Ministers reports to the Legislative Assembly.[79] The 147 elected representatives are called Members of the Legislative Assembly, or MLAs. One MLA may be nominated from the Anglo-Indian community by the Governor.[80] The term of the office is for 5 years, unless the Assembly is dissolved prior to the completion of the term.[78]
Administrative units
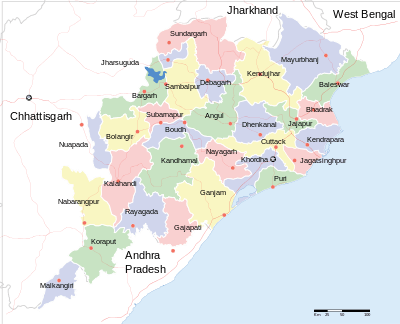
There are 30 districts in Odisha — Angul, Balangir, Balasore, Bargarh, Bhadrak, Boudh, Cuttack, Deogarh, Dhenkanal, Gajapati, Ganjam, Jagatsinghpur, Jajpur, Jharsuguda, Kandhamal, Kalahandi, Kendrapara, Keonjhar, Khordha, Koraput, Malkangiri, Mayurbhanj, Nabarangpur, Nayagarh, Nuapada, Puri, Rayagada, Sambalpur, Subarnapur, Sundargarh.[81]
These 30 districts have been placed under three different revenue divisions to streamline their governance. The divisions are North, South and Central, with their headquarters at Sambalpur, Berhampur and Cuttack respectively. Each division consists of 10 districts, and has as its administrative head a Revenue Divisional Commissioner (RDC).[82] The position of the RDC in the administrative hierarchy is that between that of the district administration and the state secretariat.[83] The RDCs report to the Board of Revenue, which is headed by a senior officer of the Indian Administrative Service.[82]
| North Division | Central Division | South Division |
|---|---|---|
Each district is governed by a District Collector, who is appointed from the Indian Administrative Service.[84][85] The Collector is responsible for collecting the revenue and maintaining law and order in the district. Each district is separated into sub-divisions, each governed by a sub-divisional collectors and sub-divisional magistrates. The sub-divisions are further divided into revenue blocks called tehsils. The tehshils are headed by Tehsildars. Odisha has 58 Sub-Divisions and 317 Tehsils.[82] Blocks consists of Panchayats (village councils) and town municipalities.
The capital and largest city of the state is Bhubaneswar. The other major cities are Berhampur, Cuttack, Rourkela, and Sambalpur. Municipal Corporations in Odisha include Bhubaneswar, Cuttack, Sambalpur, Berhampur and Rourkela.
Other municipalities of Odisha include Angul, Balangir, Balasore, Barbil, Bargarh, Baripada, Belpahar, Bhadrak, Bhawanipatna, Biramitrapur, Boudh, Byasanagar, Chhatrapur, Deogarh, Dhenkanal, Gopalpur, Gunupur, Jagatsinghpur, Jajpur, Jeypore, Jharsuguda, Kendrapara, Kendujhar, Khordha, Konark, Koraput, Malkangiri, Nabarangpur, Nayagarh, Nuapada, Paradeep, Paralakhemundi, Puri, Phulbani, Rajgangpur, Rayagada, Sonepur, Sundargarh and Talcher.
Auxiliary authorities known as panchayats, for which local body elections are regularly held, govern local affairs.
The judiciary is composed of the Odisha High Court, located at Cuttack, and a system of lower courts.
Economy
Macro-economic trend
Odisha is experiencing steady economic growth. The impressive growth in gross domestic product of the state has been reported by the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation. Odisha's growth rate is above the national average.[86] The central Government's Urban Development Ministry has recently announced the names of 20 cities selected to be developed as smart cities. The state capital Bhubaneswar is the first city in the list of smart Cities released in January 2016, a pet project of Prime Minister Narendra Modi. The announcement also marked with sanction of Rs 50,802 crore over the five years for development.[87]
Industrial development
Odisha has abundant natural resources and a large coastline. Odisha has emerged as the most preferred destination for overseas investors with investment proposals.[88] It contains a fifth of India's coal, a quarter of its iron ore, a third of its bauxite reserves and most of the chromite. Rourkela Steel Plant[89] was the first integrated steel plant in the public sector in India, built with collaboration of Germany.
Arcelor-Mittal has also announced plans to invest in another mega steel project amounting to $10 billion. Russian major Magnitogorsk Iron and Steel Company (MMK) plans to set up a 10 MT steel plant in Odisha, too. Bandhabahal is a major area of open cast coal mines in Odisha. The state is attracting an unprecedented amount of investment in aluminium, coal-based power plants, petrochemicals, and information technology as well. In power generation, Reliance Power (Anil Ambani Group) is putting up the world's largest power plant with an investment of US $13 billion at Hirma in Jharsuguda district.[90]
In the year 2009 Odisha was the second top domestic investment destination with Gujarat first and Andhra Pradesh in third place according to an analysis of ASSOCHAM Investment Meter (AIM) study on corporate investments. Odisha's share was 12.6 percent in total investment in the country. It received investment proposal worth ₹. 2,00,846 crore during the last year. Steel and power were among the sectors which attracted maximum investments in the state.[91] Flood and cyclone are the major hurdles in Odisha's development as the important districts are situated near to the Bay of Bengal. In the five-year period between 2004 and 2005 and 2008–09, Odisha's GDP has grown by a stunning 8.74% way beyond the definition of 7% growth. It should be noted that the all-India growth during this period was 8.49%. In this period, Odisha was the fourth fastest growing state, just behind Gujarat, Bihar, Uttarakhand.
Transportation
Odisha has a network of roads, railways, airports and seaports. Bhubaneswar is well connected by air, rail and road with the rest of India. Some highways are getting expanded to four lanes.[92] Plans for metro rail connecting Bhubaneshwar and Cuttack, a journey of 30 km, have also started.[93]
Air
Odisha has a total of 17 airstrips and 16 helipads.[94][95][96] The Government of Odisha have announced to develop an airport at Jharsuguda, making it a full-fledged domestic airport. Five greenfield airports were also to be upgraded at Angul, Dhamra, Kalinganagar, Paradip and Rayagada in an effort to boost intra-State and inter-State civil aviation. Existing aerodromes at Barbil, Gopalpur, Jharsuguda and Rourkela were also to be upgraded.[97] Air Odisha, is Odisha's sole air charter company based in Bhubaneswar.
Seaports
There are many sea ports in the long seacoast of odisha. some of them are:
- Port of Dhamara
- Port of Gopalpur
- Port of Paradip
- Port of Subarnarekha
- Port of Astarang
- Port of Chandipur
Railways

Major cities of Odisha are well connected to all the major cities of India by direct daily trains and weekly trains. Most of the railway network in Odisha lies under the jurisdiction of the East Coast Railway (ECoR) with headquarters at Bhubaneswar and some parts under South Eastern Railway and South East Central Railway.
Demographics
According to the 2011 census of India, the total population of Odisha is 41,947,358, of which 21,201,678 (50.54%) are male and 20,745,680 (49.46%) are female, or 978 females per 1000 males. This represents a 13.97% increase over the population in 2001. The population density is 269 per km2.
The dominant ethnic group is the Odia people, and Odia is the official language; it is spoken as a native language by 81.8% of the population.[98] Linguistic minorities in the state are Bengali, Hindi, Urdu, Telugu, Ho, Santali. Some of the important tribes are Ho, Santhal, Bonda, Munda, Oraon, Kandha, Mahali and Kora.
The literacy rate is 73%, with 82% of males and 64% of females being literate, according to the 2011 census.
The proportion of people living below the poverty line in 1999–2000 was 47.15% which is nearly double the Indian average of 26.10%.
Data of 1996–2001 showed the life expectancy in the state was 61.64 years, higher than the national value of years. The state has a birth rate of 23.2 per 1,000 people per year, a death rate of 9.1 per 1,000 people per year, an infant mortality rate of 65 per 1000 live birth and a maternal mortality rate of 358 per 1,000,000 live births. Odisha has a Human Development Index of 0.442 as of 2011.
| District | Headquarters | Population (2011) | Males | Females | Percentage decadal growth 2001–2011 | Sex ratio | Density (persons per km2) | Child population 0–6 years | Child sex ratio | Literacy rate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Angul | Angul | 1,271,703 | 654,898 | 616,805 | 11.55 | 942 | 199 | 145,690 | 884 | 78.96 |
| 2 | Balangir | Balangir | 1,648,574 | 831,349 | 817,225 | 23.29 | 983 | 251 | 206,964 | 951 | 65.50 |
| 3 | Balasore | Baleswar | 2,317,419 | 1,184,371 | 1,133,048 | 14.47 | 957 | 609 | 274,432 | 941 | 80.66 |
| 4 | Bargarh | Bargarh | 1,478,833 | 748,332 | 730,501 | 9.84 | 976 | 253 | 156,185 | 946 | 75.16 |
| 5 | Bhadrak | Bhadrak | 1,506,522 | 760,591 | 745,931 | 12.95 | 981 | 601 | 176,793 | 931 | 83.25 |
| 6 | Boudh | Boudh | 439,917 | 220,993 | 218,924 | 17.82 | 991 | 142 | 59,094 | 975 | 72.51 |
| 7 | Cuttack | Cuttack | 2,618,708 | 1,339,153 | 1,279,555 | 11.87 | 955 | 666 | 251,152 | 913 | 84.20 |
| 8 | Debagarh | Debagarh | 312,164 | 158,017 | 154,147 | 13.88 | 976 | 106 | 38,621 | 917 | 73.07 |
| 9 | Dhenkanal | Dhenkanal | 1,192,948 | 612,597 | 580,351 | 11.82 | 947 | 268 | 132,647 | 870 | 79.41 |
| 10 | Gajapati | Paralakhemundi | 575,880 | 282,041 | 293,839 | 10.99 | 1,042 | 133 | 82,777 | 964 | 54.29 |
| 11 | Ganjam | Chhatrapur | 3,520,151 | 1,777,324 | 1,742,827 | 11.37 | 981 | 429 | 397,920 | 899 | 71.88 |
| 12 | Jagatsinghpur | Jagatsinghpur | 1,136,604 | 577,699 | 558,905 | 7.44 | 967 | 681 | 103,517 | 929 | 87.13 |
| 13 | Jajpur | Jajpur | 1,826,275 | 926,058 | 900,217 | 12.43 | 972 | 630 | 207,310 | 921 | 80.44 |
| 14 | Jharsuguda | Jharsuguda | 579,499 | 297,014 | 282,485 | 12.56 | 951 | 274 | 61,823 | 938 | 78.36 |
| 15 | Kalahandi | Bhawanipatna | 1,573,054 | 785,179 | 787,875 | 17.79 | 1,003 | 199 | 214,111 | 947 | 60.22 |
| 16 | Kandhamal | Phulbani | 731,952 | 359,401 | 372,551 | 12.92 | 1,037 | 91 | 106,379 | 960 | 65.12 |
| 17 | Kendrapara | Kendrapara | 1,439,891 | 717,695 | 722,196 | 10.59 | 1,006 | 545 | 153,443 | 921 | 85.93 |
| 18 | Kendujhar | Kendujhar | 1,802,777 | 907,135 | 895,642 | 15.42 | 987 | 217 | 253,418 | 957 | 69.00 |
| 19 | Khordha | Khordha | 2,246,341 | 1,166,949 | 1,079,392 | 19.65 | 925 | 799 | 222,275 | 910 | 87.51 |
| 20 | Koraput | Koraput | 1,376,934 | 677,864 | 699,070 | 16.63 | 1,031 | 156 | 215,518 | 970 | 49.87 |
| 21 | Malkangiri | Malkangiri | 612,727 | 303,913 | 308,814 | 21.53 | 1,016 | 106 | 105,636 | 979 | 49.49 |
| 22 | Mayurbhanj | Baripada | 2,513,895 | 1,253,633 | 1,260,262 | 13.06 | 1,005 | 241 | 337,757 | 952 | 63.98 |
| 23 | Nabarangapur | Nabarangpur | 1,218,762 | 604,046 | 614,716 | 18.81 | 1,018 | 230 | 201,901 | 988 | 48.20 |
| 24 | Nayagarh | Nayagarh | 962,215 | 502,194 | 460,021 | 11.30 | 916 | 247 | 101,337 | 851 | 79.17 |
| 25 | Nuapada | Nuapada | 606,490 | 300,307 | 306,183 | 14.28 | 1,020 | 157 | 84,893 | 971 | 58.20 |
| 26 | Puri | Puri | 1,697,983 | 865,209 | 832,774 | 13.00 | 963 | 488 | 164,388 | 924 | 85.37 |
| 27 | Rayagada | Rayagada | 961,959 | 469,672 | 492,287 | 15.74 | 1,048 | 136 | 141,167 | 955 | 50.88 |
| 28 | Sambalpur | Sambalpur | 1,044,410 | 529,424 | 514,986 | 12.24 | 973 | 158 | 112,946 | 931 | 76.91 |
| 29 | Subarnapur | Sonepur | 652,107 | 332,897 | 319,210 | 20.35 | 959 | 279 | 76,536 | 947 | 74.42 |
| 30 | Sundergarh | Sundergarh | 2,080,664 | 1,055,723 | 1,024,941 | 13.66 | 971 | 214 | 249,020 | 937 | 74.13 |
Religion
The majority (over 94%[100]) of people in the state of Odisha are Hindu and there is also a rich cultural heritage in the state. For example, Odisha is home to several Hindu figures. Sant Bhima Bhoi was a leader of the Mahima sect movement. Sarala Das, a Hindu Khandayat, was the translator of the epic Mahabharata in Odia. Chaitanya Das was a Buddhistic-Vaishnava and writer of the Nirguna Mahatmya. Jayadeva was the author of the Gita Govinda.
The Odisha Temple Authorisation Act of 1948 empowered the Government of Odisha to have Hindu temples open for all Hindus including the Harijans.[101]
Perhaps the oldest scripture of Odisha is the Madala Panji from the Puri Temple believed from 1042 AD. Famous Hindu Odia scripture includes the 16th-century Bhagabata of Jagannatha Dasa.[102] In the modern times Madhusudan Rao was a major Odia writer, who was a Brahmo Samajist and shaped modern Odia literature at the start of the 20th century.[103]
Christians in Odisha account for about 2.8% of the population while Odia Muslims account for 2.2% as per census figures of 2001. The Sikh, Buddhist and Jain communities together account for 0.1% of the population[100] Large sections of the indigenous tribes follow Sarnaism, their indigenous natural religion.
Education
- Educational Institutions
- National Institute of Science Education and Research (NISER) at Bhubaneswar
- All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) at Bhubaneswar
- Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) at Bhubaneswar
- National Institute of Technology Rourkela (NIT) at Rourkela
- Indian Institute of Management (IIM-SB) at Sambalpur
- Indian Institutes of Science Education and Research (IISER) at Brahmapur
- Veer Surendra Sai University of Technology (VSSUT) at Burla
- National Law University at Cuttack
- International Institute of Information Technology (IIIT) at Bhubaneswar
- Berhampur University at Brahmapur
- Biju Patnaik University of Technology at Rourkela
- Buxi Jagabandhu Bidyadhar College at Bhubaneswar
- Central University of Orissa at Koraput
- College of Agriculture, Bhawanipatna
- College of Engineering and Technology at Bhubaneswar
- Dharanidhar College at Keonjhar
- Fakir Mohan University at Balasore
- Gangadhar Meher University at Sambalpur
- Government College of Engineering, Kalahandi at Bhawanipatna
- Hi-Tech Medical College & Hospital, Bhubaneswar at Bhubaneswar
- Indira Gandhi Institute of Technology at Sarang
- KIIT University at Bhubaneswar
- Khallikote University at Brahmapur
- Maharaja Krishna Chandra Gajapati Medical College and Hospital at Brahmapur
- National Institute of Science and Technology at Brahmapur
- North Orissa University at Baripada
- Odisha State Open University at Sambalpur
- Orissa University of Agriculture and Technology at Bhubaneswar
- Parala Maharaja Engineering College at Brahmapur
- Rama Devi Women's University at Bhubaneswar
- Ravenshaw University at Cuttack
- Sambalpur University at Sambalpur
- Sardar Raja's Medical College, Hospital and Research Center at Bhawanipatna
- Shri Ramachandra Bhanj Medical College at Cuttack
- Siksha O Anusandhan University at Bhubaneswar
- Utkal University at Bhubaneswar
- Utkal University of Culture at Bhubaneswar
- Veer Surendra Sai Medical College at Burla
- Xavier Institute of Management, Bhubaneswar
- Xavier University, Bhubaneswar
- Institute of Mathematics and Applications, Bhubaneswar
- Sri Sri University at Cuttack
- Centurion University at Jatni, Bhubaneswar
- National Institute of Rehabilitation Training and Research at Cuttack
Entry to various institutes of higher education especially into engineering degrees is through a centralised Odisha Joint Entrance Examination, conducted by the Biju Patnaik University of Technology (BPUT), Rourkela, since 2003, where seats are provided according to order of merit.[104] Few of the engineering institutes enroll students by through Joint Entrance Examination. For medical courses, there is a corresponding All India Pre Medical Test.
Kalinga Prize
The people of Odisha have been very appreciative of science and technology. The Kalinga Prize has been instituted by them under the visionary leadership of Biju Patnaik since 1952.[105] Kalinga Foundation Trust is currently responsible for this award. The award is given under is UNESCO for popularising of science and technology among common people. It is observed that approximately 25 people who got the Kalinga Prize later won the Nobel Prize.
Culture
Cuisine
Odisha has a culinary tradition spanning centuries. The kitchen of the Jagannath Temple, Puri is reputed to be the largest in the world, with 1,000 chefs, working around 752 wood-burning clay hearths called chulas, to feed over 10,000 people each day.[106][107]
The syrupy dessert Pahala rasgulla made in Odisha is known throughout the world.[108] Chhenapoda is another major Odisha sweet cuisine, which originated in Nayagarh.[109]
Dance


Odissi (Orissi) dance and music are classical art forms. Odissi is the oldest surviving dance form in India on the basis of archaeological evidence.[110] Odissi has a long, unbroken tradition of 2,000 years, and finds mention in the Natyashastra of Bharatamuni, possibly written c. 200 BC. However, the dance form nearly became extinct during the British period, only to be revived after India's independence by a few gurus.
The variety of dances includes Ghumura Dance, Chhau dance, Mahari dance, and Gotipua.
Tourism

The Lingaraja Temple at Bhubaneswar has a 150-foot (46 m) high deula while the Jagannath Temple, Puri is about 200 feet (61 m) high and dominates the skyline. Only a portion of the Konark Sun Temple, the largest of the temples of the "Holy Golden Triangle" exists today, and it is still staggering in size. It stands out as a masterpiece in Odisha architecture. Sarala Temple, regarded as one of the most spiritually elevated expressions of Shaktism is in Jagatsinghpur district. It is also one of the holiest places in Odisha & a major tourist attraction. Maa tarini temple situated in Kendujhar district is also a famous pilgrimage destination. Every day thousands of coconuts are given to Maa Tarini by devotees for fulfilling their wishes.[111]
Odisha's varying topography – from the wooded Eastern Ghats to the fertile river basin – has proven ideal for evolution of compact and unique ecosystems. This creates treasure troves of flora and fauna that are inviting to many migratory species of birds and reptiles. Bhitarkanika National Park is famous for its second largest mangrove ecosystem. The bird sanctuary in Chilika Lake (Asia's largest brackish water lake) and the tiger reserve and waterfalls in Simlipal National Park are integral parts eco-tourism in Odisha, arranged by Odisha Tourism.[112] Daringbadi, known as "Kashmir of Odisha," is a hill station in the Kandhamal district of Odisha. Chandipur, a calm and serene site, is mostly unexplored by tourists. The unique specialty of this beach is the ebb tides that recede up to 4km and tend to disappear rhythmically.
The share of foreign tourists’ arrival in the State is below one percent of total foreign tourist arrivals at all India level.[113]
See also
- Bibliography of India
- Cinema of Odisha
- Culture of Odisha
- Index of India-related articles
- List of Odia writers
- Odia literature
- Odisha Government Schemes List
- Odissi music
- Outline of India
- Western Odisha
-
 India – Wikipedia book
India – Wikipedia book
References
- ↑ "Cities having population 1 lakh and above, Census 2011" (PDF). Government of India. Retrieved 2 February 2015.
- 1 2 "Our Parliament" (PDF). Lok Sabha. Government of India. Retrieved 2 February 2015.
- ↑ "State of Literacy" (PDF). Census of India. p. 110. Retrieved 5 August 2015.
- ↑ "Report of the Commissioner for linguistic minorities: 47th report (July 2008 to June 2010)" (PDF). Commissioner for Linguistic Minorities, Ministry of Minority Affairs, Government of India. pp. 122–126. Retrieved 16 February 2012.
- ↑ "Odisha (əˈdɪsə)". Collins English Dictionary.
- ↑ "Orissa celebrates Odisha". The Times of India. 5 November 2011. Retrieved 18 November 2011.
- ↑ "Mixed views emerge as Orissa becomes Odisha". India Today. 6 November 2011. Retrieved 10 November 2011.
- ↑ Jones, Daniel (2003) [1917], Peter Roach, James Hartmann and Jane Setter, eds., English Pronouncing Dictionary, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, ISBN 3-12-539683-2
- ↑ "Coastal security". Odisha Police. Retrieved 1 February 2015.
- ↑ http://www.stscodisha.gov.in/Aboutus.asp?GL=abt&PL=1
- ↑ "Orissa's new name is Odisha". The Times of India. 24 March 2011.
- ↑ "Indiaspeak: English is our 2nd language". The Times of India. 14 March 2010. Retrieved 3 February 2015.
- 1 2 3 4 "Detail History of Orissa". Government of Odisha. Archived from the original on 12 November 2006.
- ↑ "Utkala Dibasa hails colours, flavours of Odisha". The Times of India. 2 April 2014. Retrieved 1 February 2015.
- ↑ "The National Anthem of India" (PDF). Columbia University. Retrieved 1 February 2015.
- ↑ Rabindra Nath Chakraborty (1985). National Integration in Historical Perspective: A Cultural Regeneration in Eastern India. Mittal Publications. pp. 17–. GGKEY:CNFHULBK119. Retrieved 30 November 2012.
- ↑ Ravi Kalia (1994). Bhubaneswar: From a Temple Town to a Capital City. SIU Press. p. 23. ISBN 978-0-8093-1876-6. Retrieved 2 February 2015.
- ↑ Patel, C.B (April 2010). Origin and Evolution of the Name ODISA (PDF). Bhubaneswar: I&PR Department, Government of Odisha. pp. 28, 29, 30. Retrieved 19 June 2015.
- ↑ Pritish Acharya (11 March 2008). National Movement and Politics in Orissa, 1920–1929. SAGE Publications. p. 19. ISBN 978-81-321-0001-0. Retrieved 3 February 2015.
- ↑ "Amid clash, House passes Bills to rename Orissa, its language". The Hindu. 9 November 2010. Retrieved 2 February 2015.
- ↑ "Parliament passes bill to change Orissa's name". NDTV. 24 March 2011. Retrieved 2 February 2015.
- ↑ Amalananda Ghosh (1990). An Encyclopaedia of Indian Archaeology. BRILL. p. 24. Retrieved 29 October 2012.
- ↑ Subodh Kapoor, ed. (2004). An Introduction to Epic Philosophy: Epic Period, History, Literature, Pantheon, Philosophy, Traditions, and Mythology, Volume 3. Genesis Publishing. p. 784. Retrieved 10 November 2012.
Finally Srutayudha, a valiant hero, was son Varuna and of the river Parnasa.
- ↑ Devendrakumar Rajaram Patil (1946). Cultural History from the Vāyu Purāna. Motilal Banarsidass Pub. p. 46.
- ↑ "Dance bow (1965.3.5)". Pitt Rivers Museum.
- ↑ Rabindra Nath Pati (1 January 2008). Family Planning. APH Publishing. p. 97. ISBN 978-81-313-0352-8. Retrieved 2 February 2015.
- ↑ Suhas Chatterjee (1 January 1998). Indian Civilization And Culture. M.D. Publications Pvt. Ltd. p. 68. ISBN 978-81-7533-083-2. Retrieved 11 February 2013.
- 1 2 Hermann Kulke; Dietmar Rothermund (2004). A History of India. Routledge. p. 66. Retrieved 12 November 2012.
- 1 2 Mookerji Radhakumud (1995). Asoka. Motilal Banarsidass Publishe. p. 214. ISBN 978-81-208-0582-8. Retrieved 6 August 2015.
- ↑ Sailendra Nath Sen (1 January 1999). Ancient Indian History and Civilization. New Age International. p. 153. ISBN 978-81-224-1198-0. Retrieved 6 August 2015.
- ↑ Austin Patrick Olivelle Alma Cowden Madden Centennial Professor in Liberal Arts University of Texas (19 June 2006). Between the Empires : Society in India 300 BCE to 400 CE: Society in India 300 BCE to 400 CE. Oxford University Press. p. 78. ISBN 978-0-19-977507-1. Retrieved 3 February 2015.
- ↑ Reddy (1 December 2006). Indian Hist (Opt). Tata McGraw-Hill Education. p. A254. ISBN 978-0-07-063577-7. Retrieved 3 February 2015.
- ↑ Indian History. Allied Publishers. p. 74. ISBN 978-81-8424-568-4. Retrieved 3 February 2015.
- ↑ Ronald M. Davidson (13 August 2013). Indian Esoteric Buddhism: A Social History of the Tantric Movement. Columbia University Press. p. 60. ISBN 978-0-231-50102-6. Retrieved 3 February 2015.
- ↑ R. C. Majumdar (1996). Outline of the History of Kalinga. Asian Educational Services. p. 28. ISBN 978-81-206-1194-8. Retrieved 3 February 2015.
- ↑ Roshen Dalal (18 April 2014). The Religions of India: A Concise Guide to Nine Major Faiths. Penguin Books Limited. p. 559. ISBN 978-81-8475-396-7. Retrieved 3 February 2015.
- ↑ Indian History. Tata McGraw-Hill Education. p. 2. ISBN 978-0-07-132923-1. Retrieved 3 May 2013.
- ↑ Sen, Sailendra (2013). A Textbook of Medieval Indian History. Primus Books. pp. 121–122. ISBN 978-93-80607-34-4.
- ↑ Orissa General Knowledge. Bright Publications. p. 27. ISBN 978-81-7199-574-5. Retrieved 3 February 2015.
- ↑ L.S.S. O'Malley (1 January 2007). Bengal District Gazetteer : Puri. Concept Publishing Company. p. 33. ISBN 978-81-7268-138-8. Retrieved 3 February 2015.
- ↑ Sailendra Nath Sen (2010). An Advanced History of Modern India. Macmillan India. p. 32. ISBN 978-0-230-32885-3. Retrieved 3 February 2015.
- ↑ Devi, Bandita (January 1992). Some Aspects of British Administration in Orissa, 1912–1936. Academic Foundation. p. 14. ISBN 978-81-7188-072-0.
- ↑ William A. Dando (13 February 2012). Food and Famine in the 21st Century [2 volumes]. ABC-CLIO. p. 47. ISBN 978-1-59884-731-4. Retrieved 3 February 2015.
- ↑ J. K. Samal; Pradip Kumar Nayak (1 January 1996). Makers of Modern Orissa: Contributions of Some Leading Personalities of Orissa in the 2nd Half of the 19th Century. Abhinav Publications. p. 32. ISBN 978-81-7017-322-9. Retrieved 3 February 2015.
- ↑ K.S. Padhy (30 July 2011). Indian Political Thought. PHI Learning Pvt. Ltd. p. 287. ISBN 978-81-203-4305-4. Retrieved 3 February 2015.
- ↑ Usha Jha (1 January 2003). Land, Labour, and Power: Agrarian Crisis and the State in Bihar (1937–52). Aakar Books. p. 246. ISBN 978-81-87879-07-7. Retrieved 3 February 2015.
- 1 2 Bandita Devi (1 January 1992). Some Aspects of British Administration in Orissa, 1912–1936. Academic Foundation. p. 214. ISBN 978-81-7188-072-0. Retrieved 3 February 2015.
- ↑ "Hubback's memoirs: First Governor Of State Reserved Tone Of Mild Contempt For Indians". The Telegraph (India). 29 November 2010. Retrieved 3 February 2015.
- ↑ B. Krishna (2007). India's Bismarck, Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel. Indus Source. pp. 243–244. ISBN 978-81-88569-14-4. Retrieved 3 February 2015.
- 1 2 3 4 "Geography of Odisha". Know India. Government of India. Retrieved 3 February 2015.
- ↑ "Cuttack". Government of Odisha. Archived from the original on 6 December 2012. Retrieved 6 August 2015.
- ↑ Socio-economic Profile of Rural India (series II).: Eastern India (Orissa, Jharkhand, West Bengal, Bihar and Uttar Pradesh). Concept Publishing Company. 2011. p. 73. ISBN 978-81-8069-723-4. Retrieved 4 February 2015.
- ↑ "Monthly mean maximum & minimum temperature and total rainfall based upon 1901–2000 data" (PDF). India Meteorological Department. Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 April 2015. Retrieved 6 February 2015.
- ↑ P.K. Dash; Santilata Sahoo; Subhasisa Bal (2008). "Ethnobotanical Studies on Orchids of Niyamgiri Hill Ranges, Orissa, India". Ethnobotanical Leaflets (12): 70–78.
- ↑ "Study shows Odisha forest cover shrinking". The Times of India. 16 February 2012. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
- ↑ Underutilized and Underexploited Horticultural Crops. New India Publishing. 1 January 2007. p. 116. ISBN 978-81-89422-60-8. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
- ↑ "Orchid House a haven for nature lovers". The Telegraph (India). 23 August 2010. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
- ↑ "Similipal Tiger Reserve". World Wide Fund for Nature, India. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
- ↑ "Banished from their homes". The Pioneer (newspaper). 29 August 2012. Archived from the original on 4 September 2012. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
- ↑ "Away from home, Chandaka elephants face a wipeout". The New Indian Express. 23 August 2013.
- ↑ Sharad Singh Negi (1 January 1993). Biodiversity and Its Conservation in India. Indus Publishing. p. 242. ISBN 978-81-85182-88-9. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
- ↑ Venkatesh Salagrama (2006). Trends in Poverty and Livelihoods in Coastal Fishing Communities of Orissa State, India. Food & Agriculture Org. pp. 16–17. ISBN 978-92-5-105566-3. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
- ↑ "Olive Ridley turtles begin mass nesting". The Hindu. 12 February 2014. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
- ↑ "Mass nesting of Olive Ridleys begins at Rushikulya beach". The Hindu. 15 March 2004. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
- ↑ "Bhitarkanika Park to be Closed for Crocodile Census". The New Indian Express. 3 December 2013. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
- ↑ "Bird Count Rises in Bhitarkanika". The New Indian Express. 14 September 2014. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
- ↑ "Concern over dwindling horseshoe crab population". The Hindu. 8 December 2013. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
- ↑ Pushpendra K. Agarwal; Vijay P. Singh (16 May 2007). Hydrology and Water Resources of India. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 984. ISBN 978-1-4020-5180-7. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
- ↑ "Number of birds visiting Chilika falls but new species found". The Hindu. 9 January 2013. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
- ↑ "Chilika registers sharp drop in winged visitors". The Hindu. 13 January 2014. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
- ↑ "Two new species of migratory birds sighted in Chilika Lake". The Hindu. 8 January 2013. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
- ↑ "Dolphin population on rise in Chilika Lake". The Hindu. 18 February 2010. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
- ↑ "Maiden Dolphin Census in State's Multiple Places on Cards". The New Indian Express. 20 January 2015. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
- ↑ Chandan Sengupta; Stuart Corbridge (28 October 2013). Democracy, Development and Decentralisation in India: Continuing Debates. Routledge. p. 8. ISBN 978-1-136-19848-9. Retrieved 15 February 2015.
- 1 2 Ada W. Finifter. Political Science. FK Publications. p. 94. ISBN 978-81-89597-13-9. Retrieved 15 February 2015.
- ↑ "Frequently Asked Questions About Rajya Sabha". Rajya Sabha. Retrieved 14 February 2015.
- 1 2 "BJD's landslide victory in Odisha, wins 20 of 21 Lok Sabha seats". IBNLive. 17 May 2014. Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- 1 2 Rajesh Kumar. Universal's Guide to the Constitution of India. Universal Law Publishing. pp. 107–110. ISBN 978-93-5035-011-9. Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- ↑ Ramesh Kumar Arora; Rajni Goyal (1995). Indian Public Administration: Institutions and Issues. New Age International. pp. 205–207. ISBN 978-81-7328-068-9. Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- ↑ Subhash Shukla (2008). Issues in Indian Polity. Anamika Pub. & distributors. p. 99. ISBN 978-81-7975-217-3. Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- 1 2 "Administrative Unit". Revenue & Disaster Management Department, Government of Odisha. Archived from the original on 21 August 2013. Retrieved 27 March 2015.
- 1 2 3 "About Department". Revenue & Disaster Management Department, Government of Odisha. Archived from the original on 6 December 2012. Retrieved 27 March 2015.
- ↑ Laxmikanth. Governance In India. McGraw-Hill Education (India) Pvt Limited. pp. 6–17. ISBN 978-0-07-107466-7. Retrieved 27 March 2015.
- ↑ Siuli Sarkar (9 November 2009). Public Administration in India. PHI Learning Pvt. Ltd. p. 117. ISBN 978-81-203-3979-8. Retrieved 11 August 2015.
- ↑ Public Administration Dictionary. Tata McGraw Hill Education. 2012. p. 263. ISBN 978-1-259-00382-0. Retrieved 11 August 2015.
- ↑ "GDP growth: Most states grew faster than national rate in 2012–13". The Financial Express. 2013-12-12. Retrieved 2012-05-23.
- ↑ "Bhubaneswar leads Govt's Smart City list, Rs 50,802 crore to be invested over five years". The Indian Express. 2016-01-29. Retrieved 2016-03-21.
- ↑ "Indian states that attracted highest FDI". Rediff. 2012-08-29. Retrieved 2014-04-08.
- ↑ "Rourkela Steel Plant". Sail.co.in. Archived from the original on 31 May 2012. Retrieved 2012-05-23.
- ↑ "Reliance to invest Rs 60,000-cr for Orissa power plant". dna.
- ↑ "Gujarat, Odisha and Andhra top 3 Domestic Investment Destinations of 2009". Assocham. 21 January 2010. Archived from the original on 9 December 2010. Retrieved 2010-07-18.
- ↑ "NH 42". Odishalinks.com. 16 June 2004. Archived from the original on 9 December 2010. Retrieved 2010-07-18.
- ↑ "Odisha plans metro, signs contract for detailed project report preparation". The Times of India.
- ↑ "Ten-year roadmap for State's civil aviation". dailypioneer.com. 2012. Retrieved 5 August 2012.
at present there are 17 airstrips and 16 helipads in Odisha,
- ↑ "10-year roadmap set up to boost Odisha civil aviation". odishanow.in. 2012. Retrieved 5 August 2012.
Odisha has 17 airstrips and 16 helipads.
- ↑ "Odisha initiate steps for intra and inter state aviation facilities". news.webindia123.com. 2012. Retrieved 5 August 2012.
Odisha has 17 airstrips and 16 helipads
- ↑ "Odisha plans five new airports". The Hindu Business Line. 14 August 2012. Retrieved 14 May 2013.
- ↑ Mahapatra, B. P. (2002). Linguistic Survey of India: Orissa (PDF). Kolkata, India: Language Division, Office of the Registrar General. p. 14. Retrieved 20 February 2014.
- ↑ "Population by religion community - 2011". Census of India, 2011. The Registrar General & Census Commissioner, India. Archived from the original on 25 August 2015.
- 1 2 "Census of India – Socio-cultural aspects". Government of India, Ministry of Home Affairs. Retrieved 2011-03-02.
- ↑ P. 63 Case studies on human rights and fundamental freedoms: a world survey, Volume 4 By Willem Adriaan Veenhoven
- ↑ P. 77 Encyclopedia Americana, Volume 30 By Scholastic Library Publishing
- ↑ Madhusudan Rao By Jatindra Mohan Mohanty, Sahitya Akademi
- ↑ "Biju Patnaik University of Technology". Bput.org. Retrieved 2010-07-18.
- ↑ "Welcome to Kalinga Foundation Trust".
- ↑ National Association on Indian Affairs; American Association on Indian Affairs (1949). Indian Affairs. Retrieved 23 June 2012.
- ↑ S.P. Sharma; Seema Gupta (3 October 2006). Fairs & Festivals of India. Pustak Mahal. pp. 103–. ISBN 978-81-223-0951-5. Retrieved 23 June 2012.
- ↑ Mitra Bishwabijoy (6 July 2015). "Who invented the rasgulla?". Times of India. Retrieved 2 August 2015.
- ↑ "Chhenapoda". Simply TADKA. Retrieved 9 January 2015.
- ↑ "Odissi Kala Kendra". odissi.itgo.com. Archived from the original on 9 December 2010. Retrieved 2010-07-18.
- ↑ Norenzayan, Ara (25 August 2013). Big Gods: How Religion Transformed Cooperation and Conflict. Princeton University Press. pp. 55–56. ISBN 978-1-4008-4832-4. Retrieved 24 December 2015.
- ↑ "MTN 82:9–10 Olive ridley tagged in Odisha recovered in the coastal waters of eastern Sri Lanka". Seaturtle.org. Archived from the original on 9 December 2010. Retrieved 2010-07-18.
- ↑ http://www.odisha.gov.in/pc/Download/Economic_Survey_2014-15.pdf
External links
- Government
- General information
- Odisha Encyclopædia Britannica entry
- Odisha at DMOZ
-
 Geographic data related to Odisha at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to Odisha at OpenStreetMap
| Adjacent places of Odisha | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
Chhattisgarh | Jharkhand | West Bengal |  |
| Chhattisgarh | |
Bay of Bengal | ||
| ||||
| | ||||
| Chhattisgarh | Andhra Pradesh | Andhra Pradesh & Bay of Bengal | ||









