East African Campaign (World War II)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The East African Campaign (also known as the Abyssinian Campaign) was fought in East Africa during World War II by Allied forces, mainly from the British Empire, against Axis forces, primarily from Italy of Africa Orientale Italiana (AOI, Italian East Africa), between June 1940 and November 1941. Forces of the British Middle East Command, including units from the United Kingdom and the colonies of British East Africa, British Somaliland, British West Africa, the Indian Empire, Northern Rhodesia, Nyasaland, Mandatory Palestine, South Africa, Southern Rhodesia and Sudan participated in the campaign. Ethiopian irregulars, the Free French and Belgian troops of the Force Publique also participated.
The AOI was defended by Italian forces of the Comando Forze Armate dell'Africa Orientale Italiana (Italian East African Armed Forces Command), with units from the Regio Esercito (Italian army), Regia Aeronautica (air force) and Regia Marina (navy), about 200,000 Regio Corpo Truppe Coloniali from Italian-occupied Abyssinia (Ethiopia), Italian Eritrea and Italian Somaliland, led by Italian officers and NCOs, 70,000 Italian regulars and reservists and the small Compagnia Autocarrata Tedesca (German Motorized Company).
Hostilities began on 13 June 1940, with an Italian air raid on the base of 1 Squadron Southern Rhodesian Air Force (237 (Rhodesia) Squadron RAF) at Wajir in the East Africa Protectorate (Kenya) and continued until Italian forces had been pushed back from Kenya and Sudan, through Somaliland Eritrea and Ethiopia in 1940 and early-1941. The remnants of the Italian forces in the AOI surrendered after the Battle of Gondar in November 1941, except for groups that fought the Italian guerrilla war in Ethiopia against the British until the Armistice of Cassibile (3 September 1943) ended hostilities between Italy and the Allies. The East African Campaign was the first Allied strategic victory in the war but was overshadowed by the British defeats in Greece and Crete.
Background
Africa Orientale Italiana
On 9 May 1936, Italian dictator Benito Mussolini proclaimed Africa Orientale Italiana (AOI), formed from Ethiopia after the Second Italo-Abyssinian War with the colonies of Italian Eritrea and Italian Somaliland.[1] On 10 June 1940, Mussolini declared war on Britain and France, which made Italian military forces in Libya a threat to Egypt and those in the AOI a danger to the British and French colonies in East Africa. Italian belligerence also closed the Mediterranean to Allied merchant ships and endangered British supply routes along the coast of East Africa, the Gulf of Aden, the Red Sea and the Suez Canal. (The Kingdom of Egypt remained neutral during World War II but the Anglo-Egyptian Treaty of 1936 allowed the British to occupy Egypt and Anglo-Egyptian Sudan.)[2] Egypt, the Suez Canal, French Somaliland and British Somaliland were also vulnerable to invasion but Comando Supremo (Italian General Staff) had planned for a war after 1942. In the summer of 1940 Italy was far from ready for a long war or for the occupation of large areas of Africa.[3]
Comando Forze Armate dell'Africa Orientale
Regio Esercito

Amedeo, Duke of Aosta, was appointed Viceroy and Governor-General of the AOI in November 1937, with a headquarters in Addis Ababa, the Ethiopian capital. On 1 June 1940, as the commander in chief of Comando Forze Armate dell'Africa Orientale Italiana (Italian East African Armed Forces Command) and Generale d'Armata Aerea (General of the Air Force), Aosta had about 290,476 local and metropolitan troops (including naval and air force personnel). By 1 August, mobilisation had increased the number to 371,053 troops.[4] On 10 June, the Italian army was organised in four commands:
- Northern Sector, vicinity of Asmara
- Eritrea, Lieutenant-General Luigi Frusci
- Southern Sector, around Jimma
- Ethiopia, General Pietro Gazzera
- Eastern Sector, General Guglielmo Nasi (borders of French and British Somaliland)
- Giuba Sector, Lieutenant-General Carlo De Simone, southern Somalia near Kismayo, Italian Somaliland
.svg.png)
Aosta had two metropolitan divisions, the 40th Infantry Division Cacciatori d'Africa and the 65th Infantry Division Granatieri di Savoia, a battalion of Alpini (elite mountain troops), a Bersaglieri battalion of motorised infantry, several Milizia Volontaria per la Sicurezza Nazionale (MSVN Camicie Nere [Blackshirt]) battalions and smaller units. About 70 percent of Italian troops were locally recruited Askari. The regular Eritrean battalions and the Regio Corpo Truppe Coloniali (RCTC Royal Corps of Somali Colonial Troops) were among the best Italian units in the AOI and included Eritrean cavalry Penne di Falco (Falcon Feathers).[5] (On one occasion a squadron of horse charged British and Commonwealth troops, throwing small hand grenades from the saddle.) Most colonial troops were recruited, trained and equipped for colonial repression, although the Somali Dubats from the borderlands were useful light infantry and skirmishers. Irregular bandes were hardy and mobile, knew the country and were effective scouts and saboteurs, although sometimes confused with Shifta, undisciplined marauders who plundered and murdered at will.[6]
Italian forces in East Africa were equipped with about 3,313 heavy machine-guns, 5,313 machine-guns, 24 M11/39 medium tanks, 39 L3/35 tankettes, 126 armoured cars and 824 guns, twenty-four 20 mm anti-aircraft guns, seventy-one 81 mm mortars and 672,800 rifles.[7] Due to the isolation of the AOI from the Mediterranean, the Italians had very little opportunity for reinforcements or supply, leading to severe shortages, especially of ammunition.[8] On occasion, foreign merchant vessels captured by German merchant raiders in the Indian Ocean were brought to Somali ports but their cargoes were not always of much use to the Italian war effort. (For example, the Yugoslav steamer Durmitor, captured by the German auxiliary cruiser Atlantis, came to Warsheikh on 22 November 1940, with a cargo of salt and several hundred prisoners.)[9]
Regia Aeronautica

The Comando Aeronautica Africa Orientale Italiana (CAAOI) of the Regia Aeronautica (General Pietro Pinna) based in Addis Ababa, had three sector commands corresponding to the land fronts,
- Comando Settore Aeronautico Nord (Air Sector Headquarters North)
- Comando Settore Aeronautico Ouest (Air Sector Headquarters West)
- Comando Settore Aeronautico Sud (Air Sector Headquarters South)
In June 1940, there were 323 aircraft in the AOI, in 23 bomber squadrons with 138 aircraft, comprising 14 squadrons with six aircraft each, six Caproni Ca.133 light bomber squadrons, seven Savoia-Marchetti SM.81 squadrons and two squadrons of Savoia-Marchetti SM.79s. Four fighter squadrons had 36 aircraft, comprising two nine-aircraft Fiat CR.32 squadrons and two nine-aircraft Fiat CR.42 squadrons; CAAOI had one reconnaissance squadron with nine IMAM Ro.37 aircraft. There were 183 first line aircraft and another 140 in reserve, of which 59 were operational and 81 were unserviceable.[10][lower-alpha 1]
On the outbreak of war, the CAAOI had 10,700 t (10,500 long tons) of aviation fuel, 5,300 t (5,200 long tons) of bombs and 8,620,000 rounds of ammunition. Aircraft and engine maintenance was conducted at the main air bases and at the Caproni and Piaggio workshops, which could repair about fifteen seriously-damaged aircraft and engines each month, along with some moderately and lightly damaged aircraft and could also recycle scarce materials.[10] The Italians had reserves for 75% of their front-line strength but lacked spare parts and many aircraft were cannibalised to keep others operational.[12] The quality of the units varied. The SM.79 was the only modern bomber and the CR.32 fighter was obsolete but the Regia Aeronautica in East Africa had a cadre of highly experienced Spanish Civil War veterans.[13] There was the nucleus of a transport fleet, with nine Savoia-Marchetti S.73, nine Ca.133, six Ca.148 (a lengthened version of the Ca.133) and a Fokker F.VII, which maintained internal communications and carried urgent items and personnel between sectors.[10]
Regia Marina

The Regia Marina (Italian Royal Navy) maintained the Red Sea Flotilla at Massawa in Eritrea on the Red Sea. The port was a link between Axis-occupied Europe and the naval facilities in the Italian concession zone in Tientsin in China.[14] There were also limited port facilities at Assab, in Eritrea and at Mogadishu in Italian Somaliland. The flotilla had seven fleet destroyers, Leone-class destroyers Pantera, Leone and Tigre in the 5th Destroyer Division and the Sauro-class destroyers Cesare Battisti, Francesco Nullo, Nazario Sauro and Daniele Manin in the 3rd Destroyer Division. The flotilla also had two local defence destroyers, the Orsini and Acerbi, a squadron of five Motoscafo Armato Silurante (MAS, motor torpedo boats) and eight submarines (Archimede, Ferraris, Galilei, Torricelli, Galvani, Guglielmotto, Macalle and Perla).[15] When the Mediterranean route was closed to Allied merchant ships in April 1940, Allied convoys had to sail via the Cape and up the east coast of Africa, past the Italian naval bases to Suez. As Italian fuel supplies in Massawa dwindled, opportunities for the Red Sea Flotilla to attack Allied shipping declined.[16]
Mediterranean and Middle East Theatre

The British had based forces in Egypt since 1882 but these were greatly reduced by the terms of the Anglo-Egyptian treaty of 1936. A small British and Commonwealth force garrisoned the Suez Canal and the Red Sea route, which was vital to British communications with its Indian Ocean and Far Eastern territories. In mid-1939, General Archibald Wavell was appointed General Officer Commanding-in-Chief (GOC-in-C) of the new Middle East Command, over the Mediterranean and Middle East theatres. Wavell was responsible for the defence of Egypt through the General Officer Commanding-in-Chief, British Troops Egypt, to train the Egyptian army and co-ordinate military operations with the Commander-in-Chief Mediterranean, Admiral Andrew Cunningham, the Commander-in-Chief East Indies Station, Vice-Admiral Ralph Leatham, the Commander-in-Chief India, General Robert Cassels, the Inspector General, African Colonial Forces, Major-General Douglas Dickinson and the Air Officer Commanding-in-Chief Middle East, Air Chief Marshal William Mitchell.[17][lower-alpha 2] (French divisions in Tunisia faced the Italian 5th Army on the western Libyan border, until the Franco-Axis Armistice of 22 June 1940.) In Libya, the Regio Esercito Italiana (Royal Italian Army) had about 215,000 men and in Egypt, the British had about 36,000 troops, with another 27,500 men training in Palestine.[19] Wavell had about 86,000 troops at his disposal for Libya, Iraq, Syria, Iran and East Africa.[20]
Middle East Command
The command was established before the war to control land operations and co-ordinate with the naval and air commands in the Mediterranean and Middle East, although Wavell was only allowed five staff officers for plans and command of an area of 3,500,000 square miles (9,100,000 km2).[21] From 1940–1941, operations took place in the Western Desert of Egypt, East Africa, Greece and the Middle East. In July 1939, Wavell devised a strategy to defend and then dominate the Mediterranean as a base to attack Germany, through eastern and south-east Europe. The conquest of Italian East Africa came second only to the defence of Egypt and the Suez Canal and in August Wavell ordered plans to be made quickly to gain control of the Red Sea. Wavell specified a concept of offensive operations from Djibouti to Harar and then Addis Ababa or Kassala to Asmara then Massawa, preferably on both lines simultaneously. Wavell reconnoitred East Africa in January 1940 and the theatre was formally added to his responsibilities; he expected that the Somalilands could be defended with minor reinforcement. If Italy joined the war Ethiopia would be invaded as soon as there were sufficient troops; Wavell also co-ordinated plans with South Africa in March. On 1 May 1940, Wavell ordered British Troops Egypt to discreetly mobilise for military operations in western Egypt but after the June débâcle in France, Wavell had no option but to follow a defensive strategy.[22]
After Italian operations in Sudan at Kassala and Gallabat in June, Churchill blamed Wavell for a "static policy". Anthony Eden, the Secretary of State for War communicated to Wavell, that an Italian advance towards Khartoum should be destroyed. Wavell replied that the Italian attacks were not serious but went to Sudan and Kenya to see for himself and met the Ethiopian Emperor Haile Selassie at Khartoum.[23] Eden convened a conference in Khartoum at the end of October 1940, with Selassie, the South African General Jan Smuts (advisor to Winston Churchill), Wavell and Lieutenant-General William Platt and Lieutenant-General Alan Cunningham. A plan to attack Ethiopia, including Ethiopian irregular forces was agreed.[20] In November 1940, the British gained an intelligence advantage when the Government Code and Cypher School (GC & CS) at Bletchley Park broke the high grade cypher of the Italian army in East Africa. Later that month, the replacement cypher for the Regia Aeronautica was broken by the Combined Bureau, Middle East (CBME).[24]
In September 1940, Wavell ordered the commanders in Sudan and Kenya to make limited attacks once the rainy season ended. On the northern front Lieutenant-General William Platt was to attack Gallabat and vicinity and on the southern front Lieutenant-General Alan Cunningham was to advance northwards from Kenya, through Italian Somaliland into Ethiopia.[lower-alpha 3] While Platt advanced from the north and Cunningham from the south; Wavell planned for a third force to be landed in British Somaliland by amphibious assault and then re-take the colony prior to advancing into Ethiopia. The three forces were to rendezvous at Addis Ababa. The conquest of the AOI would remove the land threat to supplies and reinforcements coming from Australia, New Zealand India, South Africa and British East Africa via the Suez Canal for the campaign in North Africa and would re-open the land route from Cape Town to Cairo.[25]
East Africa Force
.png)
In 1940, the East Africa Force (Major-General D. P. Dickinson) was established for North East Africa, East Africa and British Central Africa. In Sudan about 8,500 troops and 80 aircraft guarded a 1,200 mi (1,900 km) frontier with the AOI.[26] Platt had 21 companies (4,500 men) of the Sudan Defence Force (SDF), of which five (later six) were organised as motor machine-gun companies. There was no artillery but the Sudan Horse was converting to a 3.7-inch mountain howitzer battery. The 1st Battalion Worcestershire Regiment, 1st Battalion Essex Regiment and the 2nd Battalion West Yorkshire Regiment, which in mid-September were incorporated into the 29th Indian Infantry Brigade, 10th Indian Infantry Brigade and 9th Indian Infantry Brigade respectively of the 5th Indian Infantry Division (Major-General Lewis Heath) when it arrived.[27] The 4th Indian Infantry Division (Major-General Noel Beresford-Peirse) was transferred from Egypt in December.[28] The British had an assortment of armoured cars and B Squadron 4th Royal Tank Regiment (4th RTR) with Matilda infantry tanks joined the 4th Indian Division in January 1941.[29] On the outbreak of hostilities, Lieutenant-Colonel Arthur Reginald Chater in British Somaliland had about 1,754 troops comprising the Somaliland Camel Corps (SCC) and a battalion of the 1st Battalion Northern Rhodesia Regiment. By August, the 1/2nd Punjab and 3/5th Punjab regiments had been transferred from Aden and 2nd Battalion KAR with the 1st East African Light Battery (3.7-inch howitzers) came from Kenya, raising the total to 4,000 troops, in the first week of August. In the Aden Protectorate, British Forces Aden (Air Vice-Marshal G. R. M. Reid) had a garrison of the two Indian infantry battalions until they were transferred to British Somaliland in August.[30]
Ethiopia

In August 1939, Wavell had ordered a plan covertly to encourage the rebellion in the western Ethiopian province of Gojjam, that the Italians had never been able to repress. In September, Colonel D. A. Sandford arrived to run the project but until the Italian declaration of war, the conspiracy was held back by the policy of appeasement.[lower-alpha 4] Mission 101 was formed to co-ordinate the activities of the Ethiopian resistance. In June 1940, Selassie arrived in Egypt and in July, went to Sudan to meet Platt and discuss plans to re-capture Ethiopia, despite Platt's reservations.[32] In July, the British recognised Selassie as emperor and in August, Mission 101 entered Gojjam province to reconnoitre. Sandford requested that supply routes be established before the rains ended, to the area north of Lake Tana and that Selassie should return in October, as a catalyst for the uprising. Gaining control of Gojjam required the Italian garrisons to be isolated along the main road from Bahrdar Giorgis south of Lake Tana, to Dangila, Debra Markos and Addis Ababa to prevent them concentrating against the Arbegnoch. Italian reinforcements arrived in October and patrolled more frequently, just as dissensions among local potentates were reconciled by Sandford's diplomacy.[33]
The Frontier Battalion of the Sudan Defence Force, set up in May 1940, was joined at Khartoum by the 2nd Ethiopian and 4th Eritrean battalions, raised from émigré volunteers in Kenya. Operational Centres consisting of an officer, five NCOs and several picked Ethiopians were formed and trained in guerilla warfare to provide leadership cadres and £1 million was set aside to finance operations. Major Orde Wingate was sent to Khartoum with an assistant to join the HQ of the SDF. On 20 November, Wingate was flown to Sakhala to meet Sandford; the RAF managed to bomb Dangila, drop propaganda leaflets and supply Mission 101, which raised Ethiopian morale, having suffered much from Italian air power since the Second Italo-Abyssinian War. Mission 101 managed to persuade the Arbegnogh north of Lake Tana to spring several ambushes on the Metemma–Gondar road and the Italian garrison at Wolkait was withdrawn in February 1941.[34]
Northern front, 1940
British Somaliland 1940

On 3 August 1940, the Italians invaded with two colonial brigades, four cavalry squadrons, 24 M11/39 medium tanks and L3/35 tankettes, several armoured cars, 21 howitzer batteries, pack artillery and air support.[35][36] The British had a garrison of two companies of the Sudan Defence Force, two motor machine-gun companies and a mounted infantry company. Kassala was bombed and then attacked, the British retiring slowly.[36] On 4 August, the Italians advanced with a western column towards Zeila, a central column (Lieutenant-General Carlo De Simone) towards Hargeisa and an eastern column towards Odweina in the south. The SCC skirmished with the advancing Italians as the main British force slowly retired. On 5 August, the towns of Zeila and Hargeisa were captured, cutting off the British from French Somaliland. Odweina fell the following day and the Italian central and eastern columns joined. On 11 August, Major-General Alfred Reade Godwin-Austen was diverted to Berbera, en route to Kenya to take command as reinforcements increased the British garrison to five battalions.[37] (From 5–19 August, RAF squadrons at Aden flew 184 sorties and dropped 60 long tons (61 t) of bombs, lost seven aircraft destroyed and ten damaged.)[38]
Battle of Tug Argan
On 11 August, the Italians began an attack at Tug Argan (tug, a dry sandy river-bed), where the road from Hargeisa crosses the Assa range and by 14 August, the British risked defeat in detail by the larger Italian force and its greater quantity of artillery. Close to being cut off and with only one battalion left in reserve, Godwin-Austen contacted Henry Maitland Wilson the General Officer Commanding-in-Chief the British Troops in Egypt in Cairo (Wavell was in London) and next day, received permission to withdraw from the colony. The 2nd battalion Black Watch, supported by two companies of the 2nd King's African Rifles and parties of the 1st/2nd Punjab Regiment covered the retreat of the British contingent to Berbera. By 2:00 p.m. on 18 August, most of the contingent had been evacuated to Aden but HMAS Hobart and the HQ stayed behind until morning before sailing and the Italians entered Berbera on the evening of 19 August.[39] In the final four days, the RAF flew twelve reconnaissance and 19 reconnaissance-bombing sorties, with 72 attacks on Italian transport and troop columns; 36 fighter sorties were flown over Berbera.[38] British casualties were 38 killed and 222 wounded; the Italians had 2,052 casualties and consumed irreplaceable resources.[40] (Churchill criticised Wavell for abandoning the colony without enough fighting but Wavell called it a textbook withdrawal in the face of superior numbers.)[41]
Anglo-Egyptian Sudan

Anglo-Egyptian Sudan shared a 1,000 mi (1,600 km) border with the AOI and on 4 July 1940, was invaded by an Italian force of about 6,500 men from Eritrea, which advanced on a railway junction at Kassala and forced the British garrison of 320 men of the SDF and some local police to retire after inflicting casualties of 43 killed and 114 wounded for ten casualties of their own.[42][43] The Italians also drove a platoon of No 3 Company, Eastern Arab Corps (EAC) of the SDF, from the small fort at Gallabat, just over the border from Metemma, about 200 mi (320 km) south of Kassala and took the villages of Qaysān, Kurmuk and Dumbode on the Blue Nile. From there the Italians ventured no further into Sudan, owing to a lack of fuel. They proceeded to fortify Kassala with anti-tank defences, machine-gun posts and strongpoints, later establishing a brigade-strong garrison. The Italians were disappointed to find no strong anti-British sentiment among the native population.[44][45] The 5th Indian Division began to arrive in Sudan in early September 1940. The 29th Indian Infantry Brigade were placed on the Red Sea coast to protect Port Sudan, the 9th Indian Infantry Brigade was based south-west of Kassala and the 10th Indian Infantry Brigade (William Slim) were sent to Gedaref, with the divisional headquarters, to block an Italian attack on Khartoum from Goz Regeb to Gallabat, on a front of 200 mi (320 km). Gazelle Force (Colonel Frank Messervy) was formed on 16 October, as a mobile unit to raid Italian territory and delay an Italian advance.[46][47][lower-alpha 5]
Gallabat fort lay in Sudan and Metemma a short way across the Ethiopian border, beyond the Boundary Khor, a dry river bed with steep banks covered by long grass. Both places were surrounded by field fortifications and Gallabat was held by a colonial infantry battalion. Metemma had two colonial battalions and a banda formation, all under the command of Lieutenant-Colonel Castagnuola. The 10th Indian Infantry Brigade, a field artillery regiment, B Squadron, 4th RTR with six Infantry - and six light tanks, attacked Gallabat on 6 November at 5:30 a.m. An RAF contingent of six Wellesley bombers and nine Gladiator fighters, were thought sufficient to overcome the 17 Italian fighters and 32 bombers believed to be in range.[48] The infantry assembled 1–2 mi (1.6–3.2 km) from Gallabat, whose garrison was unaware that an attack was coming, until the RAF bombed the fort and put the wireless out of action. The field artillery began a simultaneous bombardment; after an hour the gunners changed targets and bombarded Metemma. The previous night, the 4th/ 10th Baluch Regiment occupied a hill overlooking the fort as a flank guard. The troops on the hill covered the advance at 6:40 a.m. of the 3rd Royal Garwhal Rifles followed by the tanks. The Indians reached Gallabat and fought hand-to-hand with Granatieri di Savoia and some Eritrean troops in the fort. At 8:00 a.m. the 25th and 77th Colonial battalions counter-attacked and were repulsed but three British tanks were knocked out by mines and six by mechanical failure caused by the rocky ground.[49]
The defenders at Boundary Khor were dug in behind fields of barbed wire and Castagnuola had contacted Gondar for air support. Italian bombers and fighters attacked all day, shot down seven Gladiators for a loss of five Fiat CR-42s and destroyed the lorry carrying spare parts for the tanks. The ground was so hard and rocky that there were no trenches and when Italian bombers made their biggest attack, the infantry had no cover. An ammunition lorry was set on fire by burning grass and the sound was taken to be an Italian counter-attack from behind. When a platoon advanced towards the sound with fixed bayonets, some troops thought that they were retreating.[50] Part of the 1st Battalion, Essex Regiment at the fort broke and ran, taking some of the Gahrwalis with them. Many of the British fugitives mounted their transport and drove off, spreading the panic and some of the runaways reached Doka before being stopped.[49][lower-alpha 6] The Italian bombers returned next morning and Slim ordered a withdrawal from Gallabat Ridge 3 mi (4.8 km) west to less exposed ground that evening. Sappers from the 21st Field Company remained behind to demolish the remaining buildings and stores in the fort. The artillery bombarded Gallabat and Metemma and set off Italian ammunition dumps full of pyrotechnics. British casualties since 6 November were 42 men killed and 125 wounded.[51] The brigade patrolled to deny the fort to the Italians and on 9 November, two Baluch companies attacked and held the fort during the day and retired in the evening. During the night an Italian counter-attack was repulsed by artillery-fire and next morning the British re-occupied the fort unopposed. Ambushes were laid and prevented Italian reinforcements from occupying the fort or the hills on the flanks, despite frequent bombing by the Regia Aeronautica.[50]
Southern front, 1940
British East Africa (Kenya)
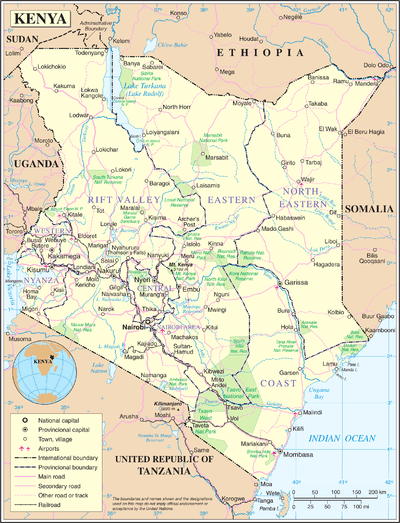
On the Italian declaration of war on 10 June 1940, Dickinson had a force of two East African brigades of the King's African Rifles (KAR) organised as a Northern Brigade and a Southern Brigade comprising a reconnaissance regiment, a light artillery battery and the 22nd Mountain Battery Royal Indian Artillery (RIA). By March 1940, the KAR strength had reached 883 officers, 1,374 non-commissioned officers and 20,026 African other ranks.[52][lower-alpha 7] Wavell ordered Dickinson to defend Kenya and to pin down as many Italian troops as possible. Dickinson planned to defend Mombasa with the 1st East African Infantry Brigade and to deny a crossing of the Tana River and the fresh water at Wajir, with the 2nd East African Infantry Brigade. Detachments were to be placed at Marsabit, Moyale and at Turkana near Lake Rudolf (now Lake Turkana), an arc of 850 mi (1,370 km). The Italians were thought to have troops at Kismayu, Mogadishu, Dolo, Moyale and Yavello, which turned out to be colonial troops and bande, with two brigades at Jimma, ready to reinforce Moyale or attack Lake Rudolf and then invade Uganda.[53] By the end of July, the 3rd East African Infantry Brigade and the 6th East African Infantry Brigade had been formed. A Coastal Division and a Northern Frontier District Division had been planned but then the 11th (African) Division and the 12th (African) Division were created instead.[52]
On 1 June, the first South African unit arrived in Mombasa, Kenya and by the end of July, the 1st South African Infantry Brigade Group had arrived. On 13 August, the 1st South African Division was formed and by the end of 1940, about 27,000 South Africans were in East Africa, in the 1st South African Division, the 11th (African) Division and the 12th (African) Division. Each South African brigade group consisted of three rifle battalions, an armoured car company and signal, engineer and medical units.[54] By July, under the terms of a war contingency plan, the 2nd (West Africa) Infantry Brigade, from the Gold Coast (Ghana) and the 1st (West Africa) Infantry Brigade from Nigeria, were provided for service in Kenya by the Royal West African Frontier Force (RWAFF). The 1st (West African) Brigade, the two KAR brigades and some South African units, formed the 11th (African) Division. The 12th (African) Division had a similar formation with the 2nd (West African) Brigade.[52]
At dawn on 17 June, the Rhodesians supported a raid by the SDF on the Italian desert outpost of El Wak in Italian Somaliland about 90 mi (140 km) north-east of Wajir. The Rhodesians bombed and burnt down thatched mud huts and generally harassed the enemy troops. Since the main fighting at that time was against Italian advances towards Moyale in Kenya, the Rhodesians concentrated there. On 1 July, an Italian attack on the border town of Moyale, on the edge of the Ethiopian escarpment, where the tracks towards Wajir and Marsabit meet, was repulsed by a company of the 1st KAR and reinforcements were moved up. The Italians carried out a larger attack by about four battalions on 10 July, after a considerable artillery bombardment and after three days the British withdrew unopposed. The Italians eventually advanced to water holes at Dabel and Buna, nearly 62 miles (100 km) inside Kenya but lack of supplies prevented a further advance.[55][44]
Italian strategy, December 1940
After the conquest of British Somaliland the Italians adopted a more defensive posture. In late 1940, Italian forces suffered defeats in the Mediterranean, the Western Desert, the Battle of Britain and in the Greco-Italian War. This prompted General Ugo Cavallero, the new Italian Chief of the General Staff in Rome, to adopt a new strategy in East Africa. In December 1940, Cavallero thought that Italian forces in East Africa should abandon offensive actions against the Sudan and the Suez Canal and concentrate on the defence of the AOI.[56] In response to Cavallero and Aosta, who had requested permission to withdraw from the Sudanese frontier, Comando Supremo ordered Italian forces in East Africa to withdraw to better defensive positions.[57] Frusci was ordered to withdraw from Kassala and Metemma in the lowlands along the Sudan–Eritrea border and hold the more easily defended mountain passes on the Kassala–Agordat and Metemma–Gondar roads. Frusci chose not to withdraw from the lowlands, because withdrawal would involve too great a loss of prestige and because Kassala was an important railway junction; holding it prevented the British from using the railway to carry supplies from Port Sudan on the Red Sea coast to the base at Gedaref.[56] Information on the Italian withdrawal was quickly decrypted by the British and Platt was able to begin his offensive into Eritrea on 18 January 1941, three weeks ahead of schedule.[24]
War in the air

In Sudan, the Royal Air Force (RAF) Air Headquarters Sudan (Headquarters 203 Group from 17 August, Air Headquarters East Africa from 19 October), subordinate to the Air Officer Commanding-in-Chief (AOC-in-C) Middle East, had 14 Squadron, 47 Squadron and 223 Squadron (Vickers Wellesley bombers).[58] A flight of Vickers Vincent biplanes from 47 Squadron performed Army Co-operation duties and were later reinforced from Egypt by 45 squadron (Bristol Blenheims). Six Gladiator biplane fighters were based in Port Sudan for trade protection and anti-submarine patrols over the Red Sea, the air defence of Port Sudan, Atbara and Khartoum and army support. In May, 1 (Fighter) Squadron South African Air Force (SAAF) arrived, was transferred to Egypt to convert to Gladiators and returned to Khartoum in August.[59] The SAAF in Kenya had 12 Squadron SAAF (Junkers Ju 86 bombers), 11 Squadron SAAF (Fairey Battle bombers), 40 Squadron SAAF (Hawker Hartebees), 2 Squadron SAAF (Hawker Fury fighters) and 237 (Rhodesia) Squadron (Hawker Hardy general-purpose aircraft). Better aircraft became available later but the first aircraft were old and slow, the South Africans even pressing an old Vickers Valencia biplane into service as a bomber.[60]
The South Africans faced experienced Italian pilots, including a cadre of Spanish Civil War veterans. Despite its lack of experience, 1 SAAF claimed 48 enemy aircraft destroyed and 57 damaged in the skies over East Africa. A further 57 were claimed destroyed on the ground; all for the loss of six pilots—it is thought the unit was guilty of severe over-claiming.[61] From November 1940 to early January 1941, Platt continued to apply constant pressure on the Italians along the Sudan–Ethiopia border with patrols and raids by ground troops and aircraft. Hawker Hurricanes and more Gloster Gladiators began to replace some of the older models. On 6 December, a large concentration of Italian motor transport was bombed and strafed by Commonwealth aircraft a few miles north of Kassala. The same aircraft then proceeded to machine-gun from low level the nearby positions of the Italian Blackshirts and colonial infantry. A few days later, the same aircraft bombed the Italian base at Keru, fifty miles east of Kassala. The Commonwealth pilots had the satisfaction of seeing supply dumps, stores and transport enveloped in flame and smoke as they flew away. One morning in mid-December, a force of Italian fighters strafed a Rhodesian landing-strip at Wajir near Kassala, where two Hawker Hardys were caught on the ground and destroyed and 5,000 US gal (19,000 l) of fuel were set alight, four Africans were killed and eleven injured fighting the fire.[62][63]
War at sea, 1940

The approaches to the Red Sea through the Gulf of Aden, the 15 nmi (17 mi; 28 km) wide Strait of Bab-el-Mandeb (Gate of Tears) and the 1,200 nmi (1,400 mi; 2,200 km) passage to Suez, became the main sea route to the Middle East when hostilities began with Italy. South of Suez the British held Port Sudan on the west coast of the Red Sea (about halfway down) and Aden, 100 nmi (120 mi; 190 km) east of Bab-el-Mandeb. About 350 nmi (400 mi; 650 km) north of the Strait, on the west side of the Red Sea, was an Italian naval base of Massawa (Rear-Admiral Mario Bonetti), well-placed for attacks by submarines and destroyers on convoys. The Red Sea was closed to merchant ships on 24 May, until convoys could be organised. The anti-aircraft cruiser HMS Carlisle, three sloops and a destroyer division of HMS Khartoum, HMS Kimberley, HMS Kingston and HMS Kandahar were sent through the Suez Canal to the Red Sea Force (Senior Naval Officer Red Sea, Rear-Admiral Murray, based at Aden) that had been established in April by Vice-Admiral R. Leatham, the Commander-in-Chief East Indies Station.[64]
On 15 June, the submarine Macalle ran aground and was captured.[65] Next day, the submarine Galileo Galilei sank a Norwegian tanker, the James Stove about 12 mi (19 km) south of Aden.[66] On 18 June, Galileo Galilei captured the Yugoslav steamship Dravo and then released it; next day off Aden, Galileo Galilei engaged the armed trawler HMS Moonstone and the commander was killed; the submarine was captured and used by the British as HMS X2.[67] On 23 June, in the Gulf of Aden off French Somaliland the Brin class submarine Evangelista Torricelli was sunk by Kandahar, Kingston and the sloop HMS Shoreham. Several hours afterwards, Khartoum suffered an internal explosion following a fire and sank in shallow water off Perim Island. On 23 June, the submarine Luigi Galvani sank the sloop HMIS Pathan in the Indian Ocean and then on 23 June, Luigi Galvani was sunk by the sloop HMS Falmouth in the Gulf of Oman.[68]
On 13 August, Galileo Ferraris made a failed attempt to intercept the battleship HMS Royal Sovereign in the Red Sea, en route from Suez to Aden. On 6 September, the submarine Guglielmo Marconi patrolled south of the Farasan Islands but sank only the oil tanker Atlas.[69] On 20 October, the Italians attacked Convoy BN 7 (31 merchantmen), escorted by the cruiser HMNZS Leander, the destroyer HMS Kimberley, five sloops and air cover from Aden. The submarines Guglielmo Marconi and Galileo Ferraris failed to intercept the convoy but next day it was attacked by four destroyers including Pantera, Leone, Francesco Nullo, 150 nmi (170 mi; 280 km) east of Massawa, which were driven off. At dawn, Leander and Kimberley forced Francesco Nullo ashore by gunfire onto an island near Massawa, where it was destroyed on 21 October, by three 45 Squadron Blenheims. Kimberley was hit in the engine room by a shore battery and had to be towed to Port Sudan.[70][71] As British land reinforcements arrived in East Africa, naval forces supported land operations and blockaded the last vessels of the Red Sea Flotilla at Massawa. By the end of 1940, the British had gained control of East African coastal routes and the Red Sea and Italian forces in the AOI declined as spare parts and supplies from Italy ran out. There were six air attacks on convoys in October and none after 4 November.[72]
French Somaliland 1940–1942
The governor of French Somaliland (now Djibouti), Brigadier-General Paul Legentilhomme had a garrison of seven battalions of Senegalese and Somali infantry, three batteries of field guns, four batteries of anti-aircraft guns, a company of light tanks, four companies of militia and irregulars, two platoons of the camel corps and an assortment of aircraft. After visiting from 8–13 January 1940, Wavell decided that Legentilhomme would command the military forces in both Somalilands should war with Italy come.[73] In June, an Italian force was assembled to capture the port city of Djibouti, the main military base.[74] After the fall of France in June, the neutralisation of Vichy French colonies allowed the Italians to concentrate on the more lightly defended British Somaliland.[75] On 23 July, Legentilhomme was ousted by the pro-Vichy naval officer Pierre Nouailhetas and left on 5 August for Aden, to join the Free French. In March 1941, the British enforcement of a strict contraband regime to prevent supplies being passed on to the Italians, lost its point after the conquest of the AOI. The British changed policy, with encouragement from the Free French, to "rally French Somaliland to the Allied cause without bloodshed". The Free French were to arrange a voluntary ralliement by propaganda (Operation Marie) and the British were to blockade the colony.[76]
Wavell considered that if British pressure was applied, a rally would appear to have been coerced. Wavell preferred to let the propaganda continue and provided a small amount of supplies under strict control. When the policy had no effect, Wavell suggested negotiations with the Vichy governor Louis Nouailhetas, to use the port and railway. The suggestion was accepted by the British government but because of the concessions granted to the Vichy regime in Syria, proposals were made to invade the colony instead. In June, Nouailhetas was given an ultimatum, the blockade was tightened and the Italian garrison at Assab was defeated by an operation from Aden. For six months, Nouailhetas remained willing to grant concessions over the port and railway but would not tolerate Free French interference. In October the blockade was reviewed but the beginning of the war with Japan in December, led to all but two blockade ships being withdrawn. On 2 January 1942, the Vichy government offered the use of the port and railway, subject to the lifting of the blockade but the British refused and ended the blockade unilaterally in March.[77]
Northern front, 1941
Operation Camilla
Operation Camilla was a deception concocted by Lieutenant-Colonel Dudley Clarke, intended to make the Italians believe that the British intended to re-conquer British Somaliland with the 4th and 5th Indian divisions, transferred from Egypt to Gedaref and Port Sudan. In December 1940, Clarke constructed a model operation for Italian military intelligence to discover and set up administration offices at Aden. Clarke arranged for the Italian defences around Berbera to be softened up by air and sea raids from Aden and distributed maps and pamphlets on the climate, geography and population of British Somaliland. "Sibs" (sibilare, hisses or whistles), were circulated among civilians in Egypt. Bogus information was planted on the Japanese consul at Port Said and indiscreet wireless messages were transmitted. The operation began on 19 December 1940, intended to mature early in January 1941 and succeeded. The plot backfired when the Italians began to evacuate British Somaliland instead of sending reinforcements. Troops were sent north into Eritrea, where the real attack was coming, instead of to the east. Part of the deception with misleading wireless transmissions, did convince the Italians that two Australian divisions were in Kenya, this time leading the Italians to reinforce the wrong area.[78]
Eritrea

In November 1940, Gazelle Force operated from the Gash river delta against Italian advanced posts around Kassala on the Ethiopian plateau, where hill ranges from 2,000–3,000 ft (610–910 m) bound wide valleys and the rainfall makes the area malarial from July to October.[79] On 11 December, Wavell ordered the 4th Indian Division to withdraw from Operation Compass in the Western Desert and move to Sudan. The transfer took until early January 1941 and Platt intended to begin the offensive on the northern front on 8 February, with a pincer attack on Kassala, by the 4th and 5th Indian divisions, less a brigade each.[80] News of the Italian disaster in Egypt, the harassment by Gazelle Force and the activities of Mission 101 in Ethiopia, led to the Italians withdrawing their northern flank to Keru and Wachai and then on 18 January to retreat hurriedly from Kassala and Tessenei, the triangle of Keru, Biscia and Aicota. Wavell had ordered Platt to advance the offensive from March to 9 February and then to 19 January, when it seemed that Italian morale was crumbling.[lower-alpha 8] The withdrawal led Wavell to order a pursuit and the troops arriving at Port Sudan (Briggs Force) to attack at Karora and advance parallel to the coast, to meet the forces coming from the west.[82][80]
Agordat and Barentu
Two roads from Kassala ran to Agordat, a track to the north through Keru and Biscia, where the road was better and the Via Imperiale, a tarmac road ran through Tessenei, Aicota and Barentu. The roads joined at Agordat and went through Keren, the only route to Asmara. The 4th Indian Division was sent 40 mi (64 km) along the road to Sabderat and Wachai, thence as far towards Keru as supplies allowed, with the 'I' tanks of B Squadron, 4th RTR to join from Egypt. The 5th Indian Division was to capture Aicota, ready to move east to Barentu or north-east to Biscia. Apart from air attacks the pursuit was not opposed until Keru Gorge, held by a rearguard of the 41st Colonial Brigade. The brigade retreated on the night of 22/23 January, leaving General Ugo Fongoli, his staff and 800 men behind as prisoners.[83] By 27 January, most of the two Indian divisions were close to Agordat and a brigade turned south to move across country towards Barentu Agordat which was defended by the 4th Colonial Division (General Orlando Lorenzini), with 76 guns and a company each of medium and light tanks.[84]
On the evening of 28 January, the 3/14th Punjab Regiment made a flanking move into the Cochen hills to the south and next day, they were joined by the 1/6th Rajputana Rifles but were unable to find a way forward. On 30 January, five Italian colonial battalions with mountain artillery in support, attacked. The Indian battalions were forced back but counter-attacked on the morning of 31 January and advanced towards the main road. The 5th Indian Brigade on the plain below, attacked with the four 'I' tanks. The armoured vehicles overran the Italian defences, knocking out several Italian tanks and cut the road to Keren. By 1 February, the 4th Colonial Division retreated up a track further north, having lost the equivalent of two battalions of infantry taken prisoner; 28 field-guns and several medium and light tanks.[83]
The 5th Indian Division, attacked Barentu, held by nine battalions of the 2nd Colonial Division (about 8,000 men), 32 guns and about 36 light tanks and armoured cars that had been dug in. The 10th Indian Infantry Brigade attacked from the north against a determined Italian defence, as the 29th Indian Infantry Brigade advanced as fast as possible from the west, slowed by demolitions and rearguards. On the night of 31 January/1 February, the Italians retreated along a track towards Tole and Arresa, pursued by a motor machine-gun group, which found on 8 February that the Italians had abandoned their vehicles and taken to the hills. The retreat left the motorable road from Tessenei–Agordat road open for British supply convoys.[85]
Battle of Keren

On 12 January, Aosta had sent a regiment of the regular army's 65th Infantry Division Granatieri di Savoia (General Amedeo Liberati) and three colonial brigades to Keren.[86] The 4th and 5th Indian divisions advanced eastwards from Agordat into the rolling countryside, which gradually increased in elevation towards the Keren Plateau, through the Ascidira Valley. There was an escarpment on the left and a spur rising to 6,000 ft (1,800 m) on the right of the road. The Italians were dug in on heights which dominated the massifs, ravines and mountains, which had been selected before the war as the main defensive position to guard Asmara and the Eritrean highlands from an attack through Sudan.[87]
On 15 March, after several days of bombing, the 4th Indian Division attacked on the north and west side of the road, to capture ground on the left flank, ready for the 5th Indian Division to attack on the east side. The 4th Indian Division met a determined defence and made limited progress but during the night, the 5th Indian Division captured Fort Dologorodoc, 1,475 ft (450 m) above the valley. The Granatieri di Savoia and Alpini counter-attacked Fort Dologorodoc seven times from 18–22 March, each attack being a costly failure. Wavell flew to Keren to assess the situation and on 15 March, as the Indians attacked again, watched with Platt as the attackers went up the road, ignoring the high ground on either side and broke through. Early on 27 March, Keren was captured after 53 days, for a loss of 536 men killed, 3,229 wounded, 3,000 Italians and 9,000 Ascaris killed and about 21,000 wounded.[87]
The 4th Indian Division mopped up at Keren before returning to Egypt and the 5th Indian Division resumed the pursuit of the Italians eastward towards Asmara, 50 mi (80 km) beyond.[88] The Italians conducted a fighting withdrawal under air attack to Ad Teclesan, in a narrow valley on the Keren–Asmara road, the last defensible position before Asmara. The Keren defeat had shattered the morale of the Italian forces and when the British attacked early on 31 March, the position fell after a battle and 460 Italian prisoners and 67 guns were captured. The Italians declared Asmara an open town next day and the British entered unopposed.[89]
Massawa
_winter_1941.jpg)
Bonetti, the commander of the Italian Red Sea Flotilla and the garrison at Massawa, had 10,000 troops and about 100 tanks to defend the port.[90] During the evening of 31 March, three of the last six destroyers at Massawa put to sea, to raid the Gulf of Suez and then scuttle themselves but Leone ran aground and sank the next morning and the sortie was cancelled. On 2 April the last five destroyers left to attack Port Sudan and then sink themselves.[91] Heath telephoned Bonetti with an ultimatum to surrender and not block the harbour by scuttling ships. If this was refused, the British would leave Italian citizens in Eritrea and Ethiopia to fend for themselves. The 7th Indian Infantry Brigade Group sent small forces towards Adowa and Adigrat and the rest advanced down the Massawa road, which declined by 7,000 ft (2,100 m) in 50 mi (80 km) and the Indians rendezvoused with Briggs Force, which had cut across country, at Massawa by 5 April.[89]
Bonetti was called upon to surrender but refused again and on 8 April, an attack by the 7th Indian Infantry Brigade Group was repulsed. A simultaneous attack by the 10th Indian Infantry Brigade and the tanks of B Squadron 4th RTR broke through the defences on the west side. The Free French overran the defences in the south-west, as the RAF bombed Italian artillery positions. In the afternoon, Bonetti surrendered and the Allied force took 9,590 prisoners and 127 guns. The harbour was found to have been blocked by the scuttling of two large floating dry docks, 16 large ships and a floating crane in the mouths of the north Naval Harbour, the central Commercial Harbour and the main South Harbour. The Italians had also dumped as much of their equipment as possible in the water. The British re-opened the Massawa–Asmara railway on 27 April and by 1 May, the port came into use to supply the 5th Indian Division.[89][lower-alpha 9] The Italian surrender ended organised resistance in Eritrea and fulfilled the strategic objective of ending the threat to shipping in the Red Sea. On 11 April, President Franklin D. Roosevelt of the USA rescinded the status of the Red Sea as a combat zone under the Neutrality Acts, freeing US ships to use the route to carry supplies to the Middle East.[93]
Ethiopia, 1941
Gideon Force was a small British and African special forces unit, which acted as a Corps d'Elite amongst the Sudan Defence Force, Ethiopian regular forces and Arbegnoch (Patriots). At its peak, Orde Wingate led fifty officers, twenty British NCOs, 800 trained Sudanese troops and 800 partially trained Ethiopian regulars. He had a few mortars, no artillery and no air support, only intermittent bombing sorties. The force operated in the difficult country of Gojjam Province at the end of a long and tenuous supply-line, on which nearly all of its 15,000 camels perished. Gideon Force and the Arbegnoch (Ethiopian Patriots) ejected the Italian forces under General Guglielmo Nasi, the conqueror of British Somaliland in six weeks and captured 1,100 Italian and 14,500 Ethiopian troops, twelve guns, many machine-guns, rifles and ammunition and over 200 pack animals. Gideon Force was disbanded on 1 June 1941, Wingate was returned to his substantive rank of Major and returned to Egypt, as did many of the troops of Gideon Force, who joined the Long Range Desert Group (LRDG) of the Eighth Army.[94][95]
Addis Ababa

While Debre Markos and Addis Derra were being captured, other Ethiopian Patriots under Ras Abebe Aregai consolidated themselves around Addis Ababa in preparation for Emperor Selassie's return. In response to the rapidly advancing British and Commonwealth forces and to the general uprising of Ethiopian Patriots, the Italians in Ethiopia retreated to the mountain fortresses of Gondar, Amba Alagi, Dessie and Gimma.[96] After negotiations prompted by Wavell, Aosta ordered the governor, Agenore Frangipani, to surrender the city to forestall a massacre of Italian civilians, as had occurred in Dire Dawa. On 6 April 1941, Addis Ababa was occupied by Wetherall, Pienaar and Fowkes escorted by East African armoured cars, who received the surrender of the city.[97] The Polizia dell'Africa Italiana (Police of Italian Africa) stayed in the city to maintain order.[98] Selassie made a formal entry to the city on 5 May.[lower-alpha 10] On 13 April, Cunningham sent a force under Brigadier Dan Pienaar comprising 1st South African Brigade and Campbell's Scouts (Ethiopian irregulars led by a British officer), to continue the northward advance and link up with Platt's forces advancing south.[99]
On 20 April, the South Africans captured Dessie on the main road north from Addis Ababa to Asmara, about 200 mi (320 km) south of Amba Alagi.[100] In eight weeks the British had advanced 1,700 mi (2,700 km) from Tana to Mogadishu at a cost of 501 casualties and eight aircraft and had destroyed the bulk of the Italian air and land forces.[101] From Debra Marqos, Wingate pursued the Italians and undertook a series of harrying actions. (In early May most of Gideon Force had to break off to provide a suitable escort for Hailie Selassie's formal entry into Addis Ababa.) By 18 May, Maraventano was dug in at Agibor, against a force of about 2,000 men, including only 160 trained soldiers (100 from the Frontier Battalion and 60 of the re-formed 2nd Ethiopian Battalion).[102] Both sides were short of food, ammunition, water and medical supplies and Wingate attempted a ruse by sending a message to Maraventano telling of reinforcements due to arrive and that the imminent withdrawal of British troops would leave the Italian column at the mercy of the Patriots. Maraventano discussed the situation with the Italian headquarters in Gondar on 21 May and was given discretion to surrender, which took place on 23 May by 1,100 Italian and 5,000 local troops, 2,000 women and children and 1,000 mule men and camp followers. Gideon Force was down to 36 regular soldiers to make the formal guard of honour at the surrender, the rest being Patriots.[103]
Southern front, 1941
Italian Somaliland
_and_Colonel_Wingate_(right)_in_Dambacha_Fort%2C_after_it_had_been_captured%2C_15_April_1941._E2462.jpg)
On 24 January, Cunningham's main force, including the 11th (African) Division and the 12th (African) Division, invaded Italian Somaliland from Kenya. Earlier in January, the Italians had already decided that the plains of Italian Somalia could not be defended. The 102nd Divisione Somala (General Adriano Santini) and bande (about 14,000 men) retired to the lower Juba river and the 101st Divisione Somala (General Italo Carnevali) and bande (about 6,000 men) to the upper Jube on the better defensive terrain of the mountains of Ethiopia. Cunningham encountered few Italians west of the Juba, only bande and a colonial battalion at Afmadu and troops at Kismayu, where the Juba River empties into the Indian Ocean.[104] Against an expected six brigades and "six groups of native levies" holding the Juba for the Italians, Cunningham began Operation Canvas with four brigade groups and captured Afmadu on 11 February and three days later took the port of Kismayu the first objective. North of Kismayu and beyond the river was the main Italian position, Jelib. On 22 February, Jelib was attacked on both flanks and from the rear. The Italians were routed and 30,000 were killed, captured or dispersed in the bush. There was nothing to hinder a British advance of 200 mi (320 km) to Mogadishu, the capital and main port of Italian Somaliland.[105][106]
On 25 February 1941, the motorised 23rd Nigerian Brigade (11th (African) Division) advanced 235 mi (378 km) up the coast in three days and occupied the Somali capital of Mogadishu unopposed. The 12th (African) Division was ordered to advance on Bardera and Isha Baidoa but was held up because of the difficulty in using Kismayu as a supply base. The division pushed up the Juba River in Italian Somaliland towards the Ethiopian border town of Dolo. After a pause, caused by the lack of equipment to sweep Mogadishu harbour of British magnetic mines dropped earlier, the 11th (African) Division began a fighting pursuit of the retreating Italian forces north from Mogadishu on 1 March. The division pursued the Italians towards the Ogaden Plateau. By 17 March, the 11th (African) Division completed a 17-day dash along the Italian Strada Imperiale (Imperial Road) from Mogadishu to Jijiga in the Somali region of Ethiopia. By early March Cunningham's forces had captured most of Italian Somaliland and were advancing through Ethiopia towards the ultimate objective, Addis Ababa. On 26 March, Harar was captured and 572 prisoners taken, with 13 guns, the 23rd Nigerian Brigade having advanced nearly 1,000 mi (1,600 km) in 32 days. (On 29 March, Dire Dawa was occupied by South African troops, after Italian colonists appealed for help against deserters, who were committing atrocities.)[107]
Amba Alagi
After the fall of Keren, Aosta retreated to Amba Alagi, an 11,186 ft (3,409 m) mountain that had been tunnelled for strongpoints, artillery positions and stores, inside a ring of similarly fortified peaks. British troops advancing from the south had captured Addis Ababa on 6 April. Wavell imposed a policy of avoiding big operations in Eritrea and northern Ethiopia, that would impede the withdrawal of troops to Egypt. The remaining Italian troops were no threat to Sudan or Eritrea but could trouble the British hold on the AOI. The 1st South African Division was needed in Egypt and Cunningham was ordered to send it north to capture the main road to Massawa and Port Sudan so the ports could be used for embarkation. Amba Alagi obstructed the road north and the 5th Indian Division advanced from southwards as the South Africans moved northwards in a pincer movement. The main attack by the 5th Indian Division began on 4 May and made slow progress. On 10 May, the 1st South African Brigade arrived and completed the encirclement of the mountain. The Indian division attacked again on 13 May, with the South Africans attacking next day and forcing the Italians out of several defensive positions. Concerned about the care of his wounded and rumours of atrocities committed by the Arbegnoch, Aosta offered to surrender, provided that the Italians were granted the honours of war. On 19 May, Aosta and 5,000 Italian troops, marched past a guard of honour, into captivity.[108]
Southern Ethiopia
The East Africa Force on the southern front included the 1st South African Division (Major-General George Brink), the 11th (African) Division (Major-General H. E. de R. Wetherall) and the 12th (African) Division (Major-General A. R. Godwin-Austen) (The African divisions were composed of East African, South African, Nigerian and Ghanaian troops under British, Rhodesian and South African officers.)[109] In January 1941, Cunningham decided to launch his first attacks across the Kenyan border directly into southern Ethiopia. Although he realised that the approaching wet season would preclude a direct advance this way to Addis Ababa, he hoped that this action would cause the Ethiopians in the south of the country to rise up in rebellion against the Italians (the plot proved abortive).[110] Cunningham sent the 1st South African Division (composed of the 2nd and 5th South African and 21st East African brigades) and an independent East African brigade into the Galla-Sidamo Province.[111] From 16 to 18 January 1941, they captured El Yibo and on 19 February, an advance force of the South African Division captured Jumbo.[112] From 24 to 25 January, Cunningham's troops fought on the Turbi Road.[24]
The southern Ethiopia attack was stopped in mid-February by heavy rain, which made movement and maintenance of the force very difficult. From 1 February, they captured Gorai and El Gumu. On 2 February, they took Hobok. From 8 to 9 February, Banno was captured. On 15 February, the fighting was on the Yavello Road. The two South African Brigades then launched a double flanking movement on Mega. After a three-day battle in which many of the South Africans, equipped for tropical conditions, suffered from exposure because of the heavy rain and near freezing temperatures, they captured Mega on 18 February. Moyale, 70 mi (110 km) south-east of Mega on the border with Kenya, was occupied on 22 February by a patrol of Abyssinian irregular troops which had been attached to the South African Division.[110]
British Somaliland 1941
The operation to recapture British Somaliland began on 16 March 1941 from Aden, in the first successful Allied landing on an enemy-held beach of the war.[113] The Aden Striking Force of about 3,000 men was to be carried about 140 mi (230 km) from Aden by eight navy ships and civilian transports carrying heavy equipment. The troops were to be put ashore onto beaches inside reefs to the east and west of Berbera to secure the town and re-conquer the territory. Some doubts were expressed as to the feasibility of negotiating offshore reefs in the dark, when the town behind was blacked out but the risk was taken. On 16 March about 10 mi (16 km) north of the town and 1,000 yd (910 m) off shore, the force prepared to land as advanced parties searched for landing places.[114] The 1/2nd Punjab Regiment and 3/15th Punjab Regiment Indian Army (which had been evacuated from the port in August 1940) and a Somali commando detachment, landed at Berbera from Force D (the cruisers HMS Glasgow and HMS Caledon, the destroyers Kandahar and Kipling, auxiliary cruisers Chakdina and Chantala, Indian trawlers Netavati and Parvati, two transports and ML 109).[113] When the Sikhs landed, the 70th Colonial Brigade "melted away".[115] On 20 March, Hargeisa was captured and the next few months were spent mopping up. The Somaliland Camel Corps was re-founded in mid-April, to resume operations against local bandits. British forces advanced westwards into eastern Ethiopia and in late March, linked with forces from the Southern Front around Harar and Diredawa. Cunningham's forces could now be supplied efficiently through Berbera.[116]
War at sea, 1941

The control established by the British of the seas off East Africa made supply of the British land forces and Operation Begum, the blockade of the AOI, much easier. Ships passing through took part in offshore operations; HMS Formidable sent Fairey Albacore aircraft to drop mines Mogadishu harbour (Operation Breach) and 14 Albacores to attack the Italian ships at Massawa (Operation Composition), sinking SS Monacalieri. HMS Hermes, with a cruiser and destroyer force, bombarded coastal defences, supply dumps and Italian troops; when Kismayu was captured on 14 February, fifteen of the sixteen Axis merchant ships there were captured.[117] On 20 February, the auxiliary cruisers Ramb I and Ramb II broke out of Massawa with the colonial ship Eritrea. On 21 February, seven Albacores from Formidable raided Massawa again. On 27 February, Ramb I was located and sunk north of the Maldive Islands in the Indian Ocean by Leander; Eritrea and Ramb II escaped and reached Kobe, Japan.[118][119] On 25 February, Mogadishu fell and British merchant sailors held there, having been captured by German commerce-raiders, were liberated.[117] On 1 March, five Albacores from Formidable raided Massawa again. From 1–4 March, the submarines Guglielmo Marconi, Galileo Ferraras, Perla and Archimede sailed for France to join BETASOM, an Italian submarine flotilla at Bordeaux, arriving from 7–20 May.[120]

On 31 March, three of the Italian destroyers at Massawa sortied to attack shipping in the Gulf of Suez. Leone ran aground outside Massawa and had to be sunk, after which the sortie was abandoned. On 2 April, five destroyers were due to attack the fuel tanks at Port Sudan and then scuttle themselves but reconnaissance aircraft from Aden spotted the ships. At dawn on 3 April, four were seen 20 nmi (23 mi; 37 km) east of Port Sudan by Swordfish aircraft of 813 Naval Air Squadron and 824 Naval Air Squadron FAA, from Port Sudan, which with five Blenheims of 14 Squadron RAF, sank Daniele Manin and Nazario Sauro. Pantera and Tigre were found near Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, where they were being abandoned and were destroyed by Wellesleys of 223 Squadron RAF from Port Sudan and the destroyer Kingston; Battisti had engine-trouble the night before and was scuttled. MAS-213 (Motoscafo armato silurante, motor torpedo boat) hit the cruiser HMS Capetown escorting a convoy off Massawa before being scuttled, Capetown having to be towed to Port Sudan and then sail for Bombay for repairs.[91]
Operations, May–November 1941
Assab

After the surrender by Aosta at Amba Alagi on 18 May 1941, some Italian forces held out at Assab, the last Italian harbour on the Red Sea.[121] Operation Chronometer took place from 10–11 June, with a surprise landing at Assab, by the 3/15th Punjab Regiment from Aden, carried by a flotilla containing HMS Dido, HMIS Indus, HMIS Clive, HMS Chakdina and SS Tuna.[122][123] Dido bombarded the shore from 5:05–5:12 a.m.; aircraft flew overhead and bombed the port to drown the sound of two motor-boats, carrying thirty soldiers each. At 5:19 a.m. the troops disembarked on the pier unopposed; two Italian Generals were taken prisoner in their beds and the success signal was fired at 6:00 a.m. The flotilla entered the harbour behind a minesweeper and landed the rest of the Punjabis, who sent parties to search the islands nearby and found nothing. At 7:00 a.m. the Civil Governor was taken to Dido and surrendered Assab to the Senior Officer Red Sea Force (Rear-Admiral R. H. C. Halifax) and Brigadier H. K. Dimoline. During the evening, Captain Bolla, the Senior Naval Officer at Assab, was captured. Bolla disclosed the positions of three minefields in the approaches to the harbour and said that the channel to the east, north of Ras Fatma was clear. The 3/15th Punjabis took 547 prisoners along with the two generals and 35 Germans.[124] On 13 June, the Indian trawler Parvati struck a magnetic mine near Assab and became the last naval casualty of the campaign.[125]
Kulkaber (Culqualber)

A force under General Pietro Gazzera, the Governor of Galla-Sidama and the new acting Viceroy and Governor-General of the AOI was faced with a growing irregular force of Arbegnoch and many local units melted away. On 21 June 1941, Gazzera abandoned Jimma and about 15,000 men surrendered. On 3 July, the Italians were cut off by the Free Belgian forces (Major-General Auguste Gilliaert) who had defeated the Italians at Asosa and Saïo.[126] On 6 July, Gazzera and 2,944 Italian, 1,535 African and 2,000 bande formally surrendered; the 79th Colonial Battalion changed sides and was renamed the 79th Foot as did a company of banda as the Wollo Banda.[127][128]
Wolchefit Pass was a position whose control was needed to launch the final attack on Gondar, was defended by a garrison of about 4,000 men (Colonel Mario Gonella) in localities distributed in depth for about 3 mi (4.8 km). The stronghold had been besieged by irregular Ethiopian forces, led by Major B. J. Ringrose, since May and on 5 May the Italians retreated from Amba Giorgis. The besieging force was later augmented by the arrival of the 3/14th Punjab Battalion from the Indian Army and part of the 12th African Division. Several attacks, counter-attacks and sorties were launched between May and August 1941. On 28 September 1941, after losing 950 casualties and running out of provisions, Gonella surrendered with 1,629 Italian and 1,450 Ethiopian soldiers to the 25th East African Brigade (Brigadier W. A. L. James). Work began to repair the road to Gondar during the autumn rains.[129]
Battle of Gondar
Gondar, the capital of Begemder Province in north-west Ethiopia, was about 120 mi (190 km) west of Amba Alagi. After Gazzera surrendered, Nasi, the acting Governor of Amhara, became the new acting Viceroy and Governor-General of the AOI. At Gondar, Nasi faced the British and a growing number of Ethiopian Patriots but held out for almost seven months. While the Regia Aeronautica in East Africa had been worn down quickly by attrition, the Italian pilots fought on to the end.[130] After the death of his commander Tenente Malavolti on 31 October, Sergente Giuseppe Mottet became the last Italian fighter pilot in the AOI and on 20 November, flew the last Regia Aeronautica sortie, a ground-attack operation in the last CR.42 (MM4033) against British artillery positions at Culqualber. Mottet fired one burst and killed Lieutenant-Colonel Ormsby, the CRA.[131] On landing, Mottet destroyed the CR.42, joined the Italian troops and fought on until the surrender.[132] On 27 November, Nasi surrendered with 10,000 Italian and 12,000 African troops, British losses being 32 men killed, 182 wounded, six men missing and 15 aircraft shot down since 7 April.[133] In 1949, Maravigna recorded Italian casualties of 4,000 killed and 8,400 sick and wounded.[134]
Aftermath
Analysis
In 2016, A. Stewart wrote that due to the British defeats in Greece and Crete the East African Campaign has been overshadowed, although it was the first victory for the Allies in the Second World War.[135] In 2004, the American historian Douglas Porch wrote that the "pearl of the fascist regime" had lasted only five years, the performance of the Italian army exceeded that in North Africa but there had still been a high ratio of prisoners to casualties. Mass defections by local forces suggested that Fascist imperialism had made little impression on the East African public. The Italian navy at Massawa had shown a "stunning" lack of energy and failed to challenge British access to Mombasa and Port Sudan or the landing at Berbera. The army had failed to exploit British supply difficulties and had left stores behind for the British to use. The British had withdrawn the 4th Indian Division and RAF squadrons for North Africa in February 1941, despite the Italian forces remaining at Amba Alagi, which from 20 April to 15 May, were steadily pressed back until they surrendered on 19 May.[136]
Ethiopia, the Somalilands and Eritrea had been conquered by the British and the end of organised Italian resistance, led to the East Africa Force and Air Headquarters East Africa being reduced by the transfer of the South African and the two Indian divisions to Egypt, along with three fighter, three bomber and a reconnaissance squadron, followed by two more in late May. The 11th and 12th (African) divisions remained, supported by six RAF and SAAF squadrons.[137] The Italians at Galla-Sidom and Gondar were mopped up and the final surrender was taken by the Belgian contingent from Congo. Mussolini blamed the disaster on the "deficiency of the Italian race" but the Fascist regime survived and the British victory had little influence on Japanese strategy in the Far East.[136] With the Red Sea and Gulf of Aden cleared of Axis forces, Roosevelt declared that the areas were no longer combat zones on 11 April 1941. Ships of the United States were able to proceed to the Suez Canal, which helped to relieve the strain on British shipping resources.[24]
Signals intelligence
The Italians had replaced their ciphers in the AOI in November 1940 but by the end of the month, the GC&CS in England and the Cipher Bureau Middle East (CBME) in Cairo had broken the new Regio Esercito and Regia Aeronautica ciphers. By 1941, sufficient low-grade ciphers had been broken to reveal the Italian order of battle and the supply situation when the British offensive began on 19 January 1941. Italian dependence on wireless communication, using frequencies on which it was easy for the British to eavesdrop, led to a flood of information, from the daily report from the Viceroy, to the operational plans of the Regia Aeronautica and Regia Esercito on the retreat from Keren.[81] On occasion, British commanders had messages before the recipients and it was reported later by the Deputy Director Military Intelligence in Cairo, that
...he could not believe that any army commander in the field had [ever] been better served by his intelligence....— DDMI (ME)[81]
Casualties
On 16 April 1941, the authorities in the AOI signalled to Rome that 426 officers had been killed, 703 wounded and 315 captured, during military operations before the surrender. Casualties among NCOs and other ranks were 4,785 killed, 6,244 wounded and 15,871 captured (inclusive). Casualties among locally recruited soldiers were 11,755 dead, 18,151 wounded and 3,076 captured before the surrender; the Truppi coloniale figures did not include forces on the Giuba and eastern fronts.[138] By May 1941, of the c. 350,000 men in the AOI available for military operations in June 1940, only the c. 80,000 men in the garrisons near Gondar and the seven colonial divisions in Galla-Sidamo remained to be taken prisoner.[139][140] More casualties among the Italian and colonial troops occurred after April 1941, in the operations against Amba Alagi (3,500 casualties), Kulkaber/Culqualber (1,003 killed and 804 wounded) and Gondar (4,000 killed and 8,400 sick and wounded).[141][134] In 1954, I. S. O. Playfair, the British official historian, recorded that from June 1940 to May 1941, the East African Force had 1,154 battle casualties and 74,550 cases of sickness or accident, of which 10,000 were of dysentery and 10,000 were of malaria, from which 744 men died. The RAF lost 138 aircraft and the Regia Aeronautica lost 250 of the 325 aeroplanes in the AOI when the war began and of the 75 flown to the region during the campaign. The Belgian Force Publique suffered 462 deaths from all causes.[142]
Subsequent operations
Guerrilla warfare, 1941–1943

Until 27 November 1941, two African divisions mopped up pockets of resistance until the last formed Italian units surrendered.[143] From the end of 1941 to September 1943, c. 7,000 men in scattered Italian units fought a guerrilla war from the deserts of Eritrea and Somalia to the forests and mountains of Ethiopia.[144] They supposedly did so in the hope of holding out until the Germans and Italians in Egypt (or even possibly the Japanese in India) intervened. Amedeo Guillet was one of the Italian officers who fought with the Italian guerrillas in Ethiopia. Another notable guerilla leader was Hamid Idris Awate, a father of the Eritrean Liberation Front. Other Italian officers were Captain Francesco De Martini in Eritrea, Colonel Calderari in western Ethiopia/Somalia, Colonel Di Marco in Ogaden/British Somaliland "blackshirt centurion" De Varda in Somalia/Ethiopia and Major Lucchetti in Ethiopia. Civilians participated and in August 1942, forces led by Dr. Rosa Dainelli sabotaged the main British ammunition dump in Addis Ababa.[145] Hostilities in East Africa officially ceased on 9 September 1943, when the Italian government signed the Armistice with Italy. Some three thousand Italian soldiers continued the guerrilla war until October 1943, as they were unaware of the agreement when Italy surrendered to the Allies.[146]
Post-war
In January 1942, with the final official surrender of the Italians, the British, under American pressure, signed an interim Anglo-Ethiopian Agreement with Selassie, acknowledging Ethiopian sovereignty. Makonnen Endelkachew was named as Prime Minister and on 19 December 1944, the final Anglo-Ethiopian Agreement was signed. Eritrea was placed under British military administration for the duration and in 1950, it became part of Ethiopia. After 1945, Britain controlled both Somalilands, as protectorates. In November 1949, during the Potsdam Conference, the United Nations granted Italy trusteeship of Italian Somaliland under close supervision, on condition that Somalia achieve independence within ten years.[147] British Somaliland became independent on 26 June 1960 as the State of Somaliland, the Trust Territory of Somalia (ex-Italian Somaliland) became independent on 1 July 1960 and the territories united as the Somali Republic.[148]
Victoria Cross
The following is a list of recipients of the Victoria Cross during this campaign:
- Eric Charles Twelves Wilson (captain, Somaliland Camel Corps) – Received during the Italian invasion of British Somaliland.[149]
- Premindra Singh Bhagat (second lieutenant, Royal Bombay Sappers and Miners) – Received during fighting on the Northern Front.[85]
- Richhpal Ram (Subedar in 6th Rajputana Rifles) – Received posthumously during fighting on the Northern Front.[150]
- Nigel Leakey (sergeant in the 1/6 Battalion King's African Rifles and cousin of the paleoanthropologist Louis Leakey) – Received posthumously during fighting on the Southern Front.[151]
See also
- Italian guerrilla war in Ethiopia
- Italian Empire
- Colonial heads of Italian East Africa
- Military history of Ethiopia
- Military production during World War II
- Military history of Italy during World War II
- North African campaign
- Western Desert Campaign
- Syria-Lebanon campaign
- West Africa Campaign
- Battle of Madagascar
- German Motorized Company
- MVSN Colonial Militia
- South African Irish Regiment
- 81st (West Africa) Division
- 82nd (West Africa) Division
- Royal Corps of Colonial Troops
- Dubats
- Zaptie
- Armoured car regiment
Notes
- ↑ Serviceable: thirty-five Ca.133, one SM.81, four SM.79, five CR.32, twelve CR.42 and two Ro.37, unserviceable: forty-eight Ca.133, sixteen SM.81, two SM.79, eleven CR.32, two CR.42 and two Ro.37.[10][11]
- ↑ Wavell also had to liaise with the ambassadors to Egypt and Iraq, the Governor-General of Sudan, the High Commissioner for Palestine and Transjordan, the governors of Cyprus, Aden and British Somaliland and the Political Resident in the Persian Gulf.[18]
- ↑ Cunningham took over East African Force at the start of November 1940, from Dickinson who was in poor health.
- ↑ Sandford had fifteen years' experience of Ethiopia and was a friend of Selassie.[31]
- ↑ 1st Duke of York's Own Skinner's Horse (the 5th Indian Division reconnaissance regiment), One Troop 'P' Battery RHA, One Troop 28 Field Regiment RA (18-pounder field guns), 4 Ordnance Workshop Section, 170 Cavalry Field Ambulance (less detachment), 1 Motor Machine-Gun Group SDF (2, 4 and 6 Coys).[46]
- ↑ The battalion was eventually replaced by the 2nd Highland Light Infantry and fought in Syria and Iraq.[49]
- ↑ In 1938, the combined strength of both units had been 94 officers, 60 Non-commissioned officers (NCOs) and 2,821 African other ranks. After the outbreak of the war in Europe, the units provided the nucleus for the rapid expansion of the KAR, the size of a KAR battalion was established at 36 officers, 44 NCOs and men, with 1,050 African other ranks.[52]
- ↑ Wireless decrypts greatly aided British preparations and the decision to attack ahead of schedule.[81]
- ↑ Edward Ellsberg later wrote that after arriving in April, with a salvage crew and specialist equipment, the United States Naval Repair Base, Massawa opened on 8 May for repairs and maintenance.[92]
- ↑ Five years after fleeing on 5 May 1936 during the Second Italo-Abyssinian War. Since 1951, 5 May has been observed in Ethiopia as Liberation Day - a national holiday.[98]
Footnotes
- ↑ Playfair 1954, p. 2.
- ↑ Playfair 1954, pp. 6–7, 69.
- ↑ Playfair 1954, pp. 38–40.
- ↑ Playfair 1954, p. 93.
- ↑ Playfair 1954, p. 166.
- ↑ Stewart 2016, pp. 55–56.
- ↑ Marino 2009, p. 31.
- ↑ Stewart 2016, p. 14.
- ↑ Mohr & Sellwood 2009, p. 126.
- 1 2 3 4 Santoro 1957, p. 146.
- ↑ Shores 1996, p. 11.
- ↑ Shores 1996, pp. 7–8.
- ↑ Shores 1996, pp. 8–9.
- ↑ Roskill 1957, pp. 49, 308, 426.
- ↑ Roskill 1957, p. 597.
- ↑ Roskill 1957, p. 271.
- ↑ Raugh 1993, pp. 39–40.
- ↑ Raugh 1993, p. 39.
- ↑ Playfair 1954, pp. 19, 93.
- 1 2 Dear & Foot 2005, p. 245.
- ↑ Raugh 1993, p. 65.
- ↑ Raugh 1993, pp. 169–170, 67.
- ↑ Raugh 1993, pp. 67, 72–73.
- 1 2 3 4 Dear & Foot 2005, p. 247.
- ↑ Raugh 1993, pp. 168–173.
- ↑ Richards 1974, pp. 249–250.
- ↑ Mackenzie 1951, pp. 21, 30.
- ↑ Playfair 1954, pp. 169, 265.
- ↑ Playfair 1954, p. 400.
- ↑ Playfair 1954, pp. 94, 172.
- ↑ Raugh 1993, p. 170.
- ↑ Barker 1971, p. 155.
- ↑ Playfair 1954, p. 403.
- ↑ Playfair 1954, pp. 404–405.
- ↑ Mackenzie 1951, p. 23.
- 1 2 Playfair 1954, p. 170.
- ↑ Playfair 1954, pp. 174–175.
- 1 2 Shores 1996, p. 54.
- ↑ Playfair 1954, pp. 172–177.
- ↑ Raugh 1993, p. 82.
- ↑ Playfair 1954, p. 178.
- ↑ Stegemann & Vogel 1995, pp. 262–263.
- ↑ Raugh 1993, p. 72.
- 1 2 Stegemann & Vogel 1995, pp. 295.
- ↑ Playfair 1954, pp. 170–171.
- 1 2 Prasad 1963, p. 160.
- ↑ Stewart 2016, pp. 151–152.
- ↑ Playfair 1954, p. 398.
- 1 2 3 Mackenzie 1951, p. 33.
- 1 2 Brett-James 1951, ch 2.
- ↑ Playfair 1954, p. 399.
- 1 2 3 4 Mollo, McGregor & Turner 1981, p. 133.
- ↑ Playfair 1954, p. 180.
- ↑ Mollo, McGregor & Turner 1981, pp. 138–139.
- ↑ Playfair 1954, pp. 180–181.
- 1 2 Mackenzie 1951, p. 42.
- ↑ Playfair 1954, p. 394.
- ↑ Richards 1974, pp. 409, 415.
- ↑ Playfair 1954, pp. 96, 169.
- ↑ Shores 1996, pp. 42–54.
- ↑ Schoeman 2002, pp. 31, 66.
- ↑ Playfair 1954, pp. 169–170.
- ↑ Orpen 1968, pp. 20–21.
- ↑ Roskill 1957, pp. 296, 426.
- ↑ Gill 1957, pp. 199–200.
- ↑ Waters 1956, p. 86.
- ↑ Gill 1957, p. 168.
- ↑ Gill 1957, pp. 200, 168.
- ↑ Roskill 1957, pp. 307–308.
- ↑ Gill 1957, pp. 227–228.
- ↑ Playfair 1954, p. 248.
- ↑ Roskill 1957, pp. 307–308, 248.
- ↑ Raugh 1993, pp. 75–76.
- ↑ Playfair 1954, p. 89.
- ↑ Mockler 1984, p. 241.
- ↑ Playfair 2004, pp. 322–323.
- ↑ Playfair 2004, pp. 323–324.
- ↑ Rankin 2009, pp. 316–317.
- ↑ Raugh 1993, pp. 172–174.
- 1 2 Playfair 1954, pp. 399–400.
- 1 2 3 Hinsley 1994, pp. 64–65.
- ↑ Raugh 1993, pp. 172–174, 175.
- 1 2 Playfair 1954, pp. 400–401.
- ↑ Mackenzie 1951, p. 48.
- 1 2 Playfair 1954, p. 401.
- ↑ Playfair 1954, p. 431.
- 1 2 Playfair 1954, p. 439.
- ↑ Raugh 1993, pp. 180–181.
- 1 2 3 Playfair 1954, pp. 441–442.
- ↑ Mackenzie 1951, p. 66.
- 1 2 Playfair 1954, p. 441.
- ↑ Ellsberg 1946, p. 160.
- ↑ Raugh 1993, pp. 181–182.
- ↑ Playfair 1954, pp. 406, 424–428, 449.
- ↑ Rooney 1994, pp. 72–73.
- ↑ Barker 1971, p. 156.
- ↑ Playfair 1954, pp. 421–422.
- 1 2 Hammerton 1941, p. 86.
- ↑ Wavell 1946a, p. 3,530.
- ↑ Mackenzie 1951, p. 68.
- ↑ Playfair 1954, pp. 422–423.
- ↑ TAC 1942, p. 66.
- ↑ Rooney 1994, pp. 70–71.
- ↑ Playfair 1954, p. 411.
- ↑ Churchill 1985, p. 75.
- ↑ Playfair 1954, p. 411–417.
- ↑ Playfair 1954, p. 417–419.
- ↑ Raugh 1993, pp. 182–183.
- ↑ Playfair 1954, p. 181.
- 1 2 Playfair 1954, p. 409.
- ↑ TAC 1942, pp. 76–77.
- ↑ Playfair 1954, p. 415.
- 1 2 Rohwer & Hümmelchen 1992, p. 54.
- ↑ Stewart 2016, p. 138.
- ↑ Playfair 1954, p. 417.
- ↑ Playfair 1954, p. 418–420.
- 1 2 Roskill 1957, p. 426.
- ↑ Roskill 1957, p. 387.
- ↑ Waters 1956, pp. 98, 96.
- ↑ Rohwer & Hümmelchen 1992, pp. 51, 61.
- ↑ Jowett 2001, p. 7.
- ↑ Collins 1964, p. 63.
- ↑ Roskill 1957, p. 517.
- ↑ Collins 1964, pp. 64–65.
- ↑ Collins 1964, pp. 58–59.
- ↑ Weller 2010, p. 117.
- ↑ Playfair 2004, pp. 309–314.
- ↑ Stewart 2016, p. 217–219.
- ↑ Playfair 2004, pp. 314–317.
- ↑ Mollo, McGregor & Turner 1981, p. 91.
- ↑ Playfair 2004, p. 319.
- ↑ Gustavsson 2014.
- ↑ Playfair 2004, p. 321.
- 1 2 Maravigna 1949, p. 191.
- ↑ Stewart 2016, p. ix.
- 1 2 Porch 2005, pp. 137–138.
- ↑ Playfair 1954, pp. 449–450.
- ↑ Rovighi 1988, p. 476.
- ↑ Playfair 1954, pp. 423, 447.
- ↑ Playfair 2004, p. 303.
- ↑ Stewart 2016, p. 187.
- ↑ BIC 1941, p. 22.
- ↑ Raugh 1993, p. 183.
- ↑ Cernuschi 1994, pp. 5, 36.
- ↑ Roselli 2007, p. 58.
- ↑ Cernuschi 1994, p. 74.
- ↑ Zolberg, Aguayo & Suhrke 1992, p. 106.
- ↑ NEB 2002, p. 835.
- ↑ Playfair 1954, p. 177.
- ↑ Playfair 1954, p. 435.
- ↑ Playfair 2004, p. 308.
References
Books
- Barker, A. J. (1971). Rape of Ethiopia, 1936. London: Ballantine Books. ISBN 978-0-345-02462-6.
- Brett-James, Antony (1951). Ball of Fire – The Fifth Indian Division in the Second World War. Aldershot: Gale & Polden. OCLC 4275700. Retrieved 5 March 2016.
- Churchill, Winston S. (1985) [1950]. The Second World War: The Grand Alliance. III. Boston: Houghton Mifflin. ISBN 978-0-395-41057-8.
- Collins, D. J. E. (1964). Prasad, B., ed. The Royal Indian Navy 1939–1945. Official History of the Indian Armed Forces In the Second World War (online ed.). Delhi: Combined Inter-Services Historical Section (India & Pakistan). OCLC 4079794. Retrieved 9 March 2016.
- Dear, I. C. B. (2005) [1995]. Foot, M. R. D., ed. Oxford Companion to World War II. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-280670-3.
- Ellsberg, Edward (1946). Under the Red Sea Sun. New York: Dodd, Mead. ISBN 978-0-8371-7264-4. OCLC 1311913.
- Gill, G. Hermon (1957). "Chapter 5, R. A. N. Ships Overseas June–December 1940" (PDF). Royal Australian Navy, 1939–1942. Australia in the War of 1939–1945, Series 2. I (online ed.). Canberra, ACT: Australian War Memorial. pp. 140–246. OCLC 848228. Retrieved 20 February 2016.
- Hinsley, F. H. (1994) [1993]. British Intelligence in the Second World War: Its Influence on Strategy and Operations (abridged edition). History of the Second World War (2nd rev. ed.). London: HMSO. ISBN 978-0-11-630961-7.
- Jowett, Philip (2001). The Italian Army 1940–45: Africa 1940–43. II. Ocford: Osprey. ISBN 978-1-85532-865-5.
- Mackenzie, Compton (1951). Eastern Epic: September 1939 – March 1943 Defence. I. London: Chatto & Windus. OCLC 59637091.
- Maravigna, P. (1949). Come abbiamo perduto la guerra in Africa [How We Lost the War in Africa] (in Italian). Roma: Tosi. OCLC 22043823.
- Mockler, Anthony (1984). Haile Selassie's War: The Italian−Ethiopian Campaign, 1935–1941. New York: Random House. ISBN 978-0-394-54222-5.
- Mohr, Ulrich; Sellwood, Arthur V. (2009). Ship 16: The Story of a German Surface Raider. Stroud: Amberley. ISBN 978-1-84868-115-6.
- Mollo, Andrew; McGregor, Malcolm; Turner, Pierre (1981). The Armed Forces of World War II : Uniforms, Insignia and Organization. New York: Crown Publishers. ISBN 978-0-517-54478-5.
- Orpen, N. (1968). East African and Abyssinian Campaigns. South African Forces, World War II. I (online ed.). Cape Town, SA: Purnell. OCLC 499914466. Retrieved 7 March 2017.
- Playfair, Major-General I. S. O.; et al. (1954). Butler, J. R. M., ed. The Mediterranean and Middle East: The Early Successes Against Italy (to May 1941). History of the Second World War, United Kingdom Military Series. I. HMSO. OCLC 494123451. Retrieved 3 September 2015.
- Playfair, Major-General I. S. O.; et al. (2004) [1st. pub. HMSO 1956]. Butler, J. R. M., ed. The Mediterranean and Middle East: The Germans come to the help of their Ally (1941). History of the Second World War, United Kingdom Military Series. II. Naval & Military Press. ISBN 978-1-84574-066-5.
- Porch, Douglas (2005) [2004]. The Path to Victory: The Mediterranean Theater in World War II (Cassell Military Paperbacks ed.). London: Weidenfeld & Nicholson. ISBN 978-0-304-36705-4.
- Qureshi, N. A.; et al. (1963). Prasad, Bisheshwar, ed. East African Campaign, 1940–41. Official History of the Indian Armed Forces In the Second World War (1939–1945) (online ed.). Delhi: Combined Inter-Services Historical Section (India & Pakistan). OCLC 480344871. Retrieved 23 February 2016.
- Rankin, N. (2009) [2008]. Churchill’s Wizards: The British Genius for Deception, 1914–1945. US title: A Genius for Deception: How Cunning Helped the British Win Two World Wars, Oxford University Press, New York. London: Faber & Faber. ISBN 978-0-19-538704-9.
- Raugh, H. E. (1993). Wavell in the Middle East, 1939–1941: A Study in Generalship. London: Brassey's. ISBN 978-0-08-040983-2.
- Richards, Denis (1974) [1953]. Royal Air Force 1939–1945: The Fight At Odds. I (pbk. ed.). London: HMSO. ISBN 978-0-11-771592-9. Retrieved 23 February 2016.
- Rohwer, Jürgen; Hümmelchen, Gerhard (1992) [1968]. Chronology of the War at Sea, 1939–1945: The Naval History of World War Two (in German) (2nd rev. ed.). Annapolis, MD: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 978-1-55750-105-9.
- Roselli, A. (2007). Storie segrete: operazioni sconosciute o dimenticate della seconda guerra mondiale [Secret History: Unknown or Forgotten Operations of World War II]. Biblioteca universale (in Italian). Pavia: Iuculano. ISBN 978-88-7072-766-1.
- Roskill, S. W. (1957) [1954]. Butler, J. R. M., ed. The Defensive. History of the Second World War United Kingdom Military Series: The War at Sea 1939–1945. I (4th impr. ed.). London: HMSO. OCLC 881709135. Retrieved 19 February 2016.
- Rooney, David (1994). Wingate and the Chindits. London: Cassell. ISBN 0-304-35452-X.
- Rovighi, Alberto (1988) [1952]. Le Operazioni in Africa Orientale: (giugno 1940 – novembre 1941) [Operations in East Africa: (June 1940 – November 1941)] (in Italian). Roma: Stato Maggiore Esercito, Ufficio storico. OCLC 848471066.
- Santoro, G. (1957). L'aeronautica italiana nella seconda guerra mondiale [The Italian Air Force in WWII] (PDF). II (1st ed.). Milano-Roma: Edizione Esse. OCLC 60102091. Retrieved 7 March 2016.
- Schoeman, Michael (2002). Springbok Fighter Victory: SAAF Fighter Operations 1939–1945: East Africa 1940–1941. I. Cape Town: Freeworld Publications. ISBN 978-0-95843-885-8.
- Shores, C. (1996). Dust Clouds in the Middle East: The Air War for East Africa, Iran, Syria, Iran and Madagascar, 1940–42. London: Grub Street. ISBN 978-1-898697-37-4.
- Stegemann, Bernd; Vogel, Detlef (1995). Germany and the Second World War: The Mediterranean, South-East Europe and North Africa, 1939–1941. London: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-822884-4.
- Stewart, A. (2016). The First Victory: The Second World War and the East Africa Campaign (1st ed.). New Haven, CT: Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-300-20855-9.
- The Abyssinian Campaigns; The Official Story of the Conquest of Italian East Africa. London: HMSO for Ministry of Information. 1942. OCLC 184818818.
- The New Encyclopædia Britannica (15th ed.). Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica. 2002. ISBN 978-0-85229-787-2.
- War Diary HQ Somaliforce Jul–Aug 1940. Ref WO 169/2870. The National Archives. Retrieved 1 January 2016.
- Waters, S. D. (1956). The Royal New Zealand Navy. Official History of New Zealand in the Second World War 1939–45 (New Zealand Electronic Text Centre ed.). Wellington, NZ: War History Branch, Dept. of Internal Affairs. OCLC 11085179. Retrieved 23 February 2016.
- Wavell, A. (10 July 1946). Official Despatch: Operations in East Africa November 1940 – July 1941 (PDF). London Gazette. pp. 3527–3599. Retrieved 27 June 2014.
- Weller, G. (1942). The Belgian Campaign in Ethiopia: A Trek of 2,500 Miles Through Jungle Swamps and Desert Wastes (online ed.). New York: Belgian Information Center. OCLC 1452395. Retrieved 3 March 2016.
- Weller, George (2010). Weller's War: A Legendary Foreign Correspondent's Saga of World War II on Five Continents. New York: Three Rivers Press. ISBN 978-0-307-34203-4.
- Zolberg, Aristide R.; Aguayo, Sergio; Suhrke, Astri (1992). Escape from Violence: Conflict and the Refugee Crisis in the Developing World. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-507916-6.
Journals
- Cernuschi, Enrico (December 1994). "La resistenza sconosciuta in Africa Orientale" [The Unknown Resistance in East Africa]. Rivista storica (in Italian). Roma: Coop. giornalisti storici. OCLC 30747124.
- Hammerton, John, ed. (25 April 1941). "South Africans Won the Race to Addis Ababa". The War Illustrated. London: William Berry. 4 (86). OCLC 220168380. Retrieved 18 October 2008.
Theses
- Marino, F. (2009). Military Operations in the Italian East Africa, 1935–1941: Conquest and Defeat (MMS). Quantico, VA: USMC Command and Staff College. OCLC 832080928. Retrieved 22 February 2016.
Websites
- Barclay, Brigadier C. N. "Mediterranean Operations: Campaigns in Africa". GI WWII Commemoration. para 6. Archived from the original on 21 January 1997. Retrieved 23 October 2013.
- Gustavsson, H. "Maresciallo Giuseppe Mottet". Håkans Aviation Page: Biplane Fighter Aces from the Second World War. Retrieved 2 September 2015.
Further reading
Books
- Antonicelli, Franco (1961). Dall'antifascismo alla resistenza: Trent'anni di storia italiana 1915–1945 [From Antifascism to Resistance: Thirty Years of Italian History 1915–1945]. Saggi (in Italian) (Mondadori ed.). Torino: Einaudi. OCLC 859627877.
- Barker, A. J. (1966). Eritrea. London: Faber. OCLC 1658053.
- Bragadin, M'A.; Fioravanzo, G.; Hoffman, G. (1957). The Italian Navy in World War II. Annapolis, MD: United States Naval Institute. OCLC 836272007.
- Brett-James, Antony (1951). "From Pillar to Post, June–October 1941". Ball of Fire: The Fifth Indian Division in the Second World War. Aldershot: Gale & Polden. OCLC 4275700. Retrieved 19 February 2016.
- Brown, J. A. (1990). The War of a Hundred Days: Springboks in Somalia and Abyssinia, 1940–41. South Africans at War. I. Johannesburg, SA: Ashanti. ISBN 978-1-874800-10-1.
- Churchill, Winston S. (1986) [1949]. The Second World War: Their Finest Hour. II. Boston: Houghton Mifflin. ISBN 978-0-395-41056-1.
- Cocchia, A. (1958). La Marina italiana nella seconda guerra mondiale [The Italian Navy in the Second World War]. Roma: Ufficio storico della marina militare. OCLC 859874678.
- Corvaja, Santi (2001). Hitler and Mussolini: The Secret Meetings. New York: Enigma Books. ISBN 978-1-929631-00-1.
- Crosskill, W. E. (1980). The Two Thousand Mile War. London: Robert Hale. OCLC 490879527.
- Del Boca, Angelo (1986). Italiani in Africa Orientale: La caduta dell'Impero [Italians in East Africa: The Fall of the Empire] (in Italian). Roma-Bari: Laterza. ISBN 978-88-420-2810-9.
- Glover, M. (1987). An Improvised War: The Ethiopian Campaign 1940–1941. London: Leo Cooper. ISBN 978-0-85052-241-9.
- Knox, MacGregor. Mussolini Unleashed, 1939–1941: Politics and Strategy in Fascist Italy's Last War. London: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-33835-6.
- Laitin, D. D. (1977). Politics, Language and Thought: The Somali Experience. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. ISBN 978-0-226-46791-7.
- Lupinacci, Pier Filippo; Cocchia, Aldo (1961). La Marina italiana nella seconda guerra mondiale: Le operazioni in Africa Orientale [The Italian Navy in the Second World War: Operations in East Africa] (in Italian). X. Rome: Ufficio Storico della Marina Militare Italiana. pp. 187–197. OCLC 955801310.
- Metz, Helen Chapin (2004) [1993]. Somalia: A Country Study. Area Handbook (Kessinger ed.). Federal Research Division. ISBN 978-0-8444-0775-3.
- Nafziger, G. (2012) [2011]. Nafziger Orders of Battle Collection: Finding Aid (online ed.). Fort Leavenworth, KS: Combined Arms Research Library (US Army Command and General Staff College). OCLC 528648446. Retrieved 10 March 2016.
- Platt, W. (17 July 1946). Operations of the East African Command 12 July 1941 to 8 January 1943 (PDF). London: London Gazette. pp. 3711–3720. Retrieved 27 June 2014.
- Revised Notes on the Italian Army (with amendments 1–3 incorporated). London: War Office. 1942. OCLC 41977582.
- Shirreff, David (2009) [1995]. Bare Feet and Bandoliers: Wingate, Sandford, the Patriots and the Liberation of Ethiopia. Barnsley: Pen & Sword Military. ISBN 978-1-84884-029-4.
- Sutherland, J.; Canwell, D. (2009). Air War East Africa 1940–41: The RAF Versus the Italian Air Force. Barnsley: Pen & Sword Aviation. ISBN 978-1-84415-816-4.
- Vincent, J-N.; Spivak, M.; Léoni, A. Les forces françaises dans la lutte contre l'Axe en Afrique [French Forces in the Fight against the Axis in Africa] (in French). 1983–1985. Paris: Ministère de la défense, Etat-major de l'Armée de terre, Service historique. ISBN 978-2-86323-017-6.
- Wavell, A. (4 June 1946). Operations in the Somaliland Protectorate, 1939–1940 (Appendix A – G. M. R. Reid and A. R. Godwin-Austen) (PDF). London Gazette. pp. 2719–2727. Retrieved 27 June 2014.
Theses
- Anglim, S. J. (2007). Orde Wingate and the British Army 1922–1944: Military Thought and Practice Compared and Contrasted (PhD). ISNI 0000 0001 3424 7296. University of Wales, Aberystwyth. OCLC 828579432. Retrieved 25 February 2016.
- Marino, F. (2009). Military Operations in the Italian East Africa, 1935–1941: Conquest and Defeat (PDF) (MMS). United states Marine Corps, Command and Staff College. OCLC 832080928. Docket AY08-09. Retrieved 23 October 2016.
- Snead, L. R. (6 May 1994). Wavell's Campaigns in the Middle East: An Analysis of Operational Art and the Implications for Today (Monograph). Command and General Staff College, School of Advanced Military Studies. Fort Leavenworth, KS: School of Advanced Military Studies, United States Army Command and General Staff College. OCLC 831935679. Docket ADA 284720. Retrieved 5 March 2016.
Websites
- Kostecka, D. J. (2012). "Making Do: the Air War in East Africa, 1940–1941". The Free Library. Retrieved 28 June 2014.
- Liebenberg, E. "The Springboks in East Africa: The role of 1 SA Survey Company (SAEC) in the East African Campaign of World War II, 1940–1941" (PDF) (pdf). no year, no isbn. Johannesburg: Department of Geography, University of South Africa.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to East African campaign. |
- Short tank on the campaign by Andrew Stewart (2016)
- Imperial War Museum talk
- Air War in East Africa
- Italian East African Armed Forces, 10 June 1940
- 1940 Colonial Brigade, 10 June 1940
- Italian East Africa Air Command 10 June 1940
- Somalihome Online: The Invasion of British Somaliland
- BBC WWII People's War: East African Campaign
- Regia Marina The Italian Royal Navy
- The Best of Enemies: 1962 film about the East African Campaign
- Ascari: I Leoni di Eritrea/Ascari: The Eritrean Lions: Eritrean Ascari pictures, videos and atlas (Italian)
- British Military History: East Africa 1940–1947