Nottaway River
| Nottaway | |
| River | |
| Country | Canada |
|---|---|
| Province | Quebec |
| Region | Jamésie |
| Tributaries | |
| - left | (upstream from the mouth)
|
| - right | (upstream from the mouth)
|
| Source | Lake Matagami |
| - location | Matagami |
| - coordinates | 50°03′00″N 77°28′10″W / 50.05000°N 77.46944°W |
| Mouth | Rupert Bay off James Bay |
| - location | About 17 km SW of Waskaganish |
| - elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| - coordinates | 51°23′30″N 78°48′00″W / 51.39167°N 78.80000°WCoordinates: 51°23′30″N 78°48′00″W / 51.39167°N 78.80000°W |
| Length | 225 km (140 mi) |
| Basin | 65,800 km2 (25,400 sq mi) [1] |
| Discharge | |
| - average | 1,190 m3/s (42,020 cu ft/s) [1] |
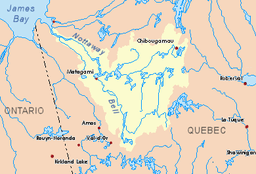 Nottaway River basin in yellow | |
The Nottaway River is a river in Quebec, Canada. The river drains Lake Matagami and travels 225 kilometers (140 mi) north-west before emptying into Rupert Bay at the south end of James Bay. Its drainage basin is 65,800 square kilometers (25,400 sq mi) and has a mean discharge of 1190 m³/s (1556 yd³/s). Its source is the head of the Mégiscane River, which is 776 kilometers (482 mi) from the mouth.[1]
Significant lakes along its course are Soscumica Lake (50°15′N 77°27′W / 50.250°N 77.450°W) and Dusaux Lake (50°45′00″N 77°53′30″W / 50.75000°N 77.89167°W).
The Nottaway, together with the Broadback and Rupert Rivers, was initially considered to be dammed and developed as part of the James Bay Project. But in 1972 hydro-electric development began on the more northerly La Grande and Eastmain Rivers, and the NBR Project was shelved. With the decision to divert the Rupert River to the La Grande, it is not likely that the Nottaway will be developed in the foreseeable future.
Geography
Nottaway means the lower course of Lake Matagami and a length of 230.2 kilometres (143.0 mi), of a watercourse which originates in the Lake Mégiscane. The whole is a long river of 776 kilometres (482 mi) units flowing through many lakes. On the way to the northwest, the Nottaway, from Lake Matagami, creates the lakes of Soscumica and Dusaux, collects the waters of several rivers - notably the Kitchigama River and ends its race in Rupert Bay at the southern end of James Bay, at the western area of the Broadway River and Rupert River.
Its drainage basin is 65,800 kilometres (40,886.22 mi) and has an average discharge of 1,190 metres (3,904.199 ft)/s. The course of the river crosses many marsh areas, especially in its lower part.
The mouth of Matagami Lake is located:
- 32.2 kilometres (20.0 mi) north of downtown Matagami;
- South of the confluence of the Nottaway River and Rupert Bay;
- In the north-west of the center of the village of Lebel-sur-Quévillon, Quebec.
From the mouth of Matagami Lake, the Nottaway River flows on 230.2 kilometres (143.0 mi) divided into the following segments:
- 13.4 kilometres (8.3 mi) to the north by collecting the waters of the Natchiowatchouan River (coming from the Southwest);
- 37.4 kilometres (23.2 mi) to the north, then westward, across Soscumica Lake (altitude: 242.1 metres (794 ft)) to its full length;
- 27.2 kilometres (16.9 mi) to the northwest, to a river bend;
- 43.7 kilometres (27.2 mi) to the northwest, to ?;
- 45.9 kilometres (28.5 mi) to the northwest, to a narrowing of the river;
- 28.1 kilometres (17.5 mi) to the North-West by collecting the waters of the Iroquois River (Nottaway River), to the confluence of the Kitchigama River (coming from South East);
- 16.7 kilometres (10.4 mi) to the North-West bypassing two large islands, until the widening of the river;
- 17.8 kilometres (11.1 mi) to the North-West, up to the mouth of the river.[2]
The confluence of the Nottaway River is located at:
- 179.6 kilometres (111.6 mi) to the northwest of downtown Matagami;
South of the village of Waskaganish (Cree village municipality);
- 91.2 kilometres (56.7 mi) to the south-east of Charlton Island in James Bay.
Toponymy
In the seventeenth century, the Iroquois invaded the Algonquin territory near James Bay along this river. So when European cartographers started to map the river in the late seventeenth century, they called it "Rivière des Iroquois" (Iroquois River), as shown on maps of Jean-Baptiste-Louis Franquelin in 1699, Guillaume Delisle in 1703, and Jacques-Nicolas Bellin in 1744.[3]
Yet various forms of "Nottaway" started to appear in the early 18th century. "Noddaways" in 1715, "Nodaway" in 1743, "Nodaoay" and "Nodway" in 1744. Geologists James Richardson and Albert Peter Low used "Notaway River" in their reports (of 1880 and 1885 respectively). The current spelling "Nottaway" was established in the early twentieth century. It is believed to have come from the Algonquin word nadowe, meaning "snake" and which the Algonquin tribes used to identify or describe their enemies, including the Iroquois. The Cree called this river Natuweu Nipi, and the Iroquois name was Nottaweou.[3]
Tributaries
Major tributaries of the Nottaway River include:
- Kitchigama River
- Lake Matagami
- Allard River
- Bell River
- Rivière Laflamme
- Rivière Mégiscane
- Waswanipi River
- Chibougamau River
- Opawica River
See also
References
- 1 2 3 Atlas of Canada
- ↑ Segments of the river measured from the Atlas of Canada (published on the Internet) of the Ministry of Natural Resources Natural Resources Canada.
- 1 2 "Rivière Nottaway" (in French). Commission de toponymie du Québec. Retrieved 2008-11-18.