Olomouc
| Olomouc | |||
| City | |||
| Horní náměstí — the largest square in Olomouc (on right, the Holy Trinity Column; to the left, Olomouc City Hall with astronomical clock) | |||
|
|||
| Country | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Region | Olomouc | ||
| District | Olomouc | ||
| River | Morava | ||
| Elevation | 219 m (719 ft) | ||
| Coordinates | 49°36′N 17°15′E / 49.600°N 17.250°ECoordinates: 49°36′N 17°15′E / 49.600°N 17.250°E | ||
| Area | 103.36 km2 (39.91 sq mi) | ||
| Population | 100 154 | ||
| Founded | 10th century | ||
| - First mentioned | 1017 | ||
| Mayor | Antonín Staněk (ČSSD) | ||
| Postal code | 779 00 | ||
| UNESCO World Heritage Site | |||
| Name | Holy Trinity Column in Olomouc | ||
| Year | 2000 (#24) | ||
| Number | 859 | ||
| Region | Europe and North America | ||
| Criteria | i, iv | ||
  Location in the Czech Republic | |||
| Wikimedia Commons: Olomouc | |||
| Statistics: statnisprava.cz | |||
| Website: http://www.olomoucko.cz/ | |||
Olomouc (Czech: [ˈolomou̯t͡s]; locally Holomóc or Olomóc; German: Olmütz; Latin: Olomucium or Iuliomontium; Polish: Ołomuniec [ɔwɔˈmuɲɛt͡s]) is a city in Moravia, in the east of the Czech Republic. Located on the Morava River, the city is the ecclesiastical metropolis and historical capital city of Moravia. Today it is an administrative centre of the Olomouc Region and sixth largest city in the Czech Republic. The city has about 100,154 residents, and its larger urban zone has a population of about 480,000 people.[1]
History
Ancient history
Olomouc is said to occupy the site of a Roman fort founded in the imperial period, the original name of which, Iuliomontium (Mount Julius), would be gradually corrupted to the present form. Although this account is not documented except as oral history, archaeological excavations close to the city have revealed the remains of a Roman military camp dating from the time of the Marcomannic Wars of the late 2nd century.
Middle Ages
During the 6th century, Slavs migrated into the area. As early as the 7th century, a centre of political power developed in the present-day quarter of Povel (in lowland, south of the city centre). Around 810 the local Slavonic ruler was defeated by troops of Great Moravian rulers and the settlement in Olomouc-Povel was destroyed.
A new centre, where the Great Moravian governor resided, developed at the gord at Předhradí, a quarter of the inner city (the eastern, smaller part of the medieval centre). This settlement survived the defeat of the Great Moravia (c. 907) and gradually became the capital of the province of Moravia.
The bishopric of Olomouc was founded in 1063. It was possibly re-founded because there are some unclear references to bishops of Moravia in the 10th century—if they were not only missionary bishops, but representatives of some remains of regular church organization, then it is very likely that these bishops had seat right here. Centuries later in 1777, it was raised to the rank of an archbishopric. The bishopric was moved from the church of St. Peter (since destroyed) to the church of Saint Wenceslas in 1141 (the date is still disputed, other suggestions are 1131, 1134) under bishop Jindřich Zdík. The bishop's palace was built in the Romanesque architectural style. The bishopric acquired large tracts of land, especially in northern Moravia, and was one of the richest in the area.
Olomouc became one of the most important settlements in Moravia and a seat of the Přemyslid government and one of the appanage princes. In 1306 King Wenceslas III stopped here on his way to Poland. He was going to fight Władysław I the Elbow-high to claim his rights to the Polish crown and was assassinated. With his death, the whole Přemyslid dynasty died out.
The city was officially founded in the mid-13th century and became one of the most important trade and power centres in the region. In the Middle Ages, it was the biggest town in Moravia and competed with Brno for the position of capital. Olomouc finally lost after the Swedes took the city and held it for eight years (1642–1650).
In 1235, the Mongols launched an invasion of Europe. After the Battle of Legnica in Poland, the Mongols carried their raids into Moravia, but were defensively defeated at the fortified town of Olomouc.[2] The Mongols subsequently invaded and defeated Hungary.[3]
In 1454 the city expelled its Jewish population as part of a wave of anti-Semitism, also seen in Spain and Portugal. The second half of the 15th century is considered the start of Olomouc's golden age. It hosted several royal meetings, and Matthias Corvinus was elected here as King of Bohemia (in fact anti-king) by the estates in 1469. In 1479 two kings of Bohemia (Vladislaus II and Matthias Corvinus) met here and concluded an agreement (Peace of Olomouc of 1479) for splitting the country.
Modern

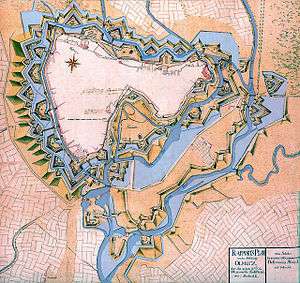
Participating in the Protestant Reformation, Moravia became mostly Protestant. During the Thirty Years' War, in 1640 Olomouc was occupied by the Swedes for eight years. They left the city in ruins, and it became second to Brno.
In 1740 the town was captured and briefly held by the Prussians. Olomouc was fortified by Maria Theresa during the wars with Frederick the Great, who besieged the city unsuccessfully for seven weeks in 1758. In 1848 Olomouc was the scene of the emperor Ferdinand's abdication. Two years later, Austrian and German statesmen held a conference here called the Punctation of Olmütz. At the conference, they agreed to restore the German Confederation and Prussia accepted leadership by the Austrians.
In 1746 the first learned society in the lands under control of the Austrian Habsburgs, the Societas eruditorum incognitorum in terris Austriacis, was founded in Olomouc to spread Enlightenment ideas. Its monthly Monatliche Auszüge was the first scientific journal published in the Habsburg empire.
Largely because of its ecclesiastical links to Austria, Salzburg in particular, the city was influenced by German culture since the Middle Ages. Demographics before censuses can only be interpreted from other documents. The town's ecclesiastical constitution, the meetings of the Diet and the locally printed hymnal, were recorded in the Czech language in the mid-16th and 17th centuries. The first treatise on music in Czech was published in Olomouc in the mid-16th century. The political and social changes that followed the Thirty Years' War increased the influence of courtly Habsburg and Austrian/German language culture. The "Germanification" of the town likely resulted from the cosmopolitan nature of the city; as the cultural, administrative and religious centre of the region, it drew officials, musicians and traders from all over Europe.
Despite these influences, the Czech language dominated, particularly in ecclesiastical publications throughout the 17th and 18th centuries. When the Austrian-born composer and musician Philip J. Rittler accepted a post at the Wenceslas Cathedral in the latter 17th century, he felt it necessary to learn Czech. With the continued dominance of the Habsburgs and migration of ethnic Germans into the area, the use of Czech declined. By the 19th century, the number of ethnic Germans in the city were recorded as three times higher than the number of Czechs.[4]
After the 1848 revolution, the government rescinded its Jewish expulsion order of 1454. Jews returned to the city and, in 1897, built a synagogue. The Jewish population reached 1,676 in 1900.


Olomouc retained its defensive city walls almost until the end of the 19th century. This suited the city council, because demolishing the walls would have allowed for expansion of the city and attracted more Czechs from neighbouring villages. The city council preferred Olomouc to be smaller and predominantly German. Greater expansion came after World War I and the establishment of Czechoslovakia. In 1919 Olomouc annexed two neighbouring towns and 11 surrounding villages, gaining new space for additional growth and development.
Serious tensions arose between ethnic Czechs and Germans during both world wars. During World War II, most of the town's ethnic German residents sided with the Nazis; the German-run town council renamed the main square (until then named after president T. G. Masaryk) after Adolf Hitler. World War II brought a rise in anti-semitism and attacks on the Jews that reflected what was happening in Germany. On Kristallnacht (10 November 1938), townspeople destroyed the synagogue. In March 1939, city police arrested 800 Jewish men, and had some deported to the Dachau concentration camp. During 1942–1943, ethnic Germans sent the remaining Jews to Theresienstadt and other German concentration camps in occupied Poland. Fewer than 300 of the town's Jews survived the Holocaust.
After Olomouc was liberated, Czech residents took back the original name of the town square. When the retreating German army passed through the city in the final weeks of the war, they shot at its 15th-century astronomical clock, leaving only a few pieces intact (these are held in the local museum). In the 1950s, the clock was reconstructed under the influence of Soviet government; it features a procession of proletarians rather than saints. After the war, the government participated in the expulsion of ethnic Germans from the country, following the Allied leaders' Potsdam Agreement, which redefined the Central European borders, although many of these people's families had lived for two centuries in the region.
Despite its considerable charms, Olomouc has fortunately not been discovered by tourists in the same way that Prague, Český Krumlov and Karlovy Vary have largely become overrun. Its inner city is the second-largest historical monuments preserve in the country, after Prague.
City monuments

Olomouc contains several large squares, the chief of which is adorned with the Holy Trinity Column, designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The column is 115 ft (35 m) high and was built between 1716 and 1754.
The city has numerous historic religious buildings. The most prominent church is Saint Wenceslas Cathedral founded before 1107 in the compound of the Olomouc Castle. At the end of the 19th century, the cathedral was rebuilt in the neo-Gothic style. It kept many features of the original church, which had renovations and additions reflecting styles of different ages: Romanesque crypt, Gothic cloister, Baroque chapels. The highest of the three spires is 328 ft (100 m), the second-highest in the country (after Cathedral of St. Bartholomew in Plzeň). The church is next to the Bishop Zdík's Palace (also called the Přemyslid Palace), a Romanesque building built after 1141 by the bishop Henry Zdík. It remains one of the most precious monuments of Olomouc: Such an early bishop's palace is unique in Central Europe. The Přemyslid Palace, used as the residence of Olomouc dukes from the governing Přemyslid dynasty, stood nearby.
Saint Maurice Church, a fine Gothic building of the 15th century, has the 6th-largest church organ in Central Europe.
Saint Michael's Church is notable. The Neo-baroque chapel of Saint John Sarkander stands on the site of a former town prison. At the beginning of the Thirty Years' War, the Catholic priest John Sarkander was imprisoned here. Accused of collaboration with the enemy, he was tortured but did not reveal anything because of the Seal of Confession and died. The torture rack and Sarkander’s gravestone are preserved here. He was canonized by Pope John Paul II during his visit in Olomouc in 1995.
John Paul II also visited Svatý Kopeček (Olomouc) ("The Holy Hillock"), which has the magnificent Baroque church of the Visitation of the Virgin Mary. It overlooks the city. The Pope promoted the church to Minor Basilica. Several monasteries are in Olomouc, including Hradisko Monastery, Convent of Dominican Sisters in Olomouc and others.
Other notable destinations are the Olomouc Orthodox Church, consecrated to Saint Gorazd, and the Mausoleum of Yugoslav Soldiers. This monument commemorates 1,188 Yugoslav soldiers who died during World War I in local hospitals after being wounded on battlefields.
The principal secular building is the town hall, completed in the 15th century. It is flanked on one side by a gothic chapel, now adapted and operated as the Olomouc Museum of Art. It has a tower 250 ft (76 m) high, adorned with an astronomical clock in an uncommon Socialist Realist style. (The original 15th-century clock was destroyed at the end of World War II. It was reconstructed in 1947–1955 by Karel Svolinský, who used the government-approved style of the time, featuring proletarians rather than saints.
Olomouc is proud of its six Baroque fountains. They survived in such number thanks to the city council's caution. While most European cities were removing old fountains after building water-supply piping, Olomouc decided to keep them as reservoirs in case of fire. The fountains feature ancient Roman motifs; five portray the Roman gods Jupiter (image), Mercury (image), Triton (image), Neptune and Hercules (image). One features Julius Caesar, the legendary founder of the city (image). In the 21st century, an Arion fountain was added to the main square, inspired by the older project.
In the largest square in Olomouc (Horní náměstí, Upper Square), in front of the astronomical clock, is a scale model of the entire old town in bronze.
University

Palacký University, the oldest in Moravia and second oldest in the Czech Republic, was founded in 1573 as part of effort to reestablish Roman Catholicism in the country. At the time, roughly nine out of ten inhabitants of the Czech Crown lands were Protestants.[5] Most of its faculties were suppressed in the 1850s by the Habsburg régime in retaliation for professor and student support for the 1848 revolution and the Czech National Revival. The university was fully restored in 1946; it was renamed Palacký University of Olomouc.
The university plays a very important role in the life of the town: With over 25,200 students (including those at Moravian College Olomouc),[6] Olomouc has the highest density of university students in Central Europe. Many of the town's services are student-oriented. They close during holidays and the university exam periods. During the summer holiday, the trams run solo (apart from rush-hours), while during the university sessions, the lines are served by two coupled trams.
The university buildings comprise about a third of the town's heritage centre; notable ones include the University Art Centre and the so-called Armoury (now Central Library).
Culture
The city is the home of the Moravian Theatre and the Moravian Philharmonic. Olomouc is the center of Hanakia.
Transport
Public transport in Olomouc is provided by trams and buses. Railway services from Olomouc hlavní nádraží (main railway station) to Senice na Hané and Prostějov make stops around the city.
The first train arrived in Olomouc on 17 October 1841 from Vienna. In 1845 the first omnibuses connected the railway station and the center of Olomouc. In 1899 omnibuses were replaced with trams
Railway station Olomouc main station is an important railway junction. From Olomouc come tracks to Prague, Ostrava, Brno, Zlín, Břeclav. Railway station Olomouc main station is very busy, all trains of Czech railways, RegioJet and LEO Express stop there.
Sport
- AK Olomouc – athletics club
- Skokani Olomouc – baseball club
- 1. HFK Olomouc – football club
- SK Sigma Olomouc – football club
- DHK Olomouc – women's handball club
- HC Olomouc – ice hockey club
- VK UP Olomouc – women's volleyball club
- RC Olomouc – rugby club
In popular culture
- Asteroid 30564 Olomouc was named after this city.
- Scenes from the 2002 television serial Doctor Zhivago were filmed in Olomouc.
- Olomouc is mentioned in the song "Disappear" by R.E.M. from the album Reveal.[7]
Photo gallery
 Red Church
Red Church Olomouc from above
Olomouc from above
 Olomouc Street
Olomouc Street Town hall
Town hall Square with Holy trinity Column
Square with Holy trinity Column The Archidiocesan Museum
The Archidiocesan Museum John Sarkander Chapel
John Sarkander Chapel.jpg) Fountain
Fountain- Hradisko
 Church of Saint Maurice
Church of Saint Maurice Church of Saint Michael
Church of Saint Michael St. Wenceslas Cathedral
St. Wenceslas Cathedral
Panorama

Notable natives and residents
Ancient times
- Hildebert and Everwin, (c 1140) 12th-century illuminators in the scriptorium of Bishop Jindřich Zdík
- Augustinus Olomucensis, (1467–1513) Moravian humanist and theologian. also known as Augustin Käsenbrot (or Käsenbrod), Augustinus Moravus or Augustinus Bemus, or, in Czech, as Augustin Moravský
- Martin Schaffner (c.1564–1608) Bohemian pharmacist and chemist at the Jesuit college in Český Krumlov
- Georg Flegel (1566 in Olomouc – 1638) German painter, best known for his still life works.
- Valentin Stansel, (1621–1705) Jesuit and astronomer who worked in Brazil
- Karel Ferdinand Irmler (1650–?) Moravian lawyer and the first professor of secular law at University of Olomouc
- Gottfried Finger, (1655/6–1730) Moravian Baroque composer and virtuoso on the Viol
- Charles Joseph of Lorraine, (1680–1715) prelate, also known as Charles III when bishop of Olomouc
- Karl Josef Aigen (1684 in Olomouc – 1762) landscape painter
- Joseph Leopold Freiherr von Petrasch (1714 – 1772) was a soldier, writer and philologist. In 1746 he founded the Olomouc-based Societas incognitorum, the first Enlightenment-inspired learned society in the Habsburg territories
- Joseph Ignatz Sadler, (1725–1767) painter, primarily painted religious-themed frescoes
- Josef Vratislav Monse, (1733–1793) lawyer, historian and professor of law, Rector at the University of Olomouc in 1780
- Anton Schubirz von Chobinin (1748 in Olomouc – 1801) General-major fought for Habsburg Austria against Ottoman Turkey
- In 1767 Mozart (1756–1791) and his family took refuge here during the Smallpox epidemic in Vienna [8]
- Archduke Rudolf of Austria (1788–1831) consecrated as Archbishop of Olomouc in 1819
- Anton Felix Schindler (1795 in Medlov – 1864) was an associate, secretary, and early biographer of Ludwig van Beethoven
1800 to 1875
- Anton Schrötter von Kristelli, (1802–1875) chemist and mineralogist; son of an apothecary
- Rudolf Eitelberger von Edelberg (1817 in Olomouc – 1885) art historian and founder of the Vienna School of Art History.
- Ludwig Karl Schmarda (1819 in Olomouc – 1908) Austrian naturalist and traveler
- The operatic sopranos Jenny Bürde-Ney (1824–1886) and her sister Caroline Denemy-Ney (1823–1894) were associated with the city. Jenny made her official debut here in 1845 as Norma in the eponymous opera by Vincenzo Bellini, and Caroline died here.[9]
- Hans Balatka (1827 in Bouzov – 1899) was a United States conductor and composer.
- Franziskus von Sales Bauer, (1841–1915) Cardinal of the Roman Catholic Church and Archbishop of Olomouc from 1904
- Wilhelm Tomaschek or Vilém Tomášek (1841 in Olomouc – 1901) Czech-Austrian geographer and orientalist worked on historical topography and historical ethnography
- Alexander Freiherr von Krobatin (1849 in Olomouc – 1933) Austrian Field Marshal Imperial Minister for War from 1912 to 1917
- Adolf Hölzel, (1853–1934) artist/painter, his style developed from Impressionism to Expressive modernism
- Berthold Hatschek (1854 – 1941) Austrian zoologist, did embryological and morphological studies of invertebrates.
- Berthold Oppenheim (1867–1942), rabbi
- Hermann Hiltl (1872 in Olomouc – 1930) Austrian army officer who became leader of his own right wing militia, embraced both fascism and Pan-Germanism without fully committing to Nazism.
- Leo Fall (1873 in Olomouc – 1925) Austrian composer of operettas.
1875 to 1940
- Adolf Kašpar (1877 in Bludov – 1934) Czech painter and illustrator.
- Paul Engelmann (1891 in Olomouc – 1965) architect known for his friendship with Ludwig Wittgenstein between 1916 and 1928, partner in the design and building of the Stonborough House in Vienna
- Egon Kornauth (1891 in Olomouc – 1959) Austrian composer and music teacher, cellist and pianist
- Zdeněk Fierlinger (1891 in Olomouc – 1976) Czech diplomat and politician. He served as the Prime Minister of Czechoslovakia from 1944 to 1946, first in the London-based Czechoslovak government-in-exile and later in liberated Czechoslovakia.
- Franz Karmasin (1901 in Olomouc –1970) ethnic German politician in Czechoslovakia and SS Officer, helped found the Carpathian German Party [10]
- Monsignor John Maria Oesterreicher (1904 in Město Libavá – 1993) Roman Catholic theologian and a leading advocate of Jewish–Catholic reconciliation
- Edgar G. Ulmer (1904–1972) filmmaker, born in Olomouc but claimed Vienna as his birthplace, as it sounded less provincial.[11]
- Olga Taussky-Todd (1906 in Olomouc – 1995) Austrian and later Czech-American mathematician
- Evžen Rošický (1914 in Olomouc - 1942) Czech athlete, journalist and resistance fighter. Stadion Evžena Rošického is a Czech stadium named after him.
- Dr. Jaroslav Otruba (1916–2007) Czech architect, urban planner, designer and artist
- Jiří Pelikán (1923 in Olomouc – 1999) Czechoslovakian journalist and MP and member of the European Parliament for the Italian Socialist Party.
Modern times
- Peter Schmidl (born 1942) clarinetist
- Pavel Dostál (1943–2005) Minister of Culture in the Czech Republic
- Jan Graubner (born 1948) Roman Catholic archbishop of Olomouc
- Emil Viklický (born 1948 in Olomouc) is a Czech jazz pianist and composer.
- Lenka Procházková (born 1951 in Olomouc) daughter of writer Jan Procházka
- Jiří Paroubek (born 1952) Czech politician and Prime Minister from 25 April 2005 to 16 August 2006
- Vladimír Havlík (born 1959) action artist, painter and pedagogue
- Pavel Vítek (born 1962) Czech singer, actor and pop star
- Rostislav Čtvrtlík (1963–2011) stage, television and voice actor from Olomouc
- Jan G. Švec (born 1966 in Olomouc) Czech voice scientist, invented videokymography, used for diagnosis of voice disorders.
- Ivan Langer (born 1967 in Olomouc) former Czech politician
- Zora Vesecká (born 1967 in Olomouc) former Czech child actress, subsequently a dentist
- Prof. Mgr. Jaroslav Miller, M.A., Ph.D. (born 1971 in Šumperk) professor of history and rector at Palacký University in Olomouc.
- Tomáš Hudeček (born in Olomouc 1979) is a Czech politician and university professor
- Veronika Varekova, (born c.1985) Sports Illustrated model
- Lerika (born 1999) child singer who has represented Moldova and Russia in the Junior Eurovision Song Contest
Sport
- Alena Chadimová (born 1931) former gymnast who competed in the 1952 Summer Olympics
- Karel Brückner (born 1939) formerly head coach of the Czech Republic national football team and later of Austria
- Jiří Kavan (1943–2010) handball player who competed in the 1972 and 1976 Summer Olympics
- Mirro Roder (born 1944 in Olomouc) former American football placekicker, played 3 seasons in the National Football League
- Martin Kotůlek (born 1969) football manager, former player and current caretaker-manager of Sigma Olomouc
- David Prinosil (born 1973 in Olomouc) former tennis player
- Radim Kořínek (born 1973 in Olomouc) former competitive bicyclist
- Josef Karas (born 1978 in Olomouc) Czech male decathlete and beauty pageant titleholder
- František Huf (born 1981) bodybuilder and model
- Jiri Hudler (born 1984), professional ice hockey player with National Hockey League and the Detroit Red Wings in 2002
- Karel "Karlos" Vémola (born Olomouc 1985) Czech professional mixed martial artist, bodybuilder, wrestler and member of Sokol.
- Tomáš Kalas (born 1993) footballer who plays for English club Fulham F.C. on loan from Chelsea F.C.
International relations
Twin towns – Sister cities
Olomouc is twinned with:
|
|
Mayors
List of Olomouc mayors:
|
|
See also
Footnotes
- ↑ Nařízení vlády č. 212/1997, kterým se vyhlašuje závazná část územního plánu velkého územního celku Olomoucké aglomerace
- ↑ Grousset, René (1970). The Empire of the Steppes. Rutgers University Press. p. 266. ISBN 978-0-8135-1304-1.
- ↑ Jan Dugosz, Maurice Michael (1997) The Annals of Jan Dlugosz, IM Publications, ISBN 1-901019-00-4
- ↑ Tichák, Milan (1997). Vzpomínky na starou Olomouc. Olomouc: Votobia. p. 13. ISBN 80-7198-184-2.
- ↑ Václavík, David (2010). Náboženství a moderní česká společnost. Grada Publishing a.s.
- ↑ mvso.cz
- ↑ "Disappear Lyrics - R.E.M.". LyricsFreak.com. Retrieved 29 February 2016.
- ↑ [See H. C. Robbins Landon, Mozart and Vienna, 1991, p. 24f.]
- ↑ [See Daniel O'Hara, Richard Tauber Chronology, Appendix 2, http://www.richard-tauber.de/wp-content/pdf/TAUBER-CHRONOLOGY.pdf]
- ↑ Adams, Jefferson (2009). "Karmasin, Franz (1901-1970)". Historical Dictionary of German Intelligence. Scarecrow Press. p. 223. ISBN 9780810863200.
- ↑ Through archival research, Bernd Herzogenrath located the address where Ulmer was born in Olomouc. In 1904, the address was known as "Resselgasse 1, Ort Neugasse." Today, the name is Resslova 1. A memorial plaque, designed by artist Bohumil Teplý to commemorate Ulmer's birthplace, was unveiled on 17 September 2006, on the occasion of the Ulmerfest 2006, the first academic conference devoted to Ulmer's work. His daughter Arianné Ulmer-Cipes and her family were guests of honor.
- ↑ "Twin-cities of Azerbaijan". Azerbaijans.com. Retrieved 2013-08-09.
- ↑ "Partnerstädte der Stadt Luzern". Stadt Luzern (in German). Archived from the original on 2013-06-21. Retrieved 2013-08-01.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Olomouc. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Olomouc. |
| Wikisource has the text of the 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica article Olmütz. |
| Wikisource has the text of the 1879 American Cyclopædia article Olmütz. |
- Municipal website
- Portal Olomouc
- Olomouc – Czech.cz, official portal of the Czech Republic
- UNESCO World Heritage Site: Holy Trinity Column
- Palacký University
- Moravian college
- Filmmaker Albert Maysles in Olomouc
Webcams
- Olomouc town hall with an astronomical clock
- Horní náměstí (Upper Square) with the Holy Trinity Column
Tourism
- Official portal for tourist – information, services, leisure time, monuments, culture
- Olomouc-travel.cz



.jpg)
.jpg)